Climate Change.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14

GEOGRAPHY OF GLOBAL PROBLEMS: CLIMATE CHANGE Made by Yaroslav Lys Student of PG & Geopolitics Group

Plan 1. Terminology. 2. Causes. 3. Physical evidence. 4. Global warming. 5. Summary. 6. Sources.

Terminology The most general definition of climate change is a change in the statistical properties of the climate system when considered over long periods of time, regardless of cause. Accordingly, fluctuations over periods shorter than a few decades, such as El Niño, do not represent climate change. The term sometimes is used to refer specifically to climate change caused by human activity, as opposed to changes in climate that may have resulted as part of Earth's natural processes. In this sense, especially in the context of environmental policy, the term climate change has become synonymous with anthropogenic global warming. Within scientific journals, global warming refers to surface temperature increases while climate change includes global warming and everything else that increasing greenhouse gas levels will affect.

Terminology Climate change is a change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns when that change lasts for an extended period of time (for example, decades to millions of years). Climate change may refer to a change in average weather conditions, or in the time variation of weather around longer-term average conditions (i. e. , more or fewer extreme weather events).

Causes Climate change is caused by factors such as biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics, and volcanic eruptions. Certain human activities have also been identified as significant causes of recent climate change, often referred to as "global warming".
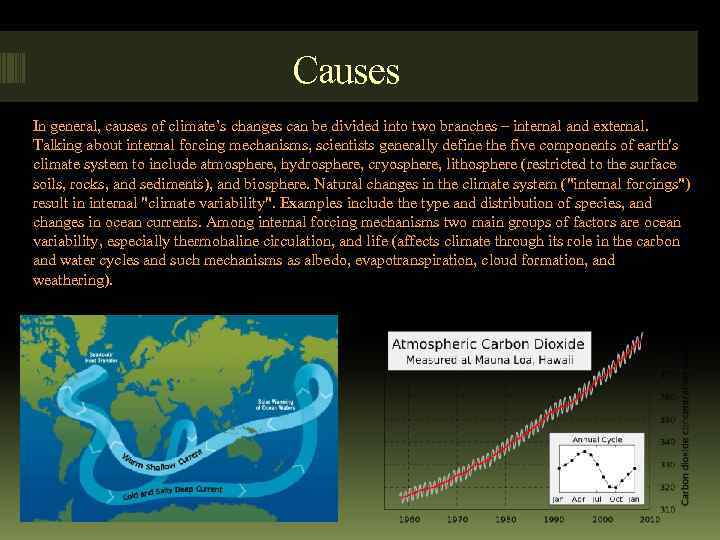
Causes In general, causes of climate’s changes can be divided into two branches – internal and external. Talking about internal forcing mechanisms, scientists generally define the five components of earth's climate system to include atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere (restricted to the surface soils, rocks, and sediments), and biosphere. Natural changes in the climate system ("internal forcings") result in internal "climate variability". Examples include the type and distribution of species, and changes in ocean currents. Among internal forcing mechanisms two main groups of factors are ocean variability, especially thermohaline circulation, and life (affects climate through its role in the carbon and water cycles and such mechanisms as albedo, evapotranspiration, cloud formation, and weathering).
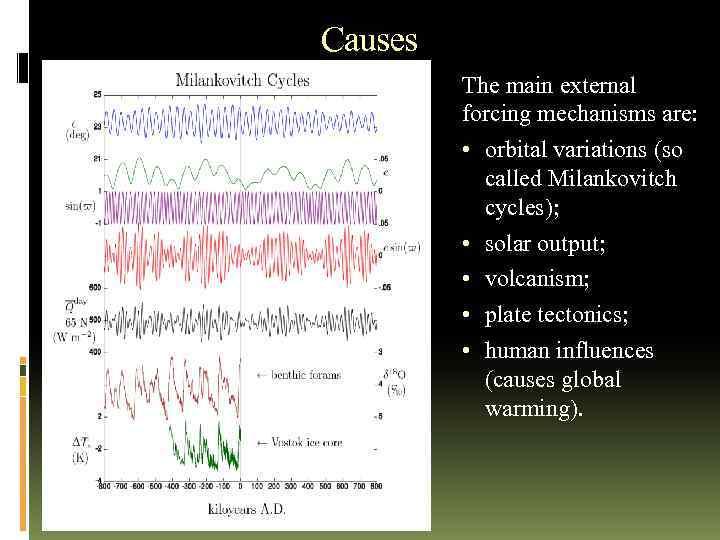
Causes The main external forcing mechanisms are: • orbital variations (so called Milankovitch cycles); • solar output; • volcanism; • plate tectonics; • human influences (causes global warming).
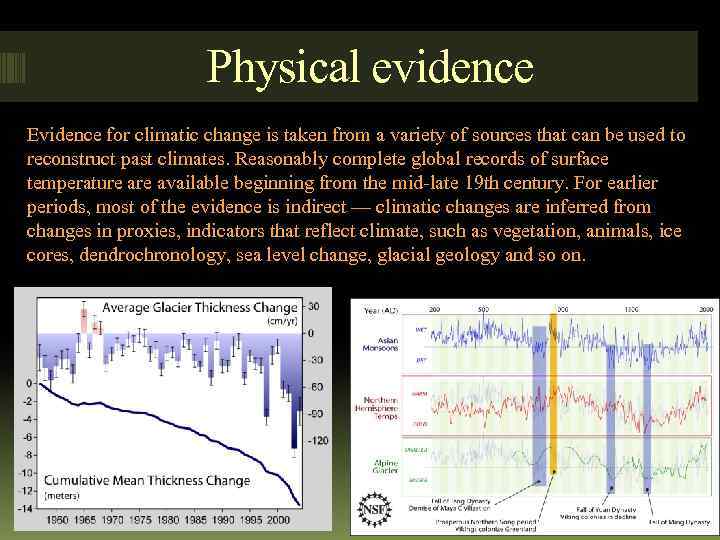
Physical evidence Evidence for climatic change is taken from a variety of sources that can be used to reconstruct past climates. Reasonably complete global records of surface temperature available beginning from the mid-late 19 th century. For earlier periods, most of the evidence is indirect — climatic changes are inferred from changes in proxies, indicators that reflect climate, such as vegetation, animals, ice cores, dendrochronology, sea level change, glacial geology and so on.
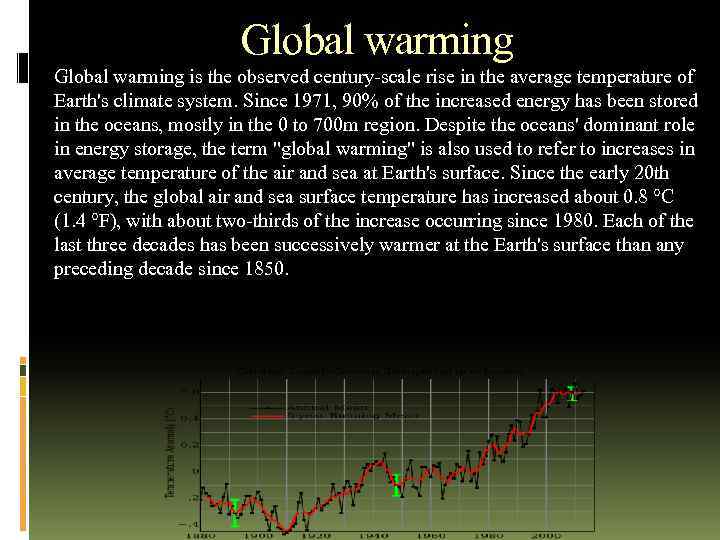
Global warming is the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of Earth's climate system. Since 1971, 90% of the increased energy has been stored in the oceans, mostly in the 0 to 700 m region. Despite the oceans' dominant role in energy storage, the term "global warming" is also used to refer to increases in average temperature of the air and sea at Earth's surface. Since the early 20 th century, the global air and sea surface temperature has increased about 0. 8 °C (1. 4 °F), with about two-thirds of the increase occurring since 1980. Each of the last three decades has been successively warmer at the Earth's surface than any preceding decade since 1850.
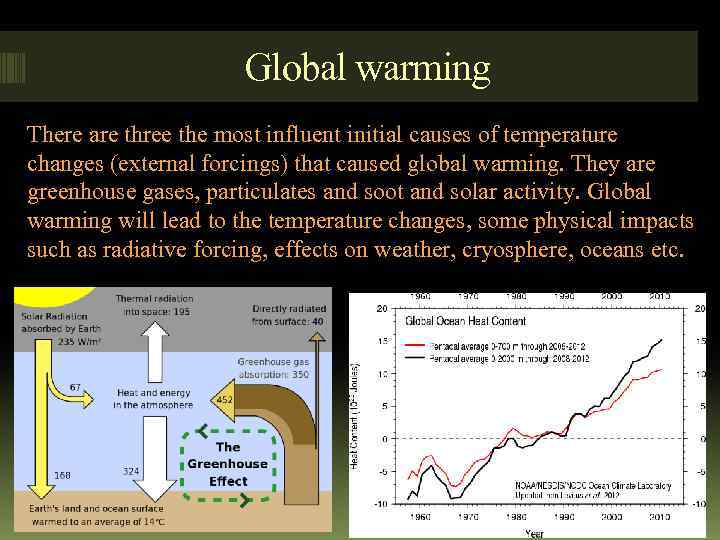
Global warming There are three the most influent initial causes of temperature changes (external forcings) that caused global warming. They are greenhouse gases, particulates and soot and solar activity. Global warming will lead to the temperature changes, some physical impacts such as radiative forcing, effects on weather, cryosphere, oceans etc.

Global warming And, to finish with, some scientific opinions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has published several major assessments on the effects of global warming. Its most recent comprehensive impact assessment was published in 2014. Publications describing the effects of climate change have also been produced by the following organizations: 1) American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS); 2) A report by the Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, and Wageningen University and Research Centre; 3) UK AVOID research programme; 4) A report by the UK Royal Society and US National Academy of Sciences; 5) University of New South Wales Climate Change Research Centre; 6) US National Research Council.

Summary A report by Molina et al. states that the overwhelming evidence of human-caused climate change documents both current impacts with significant costs and extraordinary future risks to society and natural systems. Although, it also means we can deal with the problems are made by climate changes. In this presentation all the main factors that cause the climate changes were given and the results of these changes were shown. Also, here were mentioned some general information and terminology that touch this theme.

Sources 1. Molina, M. , et al. (n. d. ), What We Know: The Reality, Risks and Response to Climate Change. A report by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Climate Science Panel. 2. IPCC Fourth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2007. 3. America's Climate Choices: Panel on Advancing the Science of Climate Change; National Research Council (2010). Advancing the Science of Climate Change. Washington, D. C. : The National Academies Press. 4. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. 5. NASA – What's in a Name? Global Warming vs. Climate Change. 6. en. wikipedia. org. 7. Other Internet sources.

Thank you for your attention!
Climate Change.pptx