38b68e2e4da7aa182000a5bde161790e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

General Bank Management Marketing Management for Bankers MODULE D C AIIB

What is Marketing…? ? Selling? Advertising? Promotions? Making products available in stores? Maintaining inventories? All of the above, plus much more! 2

Marketing = ? Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals American Marketing Association 3

Marketing = ? Marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. 4
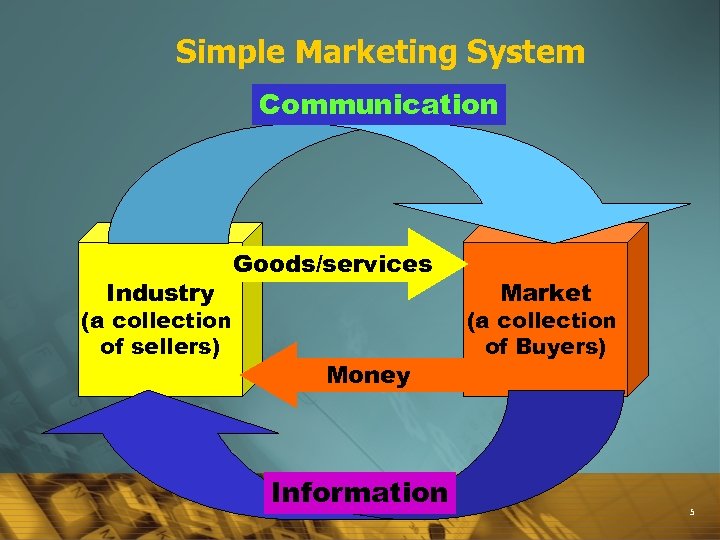
Simple Marketing System Communication Industry (a collection of sellers) Goods/services Money Information Market (a collection of Buyers) 5

Marketing = ? è Marketing is the sum of all activities that take you to a sales outlet. After that sales takes over. è Marketing is all about creating a pull, sales is all about push. è Marketing is all about managing the four P’s – è product è price è place è promotion 6
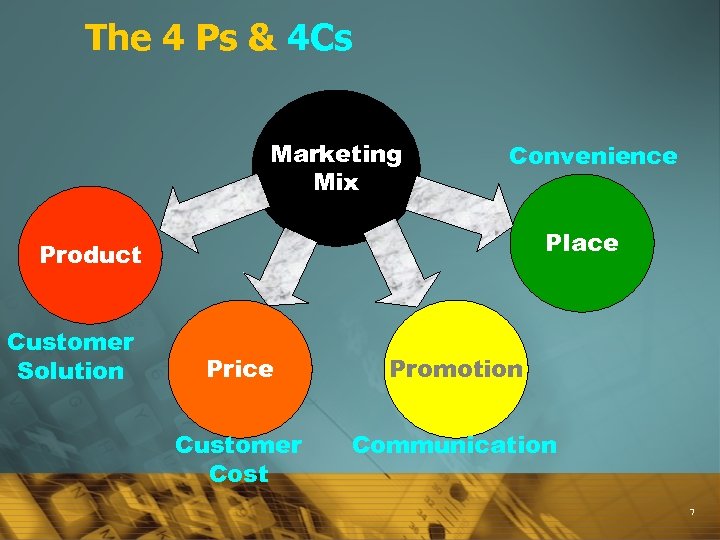
The 4 Ps & 4 Cs Marketing Mix Convenience Place Product Customer Solution Price Promotion Customer Cost Communication 7

Difference Between - Sales & Marketing ? Sales trying to get the customer to want what the company produces Marketing trying to get the company produce what the customer wants 8

Scope – What do we market è è è è è Goods Services Events Experiences Personalities Place Organizations Properties Information Ideas and concepts 9

Core Concepts of Marketing Based on : è Needs, Wants, Desires / demand è Products, Utility, Value & Satisfaction è Exchange, Transactions & Relationships è Markets, Marketing & Marketers. 10
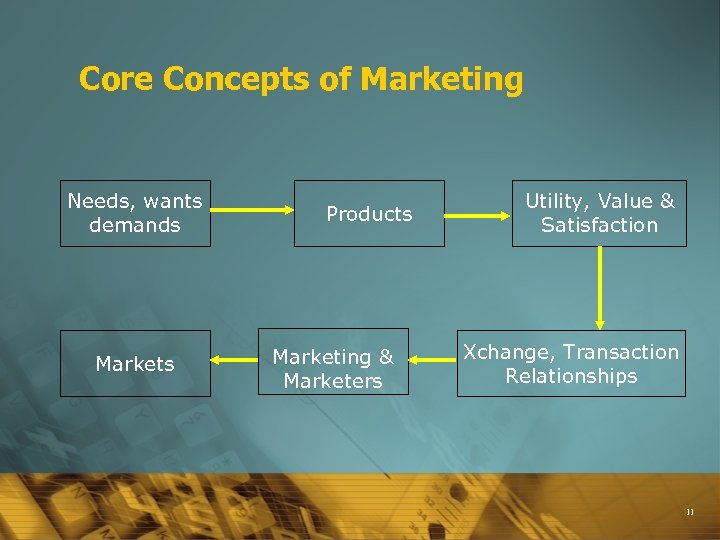
Core Concepts of Marketing Needs, wants demands Markets Products Marketing & Marketers Utility, Value & Satisfaction Xchange, Transaction Relationships 11

Core Concepts of Marketing è Need – food ( is a must ) è Want – Pizza, Burger, French fry's ( translation of a need as per our experience ) è Demand – Burger ( translation of a want as per our willingness and ability to buy ) è Desire – Have a Burger in a five star hotel 12

In order to understand Marketing let us begin with the Marketing Triangle Customers Company Competition 13

Who is a Customer ? ? CUSTOMER IS. . . Anyone who is in the market looking at a product / service for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that satisfies a want or a need 14

Customer – CUSTOMER has needs, wants, demands and desires Understanding these needs is starting point of the entire marketing These needs, wants …… arise within a framework or an ecosystem Understanding both the needs and the ecosystem is the starting point of a long term relationship 15

How Do Consumers Choose Among Products & Services? Value - the value or benefits the customers gain from using the product versus the cost of obtaining the product. Satisfaction - Based on a comparison of performance and expectations. Ø Performance > Expectations => Satisfaction Ø Performance < Expectations => Dissatisfaction 16

Customers - Problem Solution As a priority , we must bring to our customers “WHAT THEY NEED” We must be in a position to UNDERSTAND their problems Or in a new situation to give them a chance to AVOID the problems 17

Customer looks for Value = Benefit / Cost Benefit = Functional Benefit + Emotional Benefit Cost = Monetary Cost + Time Cost + Energy Cost + Psychic Cost 18

Strategic Marketing Strategic marketing management is concerned with how we will create value for the customer Asks two main questions Ø What is the organization’s main activity at a particular time? – Customer Value Ø What are its primary goals and how will these be achieved? – how will this value be delivered 20

Strategic Planning is the managerial process of creating and maintaining a fit between the organization’s objectives and resources and the evolving market opportunities. è Also è All called Strategic Management Process organizations have this è Can be Formal or Informal 21
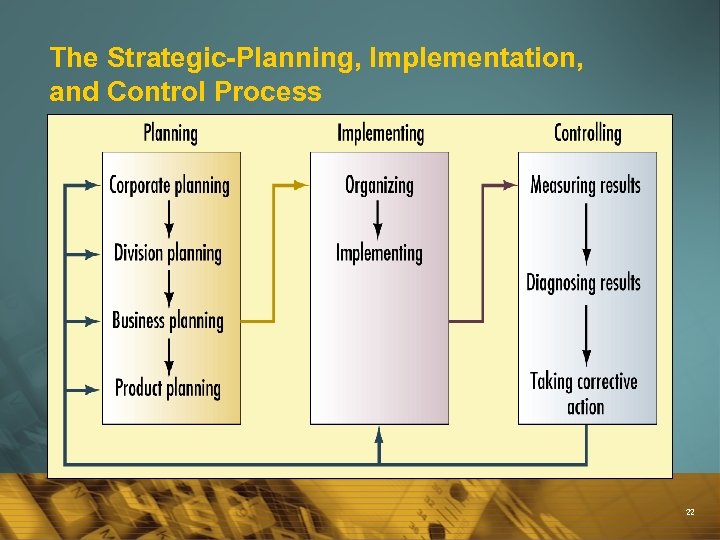
The Strategic-Planning, Implementation, and Control Process 22
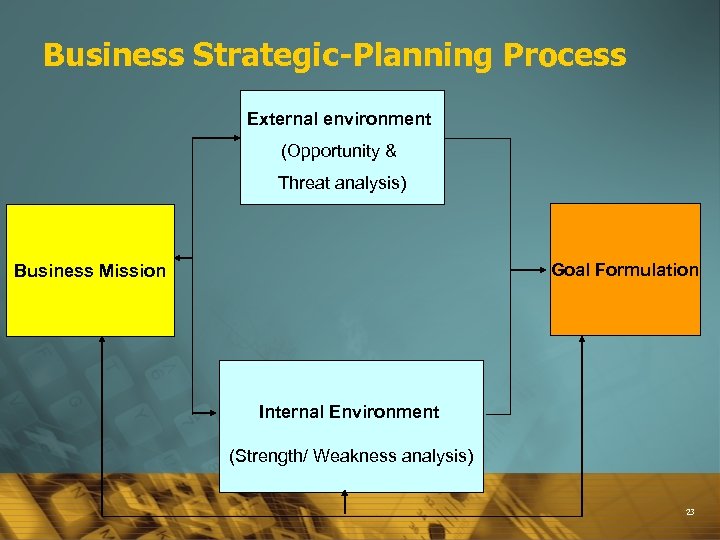
Business Strategic-Planning Process External environment (Opportunity & Threat analysis) Goal Formulation Business Mission Internal Environment (Strength/ Weakness analysis) 23
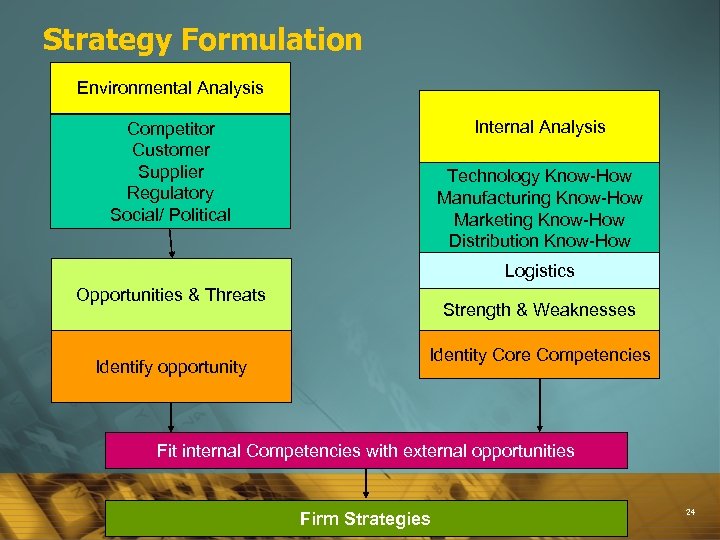
Strategy Formulation Environmental Analysis Internal Analysis Competitor Customer Supplier Regulatory Social/ Political Technology Know-How Manufacturing Know-How Marketing Know-How Distribution Know-How Logistics Opportunities & Threats Identify opportunity Strength & Weaknesses Identity Core Competencies Fit internal Competencies with external opportunities Firm Strategies 24

The Marketing Plan A written document that acts as a guidebook of marketing activities for the marketing manager 25

CONTENTS of MARKETING PLAN Business Mission Statement Objectives Situation Analysis (SWOT) Marketing Strategy Ø Target Market Strategy Ø Marketing Mix è è è è Positioning Product Promotion Price Place – Distribution People Process Implementation, Evaluation and Control 26
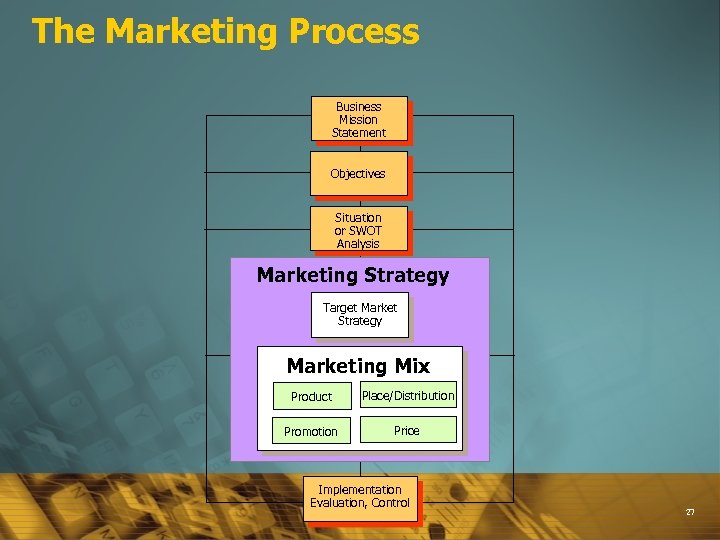
The Marketing Process Business Mission Statement Objectives Situation or SWOT Analysis Marketing Strategy Target Market Strategy Marketing Mix Product Place/Distribution Promotion Price Implementation Evaluation, Control 27

Marketing Environment

Why a product like radio declined and now once again emerging as an entertainment medium ? 29

What Were the Drivers of This Change ? Technology ? Government policy ? Other media substitutes ? 30

Why Market Leaders Suffered ? è HMT è HLL vs. Titan vs. Nirma è Bajaj vs. Honda è Dot. com boom, then bust and now resurgence è Market leadership today cannot be taken for granted. New and more efficient companies are able to upstage leaders in a much shorter period. 31
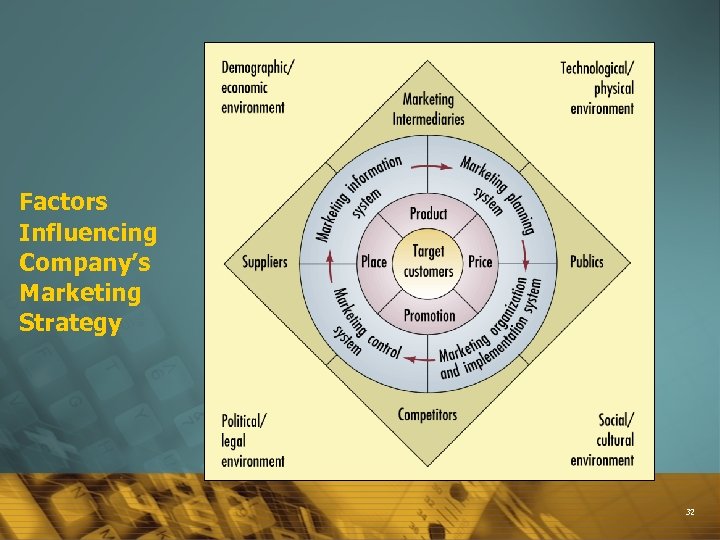
Factors Influencing Company’s Marketing Strategy 32
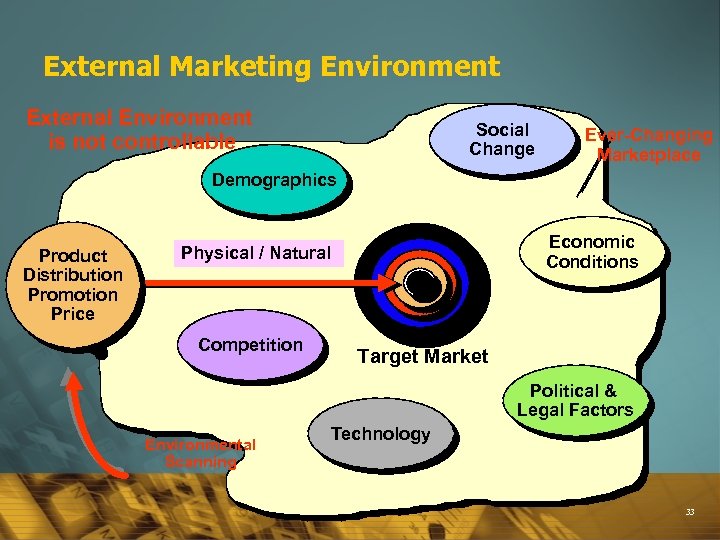
External Marketing Environment External Environment is not controllable Social Change Ever-Changing Marketplace Demographics Product Distribution Promotion Price Economic Conditions Physical / Natural Competition Target Market Political & Legal Factors Environmental Scanning Technology 33
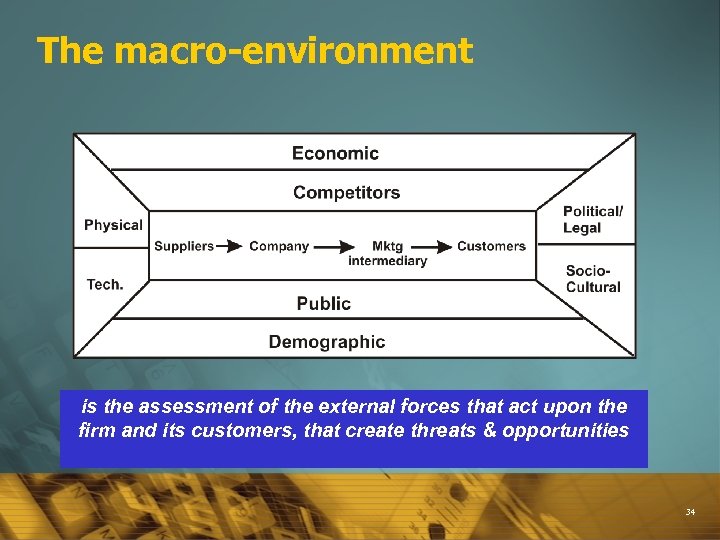
The macro-environment is the assessment of the external forces that act upon the firm and its customers, that create threats & opportunities 34

Product 35

Product is. . . Anything that is offered to the market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that satisfies a want or a need 36
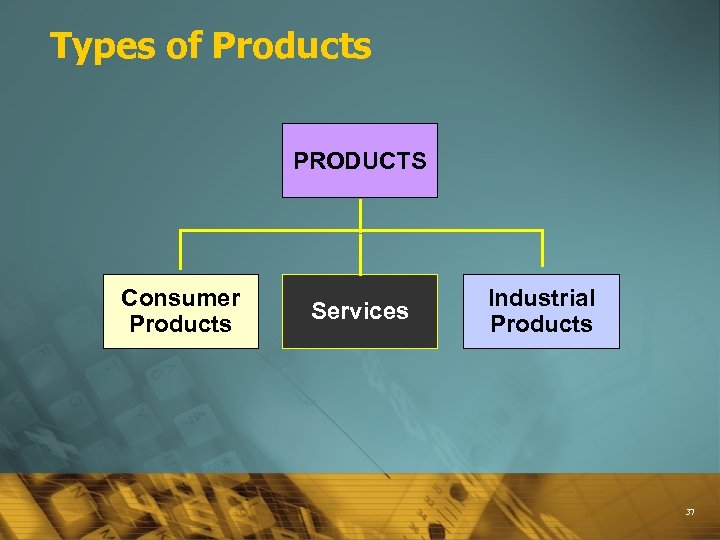
Types of Products PRODUCTS Consumer Products Services Industrial Products 37

Product Items, Lines, and Mixes Product Item A specific version of a product that can be designated as a distinct offering among an organization’s products. Product Line A group of closely-related product items. Product Mix All products that an organization sells. 38

Product Mix Width – how many product lines a company has Length – how many products are there in a product line Depth – how many variants of each product exist within a product line Consistency – how closely related the product lines are in end use 39
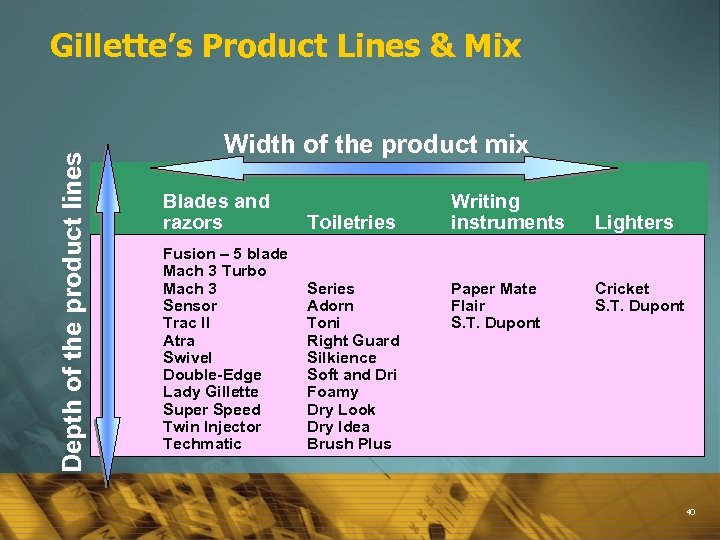
Depth of the product lines Gillette’s Product Lines & Mix Width of the product mix Blades and razors Toiletries Fusion – 5 blade Mach 3 Turbo Mach 3 Sensor Trac II Atra Swivel Double-Edge Lady Gillette Super Speed Twin Injector Techmatic Series Adorn Toni Right Guard Silkience Soft and Dri Foamy Dry Look Dry Idea Brush Plus Writing instruments Paper Mate Flair S. T. Dupont Lighters Cricket S. T. Dupont 40

What is a Service? Defining the Essence An act or performance offered by one party to another (performances are intangible, but may involve use of physical products) An economic activity that does not result in ownership A process that creates benefits by facilitating a desired change in customers themselves, or their physical possessions, or intangible assets 41

Some Industries - Service Sector Banking, stock broking Health care Lodging Education Restaurants, bars, catering Wholesaling and retailing Insurance Repair and maintenance Professional (e. g. , law, architecture, consulting) News and entertainment Transportation (freight and passenger) Laundries, dry-cleaning 42
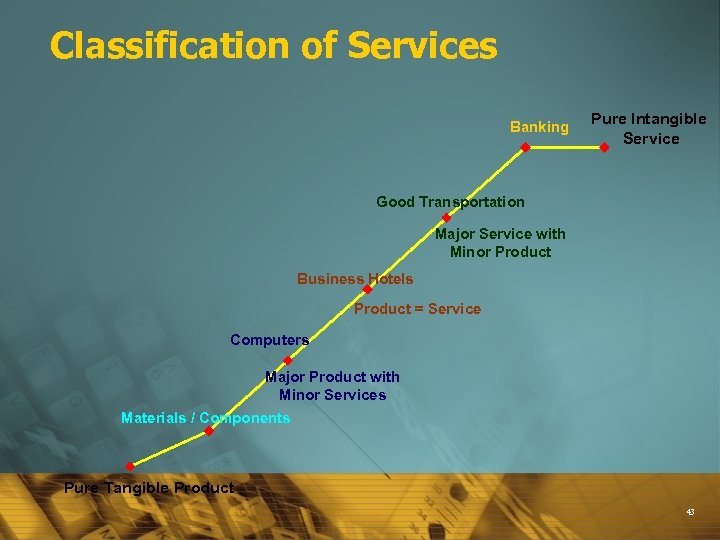
Classification of Services Banking Pure Intangible Service Good Transportation Major Service with Minor Product Business Hotels Product = Service Computers Major Product with Minor Services Materials / Components Pure Tangible Product 43

Major Characteristic of Services 1. Intangibility – Services are intangibility cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard or smelled before purchase. 2. Inseparability - Services are produced and consumed simultaneously. 3. Variability or Heterogeneity – Services are highly variable 4. Perishability – Services cannot be stored. 5. Non Ownership - Services are rendered but there is no transfer of title 44

The Marketing Mix The conventional view of the marketing mix consisted of four components (4 Ps): Product, Price, Place/ distribution and Promotion. Generally acknowledged that this is too narrow today; now includes , Processes, Productivity [technology ]People [employees], Physical evidence Marketers today are focused on virtually all aspects of the firm’s operations that have the potential to affect the relationship with customers. 45
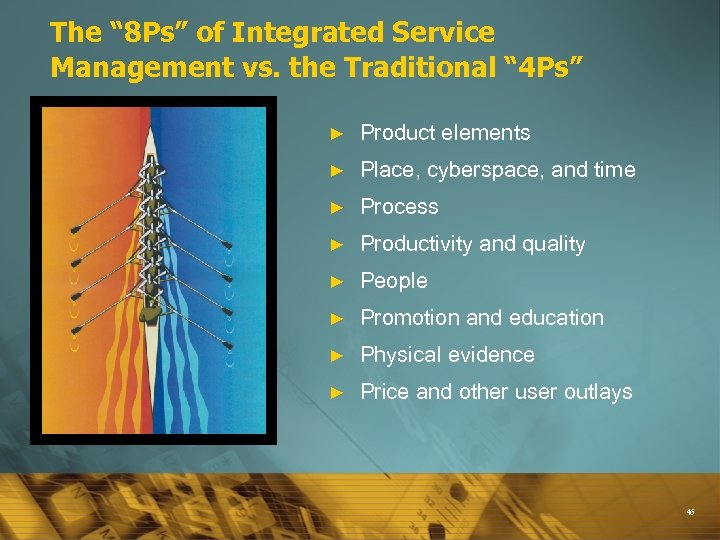
The “ 8 Ps” of Integrated Service Management vs. the Traditional “ 4 Ps” ► Product elements ► Place, cyberspace, and time ► Process ► Productivity and quality ► People ► Promotion and education ► Physical evidence ► Price and other user outlays 46

The Give and Get of Marketing 47

Great Words on Marketing 1. “The purpose of a company is ‘to create a customer…The only profit center is the customer. ’” 2. “A business has two—and only two—basic functions: marketing and innovation. Marketing and innovation produce results: all the rest are costs. ” “The aim of marketing is to make selling unnecessary. ” “While great devices are invented in the Laboratory, great products are invented in the Marketing department. ” “Marketing is too important to be left to the marketing department. ” 3. 4. 5. 48

Drivers of Customer Satisfaction Many aspects of the firm’s value proposition contribute to customer satisfaction: Ø The core product or service offered Ø Support services and systems Ø The technical performance of the firm Ø Interaction with the firm and it employees Ø The emotional connection with customers Ability to add value and to differentiate as a firm focuses more on the top levels 49

Marketers and Markets Marketers are focused on stimulating exchanges with customers who make up markets B 2 C or B 2 B. – The market is comprised of people who play a series of roles: decision makers, consumers, purchasers, and influencers. It is absolutely essential that marketers have a detailed understanding of consumers, their needs and wants. Much happens before afterthe sale to affect and customer satisfaction 50
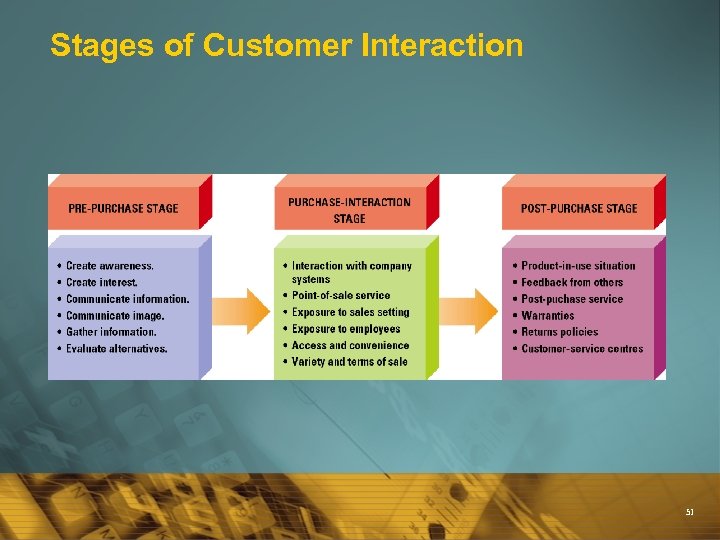
Stages of Customer Interaction 51

What Changed in Marketing… New Economy Old Economy • • Organize by product units Focus on profitable transactions Look primarily at financial scorecard Focus on shareholders Marketing does the marketing Build brands through advertising Focus on customer acquisition No customer satisfaction measurement • Over-promise, under-deliver • Organize by customer segments • Focus on customer lifetime value • Look also at marketing scorecard • • • Focus on stakeholders Everyone does the marketing Build brands through performance Focus on customer retention Measure customer satisfaction and retention rate • Under-promise, over-deliver 52

Are Banks truly marketing-savvy and customer - centric? 53

Myth 1 – The larger the range of products, the more customer-centric I am. Mythbuster – The range of products has emerged from being competition-centric. 54

Myth 2 – Better technology (read CRM) leads to better customer service. Mythbuster – Technology alone does not deliver, helps people do. 55

Myth 3 – Launch a product and the customer will start using instantly. - Give a customer a card and he will learn how to play with it immediately Mythbuster – Customers need To be educated too… 56

Myth 4 – The only way to get a customer is from competition. Mythbuster – Customers are not only present where competition is. 57

Myth 5 – Just advertise and - You will sell. Mythbuster – Advertising will only sell, Not retain customers. 58

Myth 6 – No difference between marketing & selling Mythbuster – “Selling focuses on the needs of the seller; marketing on the needs of the buyer. 59

Myth 7 – In the absence of relationships ‘trust’ builds financial brands Mythbuster – Trust is not a differentiator at all… it is the very minimum that the customer expects!! 60

So what will the differentiators be : • Technology ? • Brand ? 61

The real differentiator of customer – centricity in a commoditised world of financial products - Customer Service ! 62

Thank You sagarnarsian@yahoo. com 63
38b68e2e4da7aa182000a5bde161790e.ppt