7225dbb725f683f0f03f8527d17c7b54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Genomics for Emerging Markets Paul Van. Raden, George Wiggans, Jeff O’Connell, John Cole, Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory Tad Sonstegard, and Curt Van Tassell Bovine Functional Genomics Laboratory USDA Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville, MD, USA Paul. Van. Raden@ars. usda. gov 2009 2007
Genomics for Emerging Markets Paul Van. Raden, George Wiggans, Jeff O’Connell, John Cole, Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory Tad Sonstegard, and Curt Van Tassell Bovine Functional Genomics Laboratory USDA Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville, MD, USA Paul. Van. Raden@ars. usda. gov 2009 2007
 Proven Bulls or Emerging Bulls? Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (2) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Proven Bulls or Emerging Bulls? Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (2) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Genetic Terms Ø Predicted transmitting ability and parent average • • • Ø PTA required progeny or own records PA included only parent data Genomics provides more information Reliability = Corr 2(predicted, true TA) • • • Reliability of PA could not exceed 50% because of Mendelian sampling Genomics can predict the other 50% Reliability limit at birth theoretically 99% Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (3) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genetic Terms Ø Predicted transmitting ability and parent average • • • Ø PTA required progeny or own records PA included only parent data Genomics provides more information Reliability = Corr 2(predicted, true TA) • • • Reliability of PA could not exceed 50% because of Mendelian sampling Genomics can predict the other 50% Reliability limit at birth theoretically 99% Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (3) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Reliability = 99% ? Not Yet ! Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (4) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Reliability = 99% ? Not Yet ! Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (4) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 New Genetic Terms Ø Genomic vs. pedigree relationships • • • Ø Genomic vs. pedigree inbreeding • • Ø Expected genes in common (A) Actual genes in common (G) Several formulas to compute G Correlated by 0. 68 in Holstein Correlated by 0. 80 in Angus Daughter merit vs. son merit (X vs. Y) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (5) Paul Van. Raden 2009
New Genetic Terms Ø Genomic vs. pedigree relationships • • • Ø Genomic vs. pedigree inbreeding • • Ø Expected genes in common (A) Actual genes in common (G) Several formulas to compute G Correlated by 0. 68 in Holstein Correlated by 0. 80 in Angus Daughter merit vs. son merit (X vs. Y) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (5) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Differences in G and A G = genomic and A = pedigree relationships Ø Detected clones, identical twins, and duplicate samples Ø Detected incorrect DNA samples Ø Detected incorrect pedigrees Ø Identified correct source of DNA by genomic relationships with other animals Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (6) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Differences in G and A G = genomic and A = pedigree relationships Ø Detected clones, identical twins, and duplicate samples Ø Detected incorrect DNA samples Ø Detected incorrect pedigrees Ø Identified correct source of DNA by genomic relationships with other animals Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (6) Paul Van. Raden 2009
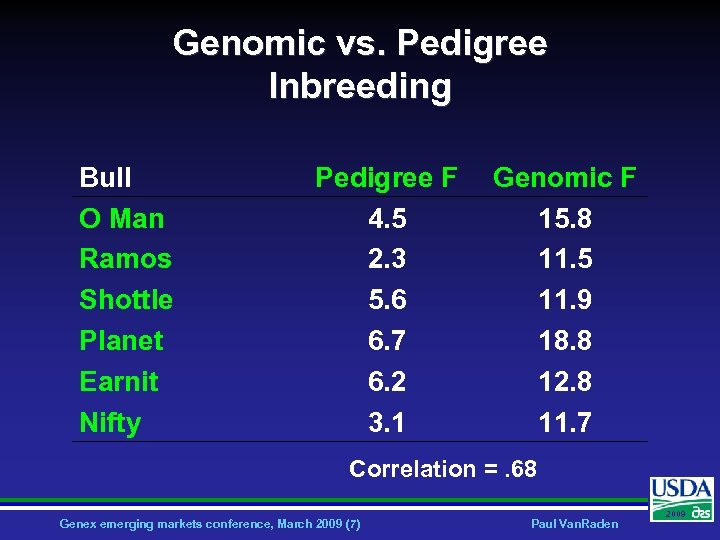 Genomic vs. Pedigree Inbreeding Bull O Man Ramos Shottle Planet Earnit Nifty Pedigree F 4. 5 2. 3 5. 6 6. 7 6. 2 3. 1 Genomic F 15. 8 11. 5 11. 9 18. 8 12. 8 11. 7 Correlation =. 68 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (7) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genomic vs. Pedigree Inbreeding Bull O Man Ramos Shottle Planet Earnit Nifty Pedigree F 4. 5 2. 3 5. 6 6. 7 6. 2 3. 1 Genomic F 15. 8 11. 5 11. 9 18. 8 12. 8 11. 7 Correlation =. 68 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (7) Paul Van. Raden 2009
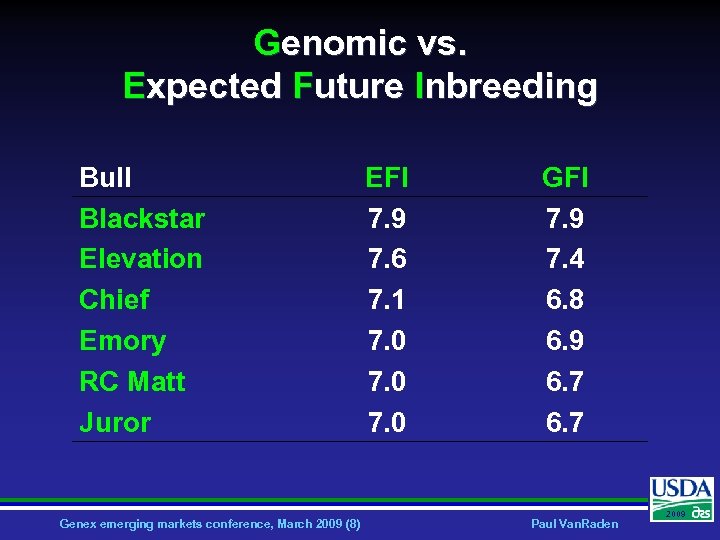 Genomic vs. Expected Future Inbreeding Bull Blackstar Elevation Chief Emory RC Matt Juror Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (8) EFI 7. 9 7. 6 7. 1 7. 0 GFI 7. 9 7. 4 6. 8 6. 9 6. 7 Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genomic vs. Expected Future Inbreeding Bull Blackstar Elevation Chief Emory RC Matt Juror Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (8) EFI 7. 9 7. 6 7. 1 7. 0 GFI 7. 9 7. 4 6. 8 6. 9 6. 7 Paul Van. Raden 2009
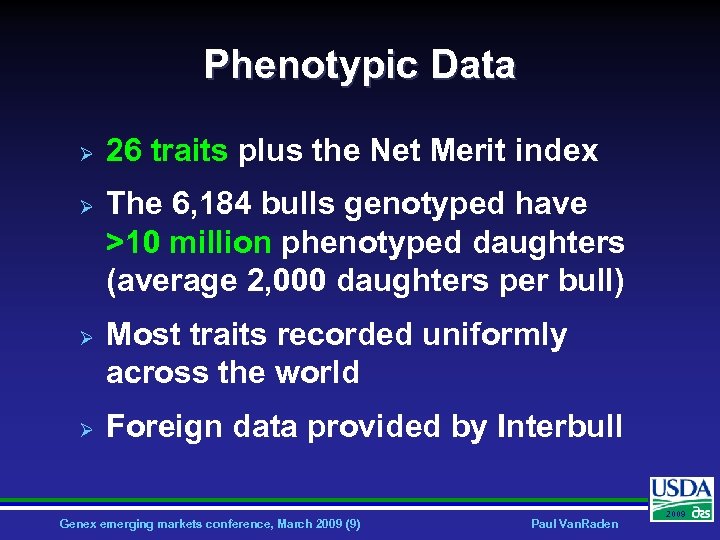 Phenotypic Data Ø Ø 26 traits plus the Net Merit index The 6, 184 bulls genotyped have >10 million phenotyped daughters (average 2, 000 daughters per bull) Most traits recorded uniformly across the world Foreign data provided by Interbull Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (9) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Phenotypic Data Ø Ø 26 traits plus the Net Merit index The 6, 184 bulls genotyped have >10 million phenotyped daughters (average 2, 000 daughters per bull) Most traits recorded uniformly across the world Foreign data provided by Interbull Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (9) Paul Van. Raden 2009
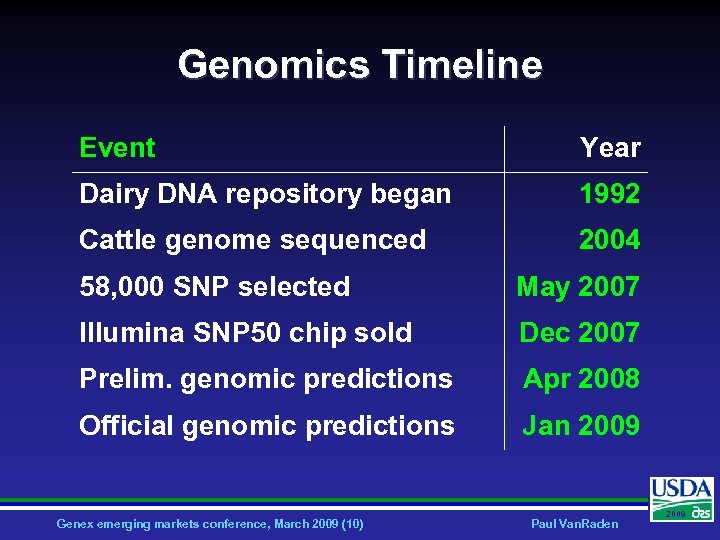 Genomics Timeline Event Year Dairy DNA repository began 1992 Cattle genome sequenced 2004 58, 000 SNP selected May 2007 Illumina SNP 50 chip sold Dec 2007 Prelim. genomic predictions Apr 2008 Official genomic predictions Jan 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (10) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genomics Timeline Event Year Dairy DNA repository began 1992 Cattle genome sequenced 2004 58, 000 SNP selected May 2007 Illumina SNP 50 chip sold Dec 2007 Prelim. genomic predictions Apr 2008 Official genomic predictions Jan 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (10) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Repeatability of Genotypes Ø 2 laboratories genotyped the same 46 bulls • • About 1% missing genotypes per lab Mean of 98% SNP same (37, 624 out of 38, 416) – • • Range across animals of 20 to 2, 244 SNP missing Mean of 99. 997% SNP concordance (conflict <0. 003%) Mean of 0. 9 errors per 38, 416 SNP – Range across animals of 0 to 7 SNP conflicts Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (11) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Repeatability of Genotypes Ø 2 laboratories genotyped the same 46 bulls • • About 1% missing genotypes per lab Mean of 98% SNP same (37, 624 out of 38, 416) – • • Range across animals of 20 to 2, 244 SNP missing Mean of 99. 997% SNP concordance (conflict <0. 003%) Mean of 0. 9 errors per 38, 416 SNP – Range across animals of 0 to 7 SNP conflicts Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (11) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Sequencing of Genomes Species Year Human - $3 billion 2000 Cow - $53 million funded by: 2004 50% Nat’l Human Genome Res Inst 50% USA, CAN, AUS, NZL Chicken 2004 Pig - < $20 million 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (12) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Sequencing of Genomes Species Year Human - $3 billion 2000 Cow - $53 million funded by: 2004 50% Nat’l Human Genome Res Inst 50% USA, CAN, AUS, NZL Chicken 2004 Pig - < $20 million 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (12) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Genomic Methods Ø Direct genomic evaluation • • Ø Combined genomic evaluation • Ø Sum of effects for 38, 416 genetic markers Not published Include phenotypes of non-genotyped ancestors by selection index Transferred genomic evaluation • Propagate info from genotyped animals to non-genotyped relatives by selection index Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (13) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genomic Methods Ø Direct genomic evaluation • • Ø Combined genomic evaluation • Ø Sum of effects for 38, 416 genetic markers Not published Include phenotypes of non-genotyped ancestors by selection index Transferred genomic evaluation • Propagate info from genotyped animals to non-genotyped relatives by selection index Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (13) Paul Van. Raden 2009
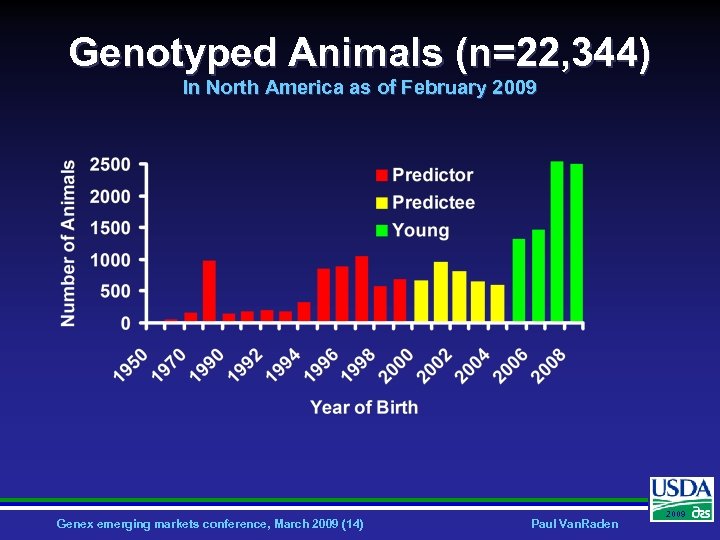 Genotyped Animals (n=22, 344) In North America as of February 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (14) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genotyped Animals (n=22, 344) In North America as of February 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (14) Paul Van. Raden 2009
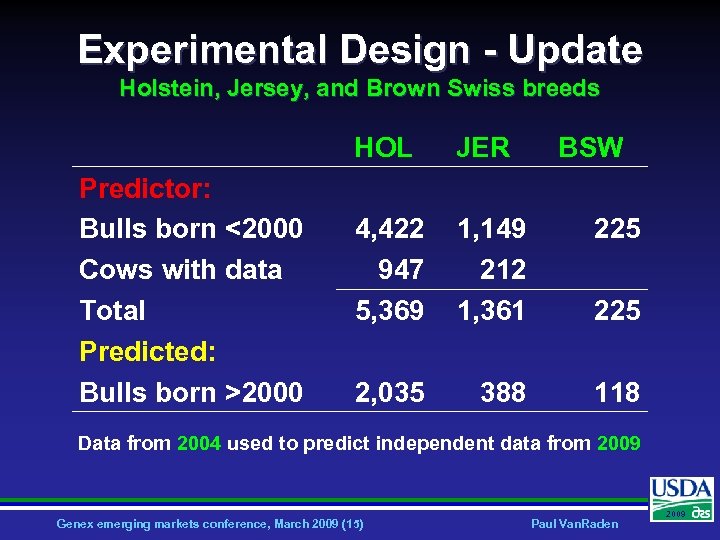 Experimental Design - Update Holstein, Jersey, and Brown Swiss breeds HOL Predictor: Bulls born <2000 Cows with data Total Predicted: Bulls born >2000 JER BSW 4, 422 947 5, 369 1, 149 212 1, 361 225 2, 035 388 118 225 Data from 2004 used to predict independent data from 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (15) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Experimental Design - Update Holstein, Jersey, and Brown Swiss breeds HOL Predictor: Bulls born <2000 Cows with data Total Predicted: Bulls born >2000 JER BSW 4, 422 947 5, 369 1, 149 212 1, 361 225 2, 035 388 118 225 Data from 2004 used to predict independent data from 2009 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (15) Paul Van. Raden 2009
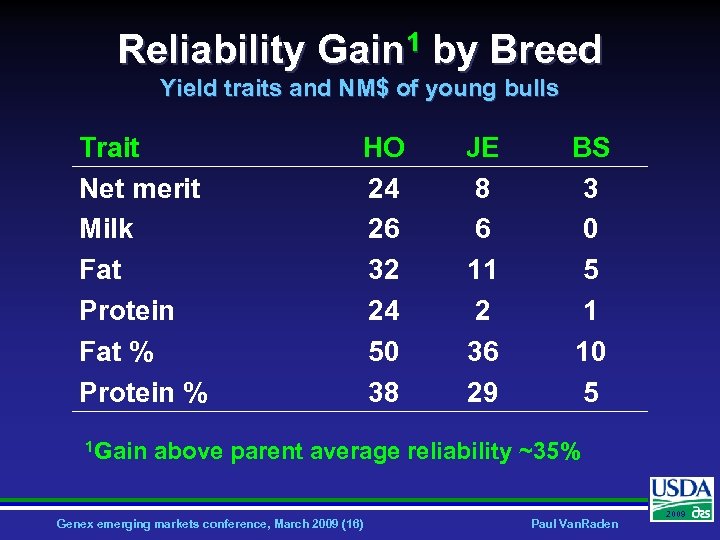 Reliability Gain 1 by Breed Yield traits and NM$ of young bulls Trait Net merit Milk Fat Protein Fat % Protein % 1 Gain HO 24 26 32 24 50 38 JE 8 6 11 2 36 29 BS 3 0 5 1 10 5 above parent average reliability ~35% Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (16) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Reliability Gain 1 by Breed Yield traits and NM$ of young bulls Trait Net merit Milk Fat Protein Fat % Protein % 1 Gain HO 24 26 32 24 50 38 JE 8 6 11 2 36 29 BS 3 0 5 1 10 5 above parent average reliability ~35% Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (16) Paul Van. Raden 2009
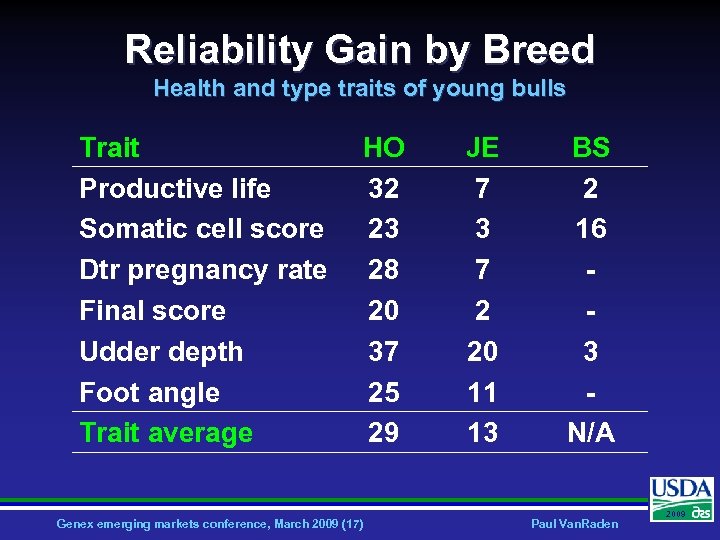 Reliability Gain by Breed Health and type traits of young bulls Trait Productive life Somatic cell score Dtr pregnancy rate Final score Udder depth Foot angle Trait average HO 32 23 28 20 37 25 29 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (17) JE 7 3 7 2 20 11 13 BS 2 16 3 N/A Paul Van. Raden 2009
Reliability Gain by Breed Health and type traits of young bulls Trait Productive life Somatic cell score Dtr pregnancy rate Final score Udder depth Foot angle Trait average HO 32 23 28 20 37 25 29 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (17) JE 7 3 7 2 20 11 13 BS 2 16 3 N/A Paul Van. Raden 2009
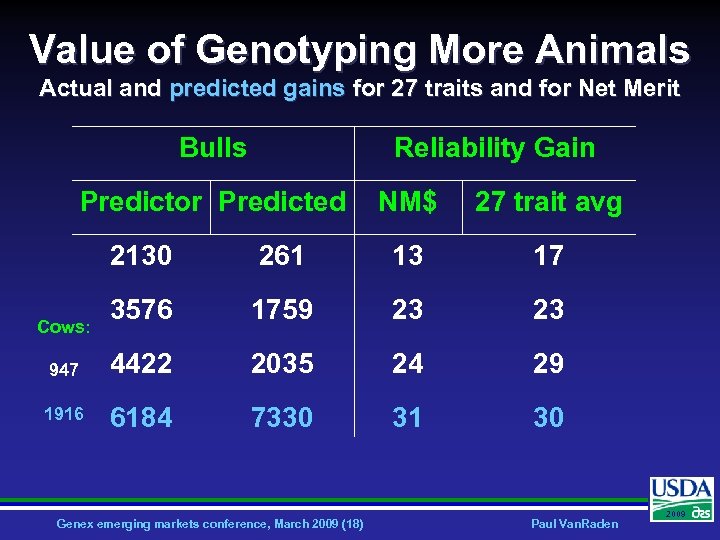 Value of Genotyping More Animals Actual and predicted gains for 27 traits and for Net Merit Bulls Reliability Gain Predictor Predicted NM$ 27 trait avg 2130 261 13 17 3576 1759 23 23 947 4422 2035 24 29 1916 6184 7330 31 30 Cows: Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (18) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Value of Genotyping More Animals Actual and predicted gains for 27 traits and for Net Merit Bulls Reliability Gain Predictor Predicted NM$ 27 trait avg 2130 261 13 17 3576 1759 23 23 947 4422 2035 24 29 1916 6184 7330 31 30 Cows: Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (18) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 USA Evaluation Ø Genomic PTAs official in January • • Traditional PTAs sent to Interbull MACE used if foreign dtrs included Genomic info used for most bulls Genomic PTA transferred to descendants (to ancestors in future) Ø Jersey results also are official Ø More Brown Swiss needed (CHE) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (19) Paul Van. Raden 2009
USA Evaluation Ø Genomic PTAs official in January • • Traditional PTAs sent to Interbull MACE used if foreign dtrs included Genomic info used for most bulls Genomic PTA transferred to descendants (to ancestors in future) Ø Jersey results also are official Ø More Brown Swiss needed (CHE) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (19) Paul Van. Raden 2009
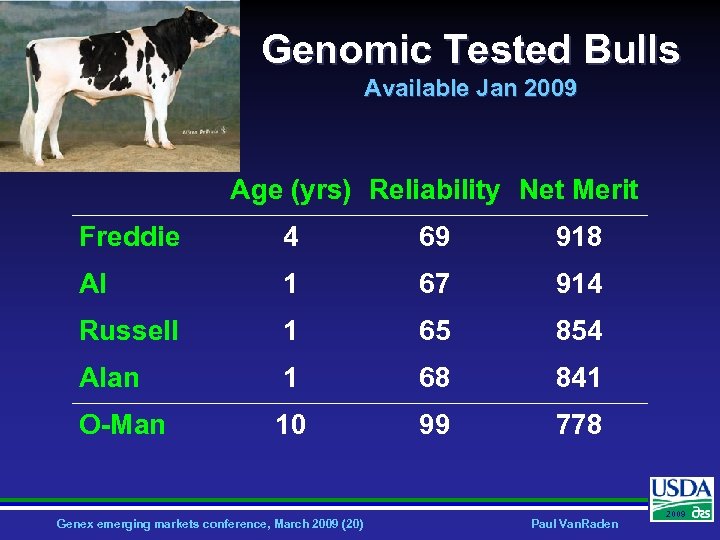 Genomic Tested Bulls Available Jan 2009 Age (yrs) Reliability Net Merit Freddie 4 69 918 Al 1 67 914 Russell 1 65 854 Alan 1 68 841 O-Man 10 99 778 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (20) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genomic Tested Bulls Available Jan 2009 Age (yrs) Reliability Net Merit Freddie 4 69 918 Al 1 67 914 Russell 1 65 854 Alan 1 68 841 O-Man 10 99 778 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (20) Paul Van. Raden 2009
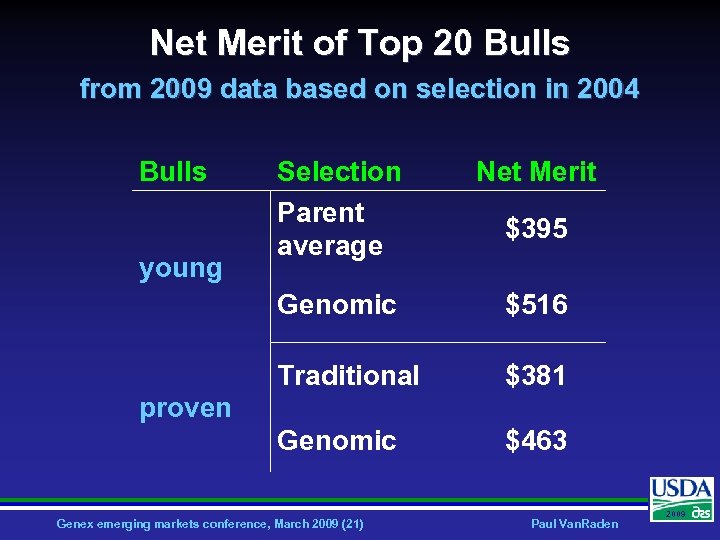 Net Merit of Top 20 Bulls from 2009 data based on selection in 2004 Bulls Net Merit Genomic $516 Traditional $381 Genomic young Selection Parent average $463 $395 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (21) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Net Merit of Top 20 Bulls from 2009 data based on selection in 2004 Bulls Net Merit Genomic $516 Traditional $381 Genomic young Selection Parent average $463 $395 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (21) Paul Van. Raden 2009
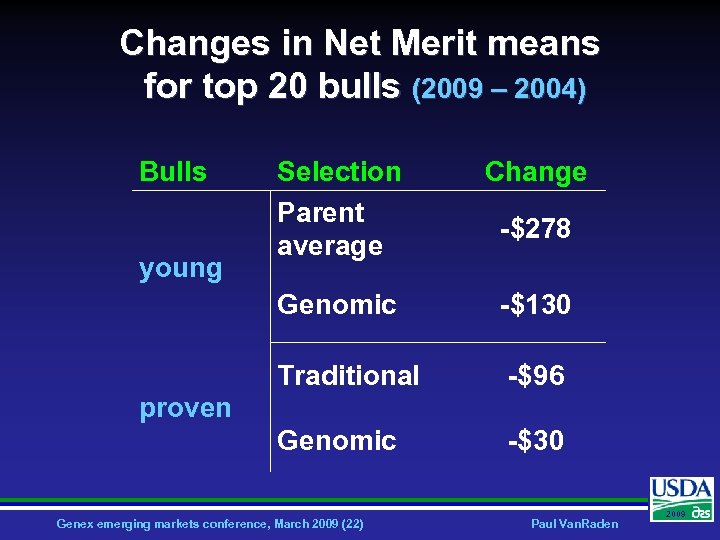 Changes in Net Merit means for top 20 bulls (2009 – 2004) Bulls Change Genomic -$130 Traditional -$96 Genomic young Selection Parent average -$30 -$278 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (22) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Changes in Net Merit means for top 20 bulls (2009 – 2004) Bulls Change Genomic -$130 Traditional -$96 Genomic young Selection Parent average -$30 -$278 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (22) Paul Van. Raden 2009
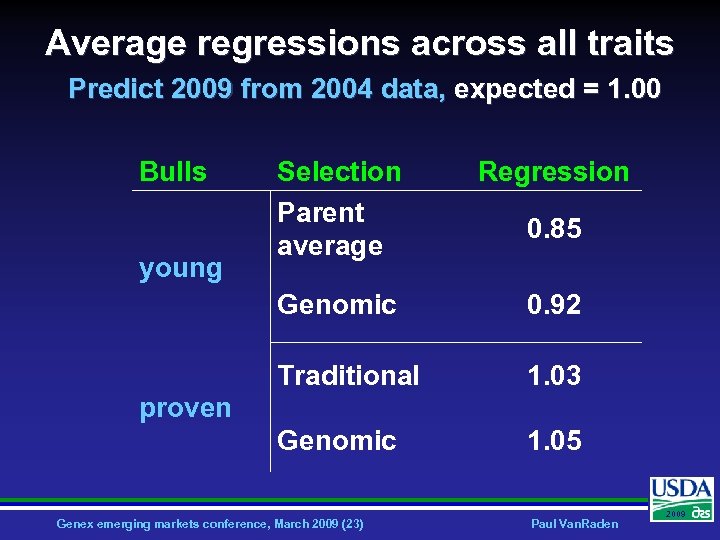 Average regressions across all traits Predict 2009 from 2004 data, expected = 1. 00 Bulls Regression Genomic 0. 92 Traditional 1. 03 Genomic young Selection Parent average 1. 05 0. 85 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (23) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Average regressions across all traits Predict 2009 from 2004 data, expected = 1. 00 Bulls Regression Genomic 0. 92 Traditional 1. 03 Genomic young Selection Parent average 1. 05 0. 85 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (23) Paul Van. Raden 2009
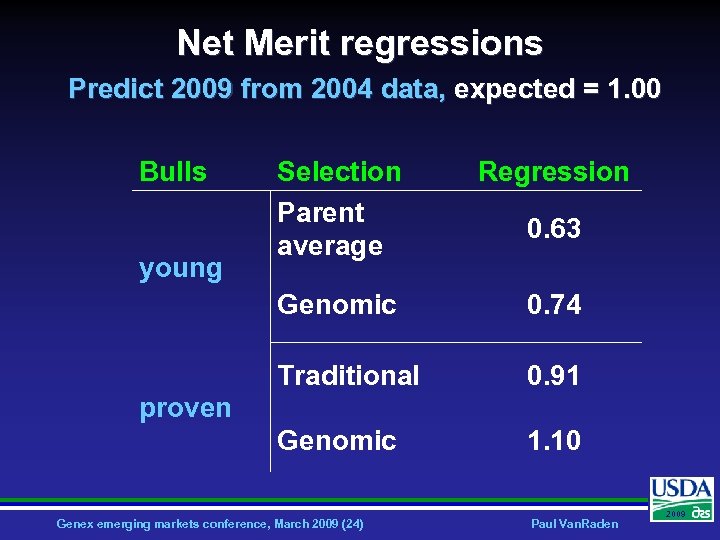 Net Merit regressions Predict 2009 from 2004 data, expected = 1. 00 Bulls Regression Genomic 0. 74 Traditional 0. 91 Genomic young Selection Parent average 1. 10 0. 63 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (24) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Net Merit regressions Predict 2009 from 2004 data, expected = 1. 00 Bulls Regression Genomic 0. 74 Traditional 0. 91 Genomic young Selection Parent average 1. 10 0. 63 proven Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (24) Paul Van. Raden 2009
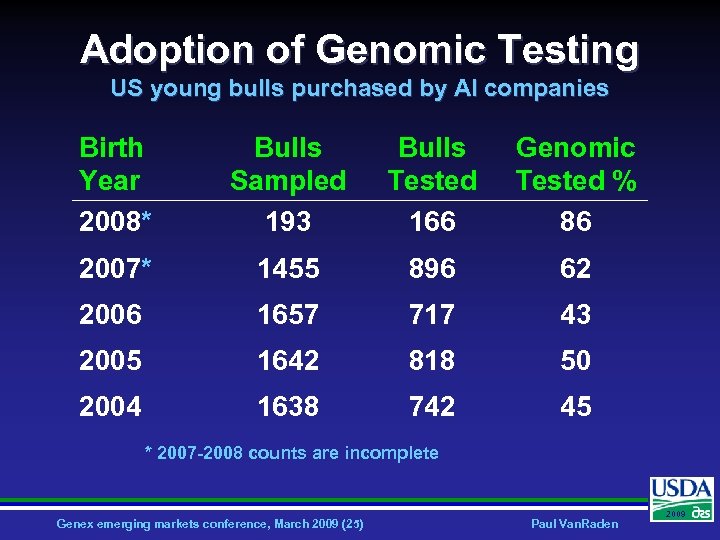 Adoption of Genomic Testing US young bulls purchased by AI companies Birth Year 2008* Bulls Sampled 193 Bulls Tested 166 Genomic Tested % 86 2007* 1455 896 62 2006 1657 717 43 2005 1642 818 50 2004 1638 742 45 * 2007 -2008 counts are incomplete Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (25) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Adoption of Genomic Testing US young bulls purchased by AI companies Birth Year 2008* Bulls Sampled 193 Bulls Tested 166 Genomic Tested % 86 2007* 1455 896 62 2006 1657 717 43 2005 1642 818 50 2004 1638 742 45 * 2007 -2008 counts are incomplete Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (25) Paul Van. Raden 2009
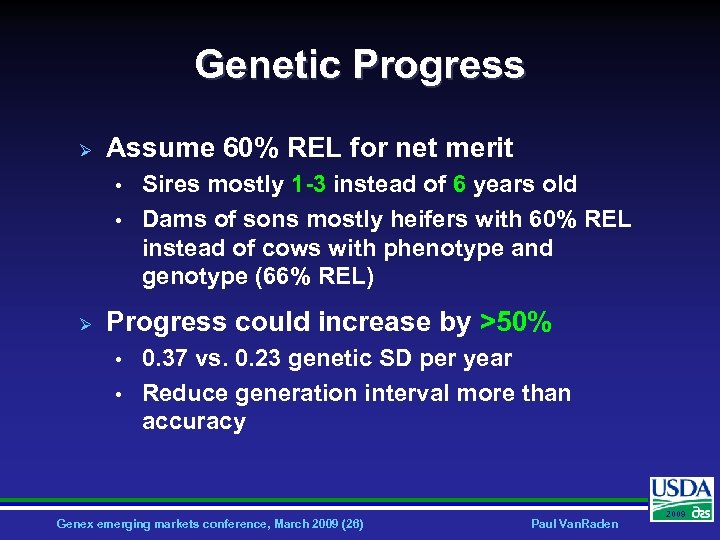 Genetic Progress Ø Assume 60% REL for net merit • • Ø Sires mostly 1 -3 instead of 6 years old Dams of sons mostly heifers with 60% REL instead of cows with phenotype and genotype (66% REL) Progress could increase by >50% • • 0. 37 vs. 0. 23 genetic SD per year Reduce generation interval more than accuracy Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (26) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genetic Progress Ø Assume 60% REL for net merit • • Ø Sires mostly 1 -3 instead of 6 years old Dams of sons mostly heifers with 60% REL instead of cows with phenotype and genotype (66% REL) Progress could increase by >50% • • 0. 37 vs. 0. 23 genetic SD per year Reduce generation interval more than accuracy Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (26) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Worldwide Dairy Genotyping as of January 2009 Countries United States and Canada France Netherlands, New Zealand 1 New Zealand Ireland Germany Australia Denmark, Finland, Sweden 1 Using Animals 22, 344 8, 500 6, 000 4, 500 3, 000 2, 000 a customized Illumina 50 K chip (different markers) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (27) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Worldwide Dairy Genotyping as of January 2009 Countries United States and Canada France Netherlands, New Zealand 1 New Zealand Ireland Germany Australia Denmark, Finland, Sweden 1 Using Animals 22, 344 8, 500 6, 000 4, 500 3, 000 2, 000 a customized Illumina 50 K chip (different markers) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (27) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 North American Cooperation Ø 174 markers, 1068 USA and CAN bulls • • Ø 367 markers, 1415 USA and CAN bulls • • Ø Illinois, Israel, and USDA researchers 1991 -1999 USDA, Illinois, and Israel 1995 -2004 38, 416 markers, 22, 344 animals • • USDA, Missouri, Canada, and Illumina Oct 2007 - Dec 2008 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (28) Paul Van. Raden 2009
North American Cooperation Ø 174 markers, 1068 USA and CAN bulls • • Ø 367 markers, 1415 USA and CAN bulls • • Ø Illinois, Israel, and USDA researchers 1991 -1999 USDA, Illinois, and Israel 1995 -2004 38, 416 markers, 22, 344 animals • • USDA, Missouri, Canada, and Illumina Oct 2007 - Dec 2008 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (28) Paul Van. Raden 2009
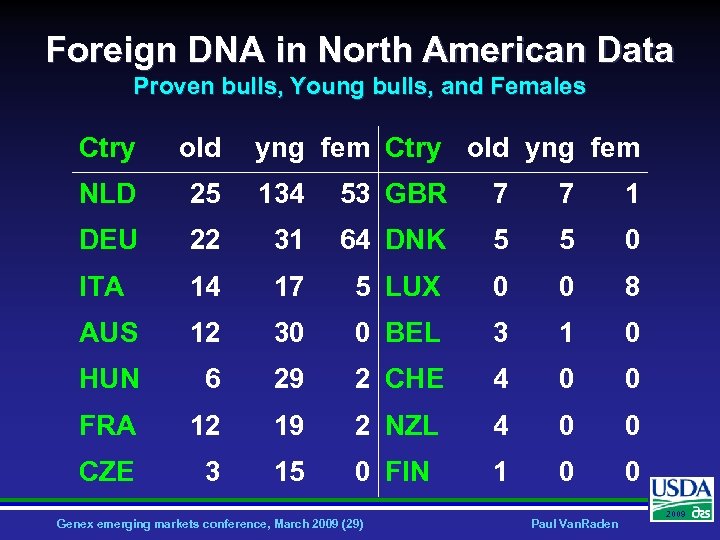 Foreign DNA in North American Data Proven bulls, Young bulls, and Females Ctry old yng fem NLD 25 134 53 GBR 7 7 1 DEU 22 31 64 DNK 5 5 0 ITA 14 17 5 LUX 0 0 8 AUS 12 30 0 BEL 3 1 0 HUN 6 29 2 CHE 4 0 0 FRA 12 19 2 NZL 4 0 0 CZE 3 15 0 FIN 1 0 0 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (29) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Foreign DNA in North American Data Proven bulls, Young bulls, and Females Ctry old yng fem NLD 25 134 53 GBR 7 7 1 DEU 22 31 64 DNK 5 5 0 ITA 14 17 5 LUX 0 0 8 AUS 12 30 0 BEL 3 1 0 HUN 6 29 2 CHE 4 0 0 FRA 12 19 2 NZL 4 0 0 CZE 3 15 0 FIN 1 0 0 Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (29) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Country Borders Ø Ø Most phenotypic data collected and stored within country Genomic data allows simple, accurate prediction across borders • • • Need traditional EBV or PA foreign animals, but not available for young bulls, cows, or heifers May need full foreign pedigrees Genomic evaluations official on USA scale for many foreign animals (not just CAN) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (30) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Country Borders Ø Ø Most phenotypic data collected and stored within country Genomic data allows simple, accurate prediction across borders • • • Need traditional EBV or PA foreign animals, but not available for young bulls, cows, or heifers May need full foreign pedigrees Genomic evaluations official on USA scale for many foreign animals (not just CAN) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (30) Paul Van. Raden 2009
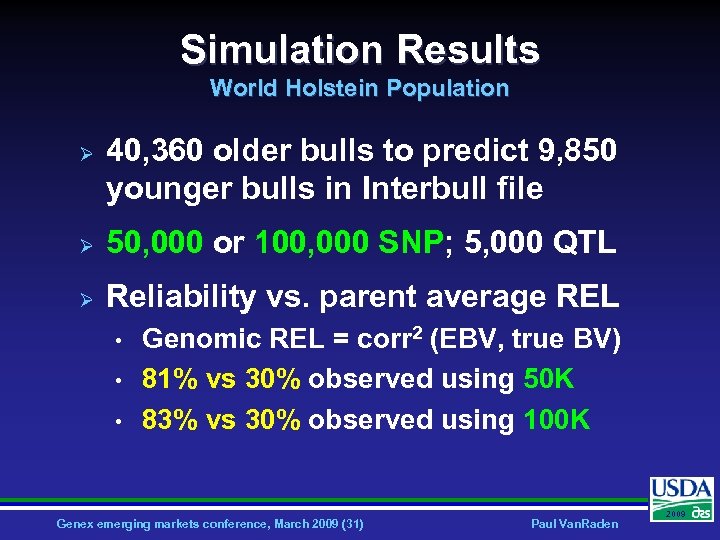 Simulation Results World Holstein Population Ø 40, 360 older bulls to predict 9, 850 younger bulls in Interbull file Ø 50, 000 or 100, 000 SNP; 5, 000 QTL Ø Reliability vs. parent average REL • • • Genomic REL = corr 2 (EBV, true BV) 81% vs 30% observed using 50 K 83% vs 30% observed using 100 K Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (31) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Simulation Results World Holstein Population Ø 40, 360 older bulls to predict 9, 850 younger bulls in Interbull file Ø 50, 000 or 100, 000 SNP; 5, 000 QTL Ø Reliability vs. parent average REL • • • Genomic REL = corr 2 (EBV, true BV) 81% vs 30% observed using 50 K 83% vs 30% observed using 100 K Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (31) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Cooperative International Projects Ø Traditional genetic evaluations • • • Ø Ø MACE instead of merging phenotypes Small benefits expected from data merger Proven bulls only, not cows or young bulls Parentage testing, genetic recessives, pedigrees done by breed associations Genomics: what role for Interbull? • Benefits of sharing genotypes are large Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (32) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Cooperative International Projects Ø Traditional genetic evaluations • • • Ø Ø MACE instead of merging phenotypes Small benefits expected from data merger Proven bulls only, not cows or young bulls Parentage testing, genetic recessives, pedigrees done by breed associations Genomics: what role for Interbull? • Benefits of sharing genotypes are large Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (32) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Genotype Exchange Options Ø Ø Give away for free (not likely) Genotype own bulls, then trade? • • • Ø Ø Trade an equal number or all bulls? Country A has 5000 and B has 1000 Proportional to population size? Trade among organization pairs or create central genomic database? Service fee for young animals to pay for ancestor genotyping? Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (33) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Genotype Exchange Options Ø Ø Give away for free (not likely) Genotype own bulls, then trade? • • • Ø Ø Trade an equal number or all bulls? Country A has 5000 and B has 1000 Proportional to population size? Trade among organization pairs or create central genomic database? Service fee for young animals to pay for ancestor genotyping? Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (33) Paul Van. Raden 2009
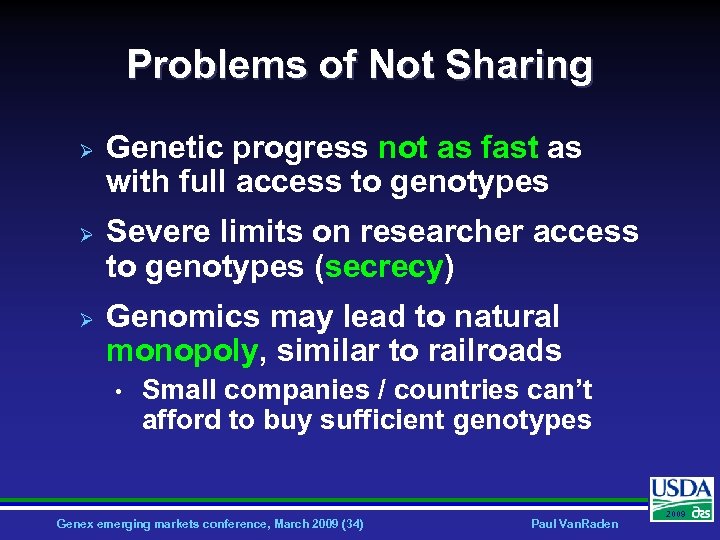 Problems of Not Sharing Ø Ø Ø Genetic progress not as fast as with full access to genotypes Severe limits on researcher access to genotypes (secrecy) Genomics may lead to natural monopoly, similar to railroads • Small companies / countries can’t afford to buy sufficient genotypes Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (34) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Problems of Not Sharing Ø Ø Ø Genetic progress not as fast as with full access to genotypes Severe limits on researcher access to genotypes (secrecy) Genomics may lead to natural monopoly, similar to railroads • Small companies / countries can’t afford to buy sufficient genotypes Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (34) Paul Van. Raden 2009
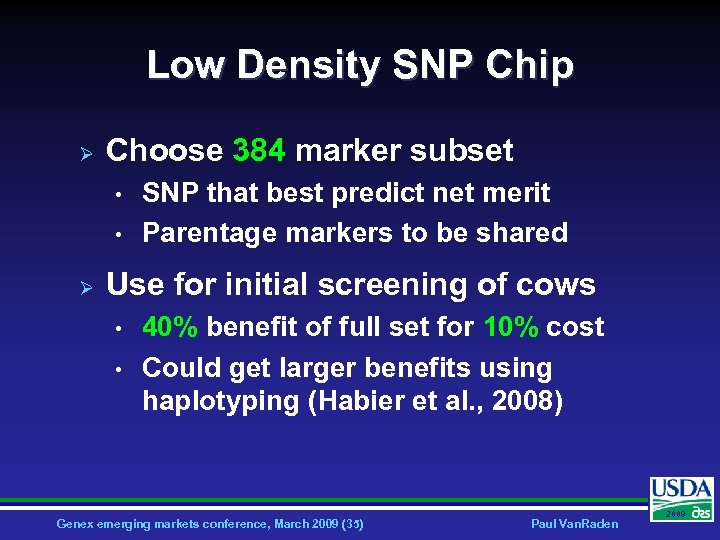 Low Density SNP Chip Ø Choose 384 marker subset • • Ø SNP that best predict net merit Parentage markers to be shared Use for initial screening of cows • • 40% benefit of full set for 10% cost Could get larger benefits using haplotyping (Habier et al. , 2008) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (35) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Low Density SNP Chip Ø Choose 384 marker subset • • Ø SNP that best predict net merit Parentage markers to be shared Use for initial screening of cows • • 40% benefit of full set for 10% cost Could get larger benefits using haplotyping (Habier et al. , 2008) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (35) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Insignificant SNP Effects Ø Traditional selection on PA • Ø 1 SNP with tiny effect • Ø 50. 01 : 49. 99 chance 38, 416 SNPs with tiny effects • Ø 50 : 50 chance of better chromosome 70 : 30 chance Only test overall sum of effects! Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (36) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Insignificant SNP Effects Ø Traditional selection on PA • Ø 1 SNP with tiny effect • Ø 50. 01 : 49. 99 chance 38, 416 SNPs with tiny effects • Ø 50 : 50 chance of better chromosome 70 : 30 chance Only test overall sum of effects! Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (36) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Conclusions - 1 Ø High accuracy requires very many genotypes and phenotypes • • Ø 100 X more markers allows MAS across rather than within families 5 X more bulls allows estimation of much smaller QTL effects (HO) Most traits are very quantitative (few major genes) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (37) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Conclusions - 1 Ø High accuracy requires very many genotypes and phenotypes • • Ø 100 X more markers allows MAS across rather than within families 5 X more bulls allows estimation of much smaller QTL effects (HO) Most traits are very quantitative (few major genes) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (37) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Conclusions - 2 Ø Ø Reliability increases by tracing actual genes inherited instead of expected average from parents Genomic reliability > traditional • • Ø 30 -40% with traditional parent average 60 -70% using 8, 100 genotyped Holsteins 81 -83% from 40, 000 simulated bulls Gains much smaller for USA JER and BSW breeds Trading, sharing, profit is needed Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (38) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Conclusions - 2 Ø Ø Reliability increases by tracing actual genes inherited instead of expected average from parents Genomic reliability > traditional • • Ø 30 -40% with traditional parent average 60 -70% using 8, 100 genotyped Holsteins 81 -83% from 40, 000 simulated bulls Gains much smaller for USA JER and BSW breeds Trading, sharing, profit is needed Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (38) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 Acknowledgments Ø Genotyping and DNA extraction: • Ø Computing: • Ø USDA Bovine Functional Genomics Lab, U. Missouri, U. Alberta, Gene. Seek, Genetics & IVF Institute, Genetic Visions, and Illumina AIPL staff (Mel Tooker, Leigh Walton, Jay Megonigal) Funding: • National Research Initiative grants – • • • 2006 -35205 -16888, 2006 -35205 -16701 Agriculture Research Service Holstein and Jersey breed associations Contributors to Cooperative Dairy DNA Repository (CDDR) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (39) Paul Van. Raden 2009
Acknowledgments Ø Genotyping and DNA extraction: • Ø Computing: • Ø USDA Bovine Functional Genomics Lab, U. Missouri, U. Alberta, Gene. Seek, Genetics & IVF Institute, Genetic Visions, and Illumina AIPL staff (Mel Tooker, Leigh Walton, Jay Megonigal) Funding: • National Research Initiative grants – • • • 2006 -35205 -16888, 2006 -35205 -16701 Agriculture Research Service Holstein and Jersey breed associations Contributors to Cooperative Dairy DNA Repository (CDDR) Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (39) Paul Van. Raden 2009
 CDDR Contributors Ø National Association of Animal Breeders (NAAB, Columbia, MO) • ABS Global (De. Forest, WI) Accelerated Genetics (Baraboo, WI) Alta (Balzac, AB, Canada) Genex (Shawano, WI) New Generation Genetics (Fort Atkinson, WI) • Select Sires (Plain City, OH) • Semex Alliance (Guelph, ON, Canada) • Taurus-Service (Mehoopany, PA) • • Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (40) Paul Van. Raden 2009
CDDR Contributors Ø National Association of Animal Breeders (NAAB, Columbia, MO) • ABS Global (De. Forest, WI) Accelerated Genetics (Baraboo, WI) Alta (Balzac, AB, Canada) Genex (Shawano, WI) New Generation Genetics (Fort Atkinson, WI) • Select Sires (Plain City, OH) • Semex Alliance (Guelph, ON, Canada) • Taurus-Service (Mehoopany, PA) • • Genex emerging markets conference, March 2009 (40) Paul Van. Raden 2009


