90cb59512934649029dbb770f443b4e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

General Data Analysis Issues and Approaches in Metabolomics Bruce S. Kristal, Ph. D. Department of Neurosurgery, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School (Pending) Secretary, Metabolomics Society

…the statistician’s task, in fact, is limited to the extraction of the whole of the available information on any particular issue. R. A. Fisher

Working Definitions

Statistics: What is the probability that was observed occurred by chance?

Informatics What was observed?

Data vs Information
Data Information

Can you group these?
Partitional Clustering

Can you group these?
Hierarchical Clustering

How much information is enough?

How much information is enough?

How much information is enough?

How much information is enough?

How much information is enough?
Principal Components Analysis

Given experience, what can we know about unknowns

Probably Sad Probably Happy
Pattern Recognition
Megavariate Analysis • • • Clustering Principal components Pattern recognition HUMANS DO MEGAVARIATE ANALYSIS INATELY

What we don’t do so well…
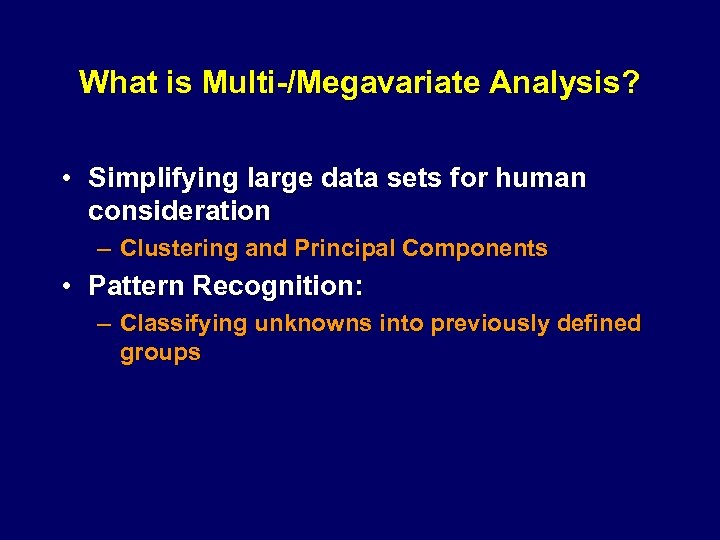
What is Multi-/Megavariate Analysis? • Simplifying large data sets for human consideration – Clustering and Principal Components • Pattern Recognition: – Classifying unknowns into previously defined groups

What is Multi-/Megavariate Analysis? • Data-mining – How many customers who buy pretzels also buy potato chips? • Estimation and prediction – Multivariate regression • • Which variables are most important? Mathematical modeling Outlier diagnostics Enables data-driven approaches

Why do it?
Omics datasets are otherwise beyond human comprehension

Informatics in Metabolomics
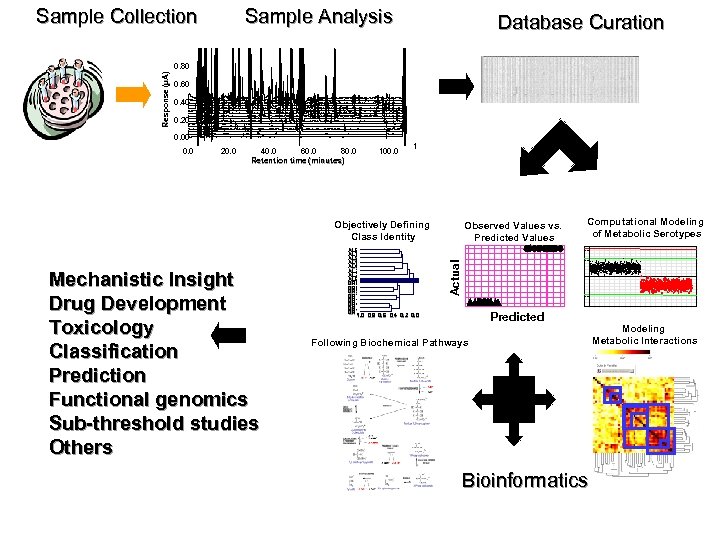
Sample Analysis Sample Collection Database Curation Response (µA) 0. 80 0. 60 0. 40 0. 20 0. 0 20. 0 40. 0 60. 0 80. 0 Retention time (minutes) 100. 0 1 Objectively Defining Class Identity Computational Modeling of Metabolic Serotypes 3 SD 2 SD Actual Mechanistic Insight Drug Development Toxicology Classification Prediction Functional genomics Sub-threshold studies Others AL 8 AL 7 AL 5 AL 1 AL 4 AL 3 AL 2 AL 6 DR 8 DR 6 DR 5 DR 7 DR 1 DR 4 DR 2 DR 3 1. 0 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 Observed Values vs. Predicted Values 2 SD Predicted Following Biochemical Pathways Bioinformatics Modeling Metabolic Interactions
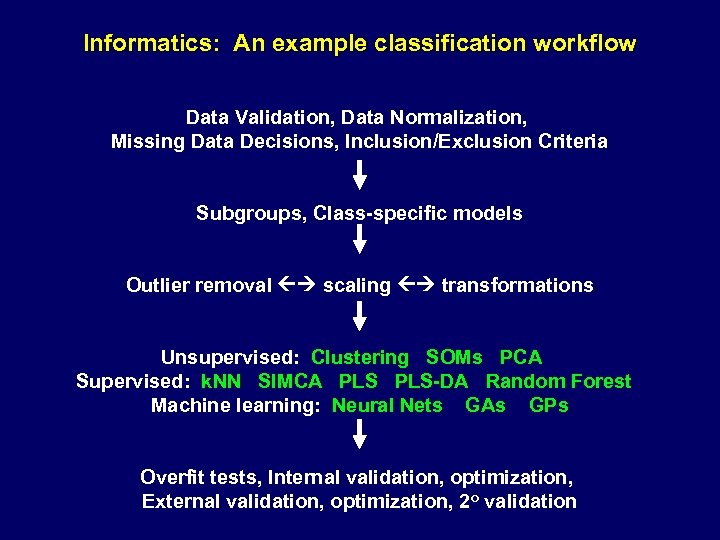
Informatics: An example classification workflow Data Validation, Data Normalization, Missing Data Decisions, Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria Subgroups, Class-specific models Outlier removal scaling transformations Unsupervised: Clustering SOMs PCA Supervised: k. NN SIMCA PLS-DA Random Forest Machine learning: Neural Nets GAs GPs Overfit tests, Internal validation, optimization, External validation, optimization, 2 o validation

Practicality important – not theory

Multivariate Analysis is Easy

But…

Art – Not Science

Multiple Approaches • Mathematical robustness • Megavariate analysis is not word processing • Different algorithms see different things! • Different answers can be both right, or both wrong

Multivariate Analysis can be easy – or too easy

…the statistician’s task, in fact, is limited to the extraction of the whole of the available information on any particular issue. R. A. Fisher

“THE” Problem: Overfitting • Beware the power of today’s tools – PLS-DA/O-PLS – GAs/GPs, neural nets, machine learning • Try to understand your tools – At least conceptually – PCA and selective reporting • choosing components is not objective • Beware of “low value” components – Clustering and rotations • DO NOT search until you like what you see – Choosing multiple tools/conditions is fine – in the model building phase

“Solutions” • Data analysis is not word processing • Permutation Testing is a step in the right direction • The Gold Standard is biological replication • Training Sets and test sets should have no members in common – Rarely recognized – Not always possible… • Set up design as rigorously as possible – In advance… • Our definition: – – Training sets are proof of principle Test sets are, theoretically, validation

Three “final” thoughts • There is an inherent statistical and informatics minefield that arises when the number of variables queried far exceeds the number of observations (“N vs P problem”) • Caution: mathematical validation in NOT biological validation • Report what you do
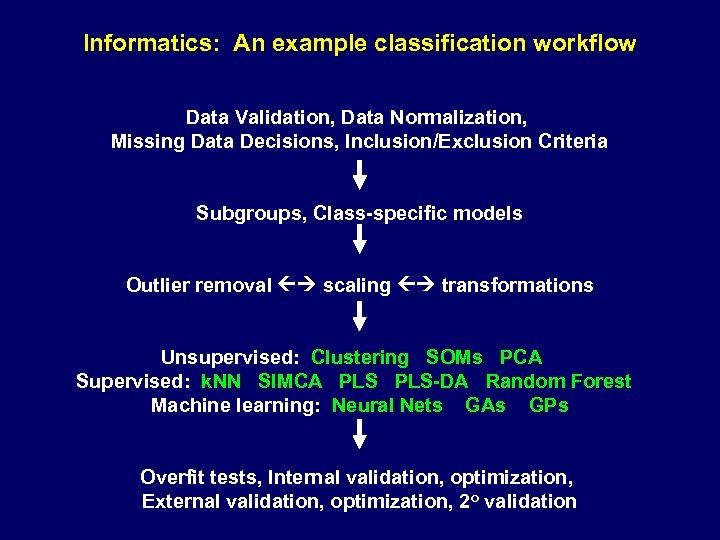
Informatics: An example classification workflow Data Validation, Data Normalization, Missing Data Decisions, Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria Subgroups, Class-specific models Outlier removal scaling transformations Unsupervised: Clustering SOMs PCA Supervised: k. NN SIMCA PLS-DA Random Forest Machine learning: Neural Nets GAs GPs Overfit tests, Internal validation, optimization, External validation, optimization, 2 o validation
90cb59512934649029dbb770f443b4e5.ppt