57c175b2a3ea91d9160846ce16cb7a15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Fundamentals for Program Managers 1
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Fundamentals for Program Managers 1
 What is GIS? § A technology of hardware, software, data, people, and processes § A technology that connects intelligence to a place on the earth § The objective: to improve overall decision making 2
What is GIS? § A technology of hardware, software, data, people, and processes § A technology that connects intelligence to a place on the earth § The objective: to improve overall decision making 2
 Geographic Information Systems GIS is an extremely effective tool for: § § § Decision Making Identifying trends and relationships Visualizing tabular data via maps Synthesizing Data Solving Problems Reports, Presentations, Trainings 3
Geographic Information Systems GIS is an extremely effective tool for: § § § Decision Making Identifying trends and relationships Visualizing tabular data via maps Synthesizing Data Solving Problems Reports, Presentations, Trainings 3
 How Can GIS Help My Customer? Rapid Eligibility Determination Data Supported Decisions Solid Demographic Analysis Strategic Planning 4
How Can GIS Help My Customer? Rapid Eligibility Determination Data Supported Decisions Solid Demographic Analysis Strategic Planning 4
 How Can GIS Help My Staff? Fast, Efficient Workload Accurate, Timely Process Data Visualization Accurate, Efficient Analysis Reliable, Automated Calculation 5
How Can GIS Help My Staff? Fast, Efficient Workload Accurate, Timely Process Data Visualization Accurate, Efficient Analysis Reliable, Automated Calculation 5
 How can GIS help Government in General? Better solutions to business requirements Maximize benefits of taxpayer money Forecast outcomes Measure targeted performance Present powerful ideas quickly 6
How can GIS help Government in General? Better solutions to business requirements Maximize benefits of taxpayer money Forecast outcomes Measure targeted performance Present powerful ideas quickly 6
 GIS Formal Definition GIS is "an automated system for the capture, storage, retrieval, analysis, and display of spatial data. " (Clarke 1995) 7
GIS Formal Definition GIS is "an automated system for the capture, storage, retrieval, analysis, and display of spatial data. " (Clarke 1995) 7
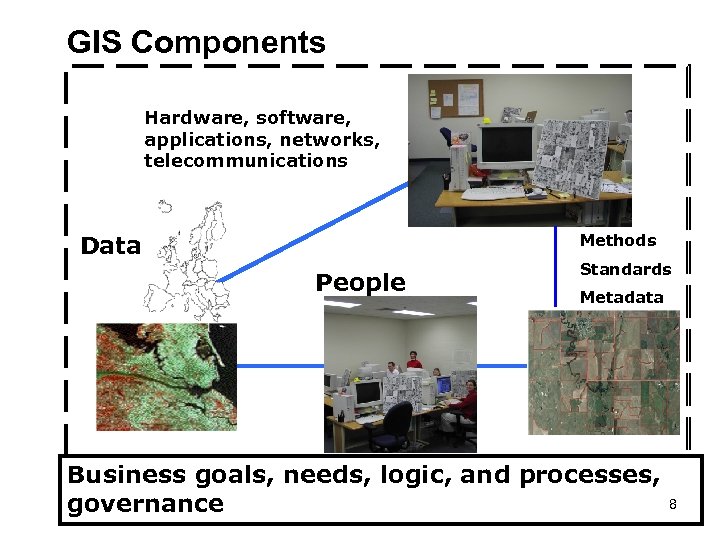 GIS Components Hardware, software, applications, networks, telecommunications Data Methods People Standards Metadata Business goals, needs, logic, and processes, governance 8
GIS Components Hardware, software, applications, networks, telecommunications Data Methods People Standards Metadata Business goals, needs, logic, and processes, governance 8
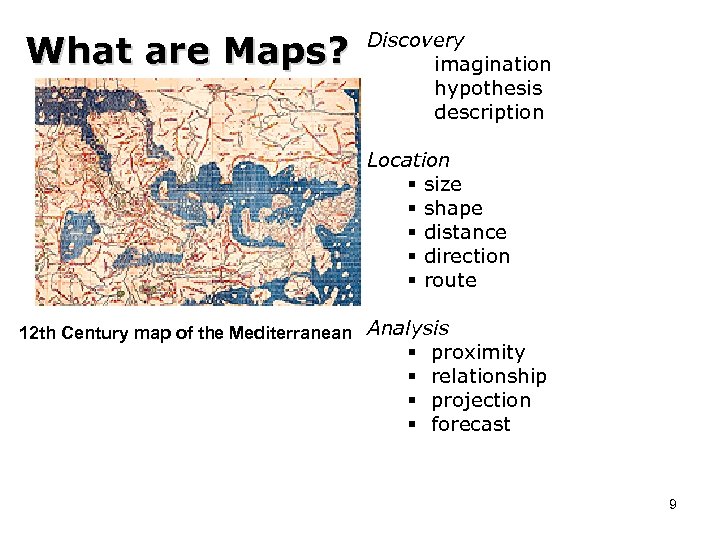 What are Maps? Discovery imagination hypothesis description Location § size § shape § distance § direction § route 12 th Century map of the Mediterranean Analysis § § proximity relationship projection forecast 9
What are Maps? Discovery imagination hypothesis description Location § size § shape § distance § direction § route 12 th Century map of the Mediterranean Analysis § § proximity relationship projection forecast 9
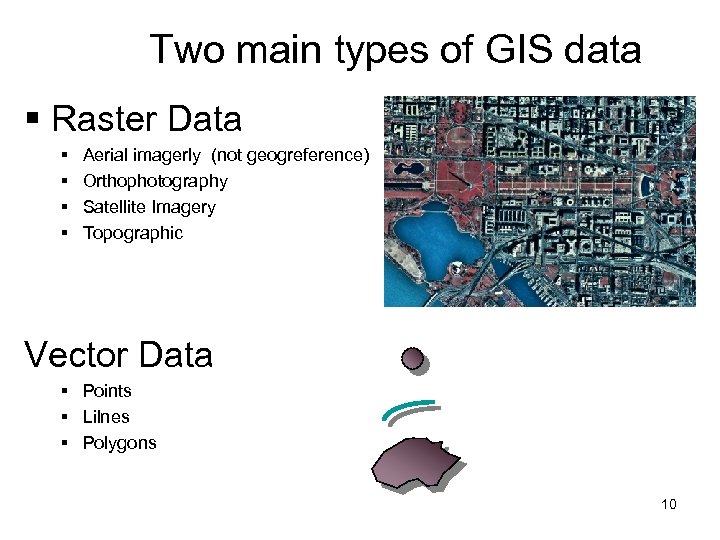 Two main types of GIS data § Raster Data § § Aerial imagerly (not geogreference) Orthophotography Satellite Imagery Topographic Vector Data § Points § Lilnes § Polygons Point Line Polygon 10
Two main types of GIS data § Raster Data § § Aerial imagerly (not geogreference) Orthophotography Satellite Imagery Topographic Vector Data § Points § Lilnes § Polygons Point Line Polygon 10
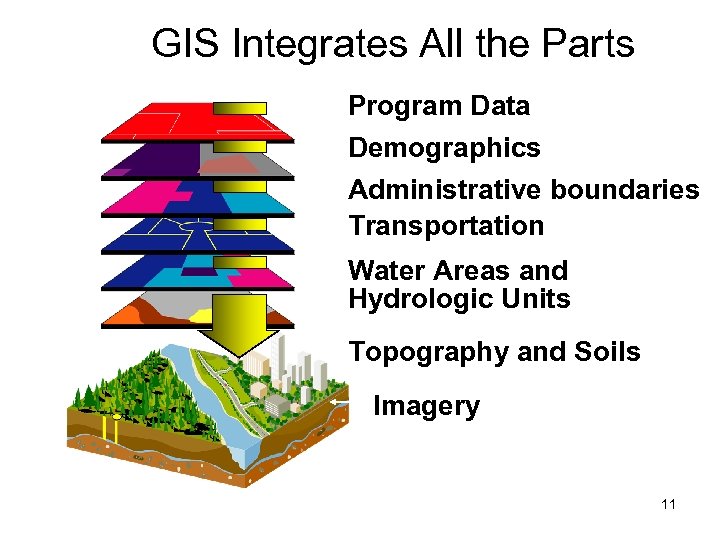 GIS Integrates All the Parts Program Data Demographics Administrative boundaries Transportation Water Areas and Hydrologic Units Topography and Soils Imagery 11
GIS Integrates All the Parts Program Data Demographics Administrative boundaries Transportation Water Areas and Hydrologic Units Topography and Soils Imagery 11
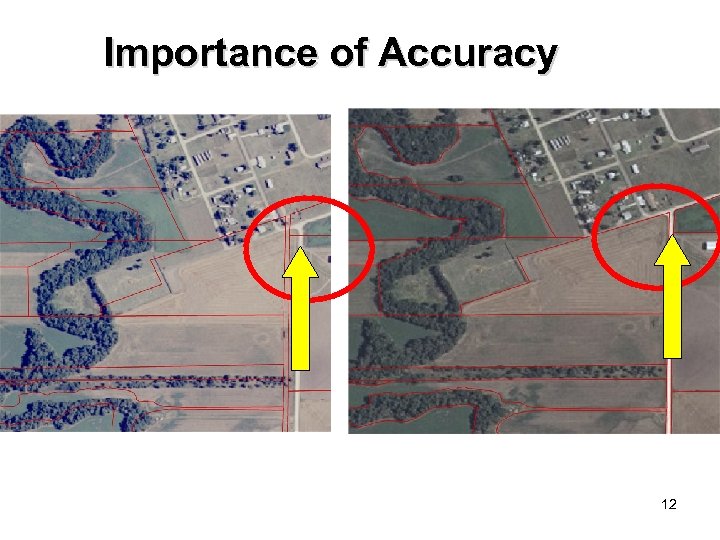 Importance of Accuracy Look at the yellow arrow to see the difference in alignment. 12
Importance of Accuracy Look at the yellow arrow to see the difference in alignment. 12
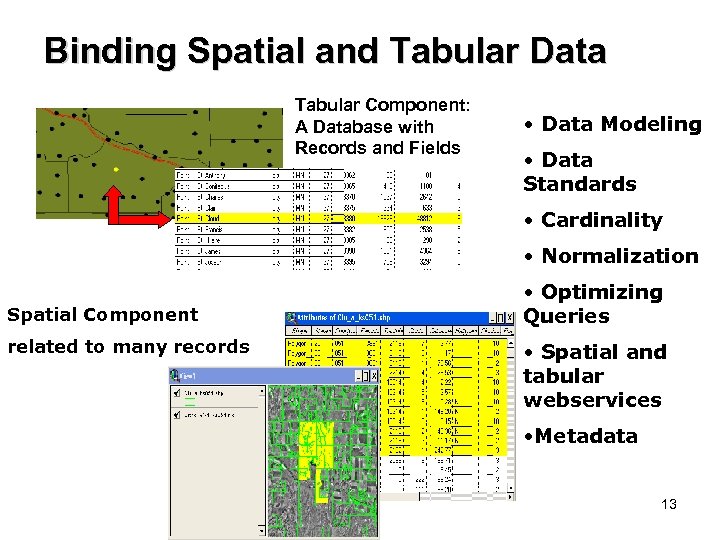 Binding Spatial and Tabular Data Spatial Component: Tabular Component: A Database with Polygons, Lines, or Points Fields Records and • Data Modeling • Data Standards • Cardinality • Normalization Spatial Component related to many records • Optimizing Queries • Spatial and tabular webservices • Metadata 13
Binding Spatial and Tabular Data Spatial Component: Tabular Component: A Database with Polygons, Lines, or Points Fields Records and • Data Modeling • Data Standards • Cardinality • Normalization Spatial Component related to many records • Optimizing Queries • Spatial and tabular webservices • Metadata 13
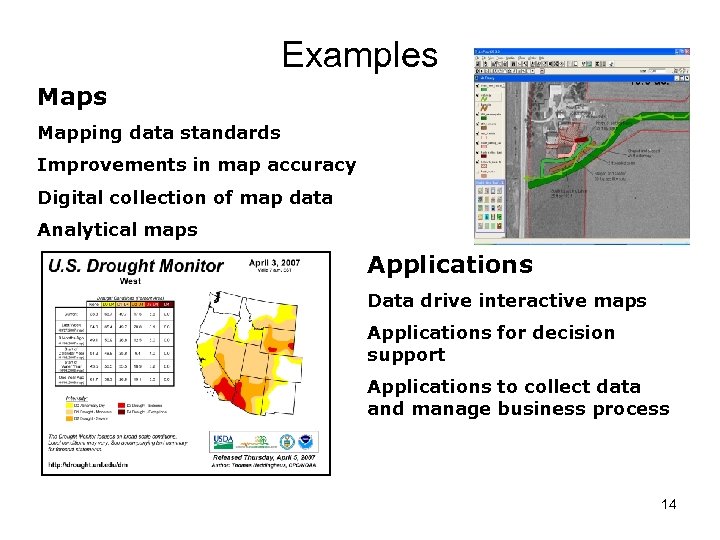 Examples Mapping data standards Improvements in map accuracy Digital collection of map data Analytical maps Applications Data drive interactive maps Applications for decision support Applications to collect data and manage business process 14
Examples Mapping data standards Improvements in map accuracy Digital collection of map data Analytical maps Applications Data drive interactive maps Applications for decision support Applications to collect data and manage business process 14
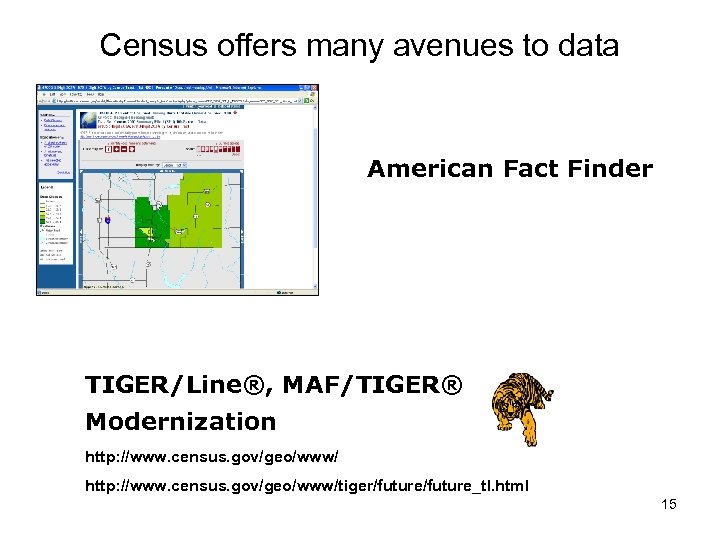 Census offers many avenues to data American Fact Finder TIGER/Line®, MAF/TIGER® Modernization http: //www. census. gov/geo/www/tiger/future_tl. html 15
Census offers many avenues to data American Fact Finder TIGER/Line®, MAF/TIGER® Modernization http: //www. census. gov/geo/www/tiger/future_tl. html 15
 Wild Fire Mapping and Resources 16
Wild Fire Mapping and Resources 16
 USGS Data Gateways Geospatial One Stop www. geodata. gov National Map 17
USGS Data Gateways Geospatial One Stop www. geodata. gov National Map 17
 EPA is a leader and pioneer Windows on My Environmental Justice Geographic Assessment Tool 18
EPA is a leader and pioneer Windows on My Environmental Justice Geographic Assessment Tool 18
 19
19
 20
20
 Trends • • • Standards Service Oriented Architecture Interoperability Shared components or services Data Modeling Metadata 21
Trends • • • Standards Service Oriented Architecture Interoperability Shared components or services Data Modeling Metadata 21
 Beyond “Maps” Integration of GPS and GIS Mobile Data Collection and Mapping USDA APHIS: Asian Longhorn Beetle treatment RD: Location correction of housing loan properties 22
Beyond “Maps” Integration of GPS and GIS Mobile Data Collection and Mapping USDA APHIS: Asian Longhorn Beetle treatment RD: Location correction of housing loan properties 22
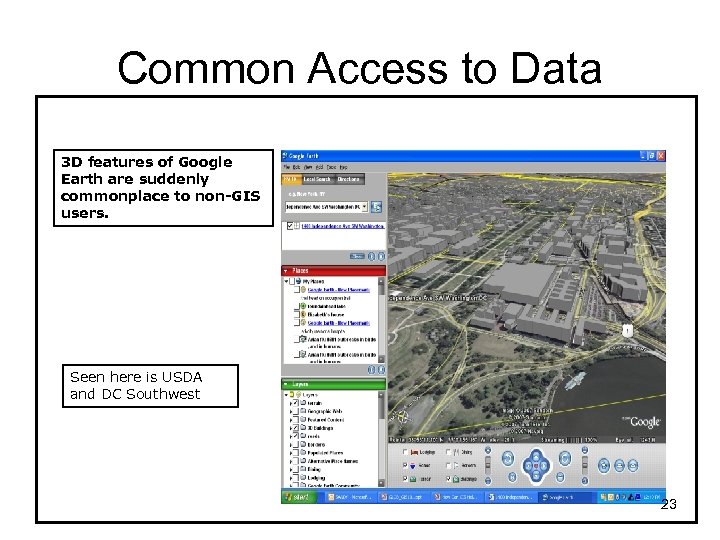 Common Access to Data 3 D features of Google Earth are suddenly commonplace to non-GIS users. Seen here is USDA and DC Southwest 23
Common Access to Data 3 D features of Google Earth are suddenly commonplace to non-GIS users. Seen here is USDA and DC Southwest 23
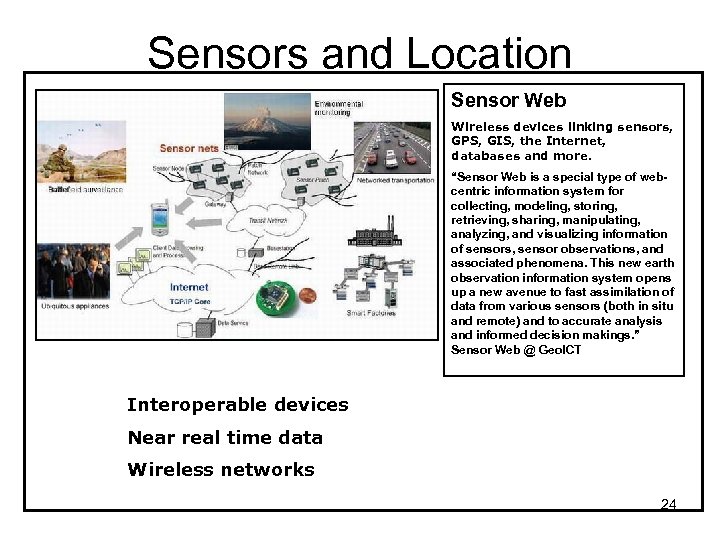 Sensors and Location Sensor Web Wireless devices linking sensors, GPS, GIS, the Internet, databases and more. “Sensor Web is a special type of webcentric information system for collecting, modeling, storing, retrieving, sharing, manipulating, analyzing, and visualizing information of sensors, sensor observations, and associated phenomena. This new earth observation information system opens up a new avenue to fast assimilation of data from various sensors (both in situ and remote) and to accurate analysis and informed decision makings. ” Sensor Web @ Geo. ICT Interoperable devices Near real time data Wireless networks 24
Sensors and Location Sensor Web Wireless devices linking sensors, GPS, GIS, the Internet, databases and more. “Sensor Web is a special type of webcentric information system for collecting, modeling, storing, retrieving, sharing, manipulating, analyzing, and visualizing information of sensors, sensor observations, and associated phenomena. This new earth observation information system opens up a new avenue to fast assimilation of data from various sensors (both in situ and remote) and to accurate analysis and informed decision makings. ” Sensor Web @ Geo. ICT Interoperable devices Near real time data Wireless networks 24
 Beyond “IT” • Business Intelligence • Enterprise Architecture • Target Architectures • Project Management • Portfolio Management • Governance • Geospatial Line of Business • Federal Geographic Data Committee • Agency coordination groups • Agency Capital Planning 25
Beyond “IT” • Business Intelligence • Enterprise Architecture • Target Architectures • Project Management • Portfolio Management • Governance • Geospatial Line of Business • Federal Geographic Data Committee • Agency coordination groups • Agency Capital Planning 25


