 General Electric Organization structure
General Electric Organization structure
 General information 6 th largest firm in the U. S. according to Fortune General Electric was formed by the 1892 merger of Edison General Electric of Schenectady, New York and Thomson-Houston Electric Company of Lynn, Massachusetts It’s an American multinational conglomerate corporation
General information 6 th largest firm in the U. S. according to Fortune General Electric was formed by the 1892 merger of Edison General Electric of Schenectady, New York and Thomson-Houston Electric Company of Lynn, Massachusetts It’s an American multinational conglomerate corporation
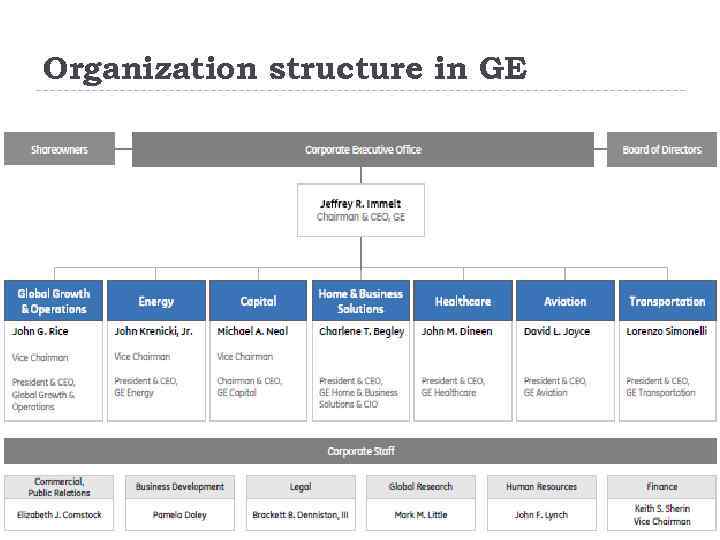 Organization structure in GE
Organization structure in GE
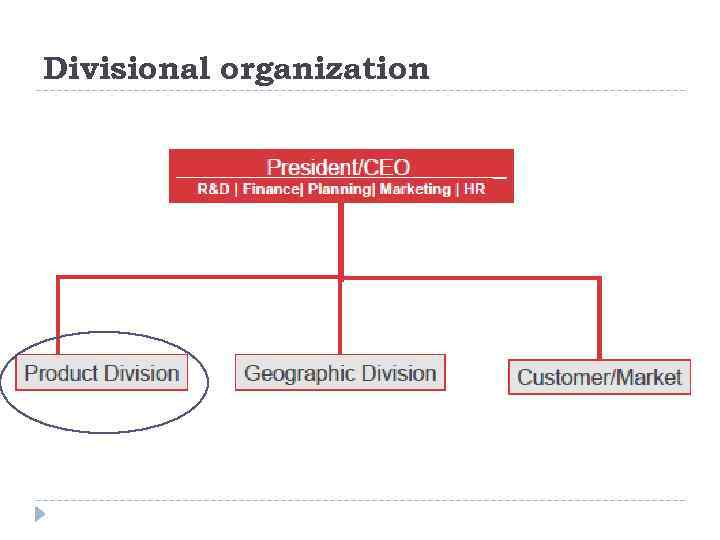 Divisional organization
Divisional organization
 Divisional organization STRENGTHS: Suited to fast change in unstable environment Leads to customer satisfaction because product responsibility and contact points are clear Involves high coordination across functions Allows units to adapt to differences in products, regions, clients (heterogeneous markets) Best in large organizations with several products Decentralizes decision-making
Divisional organization STRENGTHS: Suited to fast change in unstable environment Leads to customer satisfaction because product responsibility and contact points are clear Involves high coordination across functions Allows units to adapt to differences in products, regions, clients (heterogeneous markets) Best in large organizations with several products Decentralizes decision-making
 Divisional organization WEAKNESSES: Eliminates economies of scale in functional departments by splitting functions and allocating them to nits Leads to poor coordination across product lines Eliminates in-depth competence and technical specialization Makes integration and standardization across product lines difficult
Divisional organization WEAKNESSES: Eliminates economies of scale in functional departments by splitting functions and allocating them to nits Leads to poor coordination across product lines Eliminates in-depth competence and technical specialization Makes integration and standardization across product lines difficult
 GE's divisions Energy Services GE Oil & Gas GE Power & Water Technology Infrastructure is a business group of GE composed of three GE companies: GE Aviation, GE Healthcare, GE Transportation
GE's divisions Energy Services GE Oil & Gas GE Power & Water Technology Infrastructure is a business group of GE composed of three GE companies: GE Aviation, GE Healthcare, GE Transportation
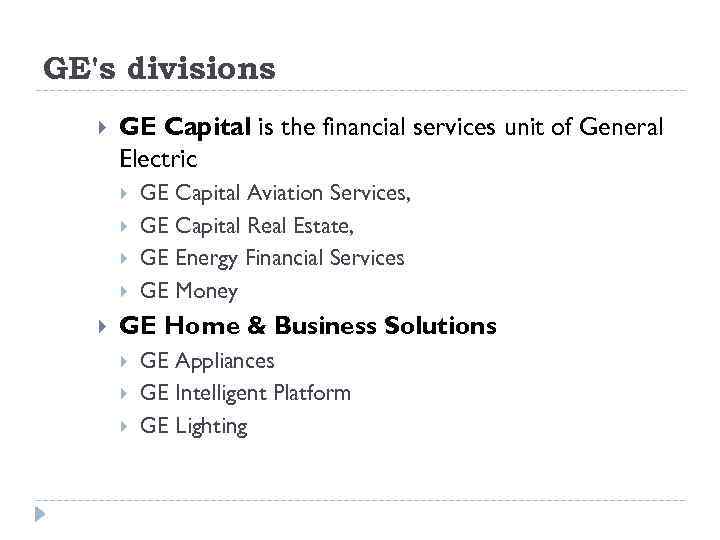 GE's divisions GE Capital is the financial services unit of General Electric GE Capital Aviation Services, GE Capital Real Estate, GE Energy Financial Services GE Money GE Home & Business Solutions GE Appliances GE Intelligent Platform GE Lighting
GE's divisions GE Capital is the financial services unit of General Electric GE Capital Aviation Services, GE Capital Real Estate, GE Energy Financial Services GE Money GE Home & Business Solutions GE Appliances GE Intelligent Platform GE Lighting
 Board of Directors The board is elected by the shareowners to oversee management and to assure that the long-term interests of the shareowners are being served. the Board is independent (GE has met its goal to have two-thirds of its Board be independent under a strict definition of independence) The directors are elected each year at the annual meeting of shareowners.
Board of Directors The board is elected by the shareowners to oversee management and to assure that the long-term interests of the shareowners are being served. the Board is independent (GE has met its goal to have two-thirds of its Board be independent under a strict definition of independence) The directors are elected each year at the annual meeting of shareowners.