9db26af6d89cf7238f2cc9980e514c20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 GENE Grupo de estudos de Neurorradiologia CASO CLÍNICO APRESENTADOR: Fábio Augusto Ribeiro Dalprá ORIENTADORES: Dr. Luis Filipe Godoy Dr. Maria da Graça Martin Dra. Simone Shibao Dr. Felipe B P Nascimento Dr. Leandro Lucato
GENE Grupo de estudos de Neurorradiologia CASO CLÍNICO APRESENTADOR: Fábio Augusto Ribeiro Dalprá ORIENTADORES: Dr. Luis Filipe Godoy Dr. Maria da Graça Martin Dra. Simone Shibao Dr. Felipe B P Nascimento Dr. Leandro Lucato
 ANAMNESE • ID: Paciente do sexo feminino, 46 anos, natural de São Paulo • QC: cefaleia frontal e occipital à esquerda progressiva e paralisia do nervo oculomotor esquerdo.
ANAMNESE • ID: Paciente do sexo feminino, 46 anos, natural de São Paulo • QC: cefaleia frontal e occipital à esquerda progressiva e paralisia do nervo oculomotor esquerdo.
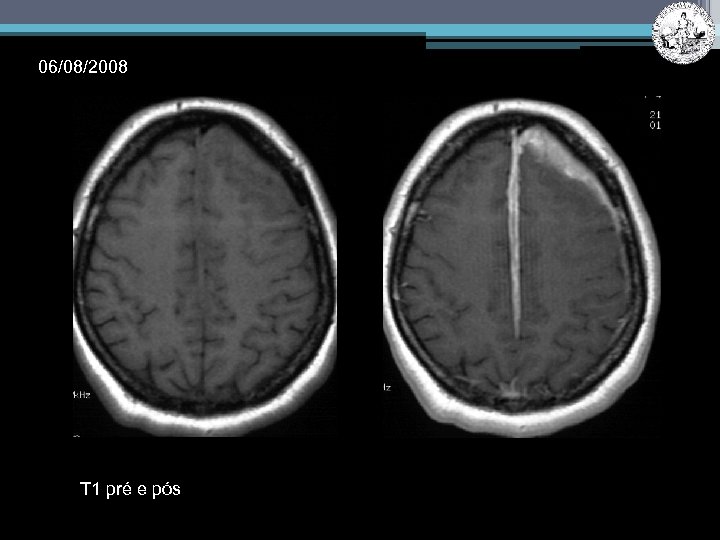 06/08/2008 T 1 pré e pós
06/08/2008 T 1 pré e pós
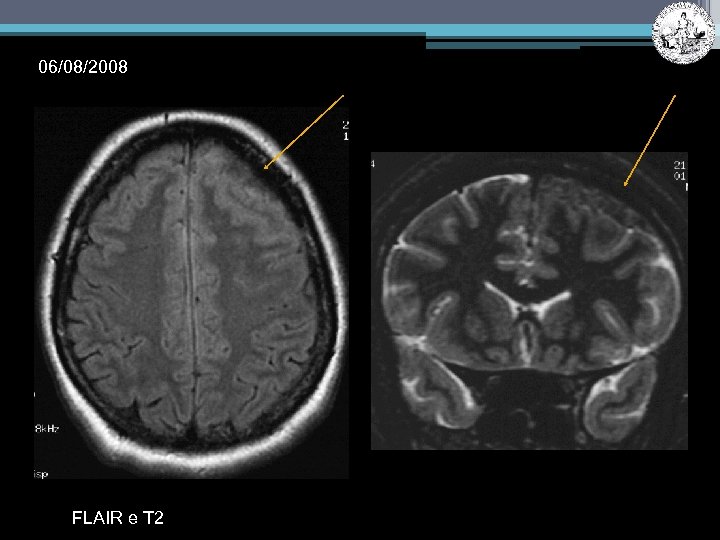 06/08/2008 FLAIR e T 2
06/08/2008 FLAIR e T 2
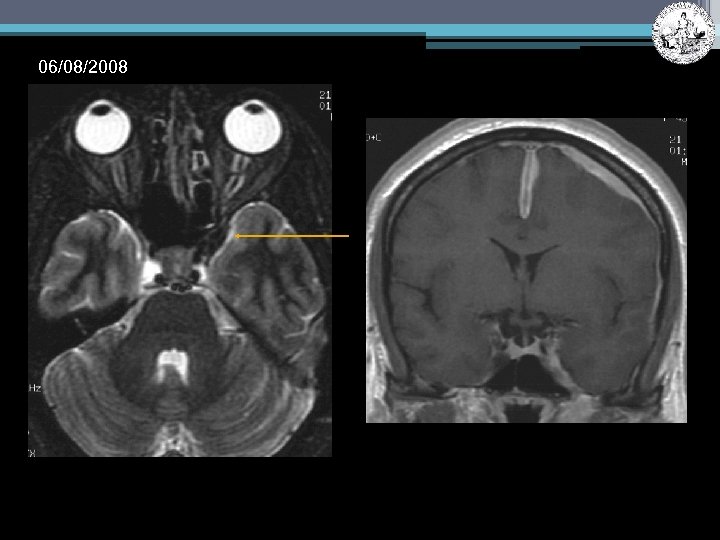 06/08/2008
06/08/2008
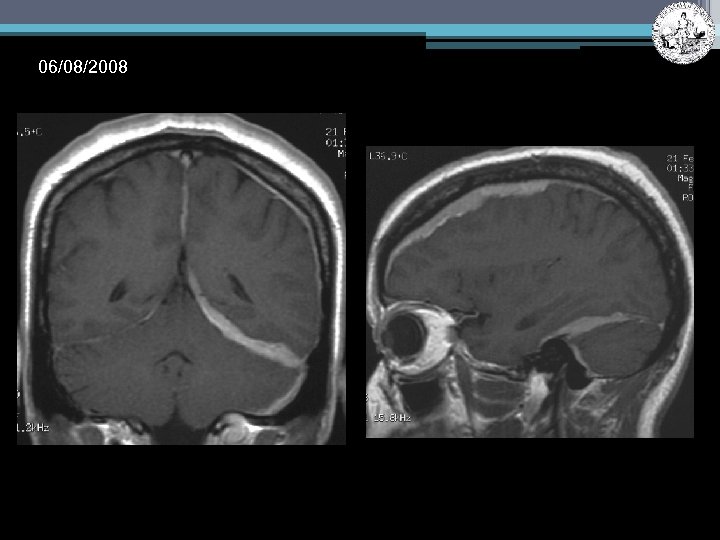 06/08/2008
06/08/2008
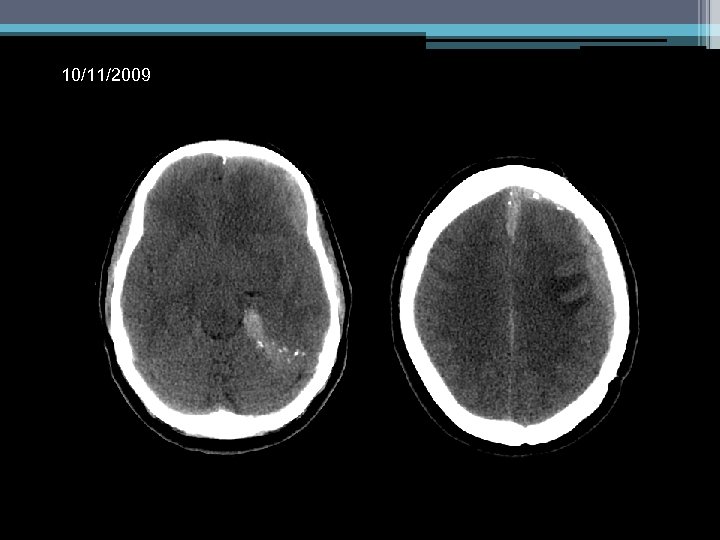 10/11/2009
10/11/2009
 Tabela 1. Líquor Variável Contagem de células brancas ( mm 3) Neutrófilos (%) 3 Linfócitos (%) 12 Monócitos (%) 81 Proteína (mg/dl) 38 Glicose (mg/dl) 81 PCR (Micobacterium tuberculosis) ADA negativo 0, 4 Micobacterium tuberculosis cultura negativa Cysticercosis (Elisa) negativa Protein electrophoresis normal Fungo cultura negativa
Tabela 1. Líquor Variável Contagem de células brancas ( mm 3) Neutrófilos (%) 3 Linfócitos (%) 12 Monócitos (%) 81 Proteína (mg/dl) 38 Glicose (mg/dl) 81 PCR (Micobacterium tuberculosis) ADA negativo 0, 4 Micobacterium tuberculosis cultura negativa Cysticercosis (Elisa) negativa Protein electrophoresis normal Fungo cultura negativa
 Table 2. Sangue Variável Ig. G 999 (700 -1600) Ig. A 144 (45 -234) Ig. M 293 (40 -230) Eletroforese de proteínas séricas normal VDRL negativo ANCA negativo PCR 5, 3 VHS 11 ANA positivo 1: 40 Anti-Rnp positivo Anti-DNA 50 (<30) Rheumatoid factor negativo
Table 2. Sangue Variável Ig. G 999 (700 -1600) Ig. A 144 (45 -234) Ig. M 293 (40 -230) Eletroforese de proteínas séricas normal VDRL negativo ANCA negativo PCR 5, 3 VHS 11 ANA positivo 1: 40 Anti-Rnp positivo Anti-DNA 50 (<30) Rheumatoid factor negativo
 ?
?
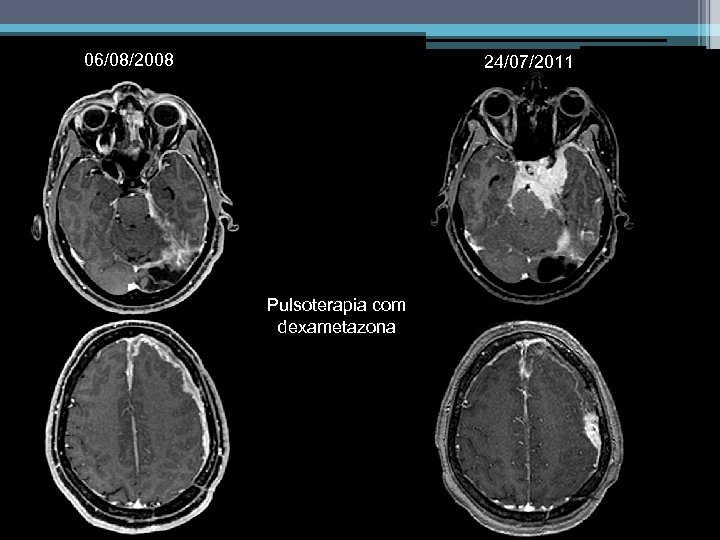 06/08/2008 24/07/2011 Pulsoterapia com dexametazona
06/08/2008 24/07/2011 Pulsoterapia com dexametazona
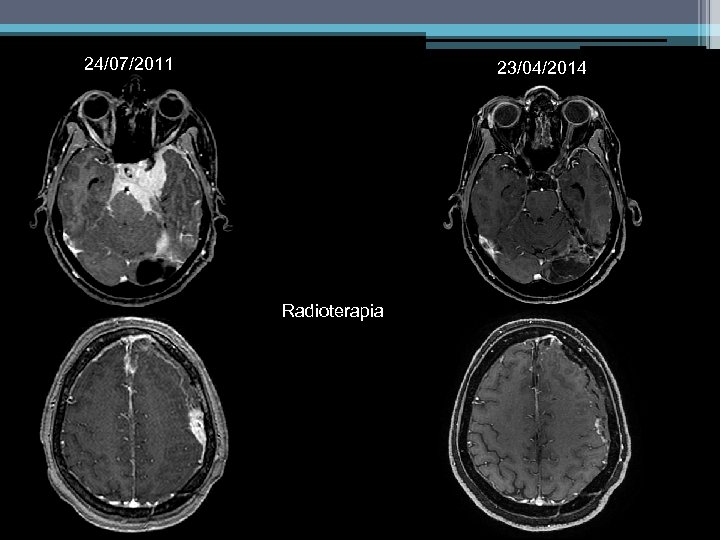 24/07/2011 23/04/2014 Radioterapia
24/07/2011 23/04/2014 Radioterapia
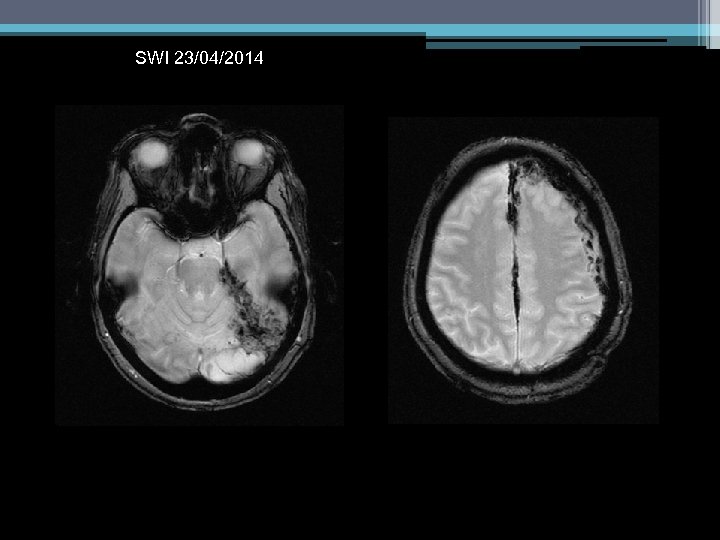 SWI 23/04/2014
SWI 23/04/2014
 Amiloidose Meníngea Difusa
Amiloidose Meníngea Difusa
 Amiloidose • Deposição extracelular e acúmulo de proteínas e derivados de proteínas, com três elementos principais: componente amilóide P do soro (Serum amyloid P component), glicosaminoglicanas, e proteínas fibrilares. Os primeiros dois componentes estão presentes em todas as formas de amiloidoses, o último componente é variável e define o tipo de amiloidose. 1 • Há 15 tipos de proteínas fibrilares diferentes indentidicadas por análise imunohistoquímica e definem o tipo de amiloidose pela classificação da organização mundial da saúde. 2 http: //drugdiscoveryopinion. com/2009/07/first-disease -modifying-compound-targeting-protein-misfolding/
Amiloidose • Deposição extracelular e acúmulo de proteínas e derivados de proteínas, com três elementos principais: componente amilóide P do soro (Serum amyloid P component), glicosaminoglicanas, e proteínas fibrilares. Os primeiros dois componentes estão presentes em todas as formas de amiloidoses, o último componente é variável e define o tipo de amiloidose. 1 • Há 15 tipos de proteínas fibrilares diferentes indentidicadas por análise imunohistoquímica e definem o tipo de amiloidose pela classificação da organização mundial da saúde. 2 http: //drugdiscoveryopinion. com/2009/07/first-disease -modifying-compound-targeting-protein-misfolding/
 Amiloidose • Amiloidose envolvendo o sistema nervoso central pode se apresentar de maneiras diversas. A forma mais comum são depósitos amiloides em vasos arteriais levando a angiopatia amiloide ou angiopatia congofílica. O depósito destes materiais também pode levar a formação de placas senis na doença de Alzeimer. • Amiloidomas primários no sistema nervoso central são raros. Foram reportados 31 casos de amiloidomas no parênquima cerebral. 3 -32 e 8 casos comprometendo o gânglio de Gasser, sendo um deles com apresentação bilateral 33 -37.
Amiloidose • Amiloidose envolvendo o sistema nervoso central pode se apresentar de maneiras diversas. A forma mais comum são depósitos amiloides em vasos arteriais levando a angiopatia amiloide ou angiopatia congofílica. O depósito destes materiais também pode levar a formação de placas senis na doença de Alzeimer. • Amiloidomas primários no sistema nervoso central são raros. Foram reportados 31 casos de amiloidomas no parênquima cerebral. 3 -32 e 8 casos comprometendo o gânglio de Gasser, sendo um deles com apresentação bilateral 33 -37.
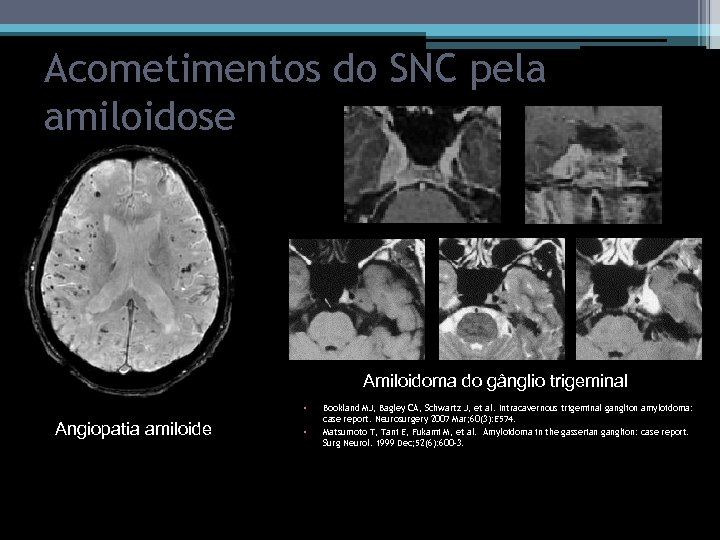 Acometimentos do SNC pela amiloidose Amiloidoma do gânglio trigeminal • Angiopatia amiloide Bookland MJ, Bagley CA, Schwartz J, et al. Intracavernous trigeminal ganglion amyloidoma: case report. Neurosurgery 2007 Mar; 60(3): E 574. • Matsumoto T, Tani E, Fukami M, et al. Amyloidoma in the gasserian ganglion: case report. Surg Neurol. 1999 Dec; 52(6): 600 -3.
Acometimentos do SNC pela amiloidose Amiloidoma do gânglio trigeminal • Angiopatia amiloide Bookland MJ, Bagley CA, Schwartz J, et al. Intracavernous trigeminal ganglion amyloidoma: case report. Neurosurgery 2007 Mar; 60(3): E 574. • Matsumoto T, Tani E, Fukami M, et al. Amyloidoma in the gasserian ganglion: case report. Surg Neurol. 1999 Dec; 52(6): 600 -3.
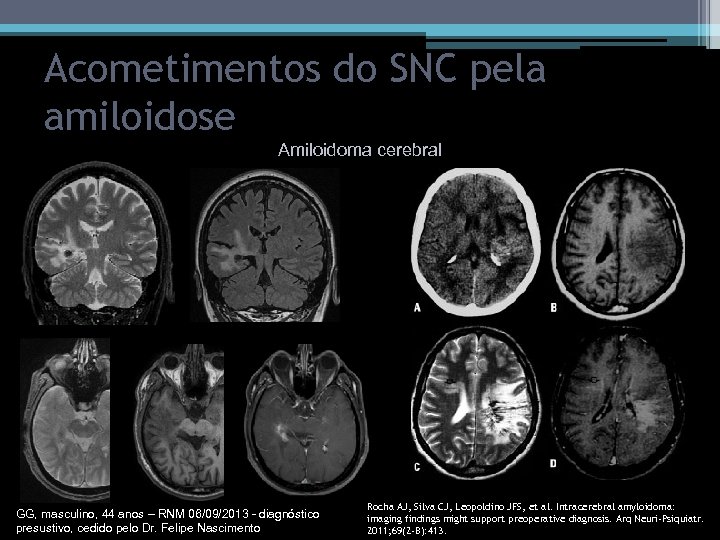 Acometimentos do SNC pela amiloidose Amiloidoma cerebral GG, masculino, 44 anos – RNM 06/09/2013 - diagnóstico presustivo, cedido pelo Dr. Felipe Nascimento Rocha AJ, Silva CJ, Leopoldino JFS, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: imaging findings might support preoperative diagnosis. Arq Neuri-Psiquiatr. 2011; 69(2 -B): 413.
Acometimentos do SNC pela amiloidose Amiloidoma cerebral GG, masculino, 44 anos – RNM 06/09/2013 - diagnóstico presustivo, cedido pelo Dr. Felipe Nascimento Rocha AJ, Silva CJ, Leopoldino JFS, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: imaging findings might support preoperative diagnosis. Arq Neuri-Psiquiatr. 2011; 69(2 -B): 413.
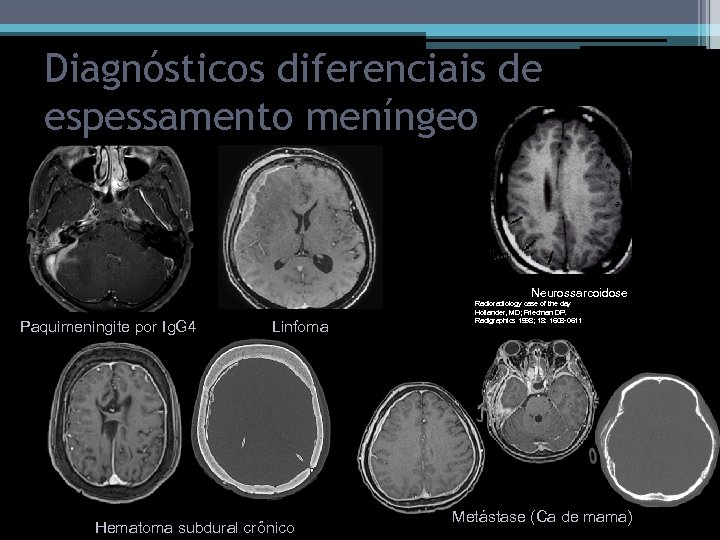 Diagnósticos diferenciais de espessamento meníngeo Neurossarcoidose Paquimeningite por Ig. G 4 Linfoma Hematoma subdural crônico Radioradiology case of the day Hollander, MD; Friedman DP. Radigraphics 1998; 18: 1608 -0611 Metástase (Ca de mama)
Diagnósticos diferenciais de espessamento meníngeo Neurossarcoidose Paquimeningite por Ig. G 4 Linfoma Hematoma subdural crônico Radioradiology case of the day Hollander, MD; Friedman DP. Radigraphics 1998; 18: 1608 -0611 Metástase (Ca de mama)
 Mensagem: • Apesar de rara a possibilidade de amiloidose deve ser incluída nas possíveis causas de espessamento meníngeo.
Mensagem: • Apesar de rara a possibilidade de amiloidose deve ser incluída nas possíveis causas de espessamento meníngeo.
 REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 1. Tabatabai G, Baehring J, Hochberg FH. Primary amyloidoma of the brain parenchyma. Arch Neurol. 2005 Mar; 62(3): 477 -80. 2. De. Castro S, Sparks JR, Lapey JD, et al. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion. Surg Neurol. 1976 Dec; 6(6): 357 -9. 3. Georgiades CS, Neyman EG, Barish MA, et al. Amyloidosis: review and CT manifestations Radiographics 2004; 24(2): 405 -16. 4. Adle-Biassette H, Vallat AV, Nochy D. [Amyloidosis: definition and classification]. " Arch Anat Cytol Pathol 1996; 44(2 -3): 101 -5. 5. Salytkov S. On the issue of local amyloid of cerebral tissue. Comments to the article by morgenstern Virchows Arch [A] 1935; 295: 590 6. Harris JH, Rayport M. Primary cerebral amyloidoma. J neuropathol Exp Neurol 1979; 38: 318 7. Spaar FW, Goebel HH, Volles E, et al. Tumor-like amyloid formation (amyloidoma) in the brain. J Neurol 1981; 224(3): 171 -82. 8. Townsend JJ, Tomiyasu U, Mac. Kay A, et al. Central nervous system amyloid presenting as a mass lesion. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1982 Mar; 56(3): 439 -42. 9. Moreno AJ, Brown JM, Brown TJ, et al. Scintigraphic findings in a primary cerebral amyloidoma. Clin Nucl Med 1983 Nov; 8(11): 528 -30. 10. Hori A, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, et al. Focal intracerebral accumulation of a novel type of amyloid protein. An early stage of cerebral amyloidoma? Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1988; 76(2): 212 -5. 11. Cohen M, Lanska D, Roessmann U, et al. Amyloidoma of the CNS. I. Clinical and pathologic study. Neurology. 1992 Oct; 42(10): 2019 -23. 12. Vidal RG, Ghiso J, Gallo G, et al. Amyloidoma of the CNS. II. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Neurology. 1992 Oct; 42(10): 2024 -8.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 1. Tabatabai G, Baehring J, Hochberg FH. Primary amyloidoma of the brain parenchyma. Arch Neurol. 2005 Mar; 62(3): 477 -80. 2. De. Castro S, Sparks JR, Lapey JD, et al. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion. Surg Neurol. 1976 Dec; 6(6): 357 -9. 3. Georgiades CS, Neyman EG, Barish MA, et al. Amyloidosis: review and CT manifestations Radiographics 2004; 24(2): 405 -16. 4. Adle-Biassette H, Vallat AV, Nochy D. [Amyloidosis: definition and classification]. " Arch Anat Cytol Pathol 1996; 44(2 -3): 101 -5. 5. Salytkov S. On the issue of local amyloid of cerebral tissue. Comments to the article by morgenstern Virchows Arch [A] 1935; 295: 590 6. Harris JH, Rayport M. Primary cerebral amyloidoma. J neuropathol Exp Neurol 1979; 38: 318 7. Spaar FW, Goebel HH, Volles E, et al. Tumor-like amyloid formation (amyloidoma) in the brain. J Neurol 1981; 224(3): 171 -82. 8. Townsend JJ, Tomiyasu U, Mac. Kay A, et al. Central nervous system amyloid presenting as a mass lesion. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1982 Mar; 56(3): 439 -42. 9. Moreno AJ, Brown JM, Brown TJ, et al. Scintigraphic findings in a primary cerebral amyloidoma. Clin Nucl Med 1983 Nov; 8(11): 528 -30. 10. Hori A, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, et al. Focal intracerebral accumulation of a novel type of amyloid protein. An early stage of cerebral amyloidoma? Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1988; 76(2): 212 -5. 11. Cohen M, Lanska D, Roessmann U, et al. Amyloidoma of the CNS. I. Clinical and pathologic study. Neurology. 1992 Oct; 42(10): 2019 -23. 12. Vidal RG, Ghiso J, Gallo G, et al. Amyloidoma of the CNS. II. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Neurology. 1992 Oct; 42(10): 2024 -8.
 REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • • 13. Eriksson L, Sletten K, Benson L, et al. Tumour-like localized amyloid of the brain is derived from immunoglobulin light chain. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jun; 37(6): 623 -6. 14. Lee J, Krol G, Rosenblum M. Primary amyloidoma of the brain: CT and MR presentation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995 Apr; 16(4): 712 -4. 15. Schroder R, Linke RP, Voges J, et al. Intracerebral A lambda amyloidoma diagnosed by stereotactic biopsy. Clin Neuropathol. 1995 Nov-Dec; 14(6): 347 -50. 16. Caerts B, Mol V, Sainte T, et al. CT and MRI of amyloidoma of the CNS. Eur Radiol. 1997; 7(4): 474 -6. 17. Smadja P, Viaud B, Durand L, et al. [Amyloidoma of the central nervous system: CT and MR aspects] J Radiol. 2000 Sep; 81(9): 975 -8. 18. Blattler T, Siegel AM, Jochum W, et al. Primary cerebral amyloidoma. Neurology. 2001 Mar 27; 56(6): 777. 19. Vanhoenacker F, Van Paesschen R, Hauman R, et al. Cerebral amyloidoma. JBR-BTR. 2001 Apr; 84(2): 79. 20. Gallucci M, Caulo M, Splendiani A, et al. Neuroradiological findings in two cases of isolated amyloidoma of the central nervous system. Neuroradiology. 2002 Apr; 44(4): 333 -7. 21. Gandhi D, Wee R, Goyal M. CT and MR imaging of intracerebral amyloidoma: case report and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24(3): 519 -22. Meir K, Maly B, Shoshan Y, et al. Cerebral amyloidoma diagnosed intraoperatively with squash preparations: a case report. Acta Cytol. 2005 Mar-Apr; 49(2): 195 -8. 23. Tabatabai G, Baehring J, Hochberg FH. Primary amyloidoma of the brain parenchyma. Arch Neurol. 2005 Mar; 62(3): 477 -80. 24. Ragel BT, Blumenthal DT, Browd SR, et al. Intraccerebral amyloidoma can mimic high-grade glioma on magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Arch Neurol 2006 Jun; 63(6): 906 -7. 25. Fischer B, Palkovic S, Rickert C, et al. Cerebral AL lambda-amyloidoma: clinical and pathomorphological characteristics. Review of the literature and of a patient. Amyloid 2007 Mar; 14(1): 11 -9.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • • 13. Eriksson L, Sletten K, Benson L, et al. Tumour-like localized amyloid of the brain is derived from immunoglobulin light chain. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jun; 37(6): 623 -6. 14. Lee J, Krol G, Rosenblum M. Primary amyloidoma of the brain: CT and MR presentation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995 Apr; 16(4): 712 -4. 15. Schroder R, Linke RP, Voges J, et al. Intracerebral A lambda amyloidoma diagnosed by stereotactic biopsy. Clin Neuropathol. 1995 Nov-Dec; 14(6): 347 -50. 16. Caerts B, Mol V, Sainte T, et al. CT and MRI of amyloidoma of the CNS. Eur Radiol. 1997; 7(4): 474 -6. 17. Smadja P, Viaud B, Durand L, et al. [Amyloidoma of the central nervous system: CT and MR aspects] J Radiol. 2000 Sep; 81(9): 975 -8. 18. Blattler T, Siegel AM, Jochum W, et al. Primary cerebral amyloidoma. Neurology. 2001 Mar 27; 56(6): 777. 19. Vanhoenacker F, Van Paesschen R, Hauman R, et al. Cerebral amyloidoma. JBR-BTR. 2001 Apr; 84(2): 79. 20. Gallucci M, Caulo M, Splendiani A, et al. Neuroradiological findings in two cases of isolated amyloidoma of the central nervous system. Neuroradiology. 2002 Apr; 44(4): 333 -7. 21. Gandhi D, Wee R, Goyal M. CT and MR imaging of intracerebral amyloidoma: case report and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24(3): 519 -22. Meir K, Maly B, Shoshan Y, et al. Cerebral amyloidoma diagnosed intraoperatively with squash preparations: a case report. Acta Cytol. 2005 Mar-Apr; 49(2): 195 -8. 23. Tabatabai G, Baehring J, Hochberg FH. Primary amyloidoma of the brain parenchyma. Arch Neurol. 2005 Mar; 62(3): 477 -80. 24. Ragel BT, Blumenthal DT, Browd SR, et al. Intraccerebral amyloidoma can mimic high-grade glioma on magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Arch Neurol 2006 Jun; 63(6): 906 -7. 25. Fischer B, Palkovic S, Rickert C, et al. Cerebral AL lambda-amyloidoma: clinical and pathomorphological characteristics. Review of the literature and of a patient. Amyloid 2007 Mar; 14(1): 11 -9.
 REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 26. Mc. Million L, Melton DM, Erickson JC. Teaching neuroimage: Primary cerevral amyloidoma mimicking CNS neoplasm. Neurology 2008 Nov; 71(22): e 68. 27. Renard D, Campello C, Rigau V, et al. Primary brain amyloidoma: long-term follow-up. Arch Neurol. 2008 Jul; 65(7): 979 -80. 28. Sin AH, Gonzalez-Toledo E, Fowler M, et al. Amyloidoma presenting as a butterfly glioma on positron emission tomography scan and magnetic resonance-spectroscopy: a case report and review of the literature. J La State Med Soc 2008 Jan-Feb; 160(1): 44 -7. 29. Van roy J, De Bie J. Frontal syndrome resulting from an intracerebral amyloidoma. Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2009; 51(11): 847 -52. 30. Labro H, Al-Kadhimi Z, Djmil M, et al/ Brain amyloidoma with cerebral hemorrhage. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2009 Jul; 109(7): 372 -5. 31. Nossek E, Bashat DB, Artzi M, et al. the role of advanced MR methods in the diagnosis of cerebral amyloidoma. Amyloid. 2009; 16(2): 9 -8. 32. Landau D, Avgeropoulos N, Ma J. Cerebral amyloidoma mimicking intracranial tumor: a case report. J Med Case Reports. 2010; 4: 308. 33. Foreid H, Barroso C, Evangelista T, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: case report and review of the literature. Clin Neuropathol. 2010 Jul-Ago; 29(4): 217 -22. 34. Rocha AJ, Silva CJ, Leopoldino JFS, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: imaging findings might support preoperative diagnosis. Arq Neuri-Psiquiatr. 2011; 69(2 -B): 413. 35. Bornemann A, Bohl J, Hey O, et al. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion as a cause of symptomatic neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve: report of three cases. J Neurol. 1993 Nov; 241(1): 10 -4. 36. O'Brien TJ, Mc. Kelvie PA, Vrodos N. Bilateral trigeminal amyloidoma: an unusual case of trigeminal neuropathy with a review of the literature. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1994 Nov; 81(5): 780 -3.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 26. Mc. Million L, Melton DM, Erickson JC. Teaching neuroimage: Primary cerevral amyloidoma mimicking CNS neoplasm. Neurology 2008 Nov; 71(22): e 68. 27. Renard D, Campello C, Rigau V, et al. Primary brain amyloidoma: long-term follow-up. Arch Neurol. 2008 Jul; 65(7): 979 -80. 28. Sin AH, Gonzalez-Toledo E, Fowler M, et al. Amyloidoma presenting as a butterfly glioma on positron emission tomography scan and magnetic resonance-spectroscopy: a case report and review of the literature. J La State Med Soc 2008 Jan-Feb; 160(1): 44 -7. 29. Van roy J, De Bie J. Frontal syndrome resulting from an intracerebral amyloidoma. Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2009; 51(11): 847 -52. 30. Labro H, Al-Kadhimi Z, Djmil M, et al/ Brain amyloidoma with cerebral hemorrhage. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2009 Jul; 109(7): 372 -5. 31. Nossek E, Bashat DB, Artzi M, et al. the role of advanced MR methods in the diagnosis of cerebral amyloidoma. Amyloid. 2009; 16(2): 9 -8. 32. Landau D, Avgeropoulos N, Ma J. Cerebral amyloidoma mimicking intracranial tumor: a case report. J Med Case Reports. 2010; 4: 308. 33. Foreid H, Barroso C, Evangelista T, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: case report and review of the literature. Clin Neuropathol. 2010 Jul-Ago; 29(4): 217 -22. 34. Rocha AJ, Silva CJ, Leopoldino JFS, et al. Intracerebral amyloidoma: imaging findings might support preoperative diagnosis. Arq Neuri-Psiquiatr. 2011; 69(2 -B): 413. 35. Bornemann A, Bohl J, Hey O, et al. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion as a cause of symptomatic neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve: report of three cases. J Neurol. 1993 Nov; 241(1): 10 -4. 36. O'Brien TJ, Mc. Kelvie PA, Vrodos N. Bilateral trigeminal amyloidoma: an unusual case of trigeminal neuropathy with a review of the literature. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1994 Nov; 81(5): 780 -3.
 REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 37. Vorster SJ, Lee JH, Ruggieri P. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998 Nov. Dec; 19(10): 1853 -5. 38. Matsumoto T, Tani E, Fukami M, et al. Amyloidoma in the gasserian ganglion: case report. Surg Neurol. 1999 Dec; 52(6): 600 -3. 39. Bookland MJ, Bagley CA, Schwartz J, et al. Intracavernous trigeminal ganglion amyloidoma: case report. Neurosurgery 2007 Mar; 60(3): E 574. 40. Adle-Biassette H, Vallat AV, Nochy D. Amyloidosis: definition and classification. Arch Anat Cytol Pathol 1996; 44(2 -3): 101 -5. 41. Jährig A, Spaar FW, Lindermeyer J, et al. A historical cerebral amyloidoma (SPA) classified retrospectively as ALɣ-type. A case report. Amyloid 2011 jun; 18(1)114 -6.
REFERÊNCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS • • • 37. Vorster SJ, Lee JH, Ruggieri P. Amyloidoma of the gasserian ganglion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998 Nov. Dec; 19(10): 1853 -5. 38. Matsumoto T, Tani E, Fukami M, et al. Amyloidoma in the gasserian ganglion: case report. Surg Neurol. 1999 Dec; 52(6): 600 -3. 39. Bookland MJ, Bagley CA, Schwartz J, et al. Intracavernous trigeminal ganglion amyloidoma: case report. Neurosurgery 2007 Mar; 60(3): E 574. 40. Adle-Biassette H, Vallat AV, Nochy D. Amyloidosis: definition and classification. Arch Anat Cytol Pathol 1996; 44(2 -3): 101 -5. 41. Jährig A, Spaar FW, Lindermeyer J, et al. A historical cerebral amyloidoma (SPA) classified retrospectively as ALɣ-type. A case report. Amyloid 2011 jun; 18(1)114 -6.


