 Genetically Engineered Foods: Overview What is genetic engineering (GE) and how does it differ from traditional breeding? How predominant are GE crops & foods? How does the govt. regulate these crops & foods? FDA, USDA & EPA Video: Harvest of Fear GMO (genetically modified organism) synonymous with GE (genetically engineered) Discussion questions 1
Genetically Engineered Foods: Overview What is genetic engineering (GE) and how does it differ from traditional breeding? How predominant are GE crops & foods? How does the govt. regulate these crops & foods? FDA, USDA & EPA Video: Harvest of Fear GMO (genetically modified organism) synonymous with GE (genetically engineered) Discussion questions 1
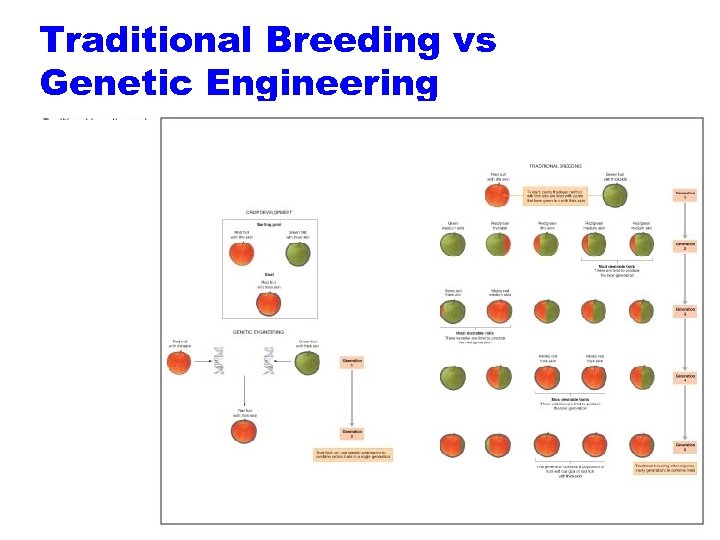 Traditional Breeding vs Genetic Engineering 2
Traditional Breeding vs Genetic Engineering 2
 Genetic Engineering A technique in which genes can be moved between different life forms. Genetically Engineered (GE) Food: Gene is taken from one organism (virus, bacteria, animal) and transferred to a plant or animal (that we eat). 3
Genetic Engineering A technique in which genes can be moved between different life forms. Genetically Engineered (GE) Food: Gene is taken from one organism (virus, bacteria, animal) and transferred to a plant or animal (that we eat). 3
 How Common are GE Foods? 1996, FDA approved genetically engineered crops mixed with non-genetically engineered crops. They became a part of our food supply (soda, cereal, chips, mayo, etc) At least 70% of processed foods contain GE ingredients. 4
How Common are GE Foods? 1996, FDA approved genetically engineered crops mixed with non-genetically engineered crops. They became a part of our food supply (soda, cereal, chips, mayo, etc) At least 70% of processed foods contain GE ingredients. 4
 Most Common GE Foods: Corn, Soy, Canola Soy, corn and canola have a herbicide tolerant (HT) gene in seed so field can be sprayed with herbicide (Round-Up) and not kill the crop. Monsanto“Round-Up Ready” seeds Corn has a gene from Bt bacteria incorporated into corn to make the plant resistant to caterpillars. Bt is a natural bacteria in the soil that is a poison for moth and butterfly larva (caterpillars).
Most Common GE Foods: Corn, Soy, Canola Soy, corn and canola have a herbicide tolerant (HT) gene in seed so field can be sprayed with herbicide (Round-Up) and not kill the crop. Monsanto“Round-Up Ready” seeds Corn has a gene from Bt bacteria incorporated into corn to make the plant resistant to caterpillars. Bt is a natural bacteria in the soil that is a poison for moth and butterfly larva (caterpillars).
 Newest GE Approved: Salmon First GE animal in the food supply Growth hormone from a Chinook salmon & gene from an ocean pout (eel like fish) keep the growth gene active all year. Salmon grows twice as fast Will be available stores in ~3 years. Will not be labeled. 6
Newest GE Approved: Salmon First GE animal in the food supply Growth hormone from a Chinook salmon & gene from an ocean pout (eel like fish) keep the growth gene active all year. Salmon grows twice as fast Will be available stores in ~3 years. Will not be labeled. 6
 Government Regulators Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Monitors GE foods when they are sold as food Makes decisions on food labeling United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Oversees GE crops when they are in the field Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Determines the environmental aspects of GE crops. Interest is in the effects that the GE crop has on the environment. They monitor Bt corn. 8
Government Regulators Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Monitors GE foods when they are sold as food Makes decisions on food labeling United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Oversees GE crops when they are in the field Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Determines the environmental aspects of GE crops. Interest is in the effects that the GE crop has on the environment. They monitor Bt corn. 8
 Substantial Equivalence Indicates that two foods (example corn & Bt corn) have similar chemical profiles. Substantial Equivalence is the reason the FDA does not label genetically engineered foods. 9
Substantial Equivalence Indicates that two foods (example corn & Bt corn) have similar chemical profiles. Substantial Equivalence is the reason the FDA does not label genetically engineered foods. 9
 To limit GE foods: Minimize processed foods Buy organic Look for labels with“not genetically engineered”: Products that contain soy, corn, canola oil. Whole Foods Market is requiring all GE foods in store be labeled by 2018. Buy food verified as “Non GMO Project Verified”: An independent, non-profit, voluntary certification Choose Trader Joe’s brand products Shop at farmer’s markets 10
To limit GE foods: Minimize processed foods Buy organic Look for labels with“not genetically engineered”: Products that contain soy, corn, canola oil. Whole Foods Market is requiring all GE foods in store be labeled by 2018. Buy food verified as “Non GMO Project Verified”: An independent, non-profit, voluntary certification Choose Trader Joe’s brand products Shop at farmer’s markets 10
 11
11