de0584426745ebb1c0a4032be46532cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 GEANT 4 and EUDET/NA 2 Geant 4 Highlights VALSIM potential work items John Apostolakis, CERN for the G 4/SFT team V 1. 1 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
GEANT 4 and EUDET/NA 2 Geant 4 Highlights VALSIM potential work items John Apostolakis, CERN for the G 4/SFT team V 1. 1 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Content • The Context: Geant 4, G 4 team in PH/SFT • Geant 4 Highlights • VALSIM potential work items 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 2
Content • The Context: Geant 4, G 4 team in PH/SFT • Geant 4 Highlights • VALSIM potential work items 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 2
 Part I: The Context Geant 4 toolkit Application Areas G 4/SFT team (LCG) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
Part I: The Context Geant 4 toolkit Application Areas G 4/SFT team (LCG) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Geant 4 Overview • Powerful structure and kernel – tracking, stacks, geometry, hits, … • Extensive & transparent physics models – electromagnetic – hadronic – decay, optical, … • Interfaces – visualization, GUI, persistency. • Efficiency enhancing techniques – Framework for fast simulation (shower parameterization) – Variance reduction / event biasing 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 4
Geant 4 Overview • Powerful structure and kernel – tracking, stacks, geometry, hits, … • Extensive & transparent physics models – electromagnetic – hadronic – decay, optical, … • Interfaces – visualization, GUI, persistency. • Efficiency enhancing techniques – Framework for fast simulation (shower parameterization) – Variance reduction / event biasing 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 4
 Application Areas • Geant 4 in HEP production – – Ba. Bar ATLAS(Q 1 2004) CMS (Q 4 2003), LHCb (Q 2 2004) – Harp – … • Medical applications – – Imaging (PET/SPECT) Dosimetry m. Beam optics modeling Assessing treatment (hadrontherapy) • Space – Effects on electronics – Planetary radiation environment – Radiation in human flights 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 5
Application Areas • Geant 4 in HEP production – – Ba. Bar ATLAS(Q 1 2004) CMS (Q 4 2003), LHCb (Q 2 2004) – Harp – … • Medical applications – – Imaging (PET/SPECT) Dosimetry m. Beam optics modeling Assessing treatment (hadrontherapy) • Space – Effects on electronics – Planetary radiation environment – Radiation in human flights 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 5
 G 4/SFT team: work areas and people 1. Geometry, Field and Transportation • 2. G Cosmo(coord. ), V. Grichine, J. Apostolakis, O. Link (-Dec 2005) Software Management, System Testing • 3. G Folger, G Cosmo, I. Mc. Laren, (also S. Sadilov) EM Physics • 4. V. Ivantchenko (resp. /SFT), V. Grichine Hadronic Physics / Neutrons • • 5. G. Folger (resp. /SFT), M. Kossov, V Ivantchenko, V. Grichine A. Howard (from Oct 2005, also SI-Physics Validation) Regression testing / validation • 6. A. Ribon (also LCG-AA/SI/Physics Validation) Coordination / Release • 14 December 2005 J. Apostolakis, G. Cosmo J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 6
G 4/SFT team: work areas and people 1. Geometry, Field and Transportation • 2. G Cosmo(coord. ), V. Grichine, J. Apostolakis, O. Link (-Dec 2005) Software Management, System Testing • 3. G Folger, G Cosmo, I. Mc. Laren, (also S. Sadilov) EM Physics • 4. V. Ivantchenko (resp. /SFT), V. Grichine Hadronic Physics / Neutrons • • 5. G. Folger (resp. /SFT), M. Kossov, V Ivantchenko, V. Grichine A. Howard (from Oct 2005, also SI-Physics Validation) Regression testing / validation • 6. A. Ribon (also LCG-AA/SI/Physics Validation) Coordination / Release • 14 December 2005 J. Apostolakis, G. Cosmo J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 6
 Part II: Physics Using the Physics via ‘Physics lists’ & Underlying physics modeling 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
Part II: Physics Using the Physics via ‘Physics lists’ & Underlying physics modeling 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Different types of hadronic shower models • Parameterization-driven models – Started from GHEISHA, revised/improved • Theory driven models – Pre-compound – Cascades and CHIPS – String models • Data driven models – Neutrons E<20 Me. V – Photo-evaporation of nuclei 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 8
Different types of hadronic shower models • Parameterization-driven models – Started from GHEISHA, revised/improved • Theory driven models – Pre-compound – Cascades and CHIPS – String models • Data driven models – Neutrons E<20 Me. V – Photo-evaporation of nuclei 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 8
 Models in hadronic framework 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 9
Models in hadronic framework 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 9
 Theory driven models (1/2) • Models derived from approximate/phenomenological models – QCD, strings, chiral perturbation theory, statistical collective • Only thin-target data used for verification • Final states determined by sampling theoretical distributions • Philosophy implies the usage physics lists, providing wanted collection of models, such as: – Parton string models at high energies, – intra-nuclear transport models at intermediate energies, and – statistical break-up models for de-excitation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 10
Theory driven models (1/2) • Models derived from approximate/phenomenological models – QCD, strings, chiral perturbation theory, statistical collective • Only thin-target data used for verification • Final states determined by sampling theoretical distributions • Philosophy implies the usage physics lists, providing wanted collection of models, such as: – Parton string models at high energies, – intra-nuclear transport models at intermediate energies, and – statistical break-up models for de-excitation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 10
 Theory driven models (2/2) • Parton string: – Projectiles with E > 5 Ge. V – Wounded nucleus is de-excited by ‘attached’ model (precompound or Chips) • Cascade energy-range models – Bertini cascade (next slides) – Binary cascade – Chiral invariant phase space, CHIPS: • Quark-level event generator for the fragmentation of hadronic systems into hadrons – All energies • Interactions between hadrons are treated as purely kinematic effects of quark exchange • Decay of excited hadronic systems is treated as the fusion of two quarkpartons within the system • Includes non-relativistic phase space of nucleons to explain evaporation • Nuclear de-excitation and breakup 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 11
Theory driven models (2/2) • Parton string: – Projectiles with E > 5 Ge. V – Wounded nucleus is de-excited by ‘attached’ model (precompound or Chips) • Cascade energy-range models – Bertini cascade (next slides) – Binary cascade – Chiral invariant phase space, CHIPS: • Quark-level event generator for the fragmentation of hadronic systems into hadrons – All energies • Interactions between hadrons are treated as purely kinematic effects of quark exchange • Decay of excited hadronic systems is treated as the fusion of two quarkpartons within the system • Includes non-relativistic phase space of nucleons to explain evaporation • Nuclear de-excitation and breakup 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 11
 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade (1/2) • Collection of theory driven models with parametrisation features: • Intermediate energies ~100 ke. V – 10 Me. V • Models included: – – – Bertini INC model with exitons Pre-equilibrium model Nucleus explosion model Fission model Evaporation model 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 12
Bertini intra-nuclear cascade (1/2) • Collection of theory driven models with parametrisation features: • Intermediate energies ~100 ke. V – 10 Me. V • Models included: – – – Bertini INC model with exitons Pre-equilibrium model Nucleus explosion model Fission model Evaporation model 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 12
 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade (2/2) • For A>4 a nuclei model is composed of three concentric spheres • Impulse distribution in each region follows Fermi distribution with zero temperature • Particle treated p, n, pions, photon evaporation and nuclear isotope remnats • Latest addition include incident kaons up to an energy of 15 Ge. V: – Final states, will be included for K+, K-, K 0 bar, lambda, sigma+, sigma 0, sigma-, xi 0 and xi- 14 December 2005 Schematic presentation of the intranuclear cascade. A hadron with 400 Me. V energy is forming an INC history. Crosses present the Pauli exclusion principle in action. J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 13
Bertini intra-nuclear cascade (2/2) • For A>4 a nuclei model is composed of three concentric spheres • Impulse distribution in each region follows Fermi distribution with zero temperature • Particle treated p, n, pions, photon evaporation and nuclear isotope remnats • Latest addition include incident kaons up to an energy of 15 Ge. V: – Final states, will be included for K+, K-, K 0 bar, lambda, sigma+, sigma 0, sigma-, xi 0 and xi- 14 December 2005 Schematic presentation of the intranuclear cascade. A hadron with 400 Me. V energy is forming an INC history. Crosses present the Pauli exclusion principle in action. J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 13
 Hadronic model inventory 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 14
Hadronic model inventory 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 14
 pion production from 730 Me. V proton on Carbon. Geant 4 LEP model (derived from Geant 3. 21 and improved) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 15
pion production from 730 Me. V proton on Carbon. Geant 4 LEP model (derived from Geant 3. 21 and improved) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 15
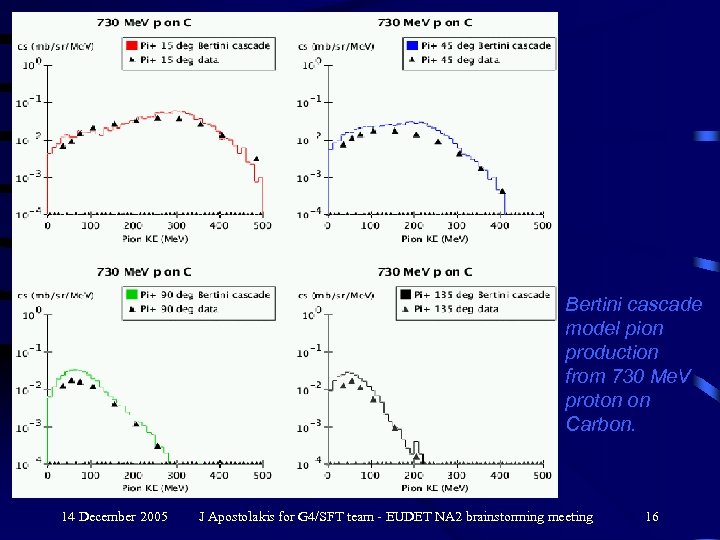 Bertini cascade model pion production from 730 Me. V proton on Carbon. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 16
Bertini cascade model pion production from 730 Me. V proton on Carbon. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 16
 Tailored Physics ‘lists’ • Created and distribute “educated guess” physics lists – correspond to major use cases of Geant 4 involving hadronic physics, – to use directly, and as a starting point for users to modify, • facilitate the specialization of those parts of hadronic physics lists that vary. – First released in September 2002 • Revised with experience of comparisons with data – This provide ‘tested’ options, with known performance – Last major revision for physics models of Geant 4 6. 2 (June 2004) • Distribution – Most up-to-date from the G 4 hadronic physics web pages http: //cern. ch/geant 4/physics_lists – Included in Geant 4 releases • Starting with Geant 4 6. 0 (Dec 2003), ported versions in major releases • Current physics lists version is included in minor releases, patches. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 17
Tailored Physics ‘lists’ • Created and distribute “educated guess” physics lists – correspond to major use cases of Geant 4 involving hadronic physics, – to use directly, and as a starting point for users to modify, • facilitate the specialization of those parts of hadronic physics lists that vary. – First released in September 2002 • Revised with experience of comparisons with data – This provide ‘tested’ options, with known performance – Last major revision for physics models of Geant 4 6. 2 (June 2004) • Distribution – Most up-to-date from the G 4 hadronic physics web pages http: //cern. ch/geant 4/physics_lists – Included in Geant 4 releases • Starting with Geant 4 6. 0 (Dec 2003), ported versions in major releases • Current physics lists version is included in minor releases, patches. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 17
 Hadronic physics: models, processes and ‘lists’ particle type, material yalternatives with different strengths and CPU requirements. Energy z. Five level implementation Components can be assembled in an optimized way for each use case. framework z. Variety of models and cross- Element sections particle yfor each energy regime, Pre-compound model Cascade Illustrative example of assembling Parameterized models into an inelastic process for set of particles – Uses levels 1 & 2 of framework 14 December 2005 QGSM J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 18
Hadronic physics: models, processes and ‘lists’ particle type, material yalternatives with different strengths and CPU requirements. Energy z. Five level implementation Components can be assembled in an optimized way for each use case. framework z. Variety of models and cross- Element sections particle yfor each energy regime, Pre-compound model Cascade Illustrative example of assembling Parameterized models into an inelastic process for set of particles – Uses levels 1 & 2 of framework 14 December 2005 QGSM J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 18
 Use cases of Physics Lists • • HEP calorimetry. HEP trackers. 'Average' HEP collider detector Low energy dosimetric applications with neutrons low energy nucleon penetration shielding linear collider neutron fluxes high energy penetration shielding medical and life-saving neutron applications 14 December 2005 • low energy dosimetric applications • high energy production targets e. g. 400 Ge. V protons on C or Be • medium energy production targets e. g. 15 -50 Ge. V p on light targets • LHC neutron fluxes • Air shower applications • low background experiments J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 19
Use cases of Physics Lists • • HEP calorimetry. HEP trackers. 'Average' HEP collider detector Low energy dosimetric applications with neutrons low energy nucleon penetration shielding linear collider neutron fluxes high energy penetration shielding medical and life-saving neutron applications 14 December 2005 • low energy dosimetric applications • high energy production targets e. g. 400 Ge. V protons on C or Be • medium energy production targets e. g. 15 -50 Ge. V p on light targets • LHC neutron fluxes • Air shower applications • low background experiments J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 19
 Physics lists / ‘engines’ for calorimetry • LHEP is the fastest for CPU • – uses the LEP and HEP parameterized models for inelastic scattering. • – The CHiral Invariant Phase-Space decay (CHIPS) – QGS now starts at 9 Ge. V QGSP – uses theory-driven modeling for reactions of ps, Ks, and nucleons • for primaries with E starting at ~ 12 Ge. V, dominant above 30 Ge. V • – A Pre-equilibrium decay model • with an extensive evaporation phase that model the nucleus 'after the punch‘ FTFP starts with QGSP and replaces the string – with a diffractive string excitation It employs – Quark Gluon String Model • for the 'punch-through' interactions of the projectile QGSC, is similar to QGSP but uses CHIPS for fragmentation • similar to that in FRITJOF, and the Lund fragmentation functions. • Note: g A (g – nuclear) interactions recently added to all options. – Previously available as _GN variants, eg QGSP_GN – For other energies uses LHEP models 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 20
Physics lists / ‘engines’ for calorimetry • LHEP is the fastest for CPU • – uses the LEP and HEP parameterized models for inelastic scattering. • – The CHiral Invariant Phase-Space decay (CHIPS) – QGS now starts at 9 Ge. V QGSP – uses theory-driven modeling for reactions of ps, Ks, and nucleons • for primaries with E starting at ~ 12 Ge. V, dominant above 30 Ge. V • – A Pre-equilibrium decay model • with an extensive evaporation phase that model the nucleus 'after the punch‘ FTFP starts with QGSP and replaces the string – with a diffractive string excitation It employs – Quark Gluon String Model • for the 'punch-through' interactions of the projectile QGSC, is similar to QGSP but uses CHIPS for fragmentation • similar to that in FRITJOF, and the Lund fragmentation functions. • Note: g A (g – nuclear) interactions recently added to all options. – Previously available as _GN variants, eg QGSP_GN – For other energies uses LHEP models 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 20
 Relevant comparisons for HEP: A partial list • ATLAS test beams FCAL m, e, p HEC m, e-, p EM Barrel Tile. Cal TRT Muon chambers (extra hits) – … – – – • Ba. Bar data – Drift Chamber • ALICE – 100 s Me. V proton microscopic – TIARA neutron benchm. • CMS – HCAL test beam • BTe. V – ECAL test beam Very hard to give just a few highlights … 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 21
Relevant comparisons for HEP: A partial list • ATLAS test beams FCAL m, e, p HEC m, e-, p EM Barrel Tile. Cal TRT Muon chambers (extra hits) – … – – – • Ba. Bar data – Drift Chamber • ALICE – 100 s Me. V proton microscopic – TIARA neutron benchm. • CMS – HCAL test beam • BTe. V – ECAL test beam Very hard to give just a few highlights … 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 21
 Hadronic Physics: theoretical models • Evaporation/pre-compound • Bertini Cascade / INUCL – extended to Kaons, up to 5 -10 Ge. V, verified isotope production • Binary cascade – Extended to ion reactions, pion projectiles • CHIPS ‘Chiral Invariant Phase-space decay’ – g-A, e-A, p absorption, p-bar annihilation at rest • QGSM string model – improved meson splitting 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 22
Hadronic Physics: theoretical models • Evaporation/pre-compound • Bertini Cascade / INUCL – extended to Kaons, up to 5 -10 Ge. V, verified isotope production • Binary cascade – Extended to ion reactions, pion projectiles • CHIPS ‘Chiral Invariant Phase-space decay’ – g-A, e-A, p absorption, p-bar annihilation at rest • QGSM string model – improved meson splitting 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 22
 http: //cern. ch/geant 4 Latest • Geant 4 8. 0 will include – Refinements and new features in the kernel – New models, improvements & refinements in EM • Revision of multiple scattering model (angle/lateral) & process (step limits) • Using & extending ‘model-based’ implementation of EM standard – Improvements & fixes models in hadronics • Revisions to ‘LElastic’, and refined precision ‘coherent’ process • Neutrino – nucleus using CHIPS – Revised ‘Physics-lists’ • Revised to use EM builders, non-static particles • Utilize revised physics processes (in most PLs). 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 23
http: //cern. ch/geant 4 Latest • Geant 4 8. 0 will include – Refinements and new features in the kernel – New models, improvements & refinements in EM • Revision of multiple scattering model (angle/lateral) & process (step limits) • Using & extending ‘model-based’ implementation of EM standard – Improvements & fixes models in hadronics • Revisions to ‘LElastic’, and refined precision ‘coherent’ process • Neutrino – nucleus using CHIPS – Revised ‘Physics-lists’ • Revised to use EM builders, non-static particles • Utilize revised physics processes (in most PLs). 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 23
 Part III: Validation / Testing Regression ‘suite’ 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
Part III: Validation / Testing Regression ‘suite’ 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Statistical testing 2004/5 • Establishment of ‘statistical testing’ suite – Automated comparison of physics quantities – Simple setups for ‘regression testing’ • Simplified, typical LHC hadronic calorimeters (only E deposit, no digitisation) • Additional testing suites – Against ‘standard’ data • T. Koi (SLAC) : hadron / ion comparison • INFN : EM interactions, per process X-sections vs. NIST • Extensions of suite under consideration – Further setups (EM calor. ), quantities – Reusing donated ‘test-beam’ comparisons • Full applications from ATLAS, CMS. – For details see presentations of A. Ribon (Tech Forum, AA meeting) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 25
Statistical testing 2004/5 • Establishment of ‘statistical testing’ suite – Automated comparison of physics quantities – Simple setups for ‘regression testing’ • Simplified, typical LHC hadronic calorimeters (only E deposit, no digitisation) • Additional testing suites – Against ‘standard’ data • T. Koi (SLAC) : hadron / ion comparison • INFN : EM interactions, per process X-sections vs. NIST • Extensions of suite under consideration – Further setups (EM calor. ), quantities – Reusing donated ‘test-beam’ comparisons • Full applications from ATLAS, CMS. – For details see presentations of A. Ribon (Tech Forum, AA meeting) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 25
 Challenges / Ongoing • Regression suite is identifying changes – Identified problems (crashes) – fixed – Must establish more ‘links’ to verification/sub-system tests – Limits to automated testing when revising models • Not to forget user/experiment acceptance tests • Performance improvement – Large productions / always a goal • Expanding use of ‘best-practice’ – Eg new methods to identify ‘hard’ problems 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 26
Challenges / Ongoing • Regression suite is identifying changes – Identified problems (crashes) – fixed – Must establish more ‘links’ to verification/sub-system tests – Limits to automated testing when revising models • Not to forget user/experiment acceptance tests • Performance improvement – Large productions / always a goal • Expanding use of ‘best-practice’ – Eg new methods to identify ‘hard’ problems 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 26
 Part IV: Potential Work Issues 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
Part IV: Potential Work Issues 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Verification of physical processes Review of physical processes for key detector materials (Verification) • Materials: Si, W, gases (Ar, CO 2, CH 4, CF 2), . . . • Verification for key processes in relevant materials (using thin target data) • Comparison/validation of detailed interaction products d 2 s / d. E d. W in particular for hadronic interactions • Potential additional 'details' – catastrophic muon energy loss – - e+ to hadrons (due to annihilation) – synchrotron radiation in medium (LPM-like effects) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 28
Verification of physical processes Review of physical processes for key detector materials (Verification) • Materials: Si, W, gases (Ar, CO 2, CH 4, CF 2), . . . • Verification for key processes in relevant materials (using thin target data) • Comparison/validation of detailed interaction products d 2 s / d. E d. W in particular for hadronic interactions • Potential additional 'details' – catastrophic muon energy loss – - e+ to hadrons (due to annihilation) – synchrotron radiation in medium (LPM-like effects) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 28
 Benchmarking of neutron modeling Key aspects of use cases: neutrons as background, activation, hazard/shielding. • Identified/candidate benchmarks – – – TIARA (shielding) (*) Los Alamos 'thin target' (neutron generation) (*) Particular CERF setups (shielding, activation, . . . ) TARC (spallation, elastic interactions, capture), new data (eg latest data with 14 Me. V n) Note: (*) comparisons exist, typically >= 2 years old • Review / update data for data-driven neutron modelling (E<20 Me. V) • Other aspects – Radiation effects in silicon: joint investigation with space community – Radiation and effects on endcap detectors 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 29
Benchmarking of neutron modeling Key aspects of use cases: neutrons as background, activation, hazard/shielding. • Identified/candidate benchmarks – – – TIARA (shielding) (*) Los Alamos 'thin target' (neutron generation) (*) Particular CERF setups (shielding, activation, . . . ) TARC (spallation, elastic interactions, capture), new data (eg latest data with 14 Me. V n) Note: (*) comparisons exist, typically >= 2 years old • Review / update data for data-driven neutron modelling (E<20 Me. V) • Other aspects – Radiation effects in silicon: joint investigation with space community – Radiation and effects on endcap detectors 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 29
 3. ) Hadronic shower development • Neutron, EM, charged fractions – identify and utilise available benchmarks for EM fraction, neutrons – comparisons with test-beam results of existing/smaller-scale segmentedcalorimeters • hadronic shower shape: comparisons with data and regression testing – extend comparisons with data – extend calorimeter regression suite with setups relevant to proposed detectors • Effect of hadronic interactions in ECAL – Identify aspects/elements affecting simulation's assessment of impact of ECal thickness, material • Comparisons of modeling of jet showers and EM showers – effect of choice of physics models – Assessing strengths/weaknesses of available physics lists for shower simulation in segmented calorimeter 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 30
3. ) Hadronic shower development • Neutron, EM, charged fractions – identify and utilise available benchmarks for EM fraction, neutrons – comparisons with test-beam results of existing/smaller-scale segmentedcalorimeters • hadronic shower shape: comparisons with data and regression testing – extend comparisons with data – extend calorimeter regression suite with setups relevant to proposed detectors • Effect of hadronic interactions in ECAL – Identify aspects/elements affecting simulation's assessment of impact of ECal thickness, material • Comparisons of modeling of jet showers and EM showers – effect of choice of physics models – Assessing strengths/weaknesses of available physics lists for shower simulation in segmented calorimeter 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 30
 4. ) Other/Technical aspects • Coupled propagation/navigation in 'parallel' geometries in presence of fields • Biasing – revision of importance biasing (for parallel navigation) • Scoring – Re-factoring/improving existing and creating new 'standard' tallies • CPU performance – Unique aspects for highly granular detectors (EM showers, field, neutrons? ) – Propagation in strong magnetic fields 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 31
4. ) Other/Technical aspects • Coupled propagation/navigation in 'parallel' geometries in presence of fields • Biasing – revision of importance biasing (for parallel navigation) • Scoring – Re-factoring/improving existing and creating new 'standard' tallies • CPU performance – Unique aspects for highly granular detectors (EM showers, field, neutrons? ) – Propagation in strong magnetic fields 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 31
 THE END 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
THE END 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Geant 4 6. 0 - general picture 1. New capabilities in Geant 4 6. 0 for HEP z Latest Physics lists distributed ‘inside’ z EM-std new ‘model’ implementation by default 2. Highlights of improvements z to existing physics modeling & models; z in physics process implementations; z in functionality z The high level of user feedback is reflected in developments, fixes & improvements 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 33
Geant 4 6. 0 - general picture 1. New capabilities in Geant 4 6. 0 for HEP z Latest Physics lists distributed ‘inside’ z EM-std new ‘model’ implementation by default 2. Highlights of improvements z to existing physics modeling & models; z in physics process implementations; z in functionality z The high level of user feedback is reflected in developments, fixes & improvements 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 33
 Hadronic Physics Lists • The latest physics lists included since 6. 0 – 8. 0 ported from lists in 7. 1 (June 2005) • Porting (new particles), revised modeling (Mult. Scat. , . . ) • Regression testing undertaken Nov/Dec on LCG/EGEE Grid – New/revised versions of physics-lists to be released • Revisions to be quickly included in Geant 4 patches, releases • When required also via physics lists Web site • Physics lists and builders are/can-be used: – As is, compiled in a ‘deployment’ directory – Altered (or additional/customized version) by user/experiment, in own installation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 34
Hadronic Physics Lists • The latest physics lists included since 6. 0 – 8. 0 ported from lists in 7. 1 (June 2005) • Porting (new particles), revised modeling (Mult. Scat. , . . ) • Regression testing undertaken Nov/Dec on LCG/EGEE Grid – New/revised versions of physics-lists to be released • Revisions to be quickly included in Geant 4 patches, releases • When required also via physics lists Web site • Physics lists and builders are/can-be used: – As is, compiled in a ‘deployment’ directory – Altered (or additional/customized version) by user/experiment, in own installation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 34
 EM Physics Processes • New “model-based” EM standard physics processes are now the default – for maintaining and refining – keeping user code unchanged • Old (frozen) implementation is still available – Issues encountered in transition • Fixed in 6. 0 patch 1 and 6. 1 • Refinements – Tail of multiple scat. angular distribution • New in Low Energy EM – New models (2 BN, 2 BS) for Bremstrahlung (Lisbon & INFN) – New processes for electrons & positrons (a-la Penelope) • Fix for repeatability issue – Multiple scattering does not use tables (due to ions) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 35
EM Physics Processes • New “model-based” EM standard physics processes are now the default – for maintaining and refining – keeping user code unchanged • Old (frozen) implementation is still available – Issues encountered in transition • Fixed in 6. 0 patch 1 and 6. 1 • Refinements – Tail of multiple scat. angular distribution • New in Low Energy EM – New models (2 BN, 2 BS) for Bremstrahlung (Lisbon & INFN) – New processes for electrons & positrons (a-la Penelope) • Fix for repeatability issue – Multiple scattering does not use tables (due to ions) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 35
 EM Physics Processes & more … • Multiple scattering • Tuning for tail of angular distribution • Improvement for muons of E>1 Pe. V • Ionisation • Updated energy intervals, fluctuation models … • Multiple scattering does not use table – Needed to ensure repeatability • Added PAI (Photon-Absorption-Ionisation) model • EM low energy physics • New models (2 BN, 2 BS) for Bremstrahlung • New processes for electrons & positrons (a-la Penelope) • Optical processes • New process for wavelength shifting • Adoption of G 4 Surface. Property class for materials 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 36
EM Physics Processes & more … • Multiple scattering • Tuning for tail of angular distribution • Improvement for muons of E>1 Pe. V • Ionisation • Updated energy intervals, fluctuation models … • Multiple scattering does not use table – Needed to ensure repeatability • Added PAI (Photon-Absorption-Ionisation) model • EM low energy physics • New models (2 BN, 2 BS) for Bremstrahlung • New processes for electrons & positrons (a-la Penelope) • Optical processes • New process for wavelength shifting • Adoption of G 4 Surface. Property class for materials 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 36
 Hadronic Models: new • Evaporation models – Ablation: new model for use with abrasion code – GEM-like model implementation – HETC emission probabilities for Weisskopf-Ewing evaporation model • Ion Reactions – Wilson’s Abrasion for induced ion reactions. – EM dissociation for ion-ion collisions • High energy elastic scattering: new Coherent_elastic model – requires a new data set for elastic scattering data (provided) • Diverse – new m- nuclear absorption code – Improved fast radioactive decay code – GNASH 2 transition probabilities now available from exciton precompound model 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 37
Hadronic Models: new • Evaporation models – Ablation: new model for use with abrasion code – GEM-like model implementation – HETC emission probabilities for Weisskopf-Ewing evaporation model • Ion Reactions – Wilson’s Abrasion for induced ion reactions. – EM dissociation for ion-ion collisions • High energy elastic scattering: new Coherent_elastic model – requires a new data set for elastic scattering data (provided) • Diverse – new m- nuclear absorption code – Improved fast radioactive decay code – GNASH 2 transition probabilities now available from exciton precompound model 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 37
 Hadronics: Cross Sections & Scattering • Cross sections: – Newest pion scattering data ‘Barashenkov’, remove discontinuities – Fix in high energy p-H cross-sections (G 3 legacy bug) – Ion-ion cross-sections • Tripathi's systematics for ion-ion cross-sections for light ions • Parameterizations from Shiver, Kox and Shen • Scattering term – extended for nucleon induced reactions to 8 Ge. V – included s-wave absorption – pion induced reactions (up to 1. 5 Ge. V) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 38
Hadronics: Cross Sections & Scattering • Cross sections: – Newest pion scattering data ‘Barashenkov’, remove discontinuities – Fix in high energy p-H cross-sections (G 3 legacy bug) – Ion-ion cross-sections • Tripathi's systematics for ion-ion cross-sections for light ions • Parameterizations from Shiver, Kox and Shen • Scattering term – extended for nucleon induced reactions to 8 Ge. V – included s-wave absorption – pion induced reactions (up to 1. 5 Ge. V) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 38
 Models: Cascade energy range • Parameterized process (1997) • Chiral Invariant Phase Space decay, “CHIPS” – For g-Nucleus, p capture, string-’backend’ • First release Dec 2001 in Geant 4 4. 0 • Refinements and extension in 2002 • Bertini cascade (Dec 2002, Geant 4 5. 0) – Re-engineered from HETC by HIP • See the presentation of A Heikinen • Binary cascade model (Frankfurt, CERN) – First release for nucleon induced interactions (in G 4 5. 0) M Kosov, P Degtyarenko, JP Wellisch A Heikinen N Stepanov JPW G Folger JPW • Extensive verification suite • – See CHEP 03 presentation by D. Wright, V. Ivantchenko, . . For further details, – see the CHEP 03 presentation by J. P. Wellisch 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 39
Models: Cascade energy range • Parameterized process (1997) • Chiral Invariant Phase Space decay, “CHIPS” – For g-Nucleus, p capture, string-’backend’ • First release Dec 2001 in Geant 4 4. 0 • Refinements and extension in 2002 • Bertini cascade (Dec 2002, Geant 4 5. 0) – Re-engineered from HETC by HIP • See the presentation of A Heikinen • Binary cascade model (Frankfurt, CERN) – First release for nucleon induced interactions (in G 4 5. 0) M Kosov, P Degtyarenko, JP Wellisch A Heikinen N Stepanov JPW G Folger JPW • Extensive verification suite • – See CHEP 03 presentation by D. Wright, V. Ivantchenko, . . For further details, – see the CHEP 03 presentation by J. P. Wellisch 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 39
 EM regression testing • Test. Em – Added check for automating regression tests • First observable: on average energy deposit • activated by UI command (in 3 of 9 tests) • Improving regression/‘acceptance’ testing 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 40
EM regression testing • Test. Em – Added check for automating regression tests • First observable: on average energy deposit • activated by UI command (in 3 of 9 tests) • Improving regression/‘acceptance’ testing 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 40
 User Interaction • Geant 4 Technical Forum (http: //cern. ch/geant 4/technical_forum) – Quarterly meeting • open to interested people – Users & developer dialog • Identify & prioritize issues • LCG ‘Physics Validation’ meeting – Comparisons with test beam data – Several new physics developments presented • We continue to emphasize identifying problems – To enable better use in large production • To solve issues seen by diverse users • Growing feedback – Requests for refinements – Problems reported (many identifying the underlying issue) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 41
User Interaction • Geant 4 Technical Forum (http: //cern. ch/geant 4/technical_forum) – Quarterly meeting • open to interested people – Users & developer dialog • Identify & prioritize issues • LCG ‘Physics Validation’ meeting – Comparisons with test beam data – Several new physics developments presented • We continue to emphasize identifying problems – To enable better use in large production • To solve issues seen by diverse users • Growing feedback – Requests for refinements – Problems reported (many identifying the underlying issue) 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 41
 Kernel: Propagation in EM Field • Transportation can keep some ‘loopers’ – From 7. 0, tracks with E > Eimportant go on for n ‘long’ steps • Default Eimportant =250 Me. V) • Ability to specialize integration accuracy v emin, emax now for each Field-Manager • Choice of Field-Manager by track v e. g. more precise for muon or for tracks E>5 Ge. V • Ability to use variant Chord-Finder (5. 2) v Can use safety, radius of curvature, other info v. For performance improvement 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 42
Kernel: Propagation in EM Field • Transportation can keep some ‘loopers’ – From 7. 0, tracks with E > Eimportant go on for n ‘long’ steps • Default Eimportant =250 Me. V) • Ability to specialize integration accuracy v emin, emax now for each Field-Manager • Choice of Field-Manager by track v e. g. more precise for muon or for tracks E>5 Ge. V • Ability to use variant Chord-Finder (5. 2) v Can use safety, radius of curvature, other info v. For performance improvement 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 42
 Kernel: summary Development • • Modular Run Manager Better HEPMC input Abstract Navigator New Biasing – Biasing: “weight-window” technique Refinements • General Particle Source – Design iteration • Improvements Navigator: • New ‘check mode’ • better verbosity Fixes • Corrected ‘safety’ in solids – Addressed propagation & photon problems • • Integration of motion in field – Enabled tuning of accuracy parameters • for particle type, Energy, … Reported by LHCb Fixes for case of missed intersections in field – purging magnet example Fixes for a 'point outside' problem seen in solids – 14 December 2005 View of Atlas toroid Courtesy of Atlas problem in displacement in field J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 43
Kernel: summary Development • • Modular Run Manager Better HEPMC input Abstract Navigator New Biasing – Biasing: “weight-window” technique Refinements • General Particle Source – Design iteration • Improvements Navigator: • New ‘check mode’ • better verbosity Fixes • Corrected ‘safety’ in solids – Addressed propagation & photon problems • • Integration of motion in field – Enabled tuning of accuracy parameters • for particle type, Energy, … Reported by LHCb Fixes for case of missed intersections in field – purging magnet example Fixes for a 'point outside' problem seen in solids – 14 December 2005 View of Atlas toroid Courtesy of Atlas problem in displacement in field J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 43
 Debugging geometries • It is easy to create overlapping volumes – During tracking Geant 4 does not check for malformed geometries • The problem of detecting ‘significant’ overlaps is now addressed by – DAVID intersects graphics volumes • Created by S. Tanaka, released ca 1997 – Commands to run verification tests • • Created by DC Williams; released in 4. 0 New capabilities added in 5. 2 (June 2003) – New example with full tracking / navigation • Created by M Liendl (CMS); released in 5. 0 Thanks to S. Tanaka 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 44
Debugging geometries • It is easy to create overlapping volumes – During tracking Geant 4 does not check for malformed geometries • The problem of detecting ‘significant’ overlaps is now addressed by – DAVID intersects graphics volumes • Created by S. Tanaka, released ca 1997 – Commands to run verification tests • • Created by DC Williams; released in 4. 0 New capabilities added in 5. 2 (June 2003) – New example with full tracking / navigation • Created by M Liendl (CMS); released in 5. 0 Thanks to S. Tanaka 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 44
 Kernel Changes for 7. 0 Several changes in kernel are planned for the 7. 0 release. In order of the effects: • New scheme of storing/retrieving physics tables – Enables user to read a portion & generate the rest • New particle “unknown” and new process “unknown decay” – For particles whose physics is not simulated, we now create – Enables full decay chains to be treated uniformly • New dedicated class for user step limitation – Separating step length limitation and track killing • Possibility of altering detector sensitivity with the parameterized volume – Categories affected: Tracking, Track, Processes/transportation • New design of particles, replacing static-singletons – Under discussion: may affect code that creates physics processes. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 45
Kernel Changes for 7. 0 Several changes in kernel are planned for the 7. 0 release. In order of the effects: • New scheme of storing/retrieving physics tables – Enables user to read a portion & generate the rest • New particle “unknown” and new process “unknown decay” – For particles whose physics is not simulated, we now create – Enables full decay chains to be treated uniformly • New dedicated class for user step limitation – Separating step length limitation and track killing • Possibility of altering detector sensitivity with the parameterized volume – Categories affected: Tracking, Track, Processes/transportation • New design of particles, replacing static-singletons – Under discussion: may affect code that creates physics processes. 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 45
 ‘Platform’ changes • OS / compiler ‘movement’ – Newly supported (June 2004) • gcc 3. 2. 3 on Linux (RH 7. 3 & SLC 3) • Visual C++. net 7. 1 on Windows XP – Emerging platforms (‘verified’) • Mac. Os 10. 3 with gcc 3. 3 • icc 8. 0 (IA-32 & IA-64) – Checking for porting • Latest gcc: 3. 3. 3 and now 3. 4 – Dropped end-2003: egcs – To drop end-2004: gcc 2. 95. 2 & Vis C++ 6 14 December 2005 • Enabled shared-library mechanism for Windows – With 6. 2, end-June 2004 – Request of LHCb Goal – keep up with needs user communities – Do integration testing on at least 3 platforms • Not more than 5, if possible J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 46
‘Platform’ changes • OS / compiler ‘movement’ – Newly supported (June 2004) • gcc 3. 2. 3 on Linux (RH 7. 3 & SLC 3) • Visual C++. net 7. 1 on Windows XP – Emerging platforms (‘verified’) • Mac. Os 10. 3 with gcc 3. 3 • icc 8. 0 (IA-32 & IA-64) – Checking for porting • Latest gcc: 3. 3. 3 and now 3. 4 – Dropped end-2003: egcs – To drop end-2004: gcc 2. 95. 2 & Vis C++ 6 14 December 2005 • Enabled shared-library mechanism for Windows – With 6. 2, end-June 2004 – Request of LHCb Goal – keep up with needs user communities – Do integration testing on at least 3 platforms • Not more than 5, if possible J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 46
 Upcoming Releases • Developments available – In monthly development tags – In open b releases each quarter • Except if there is a scheduled or consolidating minor release. • Upcoming releases – ‘Scheduled’ major release Geant 4 7. 0 in mid-December • New developments • Improvements and other refinements • Any fixes, further performance improvements. – 2004 work items & planned release contents • At URL http: //cern. ch/geant 4/source/planned_features. html • Started from requirements and requests of users/experiments 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 47
Upcoming Releases • Developments available – In monthly development tags – In open b releases each quarter • Except if there is a scheduled or consolidating minor release. • Upcoming releases – ‘Scheduled’ major release Geant 4 7. 0 in mid-December • New developments • Improvements and other refinements • Any fixes, further performance improvements. – 2004 work items & planned release contents • At URL http: //cern. ch/geant 4/source/planned_features. html • Started from requirements and requests of users/experiments 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 47
 Established new releases & new features • Established releases – End of June (minor release) – End of December (major release) • Planning the new activities for 2004 – taking into consideration requirements of all users including those from LHC experiments / LCG – Users’ Technical Forum at CERN • February 5 th, 15: 00 -17: 30 • Requirements collection and first-level prioritization 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 48
Established new releases & new features • Established releases – End of June (minor release) – End of December (major release) • Planning the new activities for 2004 – taking into consideration requirements of all users including those from LHC experiments / LCG – Users’ Technical Forum at CERN • February 5 th, 15: 00 -17: 30 • Requirements collection and first-level prioritization 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 48
 • Geant 4 is evolving – Feedback from HEP experiments, and users in medical, space domains. – Regular Users’ Technical Forum meetings to collect/sort requirements and prioritise 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 49
• Geant 4 is evolving – Feedback from HEP experiments, and users in medical, space domains. – Regular Users’ Technical Forum meetings to collect/sort requirements and prioritise 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 49
 Part II: The ‘Kernel’ New developments & improvements in Geometry, Tracking, Run & Event handling 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
Part II: The ‘Kernel’ New developments & improvements in Geometry, Tracking, Run & Event handling 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting
 Kernel: Geometry • Describing model geometries – Solids • Navigation • Field propagation • Active areas – Additional checking of navigation & model geometry – Abstraction of G 4 Navigator – Solids: • Revision of surface normals (booleans) • New shapes (twisted solids, ellipsoidal solids) – New volume types • Refinement/extensions to parameterised volumes – Optimisation of field propagation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 51
Kernel: Geometry • Describing model geometries – Solids • Navigation • Field propagation • Active areas – Additional checking of navigation & model geometry – Abstraction of G 4 Navigator – Solids: • Revision of surface normals (booleans) • New shapes (twisted solids, ellipsoidal solids) – New volume types • Refinement/extensions to parameterised volumes – Optimisation of field propagation 14 December 2005 J Apostolakis for G 4/SFT team - EUDET NA 2 brainstorming meeting 51
 Variance reduction • Importance biasing: – Splitting/Russian roulette (G 4 4. 1, June 2002). M Dressel – Importance values for a volume • In the ‘mass’ geometry or in a dedicated ‘parallel’ geometry. – Used for shielding (speedup demonstrated) – Limited in case of fields to ‘mass’ geometry • To be addressed via ‘coupled’ parallel navigation • Other ‘general’ methods (eg forced interaction) – Some existing, for G 4/SFT team - development meeting others in EUDET NA 2 brainstorming J Apostolakis 14 December 2005 N. Kanaya 52
Variance reduction • Importance biasing: – Splitting/Russian roulette (G 4 4. 1, June 2002). M Dressel – Importance values for a volume • In the ‘mass’ geometry or in a dedicated ‘parallel’ geometry. – Used for shielding (speedup demonstrated) – Limited in case of fields to ‘mass’ geometry • To be addressed via ‘coupled’ parallel navigation • Other ‘general’ methods (eg forced interaction) – Some existing, for G 4/SFT team - development meeting others in EUDET NA 2 brainstorming J Apostolakis 14 December 2005 N. Kanaya 52


