GENITAL ORGANS.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 GENITAL ORGANS
GENITAL ORGANS
 THE MALE INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS n n n n The testis The epididymis The ductus (vas) deferens The seminal vesicles The ejaculatory ducts The prostate gland The bulbourethral gland
THE MALE INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS n n n n The testis The epididymis The ductus (vas) deferens The seminal vesicles The ejaculatory ducts The prostate gland The bulbourethral gland
 THE MALE EXTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS the penis n the scrotum n the spermatic cord n
THE MALE EXTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS the penis n the scrotum n the spermatic cord n
 The testis n The exocrine function means producing male genital cells – spermatozoa n Тhe endocrine function means producing testosterone (male sexual hormone)
The testis n The exocrine function means producing male genital cells – spermatozoa n Тhe endocrine function means producing testosterone (male sexual hormone)
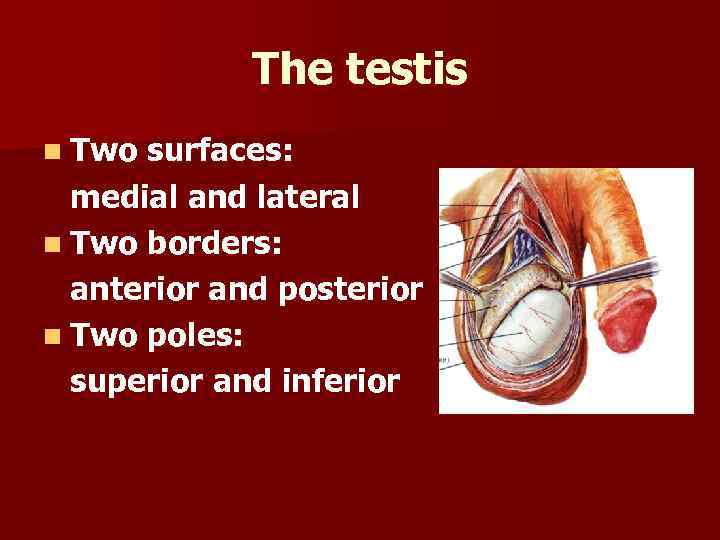 The testis n Two surfaces: medial and lateral n Тwo borders: anterior and posterior n Тwo poles: superior and inferior
The testis n Two surfaces: medial and lateral n Тwo borders: anterior and posterior n Тwo poles: superior and inferior
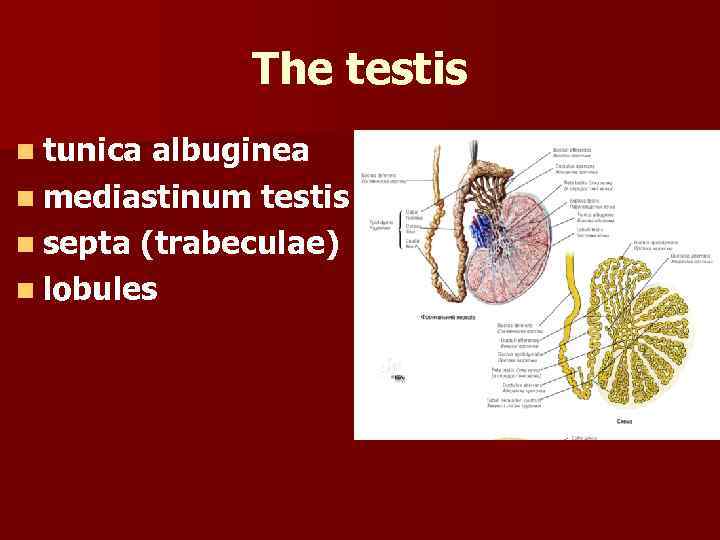 The testis n tunica albuginea n mediastinum testis n septa (trabeculae) n lobules
The testis n tunica albuginea n mediastinum testis n septa (trabeculae) n lobules
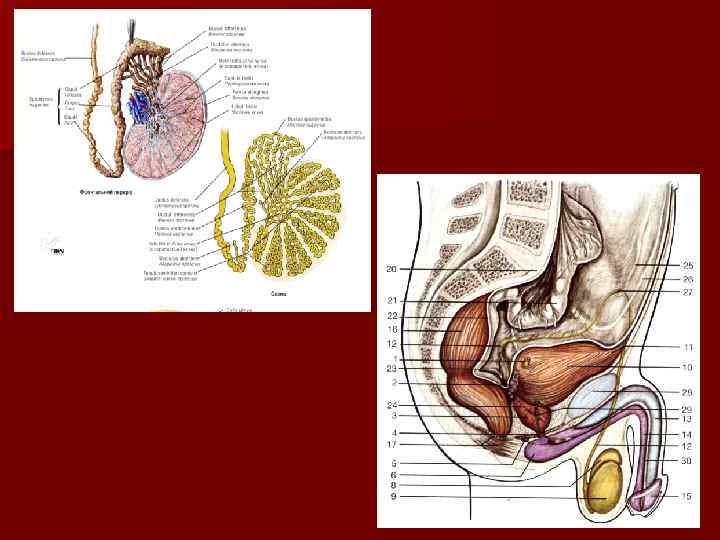
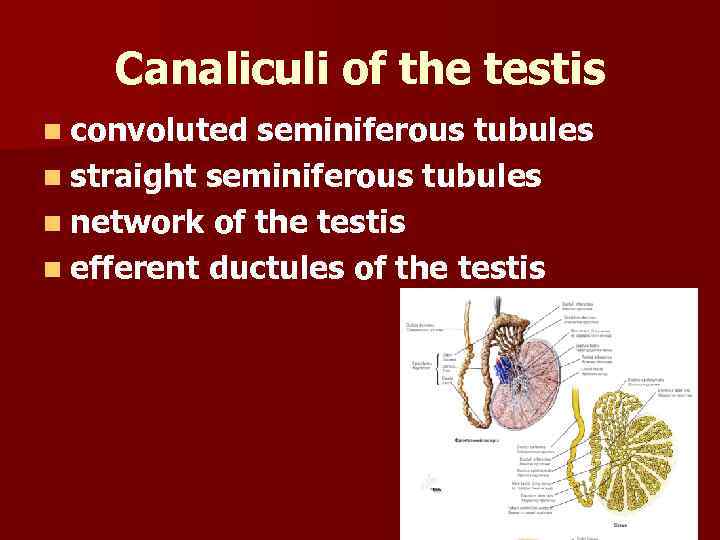 Canaliculi of the testis n convoluted seminiferous tubules n straight seminiferous tubules n network of the testis n efferent ductules of the testis
Canaliculi of the testis n convoluted seminiferous tubules n straight seminiferous tubules n network of the testis n efferent ductules of the testis
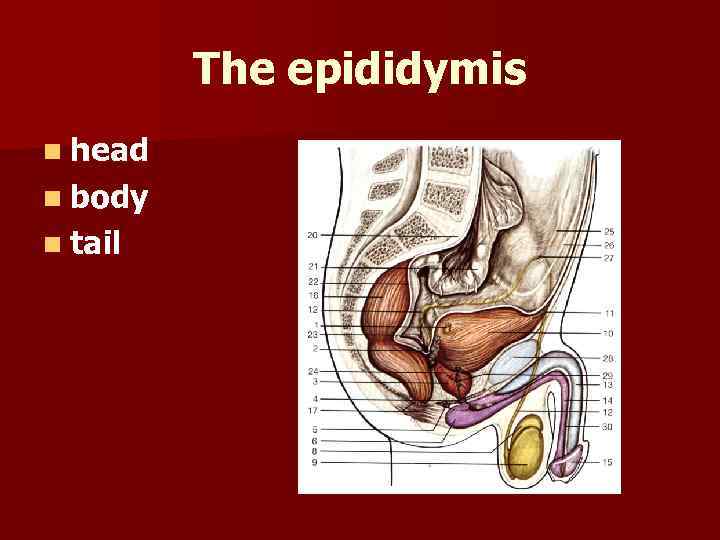 The epididymis n head n body n tail
The epididymis n head n body n tail
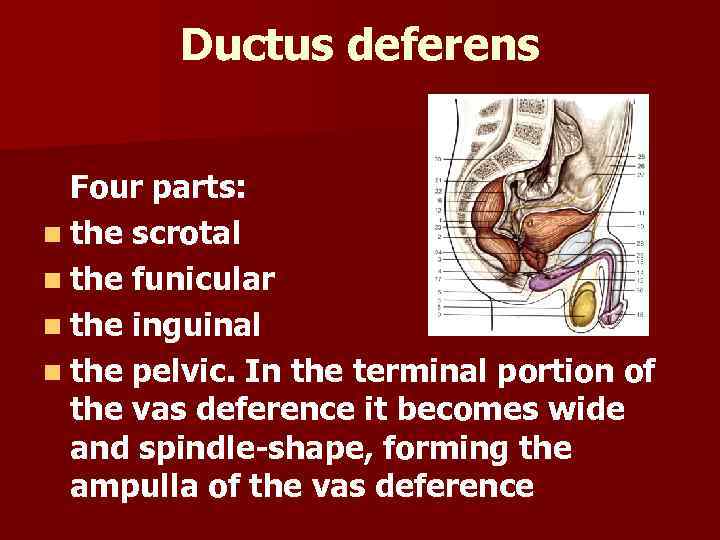 Ductus deferens Four parts: n the scrotal n the funicular n the inguinal n the pelvic. In the terminal portion of the vas deference it becomes wide and spindle-shape, forming the ampulla of the vas deference
Ductus deferens Four parts: n the scrotal n the funicular n the inguinal n the pelvic. In the terminal portion of the vas deference it becomes wide and spindle-shape, forming the ampulla of the vas deference
 The wall of the ductus deference is composed of three layers: n an outer adventitious coat n a middle muscular coat n an inner mucous coat
The wall of the ductus deference is composed of three layers: n an outer adventitious coat n a middle muscular coat n an inner mucous coat
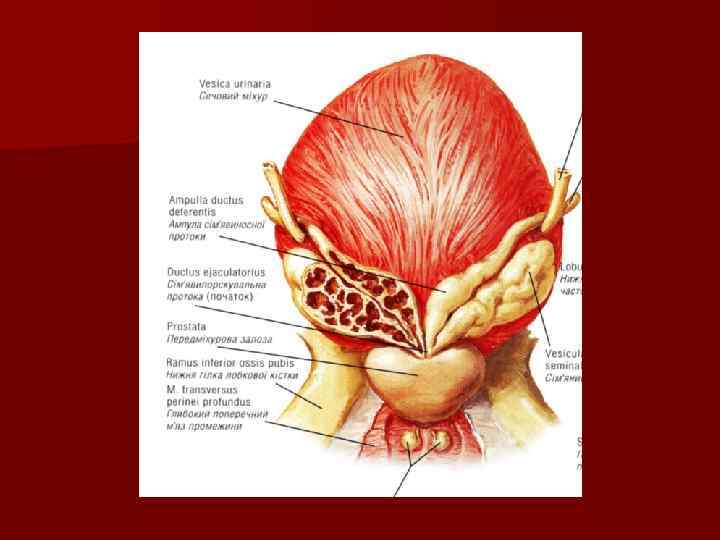
 The seminal vesicles n It is a tubular gland n The seminal vesicles contribute 60 percent of the volume of semen n The junction of the duct of the seminal vesicles with ampulla of the ductus deferens marks the ejaculatory duct n Opens into prostate part of the urethra
The seminal vesicles n It is a tubular gland n The seminal vesicles contribute 60 percent of the volume of semen n The junction of the duct of the seminal vesicles with ampulla of the ductus deferens marks the ejaculatory duct n Opens into prostate part of the urethra
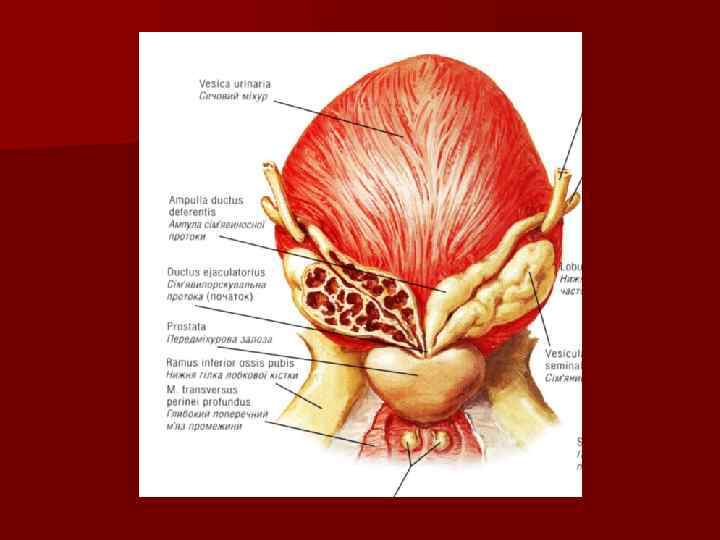
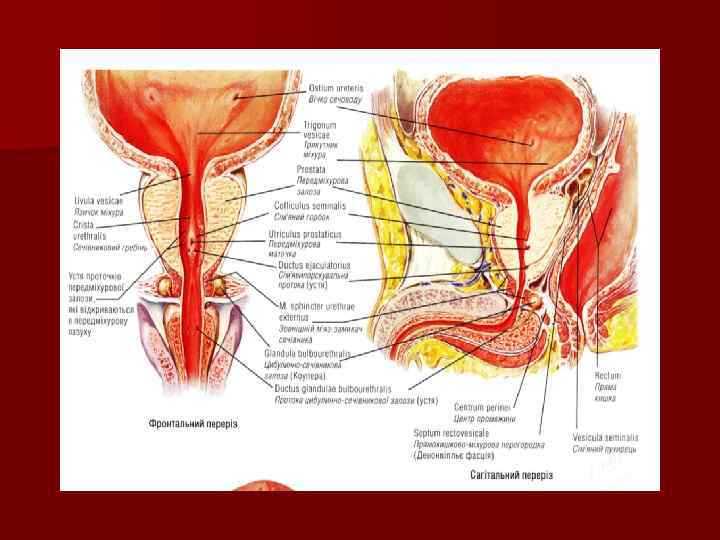
 The prostate gland n The prostate gland is partly muscular and partly glandular organ n It secretes a component of semen The prostate has: n base and apex n anterior, posterior and inferolateral surfaces n left, right and middle lobes
The prostate gland n The prostate gland is partly muscular and partly glandular organ n It secretes a component of semen The prostate has: n base and apex n anterior, posterior and inferolateral surfaces n left, right and middle lobes
 The bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands n They are situated at the base of the penis, covered by the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm n The excretory duct opens into the spongy portion of the urethra n The secretion of the glands protects the urethral walls from irritation by the urine
The bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands n They are situated at the base of the penis, covered by the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm n The excretory duct opens into the spongy portion of the urethra n The secretion of the glands protects the urethral walls from irritation by the urine
 Scrotum n Skin skin n Dartos tunic subcutaneous connective tissue n External spermatic fascia superficial fascia of the abdomen n Cremasteric fascia proper fascia of the external oblique abdominal muscle n Cremaster muscle n Internal spermatic fascia internal oblique abdominal and transversal muscles transverse fascia n Vaginal tunic peritoneum
Scrotum n Skin skin n Dartos tunic subcutaneous connective tissue n External spermatic fascia superficial fascia of the abdomen n Cremasteric fascia proper fascia of the external oblique abdominal muscle n Cremaster muscle n Internal spermatic fascia internal oblique abdominal and transversal muscles transverse fascia n Vaginal tunic peritoneum
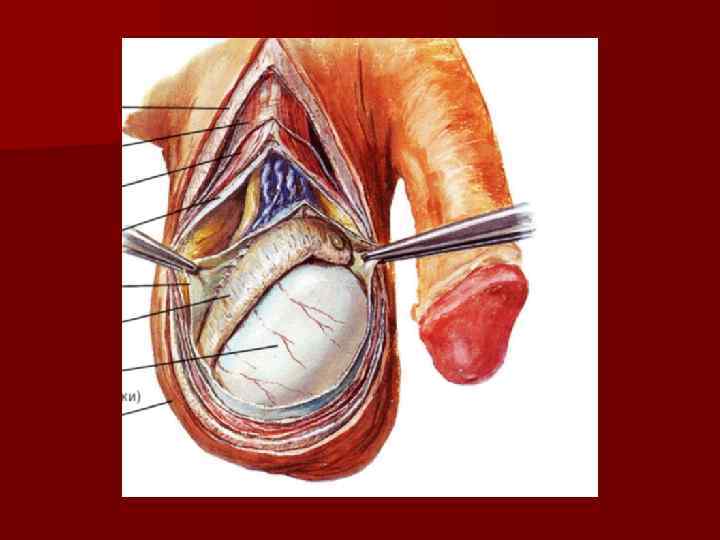
 Spermatic cord n the vas deferens; n testicular artery; n convoluted (venous) pampiniform plexus; n the artery and veins of the vas deferens; n the lymphatic vessels of the testis and the epididymis; n the nerves; n the vestige of the processus vaginalis
Spermatic cord n the vas deferens; n testicular artery; n convoluted (venous) pampiniform plexus; n the artery and veins of the vas deferens; n the lymphatic vessels of the testis and the epididymis; n the nerves; n the vestige of the processus vaginalis
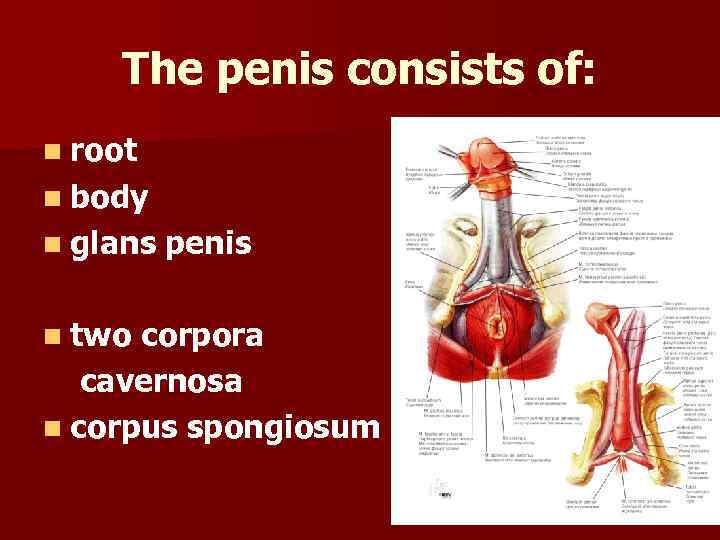 The penis consists of: n root n body n glans n two penis corpora cavernosa n corpus spongiosum
The penis consists of: n root n body n glans n two penis corpora cavernosa n corpus spongiosum
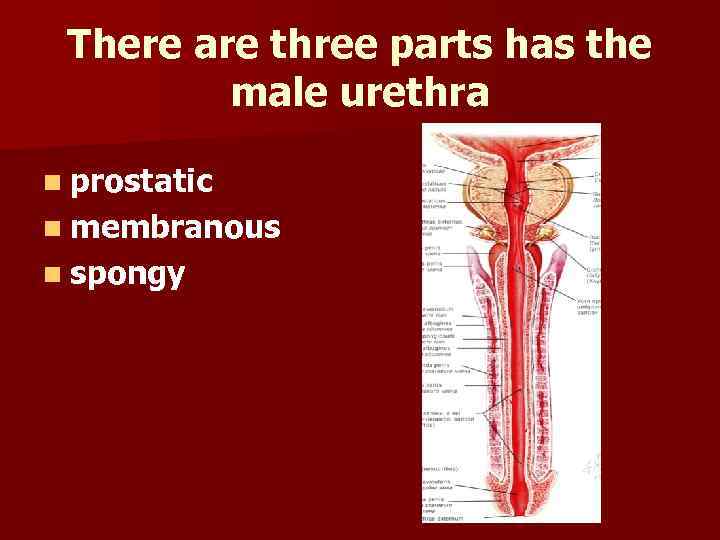 There are three parts has the male urethra n prostatic n membranous n spongy
There are three parts has the male urethra n prostatic n membranous n spongy
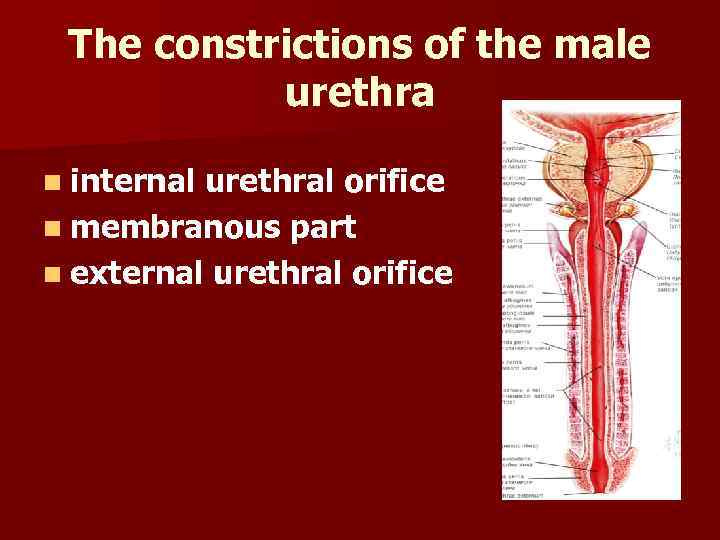 The constrictions of the male urethra n internal urethral orifice n membranous part n external urethral orifice
The constrictions of the male urethra n internal urethral orifice n membranous part n external urethral orifice
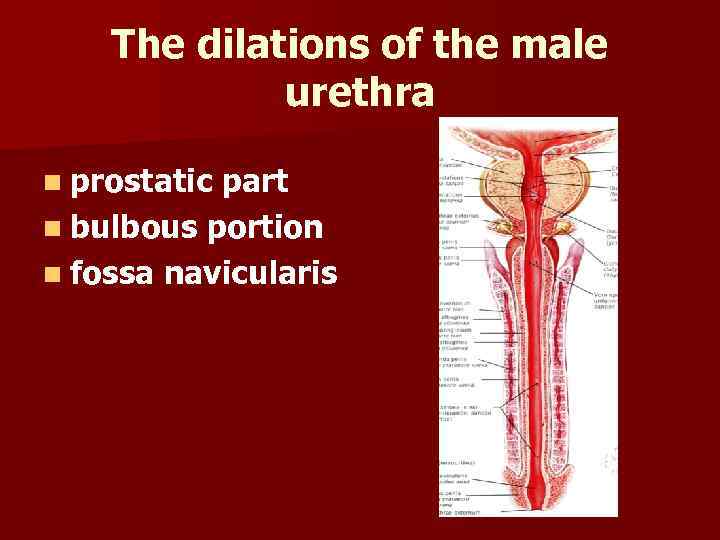 The dilations of the male urethra n prostatic part n bulbous portion n fossa navicularis
The dilations of the male urethra n prostatic part n bulbous portion n fossa navicularis
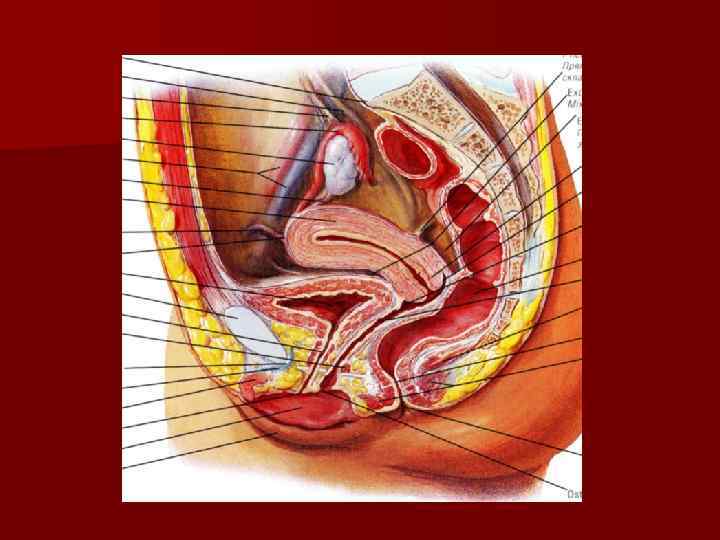
 Internal female organs n ovaries n uterine n uterus n vagina tubes
Internal female organs n ovaries n uterine n uterus n vagina tubes
 External female organs n n n n mons pubis clitoris - is a structure analogous to the corpora cavernosa of the penis labium majus limit the glottis (rima) pudendi labium minus pudenda - bound the vestibule of the vagina greater vestibular gland bulb of vestibule - is a structure analogous to the corpus spongiosum of the penis
External female organs n n n n mons pubis clitoris - is a structure analogous to the corpora cavernosa of the penis labium majus limit the glottis (rima) pudendi labium minus pudenda - bound the vestibule of the vagina greater vestibular gland bulb of vestibule - is a structure analogous to the corpus spongiosum of the penis
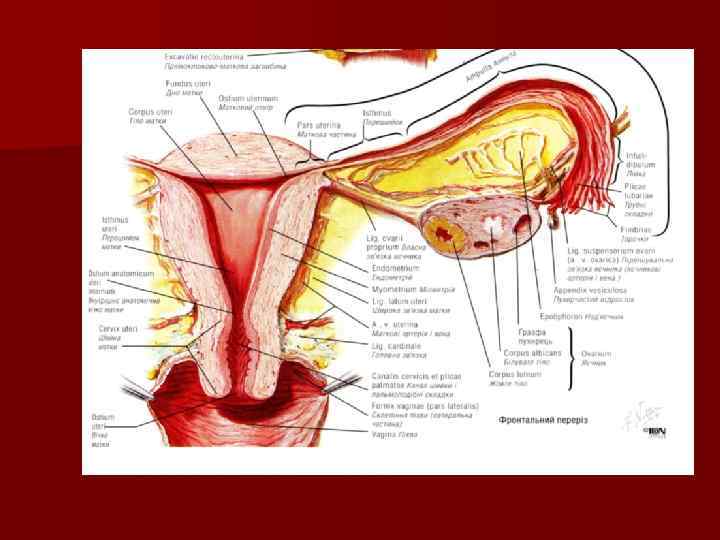
 The ovary n The exocrine function is to produce ovules n The endocrine function is to produce female sexual hormones The ovary has: n two surfaces: medial and lateral n two extremities: tubal and uterine n two borders: free posterior and anterior mesovarium
The ovary n The exocrine function is to produce ovules n The endocrine function is to produce female sexual hormones The ovary has: n two surfaces: medial and lateral n two extremities: tubal and uterine n two borders: free posterior and anterior mesovarium
 n The ovary has is lined from the outside by germinal (embryonic) epithelium under which is the connective tissue layer - tunica albuginea n The substance of the ovary is divided into: superficial cortex deeper medulla n The position of each ovary is stabilized by the mesovarium and by supporting ligaments: n the ovarian ligament and n suspensory ligament
n The ovary has is lined from the outside by germinal (embryonic) epithelium under which is the connective tissue layer - tunica albuginea n The substance of the ovary is divided into: superficial cortex deeper medulla n The position of each ovary is stabilized by the mesovarium and by supporting ligaments: n the ovarian ligament and n suspensory ligament
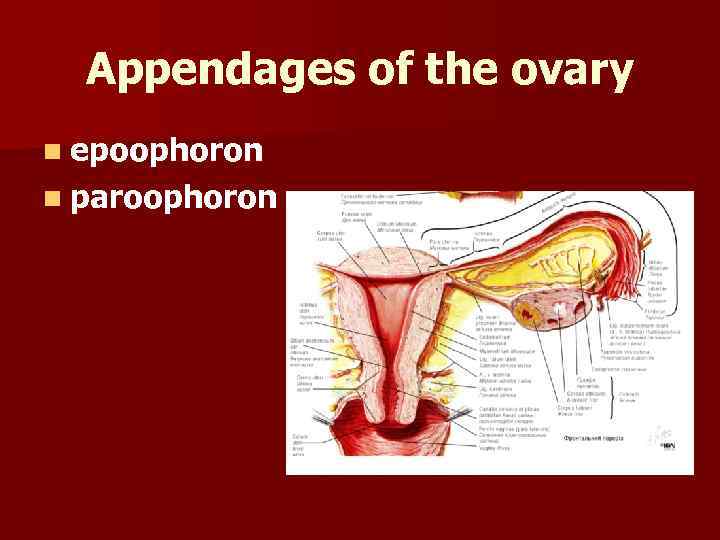 Appendages of the ovary n epoophoron n paroophoron
Appendages of the ovary n epoophoron n paroophoron
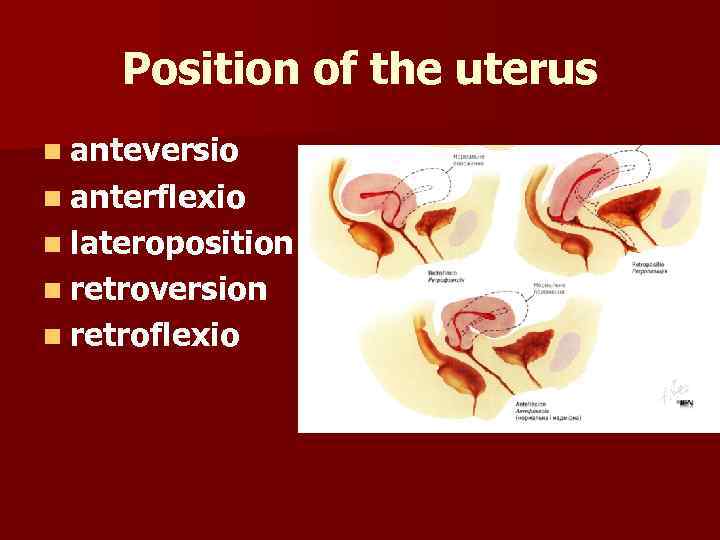 Position of the uterus n anteversio n anterflexio n lateroposition n retroversion n retroflexio
Position of the uterus n anteversio n anterflexio n lateroposition n retroversion n retroflexio
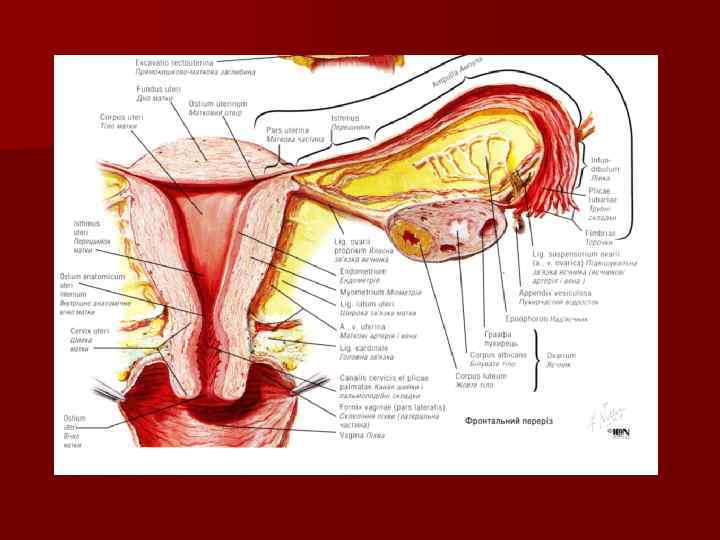
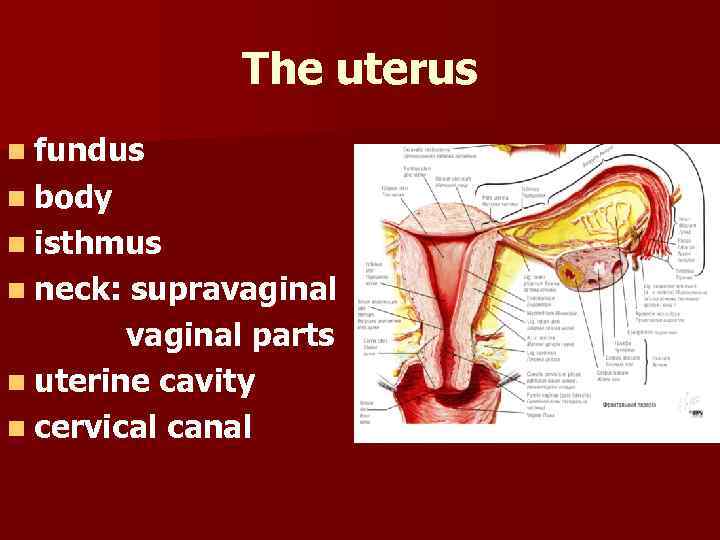 The uterus n fundus n body n isthmus n neck: supravaginal parts n uterine cavity n cervical canal
The uterus n fundus n body n isthmus n neck: supravaginal parts n uterine cavity n cervical canal
 The wall of the uterus n serous coat - the perimetrium n muscular coat – myometrium: internal and external longitudinal and middle circular layers n mucosa - endometrium
The wall of the uterus n serous coat - the perimetrium n muscular coat – myometrium: internal and external longitudinal and middle circular layers n mucosa - endometrium
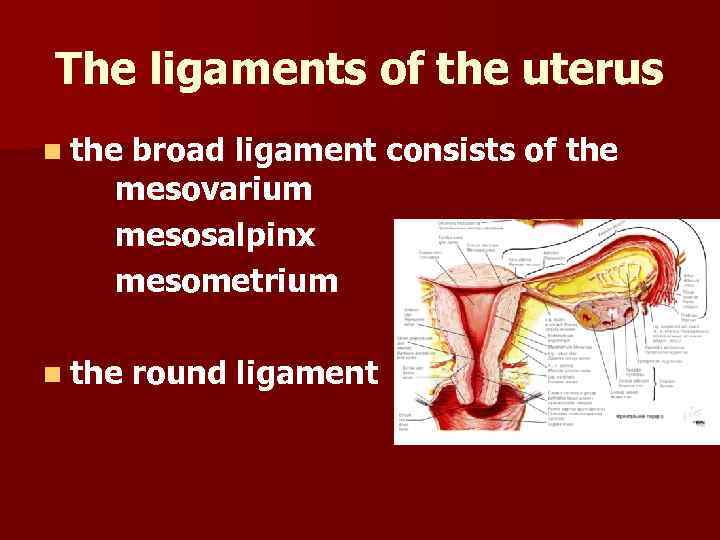 The ligaments of the uterus n the broad ligament consists of the mesovarium mesosalpinx mesometrium n the round ligament
The ligaments of the uterus n the broad ligament consists of the mesovarium mesosalpinx mesometrium n the round ligament
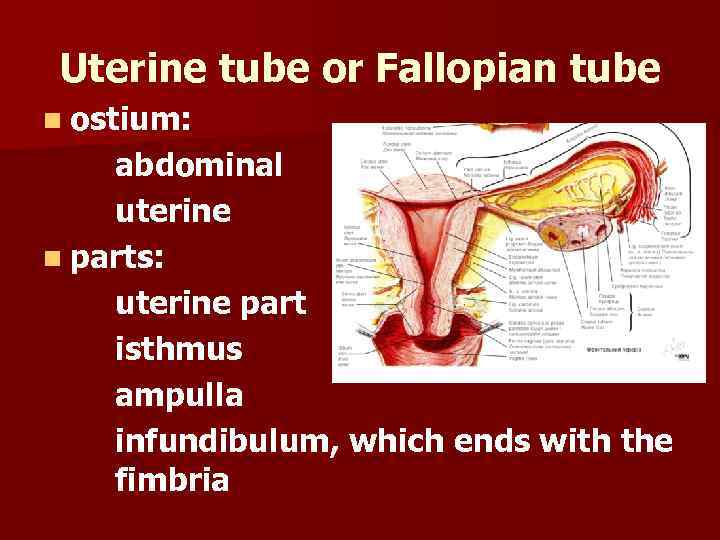 Uterine tube or Fallopian tube n ostium: abdominal uterine n parts: uterine part isthmus ampulla infundibulum, which ends with the fimbria
Uterine tube or Fallopian tube n ostium: abdominal uterine n parts: uterine part isthmus ampulla infundibulum, which ends with the fimbria
 The wall of the uterine tube n the serous coat n the muscular coat: internal circular and external longitudinal n the mucosa
The wall of the uterine tube n the serous coat n the muscular coat: internal circular and external longitudinal n the mucosa
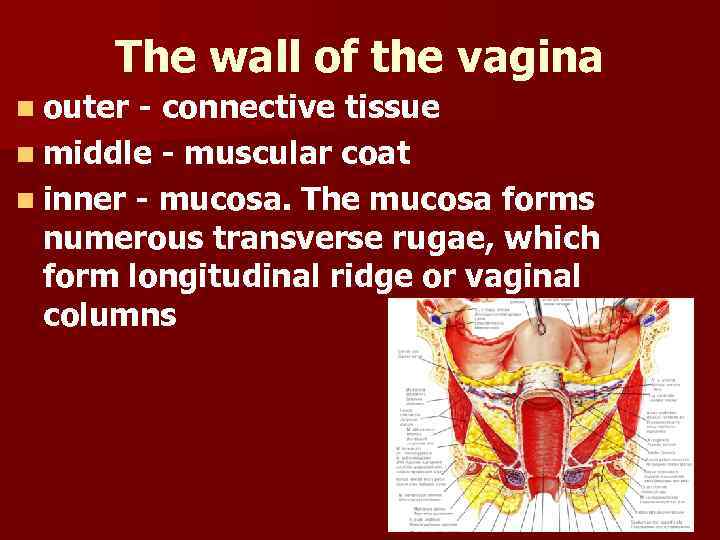 The wall of the vagina n outer - connective tissue n middle - muscular coat n inner - mucosa. The mucosa forms numerous transverse rugae, which form longitudinal ridge or vaginal columns
The wall of the vagina n outer - connective tissue n middle - muscular coat n inner - mucosa. The mucosa forms numerous transverse rugae, which form longitudinal ridge or vaginal columns


