 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) Differential diagnosis
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) Differential diagnosis
 GORD you have to differentiate with: Coronary heart disease n Infectious Esophagitis n Chemical-Induced Esophagitis n Motor disorders of esophagus n Biliary colic n Dyspepsia n
GORD you have to differentiate with: Coronary heart disease n Infectious Esophagitis n Chemical-Induced Esophagitis n Motor disorders of esophagus n Biliary colic n Dyspepsia n
 Coronary heart disease Differential diagnosis is difficult because the incidence of both GORD and coronary artery disease rises with age and body inactivity and these conditions may coexist and influence each other. For example, GORD can cause a drop in blood pressure and a rise in heart rate, which in turn may lead to angina pectoris and electrocardiographic changes. Some patients have both diseases.
Coronary heart disease Differential diagnosis is difficult because the incidence of both GORD and coronary artery disease rises with age and body inactivity and these conditions may coexist and influence each other. For example, GORD can cause a drop in blood pressure and a rise in heart rate, which in turn may lead to angina pectoris and electrocardiographic changes. Some patients have both diseases.
 The characteristics of PAIN n n n Gord depends on the position of the body (occur in a horizontal position and bending the torso) associated with food intake eliminates by taking antisecretory drugs n n n CHD appears suddenly appears during physical exertion appears during emotional stress after meals disappears at the termination of exercise or taking a shortacting nitrate
The characteristics of PAIN n n n Gord depends on the position of the body (occur in a horizontal position and bending the torso) associated with food intake eliminates by taking antisecretory drugs n n n CHD appears suddenly appears during physical exertion appears during emotional stress after meals disappears at the termination of exercise or taking a shortacting nitrate
 Previously existing diseases of cardiovascular system or gastrointestinal tract Gord Suffered from gasritis, there was a hiatal hernia, other diseases causing increased pressure in the abdominal cavity CHD Hypertension, obesity, existing angina
Previously existing diseases of cardiovascular system or gastrointestinal tract Gord Suffered from gasritis, there was a hiatal hernia, other diseases causing increased pressure in the abdominal cavity CHD Hypertension, obesity, existing angina
 GORD and Coronary heart disease • • n n Electrocardiogram Endoscopy x-ray of esophagus 24 -hour ambulatory esophageal p. H monitoring esophageal manometry provocative testing
GORD and Coronary heart disease • • n n Electrocardiogram Endoscopy x-ray of esophagus 24 -hour ambulatory esophageal p. H monitoring esophageal manometry provocative testing
 Infectious Esophagitis the most common- Candida esophagitis n odynophagia, retrosternal chest pain and/or dysphagia n The typical endoscopic appearance is the presence of small raised whitish plaques n
Infectious Esophagitis the most common- Candida esophagitis n odynophagia, retrosternal chest pain and/or dysphagia n The typical endoscopic appearance is the presence of small raised whitish plaques n
 Chemical-Induced Esophagitis Antibiotic- doxycycline n Anticholinergic- emepronium bromide n Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs n slow-release forms of potassium chloride n bisphonate alendronate sodium n
Chemical-Induced Esophagitis Antibiotic- doxycycline n Anticholinergic- emepronium bromide n Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs n slow-release forms of potassium chloride n bisphonate alendronate sodium n
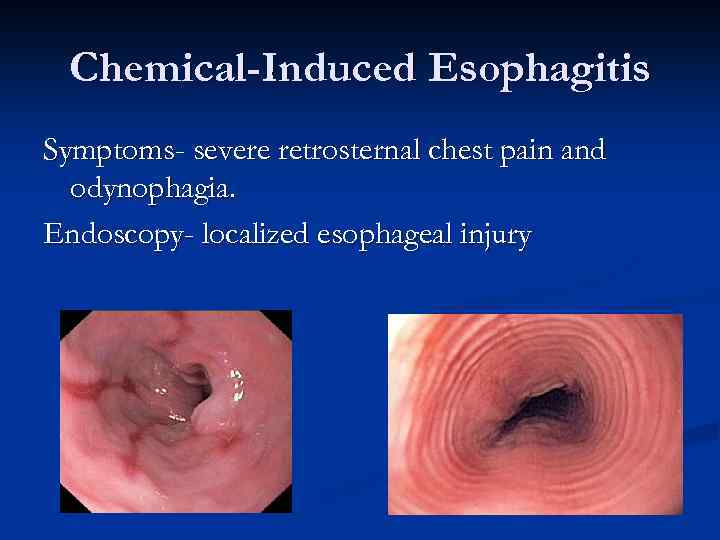 Chemical-Induced Esophagitis Symptoms- severe retrosternal chest pain and odynophagia. Endoscopy- localized esophageal injury
Chemical-Induced Esophagitis Symptoms- severe retrosternal chest pain and odynophagia. Endoscopy- localized esophageal injury
 Biliary colic Pain behind the breastbone n The gold standard imaging modality for the presence of gallstones is ultrasound of the right upper quadrant. n
Biliary colic Pain behind the breastbone n The gold standard imaging modality for the presence of gallstones is ultrasound of the right upper quadrant. n