Gender Differences in Language.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Gender Differences in Language
Gender Differences in Language
 Outline of the lecture 1. Genderlect: limitations of previous research/ present study 2. Differences in brain anatomy and physiology 3. Mars-and-Venus theory 4. The root cause of language gender differences 5. Speech practices associated with gender 6. Gender differences reflected in English 7. Gender-specific vocabulary
Outline of the lecture 1. Genderlect: limitations of previous research/ present study 2. Differences in brain anatomy and physiology 3. Mars-and-Venus theory 4. The root cause of language gender differences 5. Speech practices associated with gender 6. Gender differences reflected in English 7. Gender-specific vocabulary
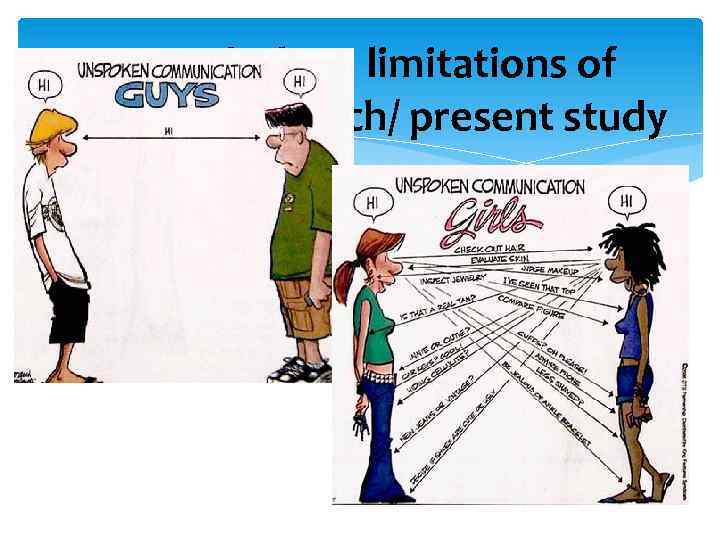 1. Genderlect: limitations of previous research/ present study Genderlect - a variety of speech or conversational style used by a particular gender.
1. Genderlect: limitations of previous research/ present study Genderlect - a variety of speech or conversational style used by a particular gender.
 Previous research Differences in the ways that men and women use language have long been of interest in the study of discourse. Men and women have different semantic goals in mind when they construct sentences.
Previous research Differences in the ways that men and women use language have long been of interest in the study of discourse. Men and women have different semantic goals in mind when they construct sentences.
 Previous research Mulac, Weimann, Widenmann, & Gibson, 1988) found that questions are more common in women’s speech. Thomson and Murachver’s (2001) study of e-mail communication found that men and women were equally likely to ask questions; offer compliments, apologies, and opinions However, the study did confirm that men used more words overall, whereas women used longer sentences
Previous research Mulac, Weimann, Widenmann, & Gibson, 1988) found that questions are more common in women’s speech. Thomson and Murachver’s (2001) study of e-mail communication found that men and women were equally likely to ask questions; offer compliments, apologies, and opinions However, the study did confirm that men used more words overall, whereas women used longer sentences
 Previous research One striking result reported by Mehl and Pennebaker (2003) was that womenwere more likely to use first-person singular However, the word “I” intuitively connotes individualism or selfishness, which fits the male stereotype better than the female stereotype.
Previous research One striking result reported by Mehl and Pennebaker (2003) was that womenwere more likely to use first-person singular However, the word “I” intuitively connotes individualism or selfishness, which fits the male stereotype better than the female stereotype.
 Limitations Many previous studies have had fewer than 50 participants per cell. Larger samples are often difficult to collect when each sample must be hand coded Previous study focused attention toward features of language that can be easily related to gender stereotypes (e. g. , hedges), potentially missing differences in less obvious language categories (e. g. , pronouns)
Limitations Many previous studies have had fewer than 50 participants per cell. Larger samples are often difficult to collect when each sample must be hand coded Previous study focused attention toward features of language that can be easily related to gender stereotypes (e. g. , hedges), potentially missing differences in less obvious language categories (e. g. , pronouns)
 Present study Based on two methodological developments 1. Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC; Pennebaker, Francis, & Booth, 2001) LIWC analyzes text samples on a word-by-word basis and compares each to a dictionary of over 2, 000 words divided into 74 linguistic categories. Output is expressed as a percentage of the total words in the text sample.
Present study Based on two methodological developments 1. Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC; Pennebaker, Francis, & Booth, 2001) LIWC analyzes text samples on a word-by-word basis and compares each to a dictionary of over 2, 000 words divided into 74 linguistic categories. Output is expressed as a percentage of the total words in the text sample.
 LIWC It cannot detect the context or underlying meaning of words. It fails to appreciate sarcasm or irony E. g. , the word “mad” is currently categorized as an anger word. § “I’m mad about you” (suggesting positive emotion) § “mad as a hatter” (indicative of mental health problems)
LIWC It cannot detect the context or underlying meaning of words. It fails to appreciate sarcasm or irony E. g. , the word “mad” is currently categorized as an anger word. § “I’m mad about you” (suggesting positive emotion) § “mad as a hatter” (indicative of mental health problems)
 Present study The second methodological development has been the creation of a text archive itself. q over 500, 000 text files q samples of books, poems, song lyrics, and other art forms This research has the opportunity to observe gender differences on a much larger scale than has been attempted in the past
Present study The second methodological development has been the creation of a text archive itself. q over 500, 000 text files q samples of books, poems, song lyrics, and other art forms This research has the opportunity to observe gender differences on a much larger scale than has been attempted in the past
 Comparison with Previous Research Different words Different phrases. Different sentences. Different messages.
Comparison with Previous Research Different words Different phrases. Different sentences. Different messages.
 Differences Brain Anatomy and Physiology 9 Differences Between the Male and Female Brain
Differences Brain Anatomy and Physiology 9 Differences Between the Male and Female Brain
 1. Brain size The male brain is typically about 10% larger than the female brain.
1. Brain size The male brain is typically about 10% larger than the female brain.
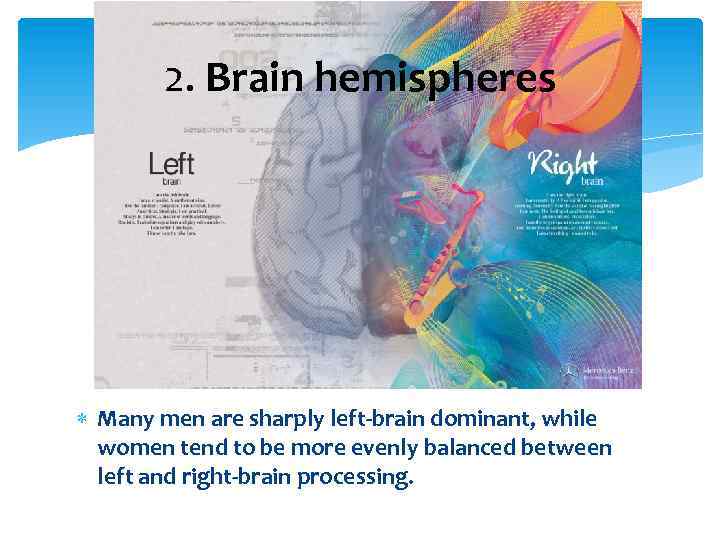 2. Brain hemispheres Many men are sharply left-brain dominant, while women tend to be more evenly balanced between left and right-brain processing.
2. Brain hemispheres Many men are sharply left-brain dominant, while women tend to be more evenly balanced between left and right-brain processing.
 3. Relationships Women tend to be group-oriented, and apt to seek solutions by talking through issues. Men can have trouble picking up on emotional cues unless they’re clearly verbalized
3. Relationships Women tend to be group-oriented, and apt to seek solutions by talking through issues. Men can have trouble picking up on emotional cues unless they’re clearly verbalized
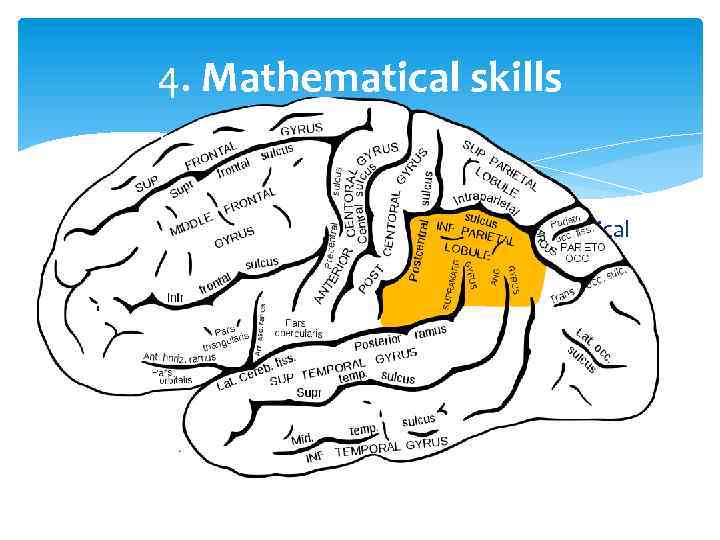 4. Mathematical skills The inferior-parietal lobule, which controls numerical brain function, is larger in males than in females
4. Mathematical skills The inferior-parietal lobule, which controls numerical brain function, is larger in males than in females
 5. Stress When faced with stressful situations, men usually employ ‘fight or flight’ tactics, while women use a ‘tend or befriend’ response that is rooted in their natural instincts for caring for their children and establishing strong group bonds.
5. Stress When faced with stressful situations, men usually employ ‘fight or flight’ tactics, while women use a ‘tend or befriend’ response that is rooted in their natural instincts for caring for their children and establishing strong group bonds.
 6. Language Women often excel at language-based tasks for two reasons: two brain areas that deal with language are larger in females, and females process language in both hemispheres while males favor a single brain half.
6. Language Women often excel at language-based tasks for two reasons: two brain areas that deal with language are larger in females, and females process language in both hemispheres while males favor a single brain half.
 7. Emotions Since women tend to have a larger deep limbic system then men, they’re more in touch with their feelings and are better at expressing their emotions.
7. Emotions Since women tend to have a larger deep limbic system then men, they’re more in touch with their feelings and are better at expressing their emotions.
 8. Spatial abilities The parietal region is thicker in the female brain, making it harder for them to mentally rotate objects – an important spatial skill. Women often report difficulty with spatial tasks, both on tests and in real life.
8. Spatial abilities The parietal region is thicker in the female brain, making it harder for them to mentally rotate objects – an important spatial skill. Women often report difficulty with spatial tasks, both on tests and in real life.
 9. Susceptibility to brain function disorders Men are more likely to be dyslexic or have other language disabilities, since they’re more often leftbrain dominant.
9. Susceptibility to brain function disorders Men are more likely to be dyslexic or have other language disabilities, since they’re more often leftbrain dominant.
 Mars-and-Venus theory John Grey “Men Are From Mars Women Are From Venus”
Mars-and-Venus theory John Grey “Men Are From Mars Women Are From Venus”
 Mars-and-Venus theory The Martian and Venusian languages had the same words, but the way they were used gave different meanings. Their expressions were similar, but t hey had different connotations or emotional emphasis. Men and women seldom mean the same things even when they use the same words.
Mars-and-Venus theory The Martian and Venusian languages had the same words, but the way they were used gave different meanings. Their expressions were similar, but t hey had different connotations or emotional emphasis. Men and women seldom mean the same things even when they use the same words.
 Mars-and-Venus theory For example, when a woman says : "I feel like you never listen, " she does not expect the word never to be taken literally. Using the word never is just a way of expressing the frustration she is feeling at the moment. It is not to be taken as if it were factual information.
Mars-and-Venus theory For example, when a woman says : "I feel like you never listen, " she does not expect the word never to be taken literally. Using the word never is just a way of expressing the frustration she is feeling at the moment. It is not to be taken as if it were factual information.
 To fully express their feelings, women assume poetic license and use various q superlatives q metaphors q generalizations Men mistakenly take these expressions literally.
To fully express their feelings, women assume poetic license and use various q superlatives q metaphors q generalizations Men mistakenly take these expressions literally.
 Women say: "You don't love me any more“ It means: “Today I am feeling as though you don't love me. I am afraid I have pushed you away. I know you really do love me, you do so much for me. Today I am just feeling a little insecure. Would you reassure me of your love and tell me those three magic words, I love you. When you do that it feels so good “
Women say: "You don't love me any more“ It means: “Today I am feeling as though you don't love me. I am afraid I have pushed you away. I know you really do love me, you do so much for me. Today I am just feeling a little insecure. Would you reassure me of your love and tell me those three magic words, I love you. When you do that it feels so good “
 Men hear I have given you the best years of my life, and you have given me nothing. You used me. You are selfish and cold. You do what you want to do, for you and only you. You do not care about anybody. I was a fool for loving you. Now I have nothing. "
Men hear I have given you the best years of my life, and you have given me nothing. You used me. You are selfish and cold. You do what you want to do, for you and only you. You do not care about anybody. I was a fool for loving you. Now I have nothing. "
 Mars-and-Venus theory The big challenge for men is correctly to interpret and support a woman when she is talking about her feelings. The biggest challenge for women is correctly to interpret and support a man when he isn't talking. Silence is most easily misinterpreted by women.
Mars-and-Venus theory The big challenge for men is correctly to interpret and support a woman when she is talking about her feelings. The biggest challenge for women is correctly to interpret and support a man when he isn't talking. Silence is most easily misinterpreted by women.
 Mars-and-Venus theory It means "I don't know what to say yet, but I am thinking about it. “ Women think: I am not responding to you because I don't care about you and I am going to ignore you. What you have said to me is not important and therefore I am not responding. "
Mars-and-Venus theory It means "I don't know what to say yet, but I am thinking about it. “ Women think: I am not responding to you because I don't care about you and I am going to ignore you. What you have said to me is not important and therefore I am not responding. "



