826bae0ed6f5d8a0d936f7fae6c5a9dd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Gas Dynamics, AGN, Star Formation and ISM in Nearby Galaxies Eva Schinnerer (MPIA) S. Haan, F. Combes, S. Garcia-Burillo, C. G. Mundell, T. Böker, D. S. Meier , E. Emsellem, U. Lisenfeld, D. Downes, D. Calzetti
Gas Dynamics, AGN, Star Formation and ISM in Nearby Galaxies Eva Schinnerer (MPIA) S. Haan, F. Combes, S. Garcia-Burillo, C. G. Mundell, T. Böker, D. S. Meier , E. Emsellem, U. Lisenfeld, D. Downes, D. Calzetti
 ISM in Nearby Galaxies Why do we care? Neutral Gas (Atomic & Molecular) fuel feedback Star Formation (SF) Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Gas Kinematics & ISM Properties PDRs -- Photon Dominated Regions XDRs -- X-ray Dominated Regions Shocks
ISM in Nearby Galaxies Why do we care? Neutral Gas (Atomic & Molecular) fuel feedback Star Formation (SF) Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Gas Kinematics & ISM Properties PDRs -- Photon Dominated Regions XDRs -- X-ray Dominated Regions Shocks
 Gas Kinematics Outer disk Main Drivers Spiral Arms (i. e. Density Waves) Large-scale Stellar bars Double/Inner/Nuclear Bars nuclear Spiral Density Waves center Fueling nearby AGNs (e. g. NUGA - see talk by M. Krips): m=1 modes warps viscosity …
Gas Kinematics Outer disk Main Drivers Spiral Arms (i. e. Density Waves) Large-scale Stellar bars Double/Inner/Nuclear Bars nuclear Spiral Density Waves center Fueling nearby AGNs (e. g. NUGA - see talk by M. Krips): m=1 modes warps viscosity …
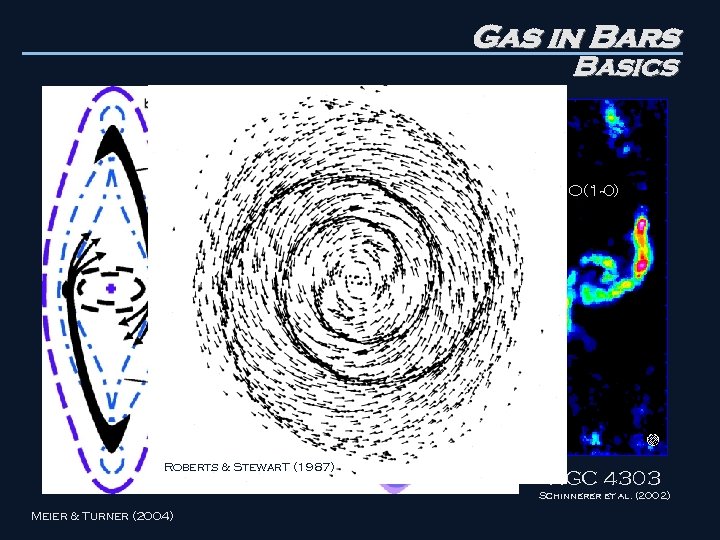 Gas in Bars Basics CO(1 -0) 2 1 Roberts & Stewar. T (1987) NGC 4303 Schinnerer et al. (2002) Meier & Turner (2004)
Gas in Bars Basics CO(1 -0) 2 1 Roberts & Stewar. T (1987) NGC 4303 Schinnerer et al. (2002) Meier & Turner (2004)
 HI-NUGA Gas Dynamics Over the Entire Disk VLA HI Survey of 16 Nearby Active Galaxies AIM: Trace Gas Flow from Outer Disk to Very Center S. Haan, Ph. D Thesis
HI-NUGA Gas Dynamics Over the Entire Disk VLA HI Survey of 16 Nearby Active Galaxies AIM: Trace Gas Flow from Outer Disk to Very Center S. Haan, Ph. D Thesis
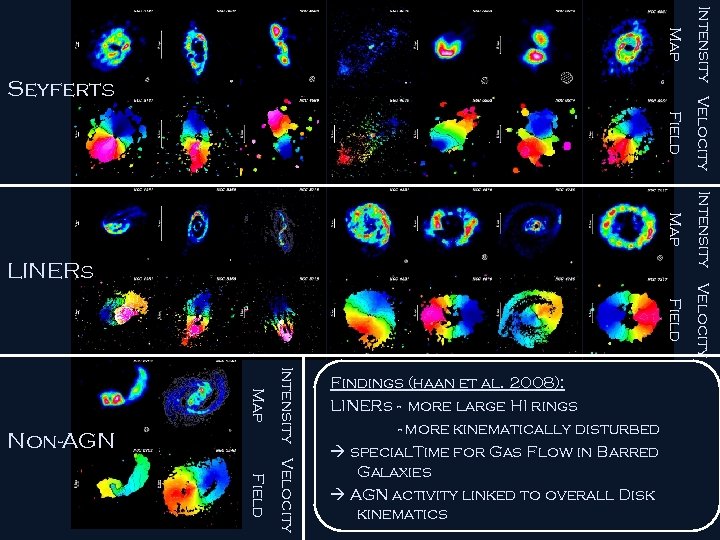 Field Intensity Velocity Map Non-AGN Findings (haan et al. 2008): LINERs - more large HI rings - more kinematically disturbed special. Time for Gas Flow in Barred Galaxies AGN activity linked to overall Disk kinematics Intensity Velocity Map LINERs Intensity Velocity Map Seyferts
Field Intensity Velocity Map Non-AGN Findings (haan et al. 2008): LINERs - more large HI rings - more kinematically disturbed special. Time for Gas Flow in Barred Galaxies AGN activity linked to overall Disk kinematics Intensity Velocity Map LINERs Intensity Velocity Map Seyferts
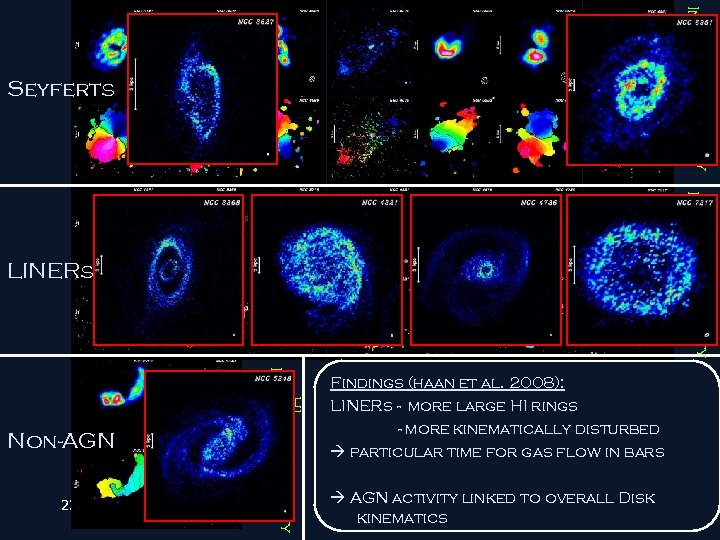 Field 22. Jan. 2008 HI Velocity Intensity Map Non-AGN Findings (haan et al. 2008): LINERs - more large HI rings - more kinematically disturbed particular time for gas flow in bars AGN activity linked to overall Disk kinematics HI Velocity Intensity Map LINERs HI Velocity Intensity Map Seyferts
Field 22. Jan. 2008 HI Velocity Intensity Map Non-AGN Findings (haan et al. 2008): LINERs - more large HI rings - more kinematically disturbed particular time for gas flow in bars AGN activity linked to overall Disk kinematics HI Velocity Intensity Map LINERs HI Velocity Intensity Map Seyferts
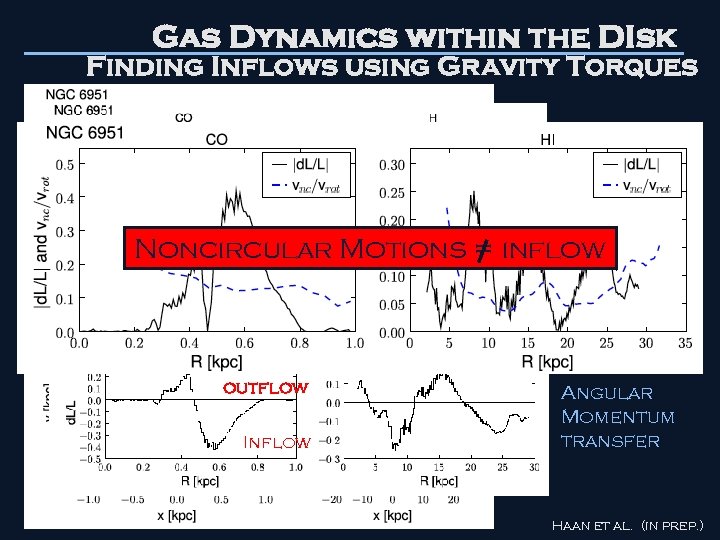 Gas Dynamics within the DIsk Finding Inflows using Gravity Torques Stellar Potential Noncircular Motions = Torque Maps Show inflow In/Outflow Gas Distribution outflow Inflow Angular Momentum transfer Haan et al. (in prep. )
Gas Dynamics within the DIsk Finding Inflows using Gravity Torques Stellar Potential Noncircular Motions = Torque Maps Show inflow In/Outflow Gas Distribution outflow Inflow Angular Momentum transfer Haan et al. (in prep. )
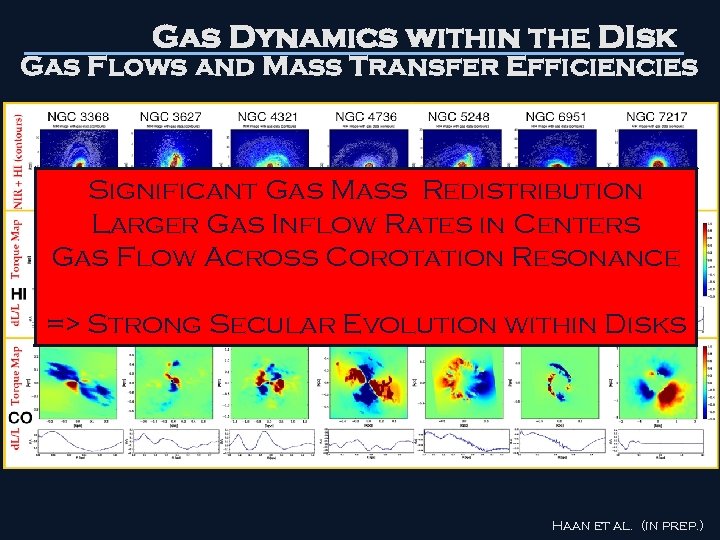 Gas Dynamics within the DIsk Gas Flows and Mass Transfer Efficiencies Significant Gas Mass Redistribution Larger Gas Inflow Rates in Centers Gas Flow Across Corotation Resonance => Strong Secular Evolution within Disks Haan et al. (in prep. )
Gas Dynamics within the DIsk Gas Flows and Mass Transfer Efficiencies Significant Gas Mass Redistribution Larger Gas Inflow Rates in Centers Gas Flow Across Corotation Resonance => Strong Secular Evolution within Disks Haan et al. (in prep. )
 NGC 6946 Central Mass Build-Up Molecular Gas Kinematics And Star Formation Tracers at High Spatial Resolution
NGC 6946 Central Mass Build-Up Molecular Gas Kinematics And Star Formation Tracers at High Spatial Resolution
 Molecular Gas at ~10 pc Resolution mm-Interferometry IRAM, Plateau de Bure High Spectral (few km/s) & Spatial (<1’’) Resolution Up-graded IRAM Plateau de Bure Interferometer: ~ 0. 3” resolution (at 1 mm) 3 x more sensitive ~ 10 x faster Multi-Line Observations --> Chemistry New Band: 2 mm
Molecular Gas at ~10 pc Resolution mm-Interferometry IRAM, Plateau de Bure High Spectral (few km/s) & Spatial (<1’’) Resolution Up-graded IRAM Plateau de Bure Interferometer: ~ 0. 3” resolution (at 1 mm) 3 x more sensitive ~ 10 x faster Multi-Line Observations --> Chemistry New Band: 2 mm
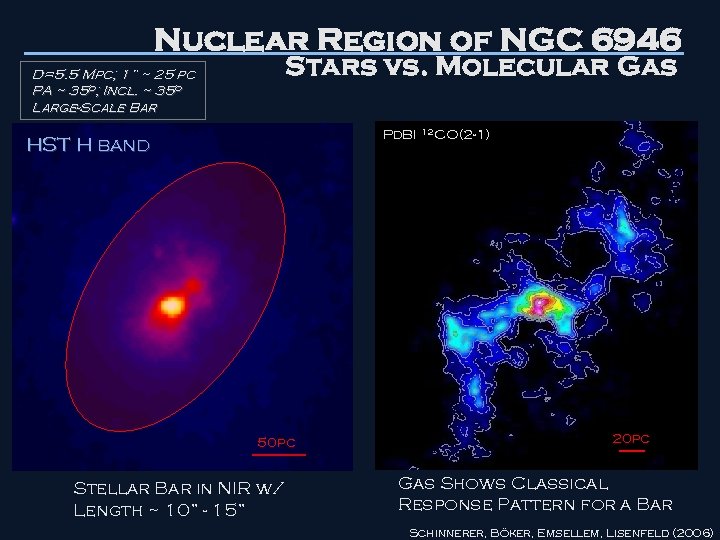 Nuclear Region of NGC 6946 Stars vs. Molecular Gas D=5. 5 Mpc; 1” ~ 25 pc PA ~ 35 o; Incl. ~ 35 o Large-Scale Bar Pd. BI 12 CO(2 -1) HST H band 50 pc Stellar Bar in NIR w/ Length ~ 10” - 15” 20 pc Gas Shows Classical Response Pattern for a Bar Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem, Lisenfeld (2006)
Nuclear Region of NGC 6946 Stars vs. Molecular Gas D=5. 5 Mpc; 1” ~ 25 pc PA ~ 35 o; Incl. ~ 35 o Large-Scale Bar Pd. BI 12 CO(2 -1) HST H band 50 pc Stellar Bar in NIR w/ Length ~ 10” - 15” 20 pc Gas Shows Classical Response Pattern for a Bar Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem, Lisenfeld (2006)
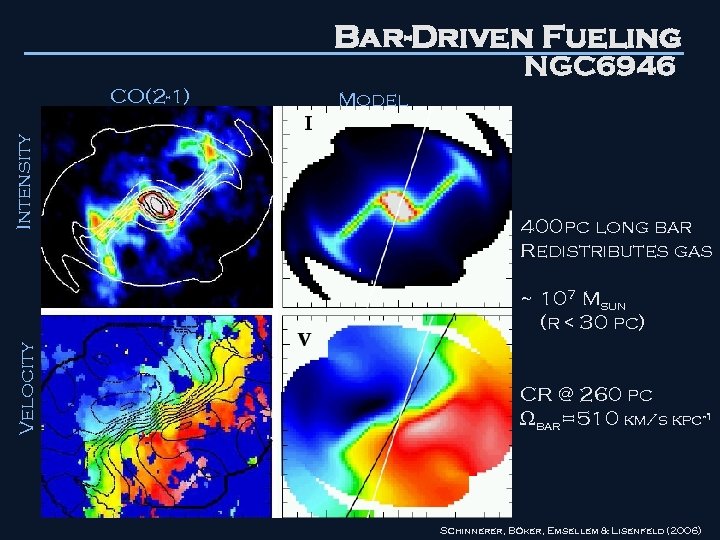 Bar-Driven Fueling NGC 6946 Intensity CO(2 -1) Model 400 pc long bar Redistributes gas Velocity ~ 107 Msun (r < 30 pc) CR @ 260 pc bar=510 km/s kpc-1 Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem & Lisenfeld (2006)
Bar-Driven Fueling NGC 6946 Intensity CO(2 -1) Model 400 pc long bar Redistributes gas Velocity ~ 107 Msun (r < 30 pc) CR @ 260 pc bar=510 km/s kpc-1 Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem & Lisenfeld (2006)
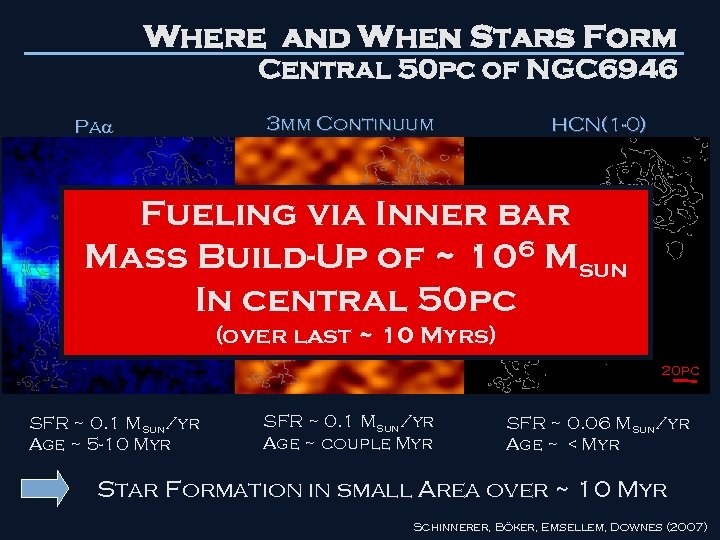 Where and When Stars Form Central 50 pc of NGC 6946 Pa 3 mm Continuum HCN(1 -0) Fueling via Inner bar Mass Build-Up of ~ 106 Msun In central 50 pc (over last ~ 10 Myrs) 20 pc SFR ~ 0. 1 Msun/yr Age ~ 5 -10 Myr SFR ~ 0. 1 Msun/yr Age ~ couple Myr SFR ~ 0. 06 Msun/yr Age ~ < Myr Star Formation in small Area over ~ 10 Myr Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem, Downes (2007)
Where and When Stars Form Central 50 pc of NGC 6946 Pa 3 mm Continuum HCN(1 -0) Fueling via Inner bar Mass Build-Up of ~ 106 Msun In central 50 pc (over last ~ 10 Myrs) 20 pc SFR ~ 0. 1 Msun/yr Age ~ 5 -10 Myr SFR ~ 0. 1 Msun/yr Age ~ couple Myr SFR ~ 0. 06 Msun/yr Age ~ < Myr Star Formation in small Area over ~ 10 Myr Schinnerer, Böker, Emsellem, Downes (2007)
 IC 342 Nuclear Fueling & Star Formation Feedback Impact of Nuclear Star Formation Onto the Gas Flow
IC 342 Nuclear Fueling & Star Formation Feedback Impact of Nuclear Star Formation Onto the Gas Flow
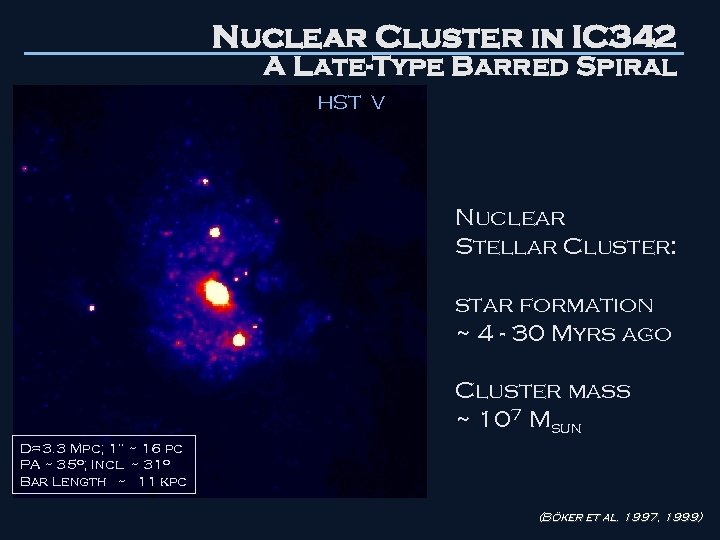 Nuclear Cluster in IC 342 A Late-Type Barred Spiral HST V Nuclear Stellar Cluster: star formation ~ 4 - 30 Myrs ago Cluster mass ~ 107 Msun D=3. 3 Mpc; 1” ~ 16 pc PA ~ 35 o; Incl. ~ 31 o Bar Length ~ 11 kpc (Böker et al. 1997, 1999)
Nuclear Cluster in IC 342 A Late-Type Barred Spiral HST V Nuclear Stellar Cluster: star formation ~ 4 - 30 Myrs ago Cluster mass ~ 107 Msun D=3. 3 Mpc; 1” ~ 16 pc PA ~ 35 o; Incl. ~ 31 o Bar Length ~ 11 kpc (Böker et al. 1997, 1999)
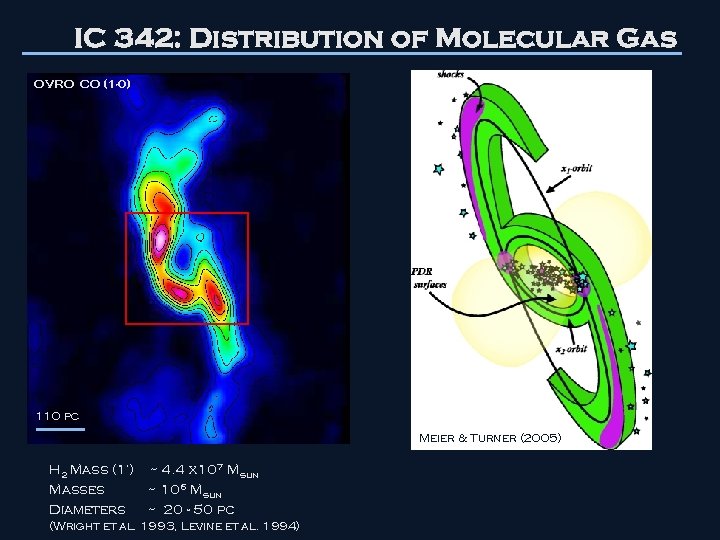 IC 342: Distribution of Molecular Gas OVRO CO (1 -0) 110 pc Meier & Turner (2005) H 2 Mass (1’) ~ 4. 4 x 107 Msun Masses ~ 106 Msun Diameters ~ 20 - 50 pc (Wright et al. 1993, Levine et al. 1994)
IC 342: Distribution of Molecular Gas OVRO CO (1 -0) 110 pc Meier & Turner (2005) H 2 Mass (1’) ~ 4. 4 x 107 Msun Masses ~ 106 Msun Diameters ~ 20 - 50 pc (Wright et al. 1993, Levine et al. 1994)
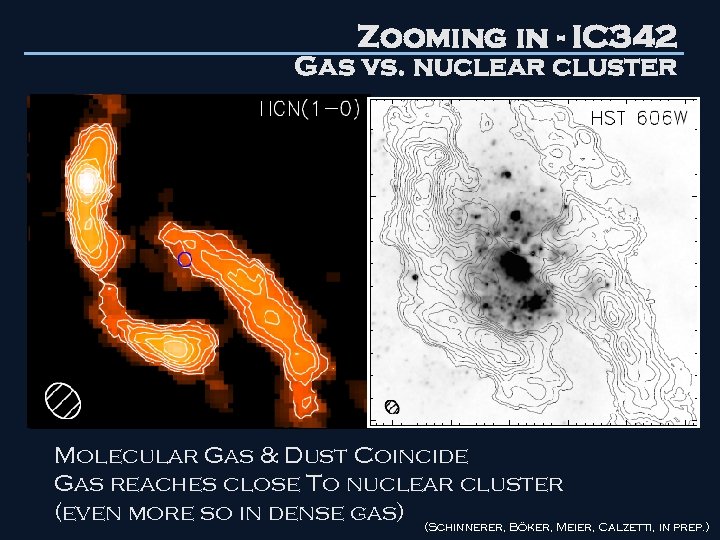 Zooming in - IC 342 Gas vs. nuclear cluster 16 pc Molecular Gas & Dust Coincide Gas reaches close To nuclear cluster (even more so in dense gas) (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
Zooming in - IC 342 Gas vs. nuclear cluster 16 pc Molecular Gas & Dust Coincide Gas reaches close To nuclear cluster (even more so in dense gas) (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
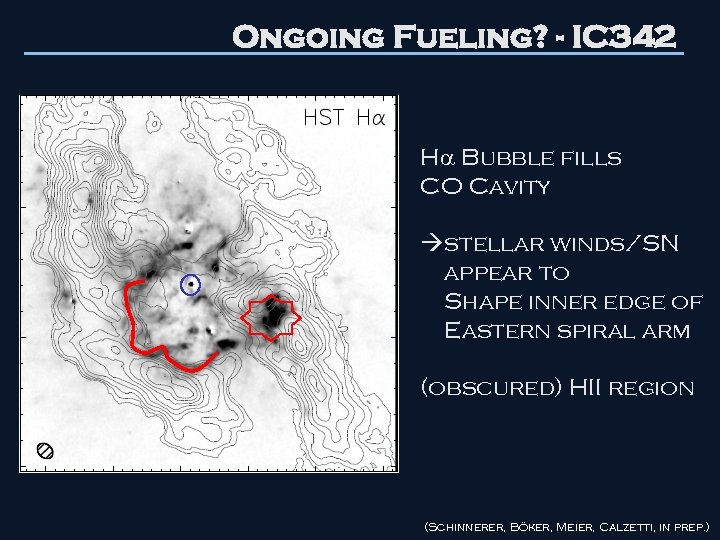 Ongoing Fueling? - IC 342 H Bubble fills CO Cavity stellar winds/SN appear to Shape inner edge of Eastern spiral arm (obscured) HII region (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
Ongoing Fueling? - IC 342 H Bubble fills CO Cavity stellar winds/SN appear to Shape inner edge of Eastern spiral arm (obscured) HII region (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
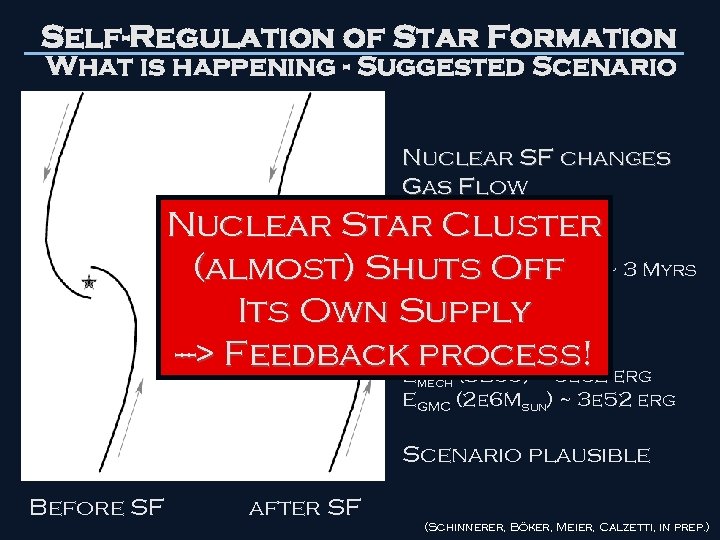 Self-Regulation of Star Formation What is happening - Suggested Scenario Nuclear SF changes Gas Flow Nuclear Star Cluster Timescales: v (15 -20 km/s): (almost) Shuts Off ~ 3 Myrs age ~ 4 -30 Myrs Its Own Supply ---> Feedback. Energies: ~ 5 e 52 erg process! E (SB 99) winds SF mech EGMC (2 e 6 Msun) ~ 3 e 52 erg Scenario plausible Before SF after SF (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
Self-Regulation of Star Formation What is happening - Suggested Scenario Nuclear SF changes Gas Flow Nuclear Star Cluster Timescales: v (15 -20 km/s): (almost) Shuts Off ~ 3 Myrs age ~ 4 -30 Myrs Its Own Supply ---> Feedback. Energies: ~ 5 e 52 erg process! E (SB 99) winds SF mech EGMC (2 e 6 Msun) ~ 3 e 52 erg Scenario plausible Before SF after SF (Schinnerer, Böker, Meier, Calzetti, in prep. )
 What’s Next: Star Formation, ISM And Gas Kinematics Molecular Gas Chemistry Utilizing Multiple Molecules
What’s Next: Star Formation, ISM And Gas Kinematics Molecular Gas Chemistry Utilizing Multiple Molecules
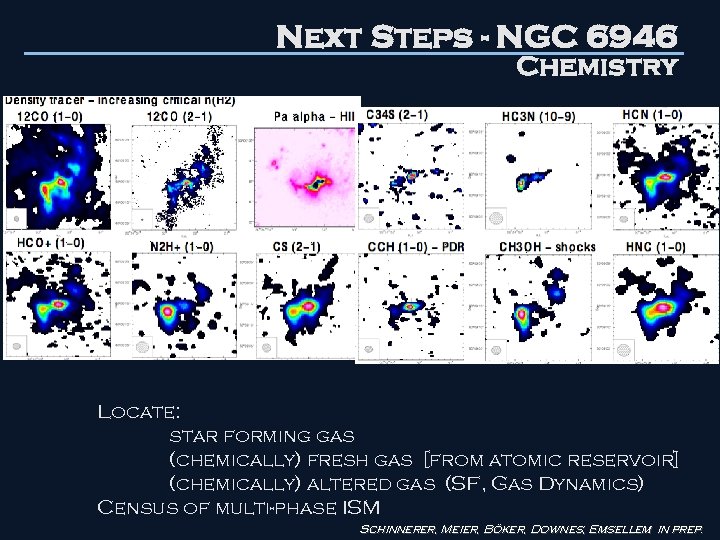 Next Steps - NGC 6946 Chemistry Locate: star forming gas (chemically) fresh gas [from atomic reservoir] (chemically) altered gas (SF, Gas Dynamics) Census of multi-phase ISM Schinnerer, Meier, Böker, Downes, Emsellem in prep.
Next Steps - NGC 6946 Chemistry Locate: star forming gas (chemically) fresh gas [from atomic reservoir] (chemically) altered gas (SF, Gas Dynamics) Census of multi-phase ISM Schinnerer, Meier, Böker, Downes, Emsellem in prep.
 (Gas) Kinematics & Star Formation Kinematics --- ionized Gas (different ISM Phase) --- Stellar Velocity Fields/Dispersion => Better Models of Kinematics (see Talk by G. Dumas) Star Formation --- History, Population, Location --- Energy Injection into ISM --- Feedback Processes
(Gas) Kinematics & Star Formation Kinematics --- ionized Gas (different ISM Phase) --- Stellar Velocity Fields/Dispersion => Better Models of Kinematics (see Talk by G. Dumas) Star Formation --- History, Population, Location --- Energy Injection into ISM --- Feedback Processes
 Summary & Conclusion Gas Kinematics --- Ongoing Gas Redistribution within Disk --- bars work (in general, Small & Large) --- Sustained Nuclear fueling for > 10 Myr Nuclear Star Formation --- can alter gas flow ALMA test facility --- self-regulated fueling => repetitive SF time-variable (models) ALMA site Future Bright: ALMA
Summary & Conclusion Gas Kinematics --- Ongoing Gas Redistribution within Disk --- bars work (in general, Small & Large) --- Sustained Nuclear fueling for > 10 Myr Nuclear Star Formation --- can alter gas flow ALMA test facility --- self-regulated fueling => repetitive SF time-variable (models) ALMA site Future Bright: ALMA



