e56e1ebf1378cc7e936fff461e18921b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATIONS (GIs) PROTECTION VS INTERNET FREEDOM: ALTERNATIVE DISPUTES RESOLUTION (ADR) AS METHOD AND MEDIATION AS OPTION Protection of Geographical Indications (GIs) in the new Internet scenario Pierfrancesco C. Fasano Mediation Case Manager EU Parliament – Representative Office in Milan – Palazzo delle Stelline Milan, 28 th February 2014
GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATIONS (GIs) PROTECTION VS INTERNET FREEDOM: ALTERNATIVE DISPUTES RESOLUTION (ADR) AS METHOD AND MEDIATION AS OPTION Protection of Geographical Indications (GIs) in the new Internet scenario Pierfrancesco C. Fasano Mediation Case Manager EU Parliament – Representative Office in Milan – Palazzo delle Stelline Milan, 28 th February 2014
 Summary ABOUT US GIs – LEGAL FRAMEWORK OFF LINE ALTERNATIVE DISPUTE RESOLUTION – OUTOF-COURT DISPUTE RESOLUTION GIs – LEGAL FRAMEWORK ONLINE PROPOSED SOLUTIONS
Summary ABOUT US GIs – LEGAL FRAMEWORK OFF LINE ALTERNATIVE DISPUTE RESOLUTION – OUTOF-COURT DISPUTE RESOLUTION GIs – LEGAL FRAMEWORK ONLINE PROPOSED SOLUTIONS
 About us Dispute Resolution Center specialized in Intellectual Property (IP) matters Accreditations: 2001 by Registry “. it” as Dispute Resolution Service Provider to resolve domain name disputes under cc. TLD “. it” 2012 by Ministry of Justice as Mediation Center in IP disputes 2013 by Ministry of Justice as Mediation Training Center
About us Dispute Resolution Center specialized in Intellectual Property (IP) matters Accreditations: 2001 by Registry “. it” as Dispute Resolution Service Provider to resolve domain name disputes under cc. TLD “. it” 2012 by Ministry of Justice as Mediation Center in IP disputes 2013 by Ministry of Justice as Mediation Training Center
 Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Paris Convention (1883): false indication Madrid Agreement (1891): false and deceptive indication Lisbon Agreement (1958): definition of appellation of origin (AO) TRIPs Agreement (1994): first international treaty bound to protect GIs and to enforce its application WTO Agreement: protection and extension
Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Paris Convention (1883): false indication Madrid Agreement (1891): false and deceptive indication Lisbon Agreement (1958): definition of appellation of origin (AO) TRIPs Agreement (1994): first international treaty bound to protect GIs and to enforce its application WTO Agreement: protection and extension
 Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Lisbon Agreement Total Contracting Parties: 28 countries Africa: Algeria, Burkina Faso, Congo, Gabon Togo, Tunisia Asia: Georgia, Islamic Rep. of Iran, Israel, DPR of Korea America: Costa Rica, Cuba Haiti, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru Europe: Bosnia and Hercegovina, Bulgaria, Czech Rep. , France, Hungary, Italy, Moldova, montenegro, Portugal, Serbia, Slovakia, The FYR of Macedonia
Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Lisbon Agreement Total Contracting Parties: 28 countries Africa: Algeria, Burkina Faso, Congo, Gabon Togo, Tunisia Asia: Georgia, Islamic Rep. of Iran, Israel, DPR of Korea America: Costa Rica, Cuba Haiti, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru Europe: Bosnia and Hercegovina, Bulgaria, Czech Rep. , France, Hungary, Italy, Moldova, montenegro, Portugal, Serbia, Slovakia, The FYR of Macedonia
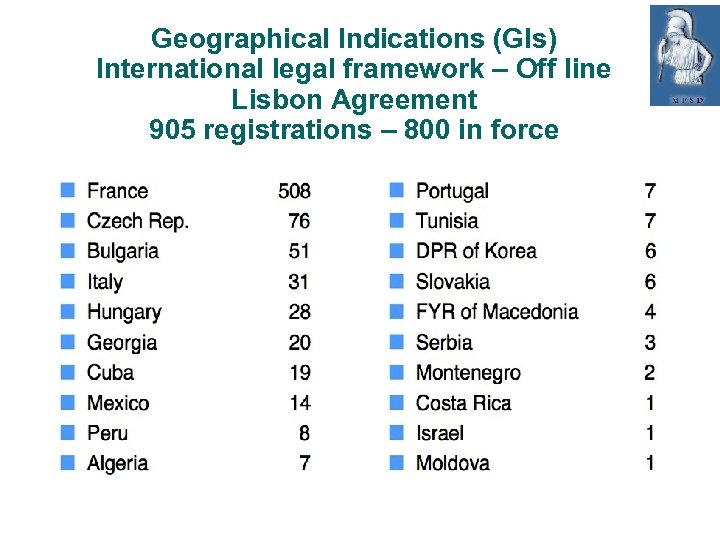 Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Lisbon Agreement 905 registrations – 800 in force
Geographical Indications (GIs) International legal framework – Off line Lisbon Agreement 905 registrations – 800 in force
 Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Collective trademarks: owned by an association whose members use them to identify themselves with a level of quality and other requirements set by the association Certification marks: given for compliance with defined standards and granted to anyone who can certify that the products involved meet certain established standards. The owner (certifier) cannot use it In many jurisdictions potection of GIs as collective or certification marks
Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Collective trademarks: owned by an association whose members use them to identify themselves with a level of quality and other requirements set by the association Certification marks: given for compliance with defined standards and granted to anyone who can certify that the products involved meet certain established standards. The owner (certifier) cannot use it In many jurisdictions potection of GIs as collective or certification marks
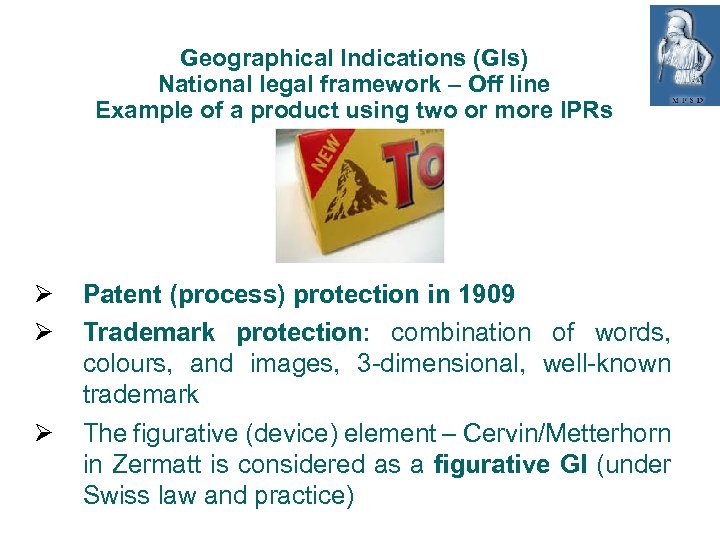 Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Example of a product using two or more IPRs Patent (process) protection in 1909 Trademark protection: combination of words, colours, and images, 3 -dimensional, well-known trademark The figurative (device) element – Cervin/Metterhorn in Zermatt is considered as a figurative GI (under Swiss law and practice)
Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Example of a product using two or more IPRs Patent (process) protection in 1909 Trademark protection: combination of words, colours, and images, 3 -dimensional, well-known trademark The figurative (device) element – Cervin/Metterhorn in Zermatt is considered as a figurative GI (under Swiss law and practice)
 Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Example of a geographical name with multiple protection AOC in France (AOP French abbreviation for PDO) Collective mark of ewe milk producers in the area of Roquefort US Certification mark
Geographical Indications (GIs) National legal framework – Off line Example of a geographical name with multiple protection AOC in France (AOP French abbreviation for PDO) Collective mark of ewe milk producers in the area of Roquefort US Certification mark
 Geographical Indications (GIs) Supranational legal framework – Off line EU logos/symbols used for products bearing a GI Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) - L Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) - C Traditional Speciality Guaranteed (TSG) - R
Geographical Indications (GIs) Supranational legal framework – Off line EU logos/symbols used for products bearing a GI Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) - L Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) - C Traditional Speciality Guaranteed (TSG) - R
 Geographical Indications (GIs) Hot key points – Off line GIs are independent category of IP = distinctive signs GIs vs free trade – Internet Freedom Complex and controversial issue at international – supranational level Commercial and economic stakes Social, historical and cultural dimensions Emotional debates Not sufficient empirical evidence on Pros and Cons Inadequate court dispute resolution system
Geographical Indications (GIs) Hot key points – Off line GIs are independent category of IP = distinctive signs GIs vs free trade – Internet Freedom Complex and controversial issue at international – supranational level Commercial and economic stakes Social, historical and cultural dimensions Emotional debates Not sufficient empirical evidence on Pros and Cons Inadequate court dispute resolution system
 Alternative Dispute Resolution Alternatives to court-based litigation which is often time and cost consuming Arbitration (expedited): binding decision on parties Mediation or Conciliation: assistance of parties to come to an agreement (court-annexed, voluntary, mandatory) Other methods: e. g. neutral assessment of facts, appraisal, ombudsman or consumer complaints boards' recommendation
Alternative Dispute Resolution Alternatives to court-based litigation which is often time and cost consuming Arbitration (expedited): binding decision on parties Mediation or Conciliation: assistance of parties to come to an agreement (court-annexed, voluntary, mandatory) Other methods: e. g. neutral assessment of facts, appraisal, ombudsman or consumer complaints boards' recommendation
 Mediation A process whereby two or more parties to a dispute attempt by themselves to reach an agreement on the settlement of their dispute with the assistance of a neutral and qualified third party (mediator) Advantages: Cost-effective Quick Voluntary (sometimes mandatory or court-annexed) Confidential Informal Personalized solution
Mediation A process whereby two or more parties to a dispute attempt by themselves to reach an agreement on the settlement of their dispute with the assistance of a neutral and qualified third party (mediator) Advantages: Cost-effective Quick Voluntary (sometimes mandatory or court-annexed) Confidential Informal Personalized solution
 EU Mediation Legal framework Directive 2008/52/CE of certain aspects of mediation in civil and commercial matters: “Mediation can provide a cost-effective and quick extra-judicial resolution in civil and commercial matters through processes tailored to the needs of the parties. Agreements resulting from mediation are more likely to be complied with voluntarily and are more likely to preserve an amicable and sustainable relationship between the parties. These benefits become even more pronounced in situations displaying cross-border elements”. Agreement enforeable in Member States (except Denmark)
EU Mediation Legal framework Directive 2008/52/CE of certain aspects of mediation in civil and commercial matters: “Mediation can provide a cost-effective and quick extra-judicial resolution in civil and commercial matters through processes tailored to the needs of the parties. Agreements resulting from mediation are more likely to be complied with voluntarily and are more likely to preserve an amicable and sustainable relationship between the parties. These benefits become even more pronounced in situations displaying cross-border elements”. Agreement enforeable in Member States (except Denmark)
 Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples co. uk - Nominet Fast trasparent process to help parties settle domain name disputes where: • Party making the complaint has rights in a name which is similar to the domain name; and • Registrant has taken unfair advantage of those rights Based on free, confidential mediation Quick: 2 weeks If no settlement or registrant does not respond → Expert decision (transfer or deletion)
Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples co. uk - Nominet Fast trasparent process to help parties settle domain name disputes where: • Party making the complaint has rights in a name which is similar to the domain name; and • Registrant has taken unfair advantage of those rights Based on free, confidential mediation Quick: 2 weeks If no settlement or registrant does not respond → Expert decision (transfer or deletion)
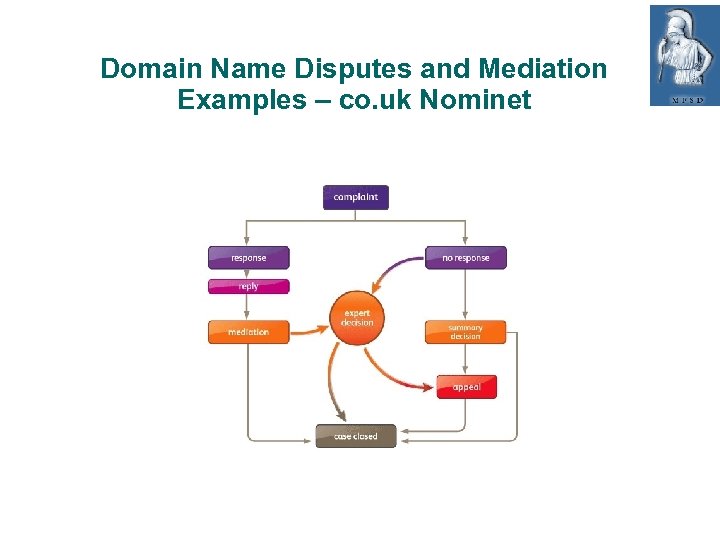 Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples – co. uk Nominet
Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples – co. uk Nominet
 Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples . sg – Singapore Mediation Centre Singapore Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy (SDRP) and Rules for SDRP Quick, convenient and relatively inexpensive mechanism to resolve domain name disputes where: • Domain name is identical or confusingly similar to name, trade mark or service mark in which petitioner has rights recognised under Singapore law, • Registrant not entitled for registration and/or use of domain name, and • Domain name registered and/or used in bad faith If parties agree Panel (called upon to decide the dispute) may mediate the dispute in 15 working days from the appointment of Panel
Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples . sg – Singapore Mediation Centre Singapore Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy (SDRP) and Rules for SDRP Quick, convenient and relatively inexpensive mechanism to resolve domain name disputes where: • Domain name is identical or confusingly similar to name, trade mark or service mark in which petitioner has rights recognised under Singapore law, • Registrant not entitled for registration and/or use of domain name, and • Domain name registered and/or used in bad faith If parties agree Panel (called upon to decide the dispute) may mediate the dispute in 15 working days from the appointment of Panel
 Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples . it – MFSD Voluntary, informal, quick procedure Upon request MFSD offers mediation service in accordance with its Mediation Rules Italian Mediation Law (D. Lgs. n. 28/2010) provides for fiscal benefits (tax credit) to incentivate the mediation: • 500 euros if mediation is successful (agreement) • 250 euros if mediation fails (no agreement or default of respondent) If mediation fails petioner may file a complaint for reassignation of domain name
Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples . it – MFSD Voluntary, informal, quick procedure Upon request MFSD offers mediation service in accordance with its Mediation Rules Italian Mediation Law (D. Lgs. n. 28/2010) provides for fiscal benefits (tax credit) to incentivate the mediation: • 500 euros if mediation is successful (agreement) • 250 euros if mediation fails (no agreement or default of respondent) If mediation fails petioner may file a complaint for reassignation of domain name
 Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples –. it MFSD Request for mediation Early evaluation meeting Appointment of mediator Initial contacts between mediator and parties Setting up the first meeting Agreeing preliminary exchange of documents First and subsequent meeting(s) Gathering information and identifying issues Exploring the interests of parties Developing options for settlement Evaluating options Concluding
Domain Name Disputes and Mediation Examples –. it MFSD Request for mediation Early evaluation meeting Appointment of mediator Initial contacts between mediator and parties Setting up the first meeting Agreeing preliminary exchange of documents First and subsequent meeting(s) Gathering information and identifying issues Exploring the interests of parties Developing options for settlement Evaluating options Concluding
 ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online 1, 930 new domain applications – 1, 408 unique applications 664 “brand applications” 116 Internationalized Domain Name applications in 12 scripts Applicants from 60 countries from all regions: Africa (17), Asia Pacific (303), Europe (675), Latin America (24), North America (911) 84 “Community-Based” applications 66 geographical applications Applications: . food, . cheese, . beer, . pizza, . wine and. vin
ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online 1, 930 new domain applications – 1, 408 unique applications 664 “brand applications” 116 Internationalized Domain Name applications in 12 scripts Applicants from 60 countries from all regions: Africa (17), Asia Pacific (303), Europe (675), Latin America (24), North America (911) 84 “Community-Based” applications 66 geographical applications Applications: . food, . cheese, . beer, . pizza, . wine and. vin
 ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online 1, 408 unique strings means c. 1, 350 registries = 56 registries launching every month for 2 yrs By end of 2015 domain name system will have grown from 275 registries to c. 1, 600 registries Short term: • New g. TLDs to run in parallel with. coms (not to replace) • Educations of consumers (farms/consortia) that. brand is a safe environment Long term: • Second and third rounds like. com boom: thousands of applications at a much lower price • Rebranding from. com to. brand • 500, 000 new g. TLD registries in a decade
ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online 1, 408 unique strings means c. 1, 350 registries = 56 registries launching every month for 2 yrs By end of 2015 domain name system will have grown from 275 registries to c. 1, 600 registries Short term: • New g. TLDs to run in parallel with. coms (not to replace) • Educations of consumers (farms/consortia) that. brand is a safe environment Long term: • Second and third rounds like. com boom: thousands of applications at a much lower price • Rebranding from. com to. brand • 500, 000 new g. TLD registries in a decade
 ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online Limit of final draft of new g. TLD Registry Agreement – Provisions of Specification 5 concerning geographical names which might be used in second level and/or other registrations (4. Country and Territory Name), in their current form, are by no means sufficient to ensure the respect of the legistimate rights deriving from GIs Proper system of dispute resolution based on the legitimate rights of GIs owners and beneficieries should be established
ICANN's New g. TLD Program State of art – Quo vadis ? GIs Legal framework Online Limit of final draft of new g. TLD Registry Agreement – Provisions of Specification 5 concerning geographical names which might be used in second level and/or other registrations (4. Country and Territory Name), in their current form, are by no means sufficient to ensure the respect of the legistimate rights deriving from GIs Proper system of dispute resolution based on the legitimate rights of GIs owners and beneficieries should be established
 New g. TLDs Rights Protection Mechanism Pre-Delegation Objections (including Legal Rights Objection - LRO) Trademark Clearinghouse • Sunrise • Trademark Claims Uniform Rapid Suspension System (URS) TM Post-Delegation Dispute Resolution (PDDRP) Registry Restriction Dispute Resolution (RRDRP) UDRP: remains applicable to all new g. TLDs
New g. TLDs Rights Protection Mechanism Pre-Delegation Objections (including Legal Rights Objection - LRO) Trademark Clearinghouse • Sunrise • Trademark Claims Uniform Rapid Suspension System (URS) TM Post-Delegation Dispute Resolution (PDDRP) Registry Restriction Dispute Resolution (RRDRP) UDRP: remains applicable to all new g. TLDs
 New g. TLDs and Mediation ICANN New g. TLD Program – Applicant Guidebook incentivate mediation – not working Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures: Attachment to Module 3 – New g. TLD Dispute Resolution Procedure Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation) Registry Restrictions Dispute Resolution Procedure: Article 21 (Availability of Court or other Administrative Proceedings)
New g. TLDs and Mediation ICANN New g. TLD Program – Applicant Guidebook incentivate mediation – not working Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures: Attachment to Module 3 – New g. TLD Dispute Resolution Procedure Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation) Registry Restrictions Dispute Resolution Procedure: Article 21 (Availability of Court or other Administrative Proceedings)
 New g. TLDs and Mediation Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation): Parties are encouraged but not required to participate negotiations and/or mediation at any time throughout the dispute resolution process aimed at settling their dispute amicably Each DRSP shall be able to propose, if requested by the parties, a person who could assist the parties as mediator A person who acts as mediator for the parties shall not serve as an Expert in a dispute or proceeding between the parties involving the same g. TLD
New g. TLDs and Mediation Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation): Parties are encouraged but not required to participate negotiations and/or mediation at any time throughout the dispute resolution process aimed at settling their dispute amicably Each DRSP shall be able to propose, if requested by the parties, a person who could assist the parties as mediator A person who acts as mediator for the parties shall not serve as an Expert in a dispute or proceeding between the parties involving the same g. TLD
 New g. TLDs and Mediation Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation): Conduct of negotiations or mediation shall not, ipso facto, be the basis for a suspension of the dispute resolution proceedings or the extension of any deadline. Upon joint request of the parties DRSP may grant an extension of deadline or the suspension of the proceedings If parties agree on a settlement of the matter, the parties shall inform the DRSP, which shall terminate the proceedings and inform ICANN and the parties accordingly
New g. TLDs and Mediation Pre-Delegation Objection Procedures Article 16 (Negotiation and Mediation): Conduct of negotiations or mediation shall not, ipso facto, be the basis for a suspension of the dispute resolution proceedings or the extension of any deadline. Upon joint request of the parties DRSP may grant an extension of deadline or the suspension of the proceedings If parties agree on a settlement of the matter, the parties shall inform the DRSP, which shall terminate the proceedings and inform ICANN and the parties accordingly
 New g. TLDs and Mediation Registry Restriction Dispute Resolution Procedures (RRDRP) Article 21. 2 (Availability of Court and other Administrative Proceedings): Parties are encouraged but not required to participate in informal negotiations and/or mediation at any time throughout the dispute resolution process but the conduct of any such settlement negotiation is not, standing alone, a reason to suspend any deadline under the proceedings
New g. TLDs and Mediation Registry Restriction Dispute Resolution Procedures (RRDRP) Article 21. 2 (Availability of Court and other Administrative Proceedings): Parties are encouraged but not required to participate in informal negotiations and/or mediation at any time throughout the dispute resolution process but the conduct of any such settlement negotiation is not, standing alone, a reason to suspend any deadline under the proceedings
 Proposed solutions ICANN → Registries List of reserved domain names GIs (adoption List of Lisbon Agreement) TMCH including GIs Enhance mediation Binding early legal opinion provided by ADR Providers
Proposed solutions ICANN → Registries List of reserved domain names GIs (adoption List of Lisbon Agreement) TMCH including GIs Enhance mediation Binding early legal opinion provided by ADR Providers
 MFSD S. r. l. www. mfsd. it E: responsabile@mfsd. it - Certified e-mail (only within Italy): mfsd@legalmail. it Registered office: Viale Beatrice D'Este, 20 – 20122 Milan T: +39 0291471104/05 – F: +39 0291471087 Administration: Giustina Cervone IP Mediation Center Viale Beatrice D'Este, 20 – 20122 Milan T: +39 0291471104/05 – F: +39 0291471087 Case Manager: Pierfrancesco C. Fasano Secretariat: Monica Milano Via dei Castani, 80 – 00172 Rome T: +39 062312031 – F: +39 062312031 “. it” Domain Name Dispute Resolution Service Provider Via Donizetti, 1/a – 20122 Milan T: +39 0245490522 – F: +39 0245490590 Case Manager: Stefano Monguzzi
MFSD S. r. l. www. mfsd. it E: responsabile@mfsd. it - Certified e-mail (only within Italy): mfsd@legalmail. it Registered office: Viale Beatrice D'Este, 20 – 20122 Milan T: +39 0291471104/05 – F: +39 0291471087 Administration: Giustina Cervone IP Mediation Center Viale Beatrice D'Este, 20 – 20122 Milan T: +39 0291471104/05 – F: +39 0291471087 Case Manager: Pierfrancesco C. Fasano Secretariat: Monica Milano Via dei Castani, 80 – 00172 Rome T: +39 062312031 – F: +39 062312031 “. it” Domain Name Dispute Resolution Service Provider Via Donizetti, 1/a – 20122 Milan T: +39 0245490522 – F: +39 0245490590 Case Manager: Stefano Monguzzi


