e220780637ac7f698c5bdb49d231c4ab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Gates automation
Gates automation
 Summary § Choosing the appropriate model § Faac Product Range (Swing gates)
Summary § Choosing the appropriate model § Faac Product Range (Swing gates)
 Choosing the appropriate model When selecting the type of operator, you need to take into account the following: The width and height of the gates. The construction of the gate i. e. open bar, mesh, palisade, close boarded etc. The duty cycle required. How many times an hour are the gates likely to be used?
Choosing the appropriate model When selecting the type of operator, you need to take into account the following: The width and height of the gates. The construction of the gate i. e. open bar, mesh, palisade, close boarded etc. The duty cycle required. How many times an hour are the gates likely to be used?
 Choosing the appropriate model The status of the gate structure has a direct influence on the automation safety and reliability The leaves must be suitable to be automated (stiff and sturdy structure) The operator maximum leaf length must comply with the gate features The leaves must move evenly and smoothly, without irregular frictions over the entire route The hinges must be in good conditions It is important to take in account the requested duty cycle The mechanical travel limit presence is mandatory
Choosing the appropriate model The status of the gate structure has a direct influence on the automation safety and reliability The leaves must be suitable to be automated (stiff and sturdy structure) The operator maximum leaf length must comply with the gate features The leaves must move evenly and smoothly, without irregular frictions over the entire route The hinges must be in good conditions It is important to take in account the requested duty cycle The mechanical travel limit presence is mandatory
 Choosing the appropriate model It is good to comply with customer requests if technically possible, otherwise it is advisable to suggest the most suitable technical solution You must choose underground operators: - When it is not possible to respect the install quotes - When the requested opening angle is more than 120° - When it isn’t possible to cut a niche into the post - When there isn’t enough space behind the leaves to install external operators - When the gate appearance must remain unchanged
Choosing the appropriate model It is good to comply with customer requests if technically possible, otherwise it is advisable to suggest the most suitable technical solution You must choose underground operators: - When it is not possible to respect the install quotes - When the requested opening angle is more than 120° - When it isn’t possible to cut a niche into the post - When there isn’t enough space behind the leaves to install external operators - When the gate appearance must remain unchanged
 Choosing the appropriate model The electromechanical operator design and content A motor coupled with a worm gear through a bevel gear A trolley, integral with the leaf, which moves along the worm gear as it rotates, thus transmitting the movement to the leaf (i. e. S 418, 413) In certain cases the leaf is fixed on a shaft which extends or retracts as the worm gear is rotating (i. e. 412, 415)
Choosing the appropriate model The electromechanical operator design and content A motor coupled with a worm gear through a bevel gear A trolley, integral with the leaf, which moves along the worm gear as it rotates, thus transmitting the movement to the leaf (i. e. S 418, 413) In certain cases the leaf is fixed on a shaft which extends or retracts as the worm gear is rotating (i. e. 412, 415)
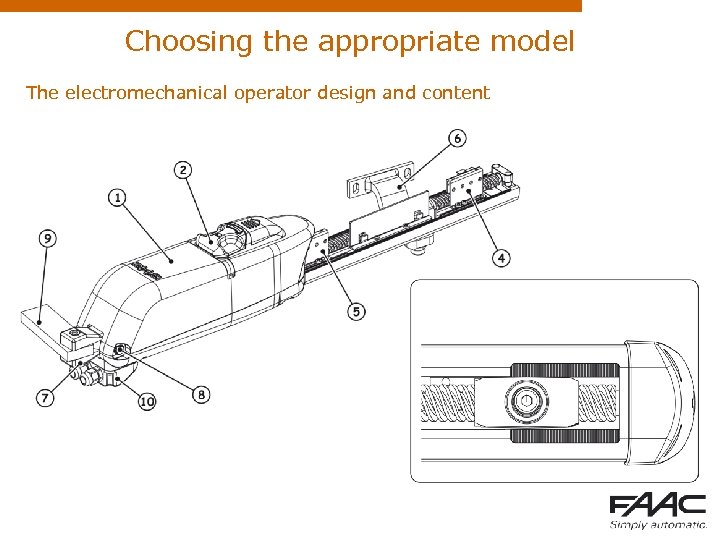 Choosing the appropriate model The electromechanical operator design and content
Choosing the appropriate model The electromechanical operator design and content
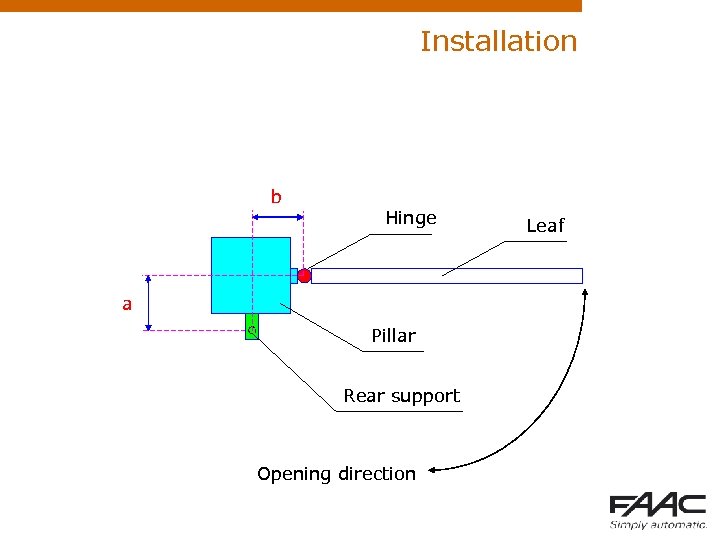 Installation b Hinge a Pillar Rear support Opening direction Leaf
Installation b Hinge a Pillar Rear support Opening direction Leaf
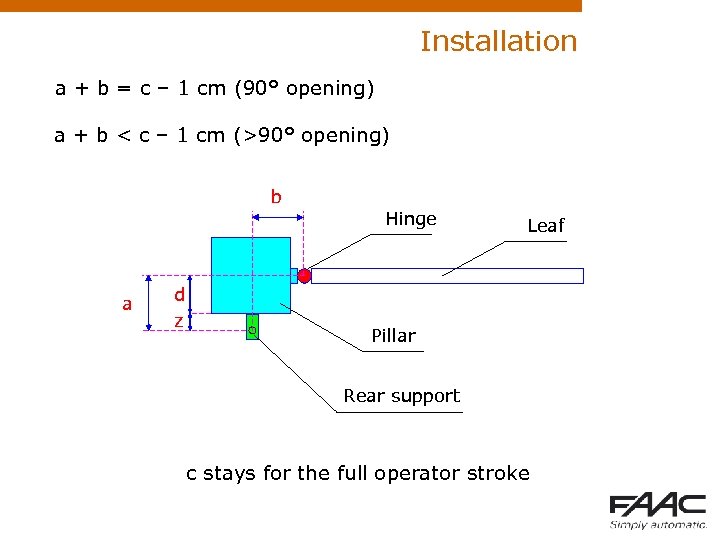 Installation a + b = c – 1 cm (90° opening) a + b < c – 1 cm (>90° opening) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support c stays for the full operator stroke
Installation a + b = c – 1 cm (90° opening) a + b < c – 1 cm (>90° opening) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support c stays for the full operator stroke
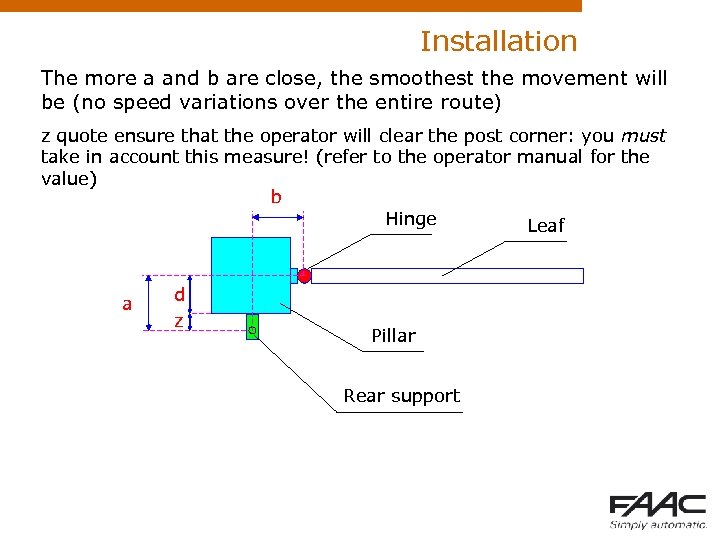 Installation The more a and b are close, the smoothest the movement will be (no speed variations over the entire route) z quote ensure that the operator will clear the post corner: you must take in account this measure! (refer to the operator manual for the value) b Hinge Leaf a d z Pillar Rear support
Installation The more a and b are close, the smoothest the movement will be (no speed variations over the entire route) z quote ensure that the operator will clear the post corner: you must take in account this measure! (refer to the operator manual for the value) b Hinge Leaf a d z Pillar Rear support
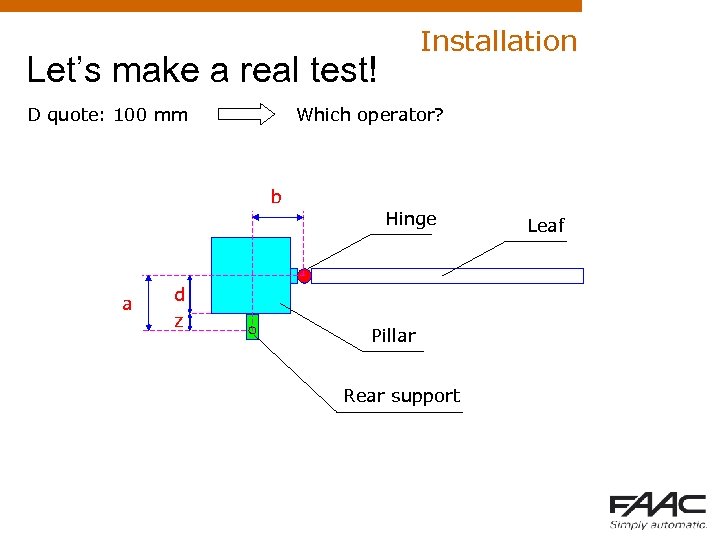 Installation Let’s make a real test! D quote: 100 mm Which operator? b a d z Hinge Pillar Rear support Leaf
Installation Let’s make a real test! D quote: 100 mm Which operator? b a d z Hinge Pillar Rear support Leaf
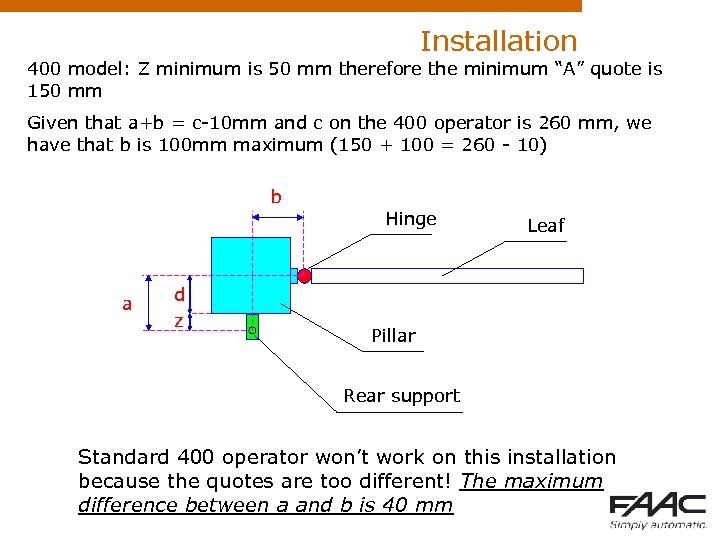 Installation 400 model: Z minimum is 50 mm therefore the minimum “A” quote is 150 mm Given that a+b = c-10 mm and c on the 400 operator is 260 mm, we have that b is 100 mm maximum (150 + 100 = 260 - 10) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support Standard 400 operator won’t work on this installation because the quotes are too different! The maximum difference between a and b is 40 mm
Installation 400 model: Z minimum is 50 mm therefore the minimum “A” quote is 150 mm Given that a+b = c-10 mm and c on the 400 operator is 260 mm, we have that b is 100 mm maximum (150 + 100 = 260 - 10) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support Standard 400 operator won’t work on this installation because the quotes are too different! The maximum difference between a and b is 40 mm
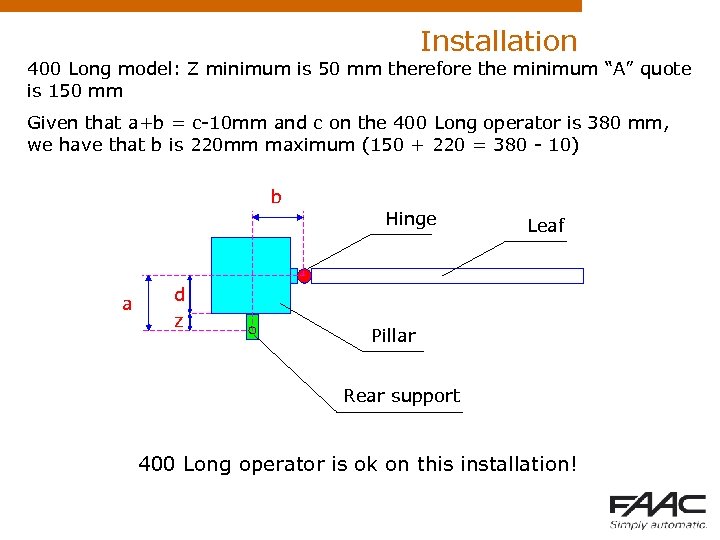 Installation 400 Long model: Z minimum is 50 mm therefore the minimum “A” quote is 150 mm Given that a+b = c-10 mm and c on the 400 Long operator is 380 mm, we have that b is 220 mm maximum (150 + 220 = 380 - 10) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support 400 Long operator is ok on this installation!
Installation 400 Long model: Z minimum is 50 mm therefore the minimum “A” quote is 150 mm Given that a+b = c-10 mm and c on the 400 Long operator is 380 mm, we have that b is 220 mm maximum (150 + 220 = 380 - 10) b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support 400 Long operator is ok on this installation!
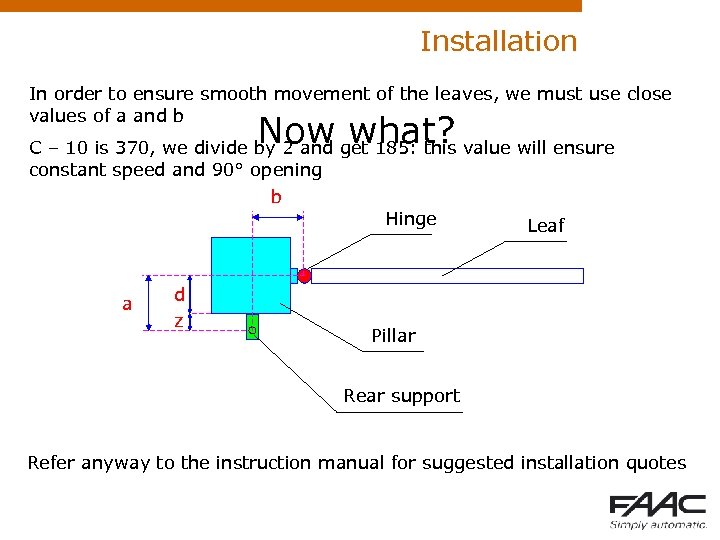 Installation In order to ensure smooth movement of the leaves, we must use close values of a and b Now what? C – 10 is 370, we divide by 2 and get 185: this value will ensure constant speed and 90° opening b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support Refer anyway to the instruction manual for suggested installation quotes
Installation In order to ensure smooth movement of the leaves, we must use close values of a and b Now what? C – 10 is 370, we divide by 2 and get 185: this value will ensure constant speed and 90° opening b a d z Hinge Leaf Pillar Rear support Refer anyway to the instruction manual for suggested installation quotes
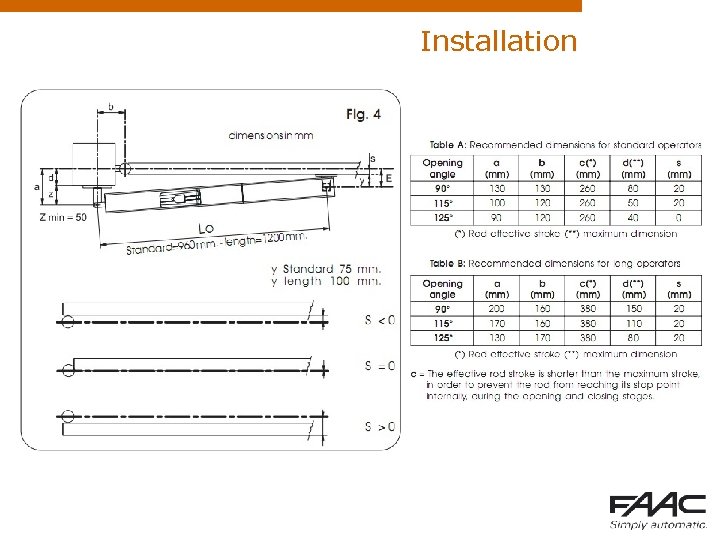 Installation
Installation
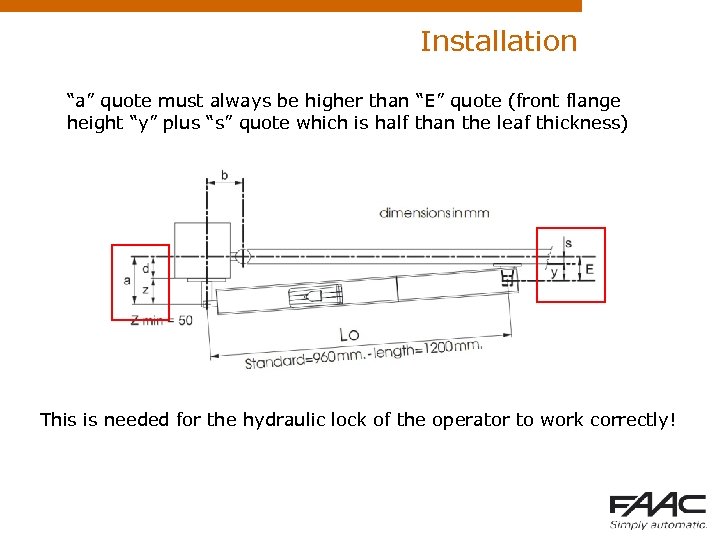 Installation “a” quote must always be higher than “E” quote (front flange height “y” plus “s” quote which is half than the leaf thickness) This is needed for the hydraulic lock of the operator to work correctly!
Installation “a” quote must always be higher than “E” quote (front flange height “y” plus “s” quote which is half than the leaf thickness) This is needed for the hydraulic lock of the operator to work correctly!
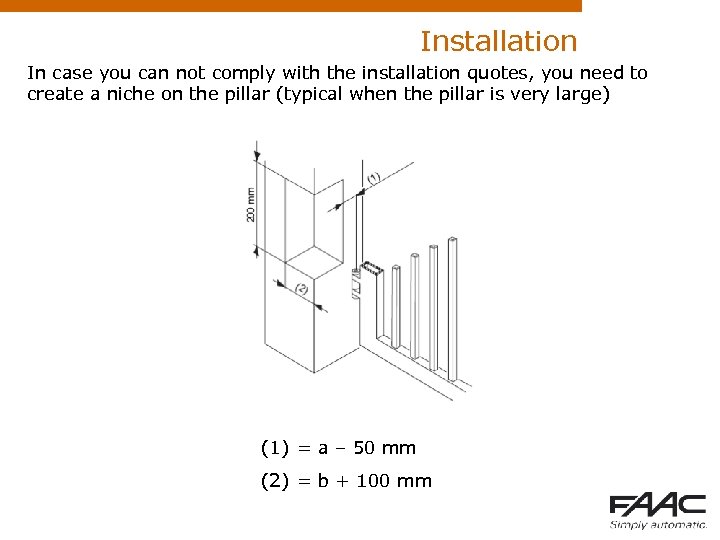 Installation In case you can not comply with the installation quotes, you need to create a niche on the pillar (typical when the pillar is very large) (1) = a – 50 mm (2) = b + 100 mm
Installation In case you can not comply with the installation quotes, you need to create a niche on the pillar (typical when the pillar is very large) (1) = a – 50 mm (2) = b + 100 mm
 Installation In case you can not comply with the installation quotes, and you can’t create the niche, you may install an electromechanical, articulated arm operator, or an underground operator (electromechanical or hydraulic)
Installation In case you can not comply with the installation quotes, and you can’t create the niche, you may install an electromechanical, articulated arm operator, or an underground operator (electromechanical or hydraulic)
 Troubleshooting Common problems to be solved -The gate moves slowly -The gate moves by jerks -The gate is not opening -The motors run but the gate doesn’t move -The leaves stop during the slowdown phase
Troubleshooting Common problems to be solved -The gate moves slowly -The gate moves by jerks -The gate is not opening -The motors run but the gate doesn’t move -The leaves stop during the slowdown phase
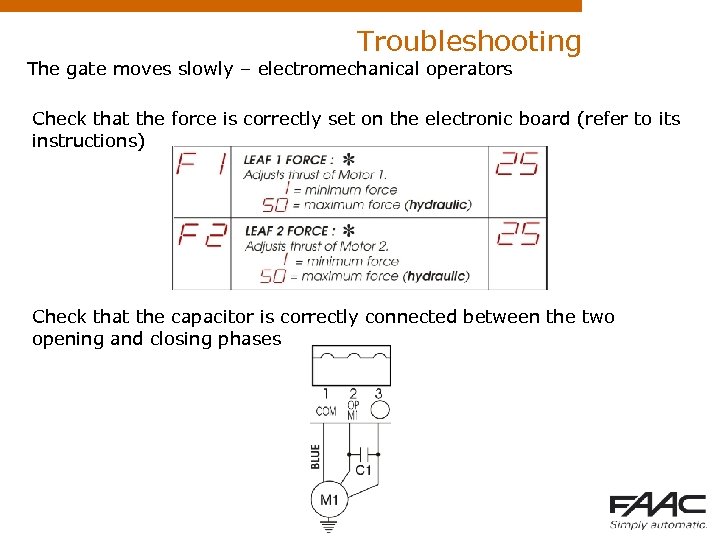 Troubleshooting The gate moves slowly – electromechanical operators Check that the force is correctly set on the electronic board (refer to its instructions) Check that the capacitor is correctly connected between the two opening and closing phases
Troubleshooting The gate moves slowly – electromechanical operators Check that the force is correctly set on the electronic board (refer to its instructions) Check that the capacitor is correctly connected between the two opening and closing phases
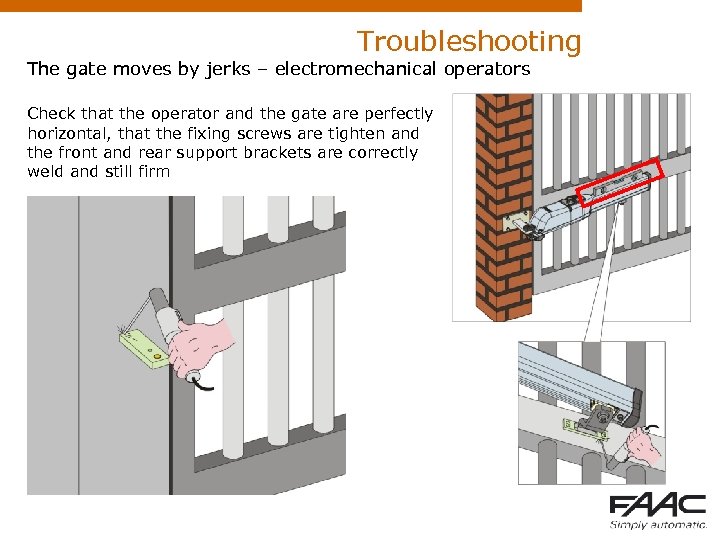 Troubleshooting The gate moves by jerks – electromechanical operators Check that the operator and the gate are perfectly horizontal, that the fixing screws are tighten and the front and rear support brackets are correctly weld and still firm
Troubleshooting The gate moves by jerks – electromechanical operators Check that the operator and the gate are perfectly horizontal, that the fixing screws are tighten and the front and rear support brackets are correctly weld and still firm
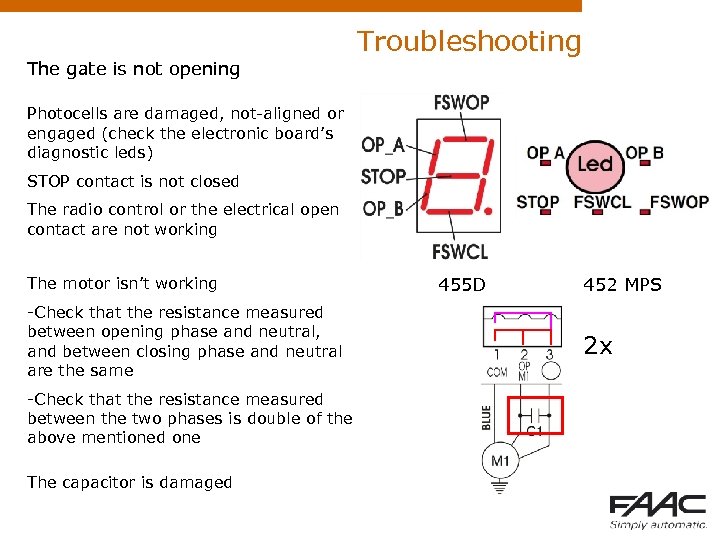 Troubleshooting The gate is not opening Photocells are damaged, not-aligned or engaged (check the electronic board’s diagnostic leds) STOP contact is not closed The radio control or the electrical open contact are not working The motor isn’t working -Check that the resistance measured between opening phase and neutral, and between closing phase and neutral are the same -Check that the resistance measured between the two phases is double of the above mentioned one The capacitor is damaged 455 D 452 MPS 2 x
Troubleshooting The gate is not opening Photocells are damaged, not-aligned or engaged (check the electronic board’s diagnostic leds) STOP contact is not closed The radio control or the electrical open contact are not working The motor isn’t working -Check that the resistance measured between opening phase and neutral, and between closing phase and neutral are the same -Check that the resistance measured between the two phases is double of the above mentioned one The capacitor is damaged 455 D 452 MPS 2 x
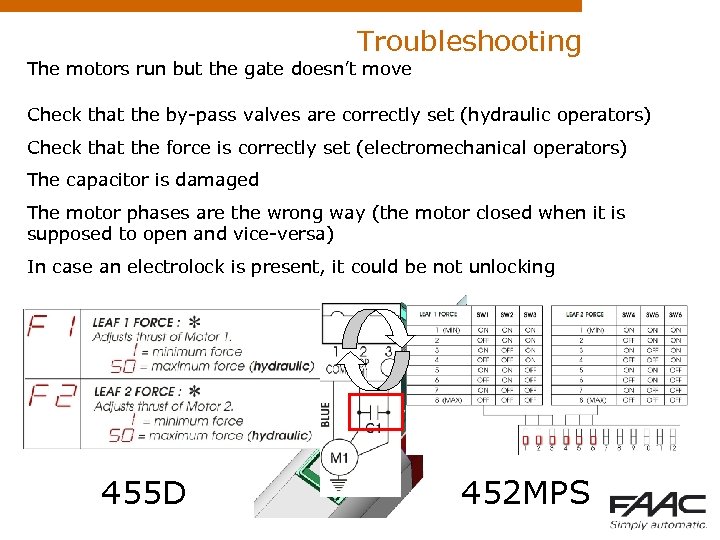 Troubleshooting The motors run but the gate doesn’t move Check that the by-pass valves are correctly set (hydraulic operators) Check that the force is correctly set (electromechanical operators) The capacitor is damaged The motor phases are the wrong way (the motor closed when it is supposed to open and vice-versa) In case an electrolock is present, it could be not unlocking 455 D 452 MPS
Troubleshooting The motors run but the gate doesn’t move Check that the by-pass valves are correctly set (hydraulic operators) Check that the force is correctly set (electromechanical operators) The capacitor is damaged The motor phases are the wrong way (the motor closed when it is supposed to open and vice-versa) In case an electrolock is present, it could be not unlocking 455 D 452 MPS
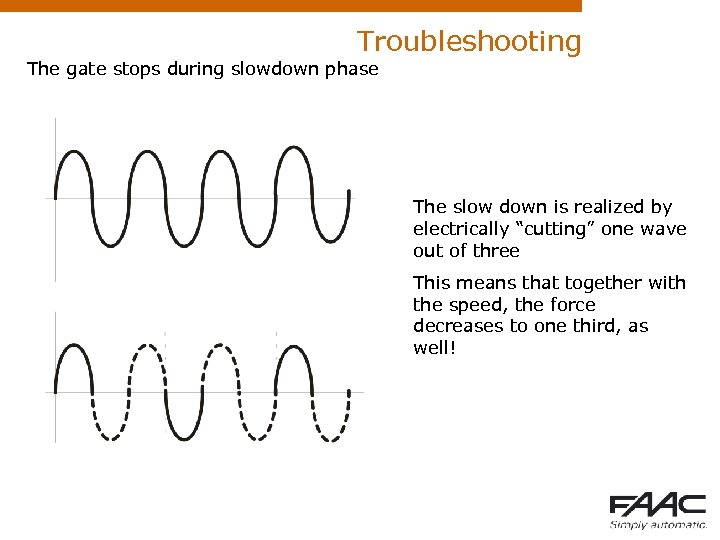 Troubleshooting The gate stops during slowdown phase The slow down is realized by electrically “cutting” one wave out of three This means that together with the speed, the force decreases to one third, as well!
Troubleshooting The gate stops during slowdown phase The slow down is realized by electrically “cutting” one wave out of three This means that together with the speed, the force decreases to one third, as well!
 Troubleshooting Basic general guidelines Do not lubricate the operator rod, nor put grease on the worm gear on electromechanical operators Always provide mechanical travel limits In case you are replacing old motors, always check the capacitor value needed for the motor or suitable for the board (some boards do not support different capacitors on the two motors)
Troubleshooting Basic general guidelines Do not lubricate the operator rod, nor put grease on the worm gear on electromechanical operators Always provide mechanical travel limits In case you are replacing old motors, always check the capacitor value needed for the motor or suitable for the board (some boards do not support different capacitors on the two motors)


