cb042ab3e155e59d34318967587daf75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Geographic Information Dissemination Network in Korea 2002. 11. 13 Sang-Ki Hong Anyang University, Korea
Geographic Information Dissemination Network in Korea 2002. 11. 13 Sang-Ki Hong Anyang University, Korea
 Contents 1. History of NGIS 2. Major Achievments 3. Vision of NGIS Masterplan 4. Objectives 5. Investment Plan 6. NGIS Laws and Regulations 7. Context 8. Background 9. Conceptual Scheme 10. How to Find and Download Spatial Data 11. Pilot Project 12. Distributed Network Building 13. Main Project (1 st stage) 14. Current Project 15. Dissemination Model 16. System Development 17. System Architecture 18. Policy Implications
Contents 1. History of NGIS 2. Major Achievments 3. Vision of NGIS Masterplan 4. Objectives 5. Investment Plan 6. NGIS Laws and Regulations 7. Context 8. Background 9. Conceptual Scheme 10. How to Find and Download Spatial Data 11. Pilot Project 12. Distributed Network Building 13. Main Project (1 st stage) 14. Current Project 15. Dissemination Model 16. System Development 17. System Architecture 18. Policy Implications
 1. History of NGIS • Early 1990 s: Development of various GIS databases begun • Mid 1990 s: Underground gas explosion accidents in Seoul and Daegu accelerated GIS development • May 1995: 1 st NGIS Master Plan established 1
1. History of NGIS • Early 1990 s: Development of various GIS databases begun • Mid 1990 s: Underground gas explosion accidents in Seoul and Daegu accelerated GIS development • May 1995: 1 st NGIS Master Plan established 1
 1. History of NGIS (cont’d) cont’d 2 • July 2000: NGIS Act and its Enforcement Decree enacted • October 2000: 2 nd NGIS Master Plan (2001~2005) established • December 2000: 1 st NGIS Master Plan completed • January 2001: Implementation of 2 nd NGIS Master Plan started
1. History of NGIS (cont’d) cont’d 2 • July 2000: NGIS Act and its Enforcement Decree enacted • October 2000: 2 nd NGIS Master Plan (2001~2005) established • December 2000: 1 st NGIS Master Plan completed • January 2001: Implementation of 2 nd NGIS Master Plan started
 2. Major Achievements • • • Completion of the National Digital Base Map Construction of various Thematic maps Construction of the Underground Facility Database Construction of Cadastral Map Development of the Applications in Public Sector Development of core GIS Technologies Human Resources Development Standardization Support for GIS Research and Development 3
2. Major Achievements • • • Completion of the National Digital Base Map Construction of various Thematic maps Construction of the Underground Facility Database Construction of Cadastral Map Development of the Applications in Public Sector Development of core GIS Technologies Human Resources Development Standardization Support for GIS Research and Development 3
 3. Vision of NGIS Master Plan For the fast and convenient access to National Spatial Information, the “Digital National Land” shall be achieved by the construction of National Spatial Data Infrastructure 4
3. Vision of NGIS Master Plan For the fast and convenient access to National Spatial Information, the “Digital National Land” shall be achieved by the construction of National Spatial Data Infrastructure 4
 4. Objectives • Establish the basis for Digital National Land • Make geographic information available on the internet for use by all people • Develop core technology and promote GIS industry • Continue improvement of information infrastructure 5
4. Objectives • Establish the basis for Digital National Land • Make geographic information available on the internet for use by all people • Develop core technology and promote GIS industry • Continue improvement of information infrastructure 5
 5. Investment Plan in 2 nd Phase of NGIS 6 (unit: million dollars) Basic geographic information (framework data) 375 GIS applications development 611 Geographic information dissemination network 20 GIS technologies development 67 GIS industry promotion 20 GIS standardization 7. 5 GIS human resources development and public relations 12 R&D support 9. 8 TOTAL 1, 125
5. Investment Plan in 2 nd Phase of NGIS 6 (unit: million dollars) Basic geographic information (framework data) 375 GIS applications development 611 Geographic information dissemination network 20 GIS technologies development 67 GIS industry promotion 20 GIS standardization 7. 5 GIS human resources development and public relations 12 R&D support 9. 8 TOTAL 1, 125
 6. NGIS Laws and Regulations • Purpose (Article 1) • NGIS Master Plan (Article 5) • NGIS Committee (Article 8) • Establishment of NGIS Infrastructure (Chapter 3) • Construction and Management (Chapter 4) • Utilization and Distribution (Chapter 5) 7
6. NGIS Laws and Regulations • Purpose (Article 1) • NGIS Master Plan (Article 5) • NGIS Committee (Article 8) • Establishment of NGIS Infrastructure (Chapter 3) • Construction and Management (Chapter 4) • Utilization and Distribution (Chapter 5) 7
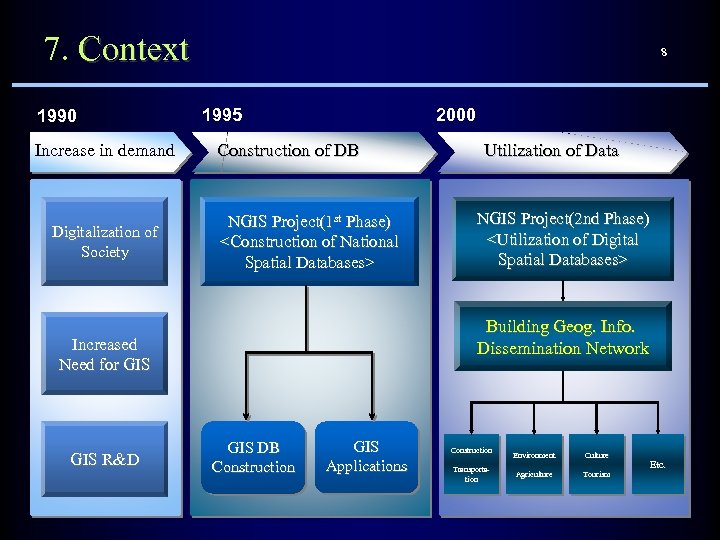 7. Context 1990 Increase in demand Digitalization of Society 8 1995 2000 Construction of DB NGIS Project(1 st Phase)
7. Context 1990 Increase in demand Digitalization of Society 8 1995 2000 Construction of DB NGIS Project(1 st Phase)
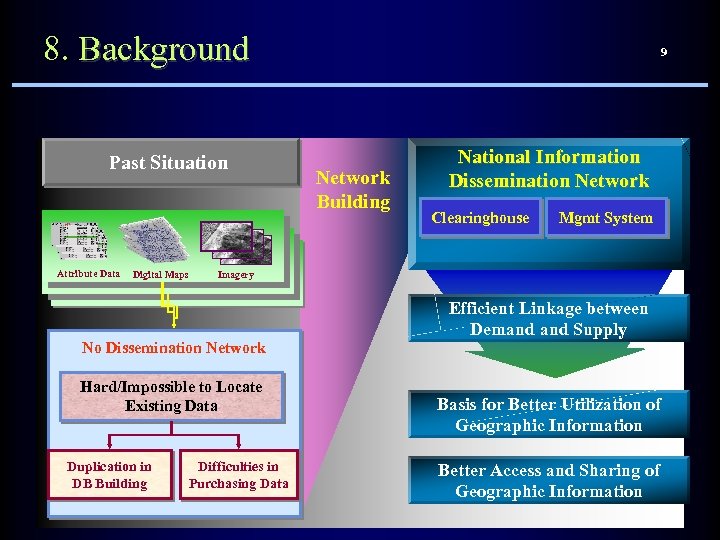 8. Background Past Situation Attribute Data Digital Maps Network Building National Information Dissemination Network Clearinghouse Mgmt System Imagery No Dissemination Network Hard/Impossible to Locate Existing Data Duplication in DB Building 9 Difficulties in Purchasing Data Efficient Linkage between Demand Supply Basis for Better Utilization of Geographic Information Better Access and Sharing of Geographic Information
8. Background Past Situation Attribute Data Digital Maps Network Building National Information Dissemination Network Clearinghouse Mgmt System Imagery No Dissemination Network Hard/Impossible to Locate Existing Data Duplication in DB Building 9 Difficulties in Purchasing Data Efficient Linkage between Demand Supply Basis for Better Utilization of Geographic Information Better Access and Sharing of Geographic Information
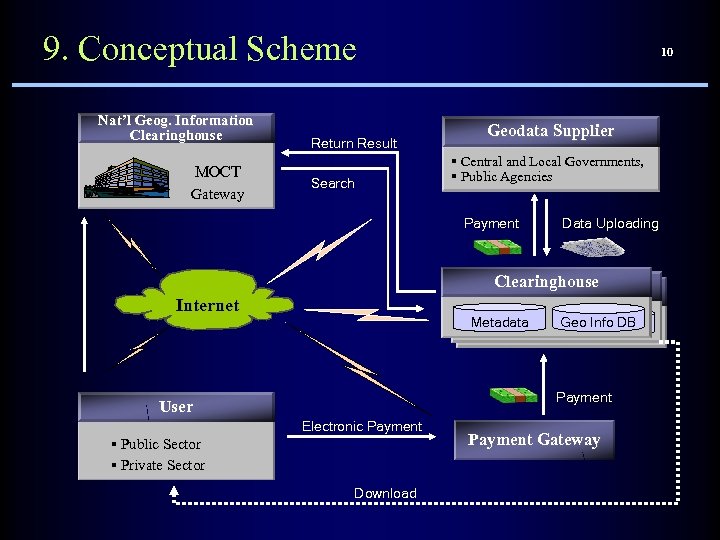 9. Conceptual Scheme Nat’l Geog. Information Clearinghouse MOCT Gateway Return Result Search 10 Geodata Supplier § Central and Local Governments, § Public Agencies Payment Data Uploading Clearinghouse Internet Metadata Geo Info DB Payment User Electronic Payment § Public Sector § Private Sector Download Payment Gateway
9. Conceptual Scheme Nat’l Geog. Information Clearinghouse MOCT Gateway Return Result Search 10 Geodata Supplier § Central and Local Governments, § Public Agencies Payment Data Uploading Clearinghouse Internet Metadata Geo Info DB Payment User Electronic Payment § Public Sector § Private Sector Download Payment Gateway
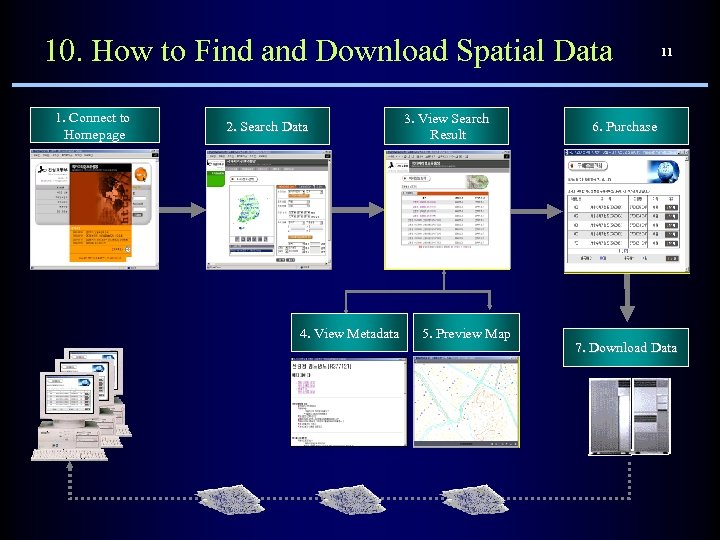 10. How to Find and Download Spatial Data 1. Connect to Homepage 2. Search Data 4. View Metadata 3. View Search Result 5. Preview Map 11 6. Purchase 7. Download Data
10. How to Find and Download Spatial Data 1. Connect to Homepage 2. Search Data 4. View Metadata 3. View Search Result 5. Preview Map 11 6. Purchase 7. Download Data
 11. Pilot Project Period 12 Contents 2000. 7. 12 - 2001. 6. 7 Building Centralized Dissemination Network Spatial Extent NGIC(MOCT) Development of Metadata Standard Construction of Metadata DB Development of Metadata Editor R&D National Clearinghouse
11. Pilot Project Period 12 Contents 2000. 7. 12 - 2001. 6. 7 Building Centralized Dissemination Network Spatial Extent NGIC(MOCT) Development of Metadata Standard Construction of Metadata DB Development of Metadata Editor R&D National Clearinghouse
 12. Distributed Network Building National Clearinghouse User CH Node Data Supplier (Pilot Project) Data Supplier 13 National Clearinghouse CH Node Data Supplier ( Main Project )
12. Distributed Network Building National Clearinghouse User CH Node Data Supplier (Pilot Project) Data Supplier 13 National Clearinghouse CH Node Data Supplier ( Main Project )
 13. Main Project (1 st stage) Project Period 14 Contents 2001. 8. 1 - 2002. 6. 26 Building Clearinghouse Node Network Spatial Extent CH Node (Incheon) Expansion of existing system NGIC(MOCT) CH Node (NGI) CH Node (Daegu) Construction of Metadata DB Development of Portal Site R&D National Clearinghouse CH Node
13. Main Project (1 st stage) Project Period 14 Contents 2001. 8. 1 - 2002. 6. 26 Building Clearinghouse Node Network Spatial Extent CH Node (Incheon) Expansion of existing system NGIC(MOCT) CH Node (NGI) CH Node (Daegu) Construction of Metadata DB Development of Portal Site R&D National Clearinghouse CH Node
 14. Current Project Period Contents 2002. 9. 30 - 2003. 8. 25 Building Integrated Dissemination Network Spatial Extent CH Node (Incheon) 15 Expansion of existing system NGIC(MOCT) Construction of Metadata DB CH Node (NGI) New CH Node (Daejeon) New CH Node (Gwangju) National Clearinghouse Existing CH Node (Daegu) New CH Node (Busan) Mgmt of existing system R&D Support Public Relations New CH Node
14. Current Project Period Contents 2002. 9. 30 - 2003. 8. 25 Building Integrated Dissemination Network Spatial Extent CH Node (Incheon) 15 Expansion of existing system NGIC(MOCT) Construction of Metadata DB CH Node (NGI) New CH Node (Daejeon) New CH Node (Gwangju) National Clearinghouse Existing CH Node (Daegu) New CH Node (Busan) Mgmt of existing system R&D Support Public Relations New CH Node
 15. Dissemination Model 16 Types of Geographic Information Dissemination Model File-based Spatial DB-based Goal Public Access to Geodata Files (G 2 C Service) Geodata Sharing (G 2 G Service) Techno -logies Catalog Service / DRM Security / Electronic Payment OGC Spec. Simple Feature Component S/W Network Internet Intranet Service Geodata File Search And Download Spatial DB Layer Sharing among orgs. Data Store CH: Mgmt, Stat. Data CH Node: Geodata Files, Metadata CH Node: Metadata Spatial DB Server: Spatial DB User’s GIS S/W to use Geodata files Display thru Web Browser Simple and Efficient No restrictions on Data format Advanced sharing technology Complicated System Characteristics Integrated Model • Integration of file and DB-based models • • Application of OGC Standard Component-based S/W Electronic Payment Security Technology • Internet • File and DB service • Expandable system architecture • CH: Mgmt, Stat. Data • CH Node: Geodata Files, Metadata, Spatial DB • Spatial DB Access thru Map Browser and Geodata File download • Users can choose the type of desired service
15. Dissemination Model 16 Types of Geographic Information Dissemination Model File-based Spatial DB-based Goal Public Access to Geodata Files (G 2 C Service) Geodata Sharing (G 2 G Service) Techno -logies Catalog Service / DRM Security / Electronic Payment OGC Spec. Simple Feature Component S/W Network Internet Intranet Service Geodata File Search And Download Spatial DB Layer Sharing among orgs. Data Store CH: Mgmt, Stat. Data CH Node: Geodata Files, Metadata CH Node: Metadata Spatial DB Server: Spatial DB User’s GIS S/W to use Geodata files Display thru Web Browser Simple and Efficient No restrictions on Data format Advanced sharing technology Complicated System Characteristics Integrated Model • Integration of file and DB-based models • • Application of OGC Standard Component-based S/W Electronic Payment Security Technology • Internet • File and DB service • Expandable system architecture • CH: Mgmt, Stat. Data • CH Node: Geodata Files, Metadata, Spatial DB • Spatial DB Access thru Map Browser and Geodata File download • Users can choose the type of desired service
 15. Dissemination Model (cont’d) 17 Technologies Involved Catalog Service Standard (Z 39. 50) • Spatial DB Engine • DP(Data Provider) Metadata Search National Clearinghouse XML DP (Data Provider) - Access to Spatial DB and Download Metadata Registration Clearinghouse Nodes Geodata Download Catalog Service - Standard for Metadata Search Geodata Supplier Simple Feature Spec. - Used for Map Browsing Function XML - Used in Metadata Editor • DRM • SSL Active X - Client Interface Technology that supports GIS Functions in Web Browser PKI Authentication • Active X • Simple Feature Spec. Elec. Payment KFTC Spatial DBMS for GIS - Mgmt of Spatial and Attribute Data, Spatial Query and Operation User DRM (Digital Right Management) - Encryption for transmitting geodata PKI/SSL - Encryption for Electronic Payment
15. Dissemination Model (cont’d) 17 Technologies Involved Catalog Service Standard (Z 39. 50) • Spatial DB Engine • DP(Data Provider) Metadata Search National Clearinghouse XML DP (Data Provider) - Access to Spatial DB and Download Metadata Registration Clearinghouse Nodes Geodata Download Catalog Service - Standard for Metadata Search Geodata Supplier Simple Feature Spec. - Used for Map Browsing Function XML - Used in Metadata Editor • DRM • SSL Active X - Client Interface Technology that supports GIS Functions in Web Browser PKI Authentication • Active X • Simple Feature Spec. Elec. Payment KFTC Spatial DBMS for GIS - Mgmt of Spatial and Attribute Data, Spatial Query and Operation User DRM (Digital Right Management) - Encryption for transmitting geodata PKI/SSL - Encryption for Electronic Payment
 15. Dissemination Model (cont’d) 18 Detailed Structure of Integrated Dissemination Model Clearinghouse Node(Spatial DB + Files) File-only DB Server Web Service Spatial DB Server : Vector, Raster Spatial DB Shp DP(Data Provider) • File Download Internet (TCP/IP) • WKB Type (Well-Known Binary) Map Browser Information User (Simple Feature Spec. ) Shp DXF Geotiff Local Store(Geodata Files) • WKB to Shp Library • Shp DP • DXF DP(Library) • Geo. Tiff DP(Library)
15. Dissemination Model (cont’d) 18 Detailed Structure of Integrated Dissemination Model Clearinghouse Node(Spatial DB + Files) File-only DB Server Web Service Spatial DB Server : Vector, Raster Spatial DB Shp DP(Data Provider) • File Download Internet (TCP/IP) • WKB Type (Well-Known Binary) Map Browser Information User (Simple Feature Spec. ) Shp DXF Geotiff Local Store(Geodata Files) • WKB to Shp Library • Shp DP • DXF DP(Library) • Geo. Tiff DP(Library)
 16. System Development 19 Data Flow v. History Info v. List of Registered Geodata • Mgmt Data • CH Node List • Gov. Geodata v. History Info v. List of Registered Geodata NGIC (NGIS Div. In MOCT) • Metadata • Geodata Files • Spatial DB • Metadata • Geodata Files CH Node (File-based) v. Geodata Files v. Metadata Geodata Users • Metadata • Geodata Files • Spatial DB Geodata Suppliers v. Spatial DB Layer v. Metadata CH Node (Spatial DB+Files) v. Spatial DB Layer v. Metadata
16. System Development 19 Data Flow v. History Info v. List of Registered Geodata • Mgmt Data • CH Node List • Gov. Geodata v. History Info v. List of Registered Geodata NGIC (NGIS Div. In MOCT) • Metadata • Geodata Files • Spatial DB • Metadata • Geodata Files CH Node (File-based) v. Geodata Files v. Metadata Geodata Users • Metadata • Geodata Files • Spatial DB Geodata Suppliers v. Spatial DB Layer v. Metadata CH Node (Spatial DB+Files) v. Spatial DB Layer v. Metadata
 16. System Development (cont’d) 20 Detailed Design Registration and Mgmt of Geodata Spatial DB(shp) NGIC Data Conversion Module Map Browser Design Spatial DB CH Node Type A Metadata Map Browser Geodata Type Files DBMS (shp/dxf) Map Display OGIS Geometry Data Access Data Conversion Meta-data Supplier Auth. Register CH Node Type B WKB Data Provider A Geodata Registration and Mgmt Service dxf shp Data Provider B Data Provider C DB - B DB - C Metadata Editing DB - A
16. System Development (cont’d) 20 Detailed Design Registration and Mgmt of Geodata Spatial DB(shp) NGIC Data Conversion Module Map Browser Design Spatial DB CH Node Type A Metadata Map Browser Geodata Type Files DBMS (shp/dxf) Map Display OGIS Geometry Data Access Data Conversion Meta-data Supplier Auth. Register CH Node Type B WKB Data Provider A Geodata Registration and Mgmt Service dxf shp Data Provider B Data Provider C DB - B DB - C Metadata Editing DB - A
 16. System Development (cont’d) 21 Application Functions National Clearinghouse User Registration Log in Gateway User Registration Metadata query Search Results Statistics Geodata Download Purchase Elec. Payment CH Nodes Map Browsing Geodata Purchase KFTC (Payment Gate. Way) Geodata Supplier Approval Metadata Geodata Metadata Search Approval of Geodata Registration Supplier Approval Geodata/Metadata Registration Geodata Upload
16. System Development (cont’d) 21 Application Functions National Clearinghouse User Registration Log in Gateway User Registration Metadata query Search Results Statistics Geodata Download Purchase Elec. Payment CH Nodes Map Browsing Geodata Purchase KFTC (Payment Gate. Way) Geodata Supplier Approval Metadata Geodata Metadata Search Approval of Geodata Registration Supplier Approval Geodata/Metadata Registration Geodata Upload
 17. System Architecture National Clearinghouse DB Server HP 9000 L 2000 440 MHz× 4 RAM 2 GB HDD 200 GB Web Server HP 9000 L 1000 440 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 36 GB IDS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB SMS(Net) Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Staff Note. Book CSU Printer Geodata user Geodata Supplier KFTC User PC Switching Hub Satelite 1955 -s 801 Pentium 4 2. 2 MHz RAM 512 MB HDD 40 GB Plotter SMS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 72 GB 22 Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 60 450 MHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18 GB Router INTERNET CSU Router Fire Wall Server IBM x 232 1. 4 GHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18. 2 GB CSU Router Switch Hub DB Server IBM 620 - 6 F 1 600 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 219 GB Web Server IBM x 250 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 216 GB New CH Nodes(3 Sites) Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 60 450 MHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18 GB Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 10 440 MHz RAM 1 GB HDD 18 GB CSU Router Switch Hub DB Server HP 9000 L 2000 440 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 219 GB* Web Server HP 9000 A 500 440 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 36 GB Existing CH Node (NGI, Daegu) Switch Hub DB Server HP NS Lxr 8500 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Web Server HP NS Lxr 8500 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB GIS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Existing CH Node (Incheon)
17. System Architecture National Clearinghouse DB Server HP 9000 L 2000 440 MHz× 4 RAM 2 GB HDD 200 GB Web Server HP 9000 L 1000 440 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 36 GB IDS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB SMS(Net) Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Staff Note. Book CSU Printer Geodata user Geodata Supplier KFTC User PC Switching Hub Satelite 1955 -s 801 Pentium 4 2. 2 MHz RAM 512 MB HDD 40 GB Plotter SMS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 72 GB 22 Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 60 450 MHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18 GB Router INTERNET CSU Router Fire Wall Server IBM x 232 1. 4 GHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18. 2 GB CSU Router Switch Hub DB Server IBM 620 - 6 F 1 600 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 219 GB Web Server IBM x 250 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 216 GB New CH Nodes(3 Sites) Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 60 450 MHz× 2 RAM 512 MB HDD 18 GB Fire Wall Server SUN Ultra 10 440 MHz RAM 1 GB HDD 18 GB CSU Router Switch Hub DB Server HP 9000 L 2000 440 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 219 GB* Web Server HP 9000 A 500 440 MHz × 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 36 GB Existing CH Node (NGI, Daegu) Switch Hub DB Server HP NS Lxr 8500 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Web Server HP NS Lxr 8500 700 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB GIS Server DELL PE 4400 933 MHz× 2 RAM 1 GB HDD 54 GB Existing CH Node (Incheon)
 18. Policy Implications 23 • Commitment and investment are necessary for successful implementation of the dissemination network • Better-informed and timely decision can be made through the use of this network • Main problem: setting up an environment for information sharing, i. e. , policy principles need to be set up • Other problems such as pricing of data, copyrights, security concerns need to be clarified
18. Policy Implications 23 • Commitment and investment are necessary for successful implementation of the dissemination network • Better-informed and timely decision can be made through the use of this network • Main problem: setting up an environment for information sharing, i. e. , policy principles need to be set up • Other problems such as pricing of data, copyrights, security concerns need to be clarified
 Thank You
Thank You



