8302983958afc4c29c9a87c70668641c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Geography GCSE : Global Tourism Unit
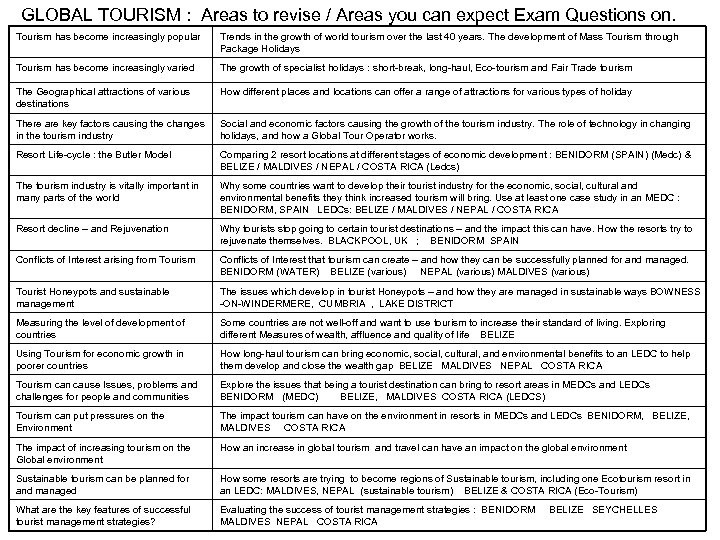
GLOBAL TOURISM : Areas to revise / Areas you can expect Exam Questions on. Tourism has become increasingly popular Trends in the growth of world tourism over the last 40 years. The development of Mass Tourism through Package Holidays Tourism has become increasingly varied The growth of specialist holidays : short-break, long-haul, Eco-tourism and Fair Trade tourism The Geographical attractions of various destinations How different places and locations can offer a range of attractions for various types of holiday There are key factors causing the changes in the tourism industry Social and economic factors causing the growth of the tourism industry. The role of technology in changing holidays, and how a Global Tour Operator works. Resort Life-cycle : the Butler Model Comparing 2 resort locations at different stages of economic development : BENIDORM (SPAIN) (Medc) & BELIZE / MALDIVES / NEPAL / COSTA RICA (Ledcs) The tourism industry is vitally important in many parts of the world Why some countries want to develop their tourist industry for the economic, social, cultural and environmental benefits they think increased tourism will bring. Use at least one case study in an MEDC : BENIDORM, SPAIN LEDCs: BELIZE / MALDIVES / NEPAL / COSTA RICA Resort decline – and Rejuvenation Why tourists stop going to certain tourist destinations – and the impact this can have. How the resorts try to rejuvenate themselves. BLACKPOOL, UK ; BENIDORM SPAIN Conflicts of Interest arising from Tourism Conflicts of Interest that tourism can create – and how they can be successfully planned for and managed. BENIDORM (WATER) BELIZE (various) NEPAL (various) MALDIVES (various) Tourist Honeypots and sustainable management The issues which develop in tourist Honeypots – and how they are managed in sustainable ways BOWNESS -ON-WINDERMERE, CUMBRIA , LAKE DISTRICT Measuring the level of development of countries Some countries are not well-off and want to use tourism to increase their standard of living. Exploring different Measures of wealth, affluence and quality of life BELIZE Using Tourism for economic growth in poorer countries How long-haul tourism can bring economic, social, cultural, and environmental benefits to an LEDC to help them develop and close the wealth gap BELIZE MALDIVES NEPAL COSTA RICA Tourism can cause Issues, problems and challenges for people and communities Explore the issues that being a tourist destination can bring to resort areas in MEDCs and LEDCs BENIDORM (MEDC) BELIZE, MALDIVES COSTA RICA (LEDCS) Tourism can put pressures on the Environment The impact tourism can have on the environment in resorts in MEDCs and LEDCs BENIDORM, BELIZE, MALDIVES COSTA RICA The impact of increasing tourism on the Global environment How an increase in global tourism and travel can have an impact on the global environment Sustainable tourism can be planned for and managed How some resorts are trying to become regions of Sustainable tourism, including one Ecotourism resort in an LEDC: MALDIVES, NEPAL (sustainable tourism) BELIZE & COSTA RICA (Eco-Tourism) What are the key features of successful tourist management strategies? Evaluating the success of tourist management strategies : BENIDORM MALDIVES NEPAL COSTA RICA BELIZE SEYCHELLES

How to do well at GCSE Geography : getting the examiner to give you the marks A Accuracy : making sure you put down accurate information. Using any info you are provided with – from maps, photos, graphs, tables of data. Referring to the data and supporting your answer by quoting it and using it to back up your points. Knowing the factual information you have learnt in class through effective revision, then using it. Saying things precisely – not just vague and general terms U Understanding : explaining points. Writing at length for higher-scoring questions – not just short, brief answers. Giving Reasons for the points you are making – showing you haven’t just ‘learnt’ them, but ‘understand’ them by explaining fully. (instead of ‘businesses do well’…. Say which types of jobs or shops can be created by the growth of tourism such as ‘people hiring out bikes & quads get more customers’) S Structure / Sections : Organising longer answers into clear paragraphs. This will need some thinking through before you start writing. You may have sections on ‘Economic’, ‘Social’ and ‘Environmental effects of tourism; or Local, Regional, National and International benefits of tourism, or ‘Long-term’ impacts and ‘Short-term’ impacts. But choose a way of organising points logically. L Links : Linking points shows that you are ‘thinking like a geographer’… that you can see the consequences and effects of something, and the causes of things. (eg. Global warming is causing oceans to be warmer…. Because of this they absorb more CO 2…. . As a result coral reefs are dying……Consequently the Maldives are at greater risk of flooding from hurricanes and rising sea levels) E Examples : make sure you refer to actual places. Geography is about the real world. You are expected to be able to name the places where certain things happen. Name actual resorts (‘Benidorm’…. . Not just ‘In Spain…. ’) but also say where it is in the world (Belize – in Central America…… The Maldives, islands in the Indian Ocean…. . ) Know which are in MEDCs & which are in LEDCs. T Terms : use geographical words and vocabulary to show you know the language of the subject. This will help you understand the questions so you can make sure you write about what the examiner is asking for (‘Describe…. . ’ means say what it’s like – but don’t go into explanations. ‘Evaluate’…means say to what extent something has worked). Put geographical terms into your answers where you can: eco-tourism, sustainable tourism, multiplier effect , carbon emissions…et

Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / What is happening to tourist numbers? Tourism Definition : Making active use of leisure time to explore places that are not part of a person’s usual routine. This is more than the annual fortnight holiday to somewhere hot and sunny. It may a day-visit to a theme park, a weekend break to city, a winter holiday which may seek out ‘winter sun’ or ‘winter snow’, and could include a 12 month ‘Gap Year’ round-the-world trip after university. Tourism takes many forms and can be to places quite near as well as far away, last a few hours or take months to complete. But always, tourists will have an impact on the places they visit – sometimes a good one – possibly a bad one, usually a mix of the two. Key Trend 1 : More people are going on holiday than ever before – it is the world’s fastest growing industry 1 Key Terms : Tourism Leisure Time Possible Questions : What are some of the main trends in Tourism in recent decades? How might tourism change in the future as a result of recent trends? Key Trend 2 : People are taking more holidays per year – not just a main ‘summer holiday’, but often a winter holiday, as well as weekend breaks in Autumn and Spring Key Trend 3 : People are travelling further for their holidays. Most people’s grandparents holidayed in Britain, your parents’ generation holidayed in Europe – and your generation is going to different continents – to Florida, Thailand Australia Key Trend 4 : There is big growth in tourists from MEDCs visiting LEDCs either for the climate, the unspoilt Weblinks : BBC video clip on tourism in Brighton http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningz one/clips/tourism-at-theseaside-in-brighton/8438. html
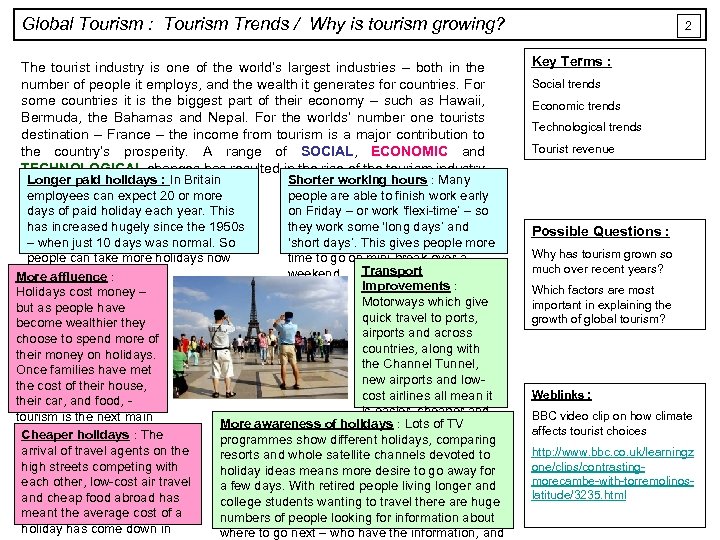
Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / Why is tourism growing? The tourist industry is one of the world’s largest industries – both in the number of people it employs, and the wealth it generates for countries. For some countries it is the biggest part of their economy – such as Hawaii, Bermuda, the Bahamas and Nepal. For the worlds’ number one tourists destination – France – the income from tourism is a major contribution to the country’s prosperity. A range of SOCIAL, ECONOMIC and TECHNOLOGICAL changes has resulted in the rise of the tourism industry Longer paid holidays : In the world. Shorter working hours : Many as a major activity around Britain employees can expect 20 or more people are able to finish work early days of paid holiday each year. This on Friday – or work ‘flexi-time’ – so has increased hugely since the 1950 s they work some ‘long days’ and – when just 10 days was normal. So ‘short days’. This gives people more people can take more holidays now time to go on mini-break over a weekend. Transport More affluence : improvements : Holidays cost money – Motorways which give but as people have quick travel to ports, become wealthier they airports and across choose to spend more of countries, along with their money on holidays. the Channel Tunnel, Once families have met new airports and lowthe cost of their house, cost airlines all mean it their car, and food, is easier, cheaper and tourism is the next main More awareness of holidays : Lots of TV quicker to travel long area of spending. : The Cheaper holidays programmes show different holidays, comparing distances than ever arrival of travel agents on the resorts and whole satellite channels devoted to before. high streets competing with holiday ideas means more desire to go away for each other, low-cost air travel a few days. With retired people living longer and cheap food abroad has college students wanting to travel there are huge meant the average cost of a numbers of people looking for information about holiday has come down in where to go next – who have the information, and 2 Key Terms : Social trends Economic trends Technological trends Tourist revenue Possible Questions : Why has tourism grown so much over recent years? Which factors are most important in explaining the growth of global tourism? Weblinks : BBC video clip on how climate affects tourist choices http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningz one/clips/contrastingmorecambe-with-torremolinoslatitude/3235. html

Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / Mass Tourism & New Technology The rise of the Package Holiday in the 1960 s caused the Mass Tourism that exists today. It made it very easy to book the whole holiday ‘package’ just by selecting a resort from a travel brochure. The travel agent then did all the bookings – flights, hotels, transfers from airport to hotel… even day-trips and sorting out the money you needed when you got there. That role of the Travel Agent is now being threatened by the internet as tourists choose to select and book their own holiday and flights from their computer at home. Advantages Booking through a Travel Agency Easy to buy the full ‘Package’ including flights, hotel & coaches Can get instant help if anything goes wrong – eg flight is cancelled Can benefit from the background knowledge of different resorts from the travel agent Can fully research the resort and use Google Earth to check hotel location and reviews from past tourists Disadvantages You may get sold a holiday which isn’t quite what you want Travel brochures don’t always give the full truth about resorts Package holidays tend to go to busy, popular places which might get crowded. Self-booking through the Internet May be able to find cheaper options for flights and hotel by searching around Can plan the flight times and Many people use a combination of the two – they do their own hotel days exactly to what research on the internet, then book you want it through a Travel Agent 3 Key Terms : Travel Agent Package holiday Mass Tourism Internet Tourism Possible Questions : Why did Mass Tourism take off during the 1960 s? How has technology influenced the tourism industry in recent years? How might new technology influence tourism trends in the future? Weblinks : Negative web stories about crime and murders may put you off a resort but these could happen anywhere Advertised holiday might be a ‘scam’ – you get there and the villa hasn’t been built yet If anything falls through – you’re on your own (flights cancelled) BBC news clip on an internet scam http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/bu siness-11458232 Video clip on the rise of package holidays and the threat of the internet: http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/pro grammes/fast_track/9300289. stm
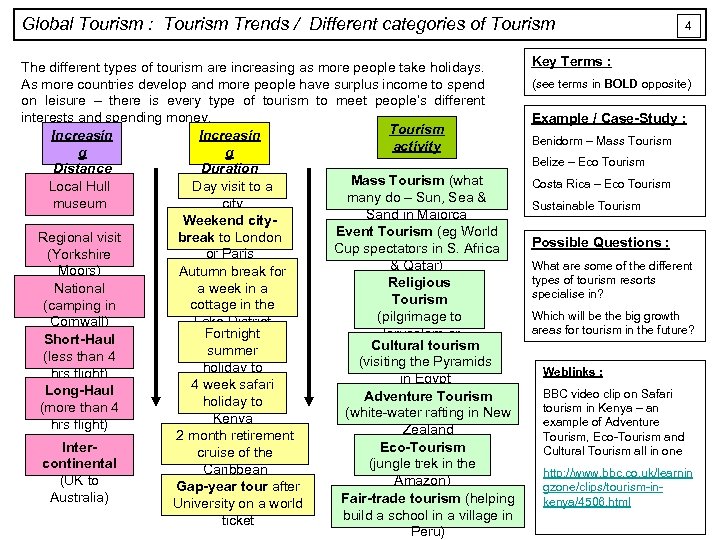
Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / Different categories of Tourism The different types of tourism are increasing as more people take holidays. As more countries develop and more people have surplus income to spend on leisure – there is every type of tourism to meet people’s different interests and spending money. Tourism Increasin activity g g Distance Duration Mass Tourism (what Local Hull Day visit to a many do – Sun, Sea & museum city Sand in Majorca Weekend city. Event Tourism (eg World break to London Regional visit Cup spectators in S. Africa or Paris (Yorkshire & Qatar) Moors) Autumn break for Religious a week in a National Tourism cottage in the (camping in (pilgrimage to Lake District Cornwall) Jerusalem or Fortnight Short-Haul Cultural tourism Mecca) summer (less than 4 (visiting the Pyramids holiday to hrs flight) in Egypt Greece 4 week safari Long-Haul Adventure Tourism holiday to (more than 4 (white-water rafting in New Kenya hrs flight) Zealand 2 month retirement Inter. Eco-Tourism cruise of the continental (jungle trek in the Caribbean (UK to Amazon) Gap-year tour after Australia) Fair-trade tourism (helping University on a world build a school in a village in ticket Peru) 4 Key Terms : (see terms in BOLD opposite) Example / Case-Study : Benidorm – Mass Tourism Belize – Eco Tourism Costa Rica – Eco Tourism Sustainable Tourism Possible Questions : What are some of the different types of tourism resorts specialise in? Which will be the big growth areas for tourism in the future? Weblinks : BBC video clip on Safari tourism in Kenya – an example of Adventure Tourism, Eco-Tourism and Cultural Tourism all in one http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learnin gzone/clips/tourism-inkenya/4506. html
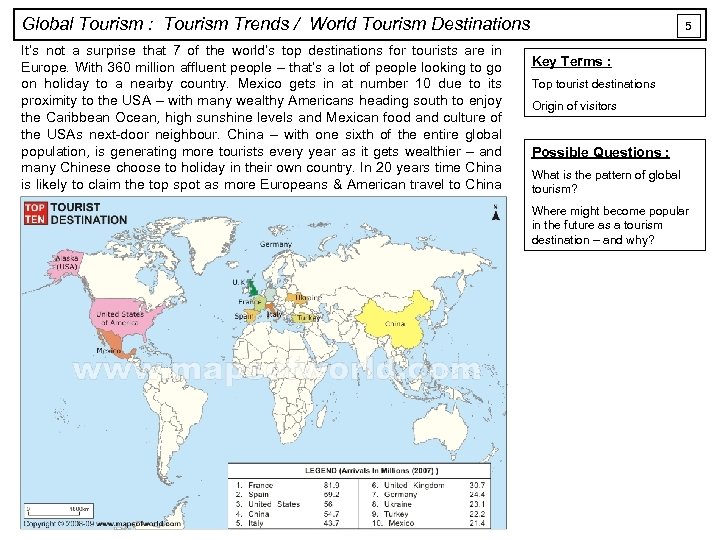
Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / World Tourism Destinations It’s not a surprise that 7 of the world’s top destinations for tourists are in Europe. With 360 million affluent people – that’s a lot of people looking to go on holiday to a nearby country. Mexico gets in at number 10 due to its proximity to the USA – with many wealthy Americans heading south to enjoy the Caribbean Ocean, high sunshine levels and Mexican food and culture of the USAs next-door neighbour. China – with one sixth of the entire global population, is generating more tourists every year as it gets wealthier – and many Chinese choose to holiday in their own country. In 20 years time China is likely to claim the top spot as more Europeans & American travel to China as it develops more airports and hotels, and more Chinese families becoming wealthy enough to take a holiday in their own country. 5 Key Terms : Top tourist destinations Origin of visitors Possible Questions : What is the pattern of global tourism? Where might become popular in the future as a tourism destination – and why?
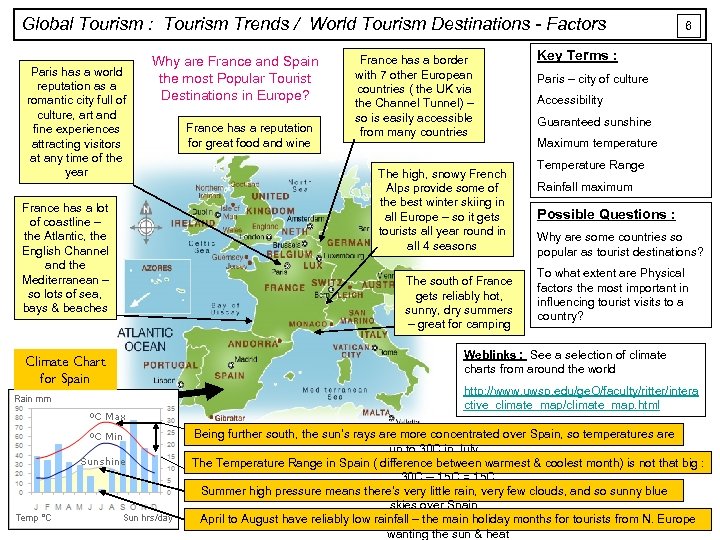
Global Tourism : Tourism Trends / World Tourism Destinations - Factors Paris has a world reputation as a romantic city full of culture, art and fine experiences attracting visitors at any time of the year France has a lot of coastline – the Atlantic, the English Channel and the Mediterranean – so lots of sea, bays & beaches Climate Chart for Spain Why are France and Spain the most Popular Tourist Destinations in Europe? France has a reputation for great food and wine France has a border with 7 other European countries ( the UK via the Channel Tunnel) – so is easily accessible from many countries The high, snowy French Alps provide some of the best winter skiing in all Europe – so it gets tourists all year round in all 4 seasons The south of France gets reliably hot, sunny, dry summers – great for camping 6 Key Terms : Paris – city of culture Accessibility Guaranteed sunshine Maximum temperature Temperature Range Rainfall maximum Possible Questions : Why are some countries so popular as tourist destinations? To what extent are Physical factors the most important in influencing tourist visits to a country? Weblinks : See a selection of climate charts from around the world http: //www. uwsp. edu/ge. O/faculty/ritter/intera ctive_climate_map/climate_map. html Being further south, the sun’s rays are more concentrated over Spain, so temperatures are up to 30 C in July The Temperature Range in Spain ( difference between warmest & coolest month) is not that big : 30 C -- 15 C = 15 C Summer high pressure means there’s very little rain, very few clouds, and so sunny blue skies over Spain April to August have reliably low rainfall – the main holiday months for tourists from N. Europe wanting the sun & heat
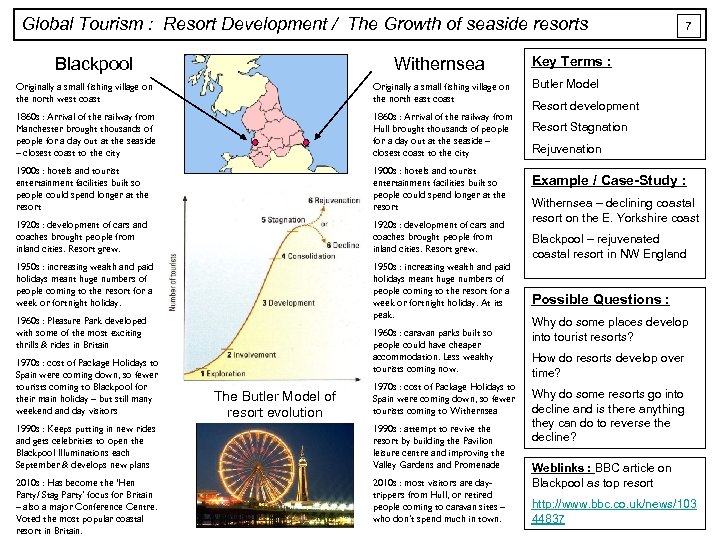
Global Tourism : Resort Development / The Growth of seaside resorts Blackpool Withernsea Originally a small fishing village on the north west coast Originally a small fishing village on the north east coast 1860 s : Arrival of the railway from Manchester brought thousands of people for a day out at the seaside – closest coast to the city 1860 s : Arrival of the railway from Hull brought thousands of people for a day out at the seaside – closest coast to the city 1900 s : hotels and tourist entertainment facilities built so people could spend longer at the resort 1920 s : development of cars and coaches brought people from inland cities. Resort grew. 1950 s : increasing wealth and paid holidays meant huge numbers of people coming to the resort for a week or fortnight holiday. At its peak. 1960 s : Pleasure Park developed with some of the most exciting thrills & rides in Britain 1970 s : cost of Package Holidays to Spain were coming down, so fewer tourists coming to Blackpool for their main holiday – but still many weekend and day visitors 1960 s : caravan parks built so people could have cheaper accommodation. Less wealthy tourists coming now. The Butler Model of resort evolution 1970 s : cost of Package Holidays to Spain were coming down, so fewer tourists coming to Withernsea 1990 s : Keeps putting in new rides and gets celebrities to open the Blackpool Illuminations each September & develops new plans 1990 s : attempt to revive the resort by building the Pavilion leisure centre and improving the Valley Gardens and Promenade 2010 s : Has become the ‘Hen Party/ Stag Party’ focus for Britain – also a major Conference Centre. Voted the most popular coastal resort in Britain. 2010 s : most visitors are daytrippers from Hull, or retired people coming to caravan sites – who don’t spend much in town. 7 Key Terms : Butler Model Resort development Resort Stagnation Rejuvenation Example / Case-Study : Withernsea – declining coastal resort on the E. Yorkshire coast Blackpool – rejuvenated coastal resort in NW England Possible Questions : Why do some places develop into tourist resorts? How do resorts develop over time? Why do some resorts go into decline and is there anything they can do to reverse the decline? Weblinks : BBC article on Blackpool as top resort http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/103 44837
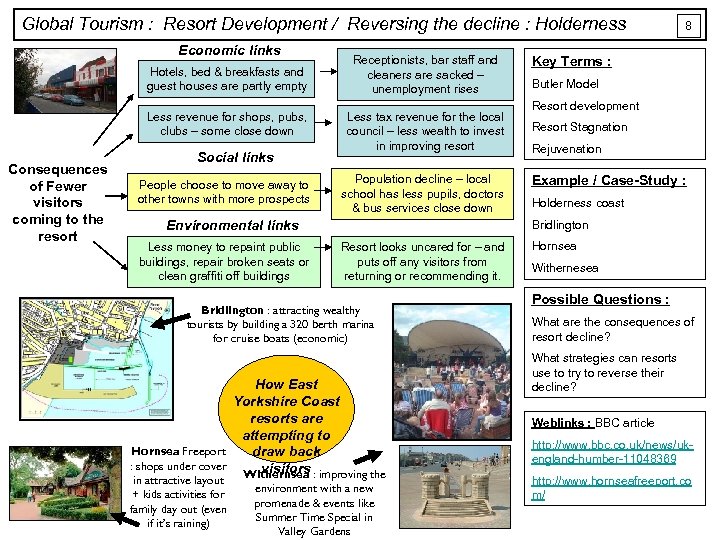
Global Tourism : Resort Development / Reversing the decline : Holderness Economic links Hotels, bed & breakfasts and guest houses are partly empty Less revenue for shops, pubs, clubs – some close down Consequences of Fewer visitors coming to the resort Social links People choose to move away to other towns with more prospects Receptionists, bar staff and cleaners are sacked – unemployment rises Less tax revenue for the local council – less wealth to invest in improving resort Population decline – local school has less pupils, doctors & bus services close down Environmental links Less money to repaint public buildings, repair broken seats or clean graffiti off buildings Key Terms : Butler Model Resort development Resort Stagnation Rejuvenation Example / Case-Study : Holderness coast Bridlington Resort looks uncared for – and puts off any visitors from returning or recommending it. Bridlington : attracting wealthy tourists by building a 320 berth marina for cruise boats (economic) How East Yorkshire Coast resorts are attempting to Hornsea Freeport draw back : shops under cover visitors Withernsea : improving the in attractive layout + kids activities for family day out (even if it’s raining) 8 environment with a new promenade & events like Summer Time Special in Valley Gardens Hornsea Withernesea Possible Questions : What are the consequences of resort decline? What strategies can resorts use to try to reverse their decline? Weblinks : BBC article http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/ukengland-humber-11048369 http: //www. hornseafreeport. co m/
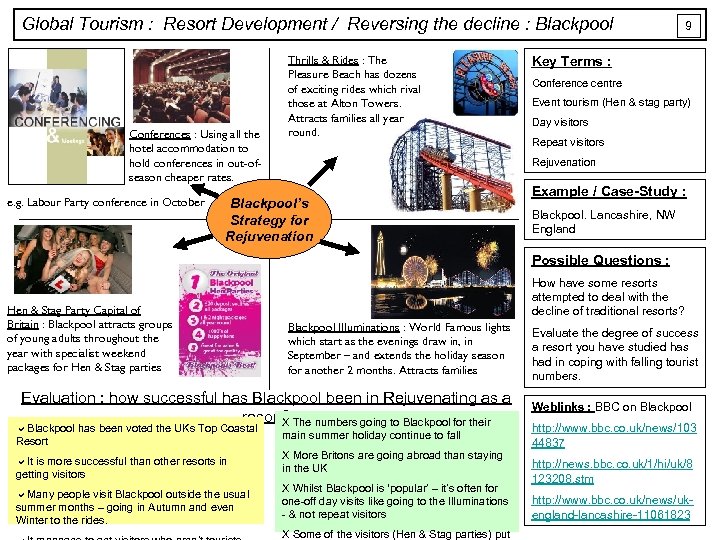
Global Tourism : Resort Development / Reversing the decline : Blackpool Conferences : Using all the hotel accommodation to hold conferences in out-ofseason cheaper rates. e. g. Labour Party conference in October Thrills & Rides : The Pleasure Beach has dozens of exciting rides which rival those at Alton Towers. Attracts families all year round. 9 Key Terms : Conference centre Event tourism (Hen & stag party) Day visitors Repeat visitors Rejuvenation Blackpool’s Strategy for Rejuvenation Example / Case-Study : Blackpool. Lancashire, NW England Possible Questions : Hen & Stag Party Capital of Britain : Blackpool attracts groups of young adults throughout the year with specialist weekend packages for Hen & Stag parties How have some resorts attempted to deal with the decline of traditional resorts? Blackpool Illuminations : World Famous lights which start as the evenings draw in, in September – and extends the holiday season for another 2 months. Attracts families Evaluation : how successful has Blackpool been in Rejuvenating as a resort? The numbers going to Blackpool for their X a. Blackpool has been voted the UKs Top Coastal Resort a. It is more successful than other resorts in getting visitors a. Many people visit Blackpool outside the usual summer months – going in Autumn and even Winter to the rides. main summer holiday continue to fall X More Britons are going abroad than staying in the UK X Whilst Blackpool is ‘popular’ – it’s often for one-off day visits like going to the Illuminations - & not repeat visitors X Some of the visitors (Hen & Stag parties) put Evaluate the degree of success a resort you have studied has had in coping with falling tourist numbers. Weblinks : BBC on Blackpool http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/103 44837 http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/uk/8 123208. stm http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/ukengland-lancashire-11061823

Global Tourism : Resort Development / Spain – Benidorm Growth Hotel on the slope only 2 minutes from the beach Forested slopes a nice cool walk or picnic away from the beach Clear blue skies long hours of reliable sunshine Clear clean sea pleasant to swim in. Jetty has been built can dive off it, or go on glass-bottom boat trips Trees by the beach give cool shade at midday for families Sun shades are provided stops you getting sunburnt Stages in the growth of Benidorm – Costa Blanca, Spain Sun-loungers means you can stay off hot sand Physical & Human attractions of the Mediterranean coast 1950 s : The mayor looks for a way to revive the declining fishing port of Benidorm as fish stocks decline. He persuades the President to allow foreign tourists to wear the new fashion of ‘bikinis’ on the beach – the only one in Spain to allow this. The resort becomes popular with US film stars and rich Europeans 1960 s : New hotels, bars, restaurants are built to make money from the growing number of rich tourists arriving on new Package Holidays 1970 s : Transport infrastructure is improved – new roads and the nearby airport at Alicante brings in larger numbers of middle income tourists to Benidorm to enjoy the guaranteed hot sunny summers, warm blue Mediterranean Sea & Spanish culture. 1980 s: Mass Tourism arrives as large numbers of hotels are built, lots of cheap fast-food outlets and pubs and clubs selling cheap beer & wine. Competition between hotels and bars forces down prices – bringing the resort to many lower income people. 10 Key Terms : Physical attractions Human attractions Package holiday Transport infrastructure Mass tourism Example / Case-Study : Benidorm – Costa Blanca, Spain Possible Questions : Annotate a photograph to show the Physical and Human factors which have attracted tourists to this resort What were the main factors leading to the growth of a resort you have studied? Weblinks : Read about how the bikini helped Benidorm grow to the top Mediterranean resort : http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/progr ammes/from_our_own_corresp ondent/2031726. stm http: //www. guardian. co. uk/worl d/2008/apr/02/spain
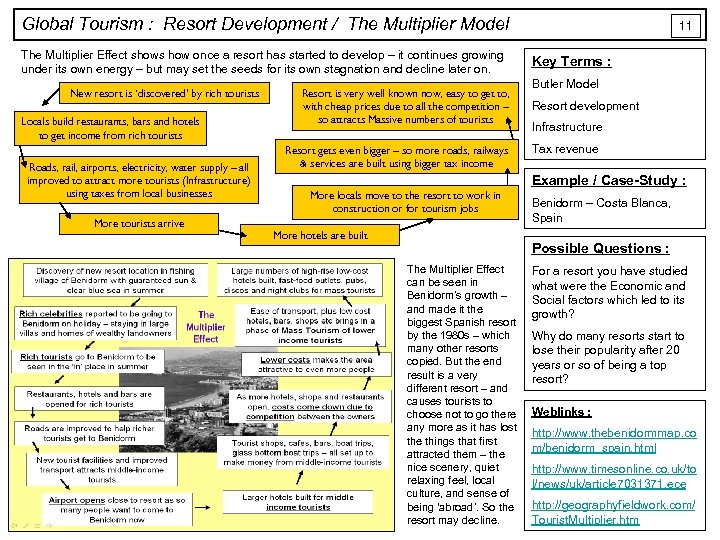
Global Tourism : Resort Development / The Multiplier Model The Multiplier Effect shows how once a resort has started to develop – it continues growing under its own energy – but may set the seeds for its own stagnation and decline later on. New resort is ‘discovered’ by rich tourists Locals build restaurants, bars and hotels to get income from rich tourists Roads, rail, airports, electricity, water supply – all improved to attract more tourists (Infrastructure) using taxes from local businesses More tourists arrive Resort is very well known now, easy to get to, with cheap prices due to all the competition – so attracts Massive numbers of tourists Resort gets even bigger – so more roads, railways & services are built using bigger tax income 11 Key Terms : Butler Model Resort development Infrastructure Tax revenue Example / Case-Study : More locals move to the resort to work in construction or for tourism jobs More hotels are built Benidorm – Costa Blanca, Spain Possible Questions : The Multiplier Effect can be seen in Benidorm’s growth – and made it the biggest Spanish resort by the 1980 s – which many other resorts copied. But the end result is a very different resort – and causes tourists to choose not to go there any more as it has lost the things that first attracted them – the nice scenery, quiet relaxing feel, local culture, and sense of being ‘abroad’. So the resort may decline. For a resort you have studied what were the Economic and Social factors which led to its growth? Why do many resorts start to lose their popularity after 20 years or so of being a top resort? Weblinks : http: //www. thebenidormmap. co m/benidorm_spain. html http: //www. timesonline. co. uk/to l/news/uk/article 7031371. ece http: //geographyfieldwork. com/ Tourist. Multiplier. htm
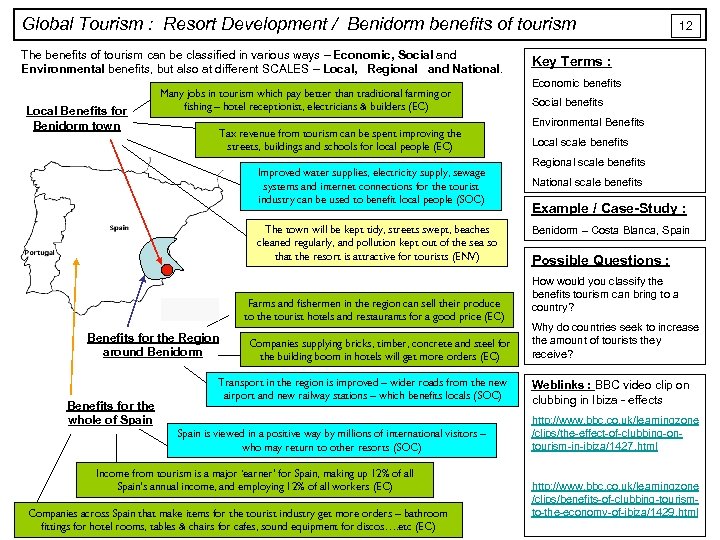
Global Tourism : Resort Development / Benidorm benefits of tourism The benefits of tourism can be classified in various ways – Economic, Social and Environmental benefits, but also at different SCALES – Local, Regional and National. Local Benefits for Benidorm town Many jobs in tourism which pay better than traditional farming or fishing – hotel receptionist, electricians & builders (EC) Tax revenue from tourism can be spent improving the streets, buildings and schools for local people (EC) Improved water supplies, electricity supply, sewage systems and internet connections for the tourist industry can be used to benefit local people (SOC) The town will be kept tidy, streets swept, beaches cleaned regularly, and pollution kept out of the sea so that the resort is attractive for tourists (ENV) Farms and fishermen in the region can sell their produce to the tourist hotels and restaurants for a good price (EC) Benefits for the Region around Benidorm Benefits for the whole of Spain Companies supplying bricks, timber, concrete and steel for the building boom in hotels will get more orders (EC) Transport in the region is improved – wider roads from the new airport and new railway stations – which benefits locals (SOC) Spain is viewed in a positive way by millions of international visitors – who may return to other resorts (SOC) Income from tourism is a major ‘earner’ for Spain, making up 12% of all Spain’s annual income, and employing 12% of all workers (EC) Companies across Spain that make items for the tourist industry get more orders – bathroom fittings for hotel rooms, tables & chairs for cafes, sound equipment for discos…. etc (EC) 12 Key Terms : Economic benefits Social benefits Environmental Benefits Local scale benefits Regional scale benefits National scale benefits Example / Case-Study : Benidorm – Costa Blanca, Spain Possible Questions : How would you classify the benefits tourism can bring to a country? Why do countries seek to increase the amount of tourists they receive? Weblinks : BBC video clip on clubbing in Ibiza - effects http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningzone /clips/the-effect-of-clubbing-ontourism-in-ibiza/1427. html http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningzone /clips/benefits-of-clubbing-tourismto-the-economy-of-ibiza/1429. html
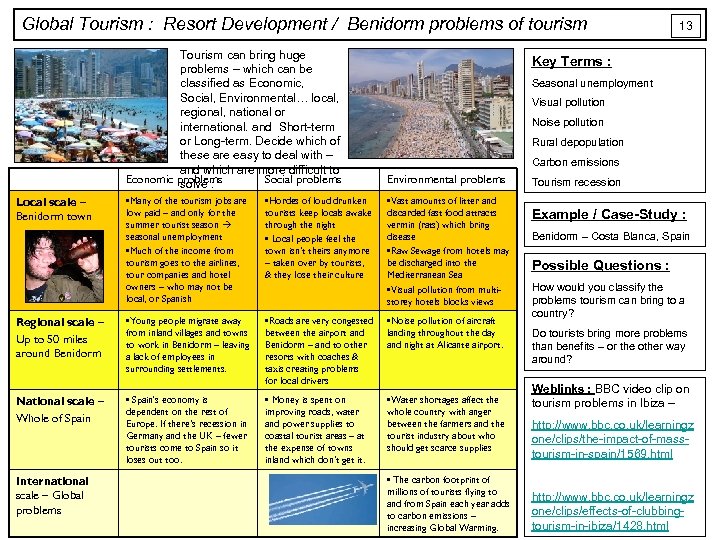
Global Tourism : Resort Development / Benidorm problems of tourism Tourism can bring huge problems – which can be classified as Economic, Social, Environmental… local, regional, national or international. and Short-term or Long-term. Decide which of these are easy to deal with – and which are more difficult to Economic problems Social problems solve : Environmental problems • Many of the tourism jobs are low paid – and only for the summer tourist seasonal unemployment • Much of the income from tourism goes to the airlines, tour companies and hotel owners – who may not be local, or Spanish • Hordes of loud drunken tourists keep locals awake through the night • Local people feel the town isn’t theirs anymore – taken over by tourists, & they lose their culture • Vast amounts of litter and discarded fast food attracts vermin (rats) which bring disease • Raw Sewage from hotels may be discharged into the Mediterranean Sea • Visual pollution from multistorey hotels blocks views Regional scale – Up to 50 miles around Benidorm • Young people migrate away from inland villages and towns to work in Benidorm – leaving a lack of employees in surrounding settlements. • Roads are very congested between the airport and Benidorm – and to other resorts with coaches & taxis creating problems for local drivers • Noise pollution of aircraft landing throughout the day and night at Alicante airport. National scale – Whole of Spain • Spain's economy is dependent on the rest of Europe. If there’s recession in Germany and the UK – fewer tourists come to Spain so it loses out too. • Money is spent on improving roads, water and power supplies to coastal tourist areas – at the expense of towns inland which don’t get it. • Water shortages affect the whole country with anger between the farmers and the tourist industry about who should get scarce supplies Local scale – Benidorm town International scale – Global problems 13 Key Terms : Seasonal unemployment Visual pollution Noise pollution Rural depopulation Carbon emissions • The carbon footprint of millions of tourists flying to and from Spain each year adds to carbon emissions – increasing Global Warming. Tourism recession Example / Case-Study : Benidorm – Costa Blanca, Spain Possible Questions : How would you classify the problems tourism can bring to a country? Do tourists bring more problems than benefits – or the other way around? Weblinks : BBC video clip on tourism problems in Ibiza – http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningz one/clips/the-impact-of-masstourism-in-spain/1569. html http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningz one/clips/effects-of-clubbingtourism-in-ibiza/1428. html

Global Tourism : Resort Development / Spanish Tourism Rejuvenation plans 14 Key Terms : Activity holidays Out of season holidays Cultural holidays Rejuvenation Example / Case-Study : Malaga, Spain – Tennis & Golf resort Spain is trying to rejuvenate its tourism by moving away from Mass Tourism at the coast and trying to encourage: • fewer but more wealthy tourists Possible Questions : How has a resort you have studied tried to stop its decline as a popular tourist destination? Is it inevitable that tourist resorts become less popular over time? • Encourage tourism throughout the year – Spring Autumn & Winter as well as summer Weblinks : • Encouraging more active tourism – golf, tennis, riding holidays. People pay more for these – and they don’t depend on hot sunny weather http: //www. guardian. co. uk/trav el/2008/aug/03/spain. travelnew s • Dispersing tourists http: //www. lamangaclub. com/L ove-Sport. html http: //www. guardian. co. uk/trav el/2011/apr/02/benidorm-spainholiday-new-alicante

Global Tourism : Tourism Environmental Impact / Spanish Water Issues Spain is facing serious water shortages which is being made worse by the needs of the tourist industry. There is a big question of who should have the main claim to Spain’s declining water – the farming sector or the tourism sector Tourism Claims for Water Farmers’ Claims for Water • Tourists expect to be able to • Growers need irrigation water for Irrigation Water shortage High-value salad crops Horticulture / polytunnels Example / Case-Study : Why Spain is facing a water shortage Climate Change : less rain is falling on Spain as the Sahara desert expands northwards over it Increased use for Farming : more farms are growing highvalue salad crops which need a lot of irrigation water to produce good crops Increased use for Tourism : more hotels, more swimming pools, more water features like fountains etc. Spain's 2020 tourism strategy wants more wealthy tourists playing golf – so irrigating golf courses uses lots of water Malaga, Spain – Tennis & Golf resort • Tourism is the biggest growth sector of Spain’s economy – rather than farming so should get first use of the water • The farms are often in the interior of Spain – providing jobs in areas outside the coastal tourist areas • Tourists are choosing to go to other resorts outside Spain – so Spain will need the farming industry for its income in the future. Key Terms : shower, use swimming pools & flumes and not face water shortages when they come on holiday – or they’ll go elsewhere high-value crops of tomatoes, lettuce, celery and peppers which can be sold to N. Europe for high prices during the winter & spring • Farming uses water very efficiently in polytunnels and greenhouses to reduce evaporation but the tourism industry wastes water 15 What are some of the negative effects of tourism on the environment? • Tourism is going to be a big earner in the future for Spain – but farming is traditional and old • Farmers should concentrate on crops which need less water – like olives for olive oil & grapes for wine Possible Questions : How can tourism bring problems as well as benefits to an area? Weblinks BBC video clip on water shortages in Spain http: //www. bbc. co. uk/learningz one/clips/water-shortages-theebro-river-dam/1570. html

Global Tourism : Tourism Environmental Impact / Spanish Water Solutions 16 Key Terms : Underground aquifer Boreholes Water transfer scheme Reservoirs De-salination plant Sustainable solution Example / Case-Study : Malaga, Spain – Tennis & Golf resort – water shortage Possible Questions : How can the negative effects of tourism be managed? What do you understand by ‘sustainable tourism’? Weblinks Water shortages could reduce Spain’s economic progress – either by reducing the amount of high-value food crops it is able to export, or by reducing the number tourists it attracts compared with other countries with better water supplies. The solution Spain chooses should allow for SUSTAINABLE uses of limited water – and sustainable economic growth into the future. http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/world /europe/912127. stm http: //economatters. wordpress. com/2008/05/04/water-scarcityin-spain-barcelona-is-drying-up/
8302983958afc4c29c9a87c70668641c.ppt