403dfa4e4122ed10c1c280f1e1798981.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Gas Chromatography
Gas Chromatography
 Gas Chromatograph: an overview ä What is “chromatography” ä History of chromatography ä Applications ä Theory of operation ä Detectors ä Syringe technique
Gas Chromatograph: an overview ä What is “chromatography” ä History of chromatography ä Applications ä Theory of operation ä Detectors ä Syringe technique
 What is “Chromatography” “color writing” ä the separation of mixtures into their constituents by preferential adsorption by a solid” (Random House College Dictionary, 1988) ä “Chromatography is a physical method of separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of the phases constituting a _______ of large surface area, stationary bed the other being a ______ that percolates through or fluid along the stationary bed. ” (Ettre & Zlatkis, 1967, “The Practice of Gas Chromatography) ä
What is “Chromatography” “color writing” ä the separation of mixtures into their constituents by preferential adsorption by a solid” (Random House College Dictionary, 1988) ä “Chromatography is a physical method of separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of the phases constituting a _______ of large surface area, stationary bed the other being a ______ that percolates through or fluid along the stationary bed. ” (Ettre & Zlatkis, 1967, “The Practice of Gas Chromatography) ä
 History of Chromatography ä 1903 - Mikhail Tswett separated plant pigments using paper chromatography ä liquid-solid chromatography ä 1930’s - Schuftan & Eucken use vapor as the mobile phase ä gas solid chromatography
History of Chromatography ä 1903 - Mikhail Tswett separated plant pigments using paper chromatography ä liquid-solid chromatography ä 1930’s - Schuftan & Eucken use vapor as the mobile phase ä gas solid chromatography
 Applications Compound must exist as a ____ at a temperature that gas can be produced by the GC and withstood by the column (up to 450°C) ä Alcohols in blood ä Aromatics (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene) ä Flavors and Fragrances ä Permanent gases (H 2, N 2, O 2, Ar, CO 2, CO, CH 4) ä Hydrocarbons ä Pesticides, Herbicides, PCBs, and Dioxins ä Solvents ä
Applications Compound must exist as a ____ at a temperature that gas can be produced by the GC and withstood by the column (up to 450°C) ä Alcohols in blood ä Aromatics (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene) ä Flavors and Fragrances ä Permanent gases (H 2, N 2, O 2, Ar, CO 2, CO, CH 4) ä Hydrocarbons ä Pesticides, Herbicides, PCBs, and Dioxins ä Solvents ä
 Advantages of Gas Chromatography Requires only very small samples with little preparation ä Good at separating complex mixtures into components ä Results are rapidly obtained (1 to 100 minutes) ä Very high precision ä Only instrument with the sensitivity to detect volatile organic mixtures of low concentrations ä Equipment is not very complex (sophisticated oven) ä
Advantages of Gas Chromatography Requires only very small samples with little preparation ä Good at separating complex mixtures into components ä Results are rapidly obtained (1 to 100 minutes) ä Very high precision ä Only instrument with the sensitivity to detect volatile organic mixtures of low concentrations ä Equipment is not very complex (sophisticated oven) ä
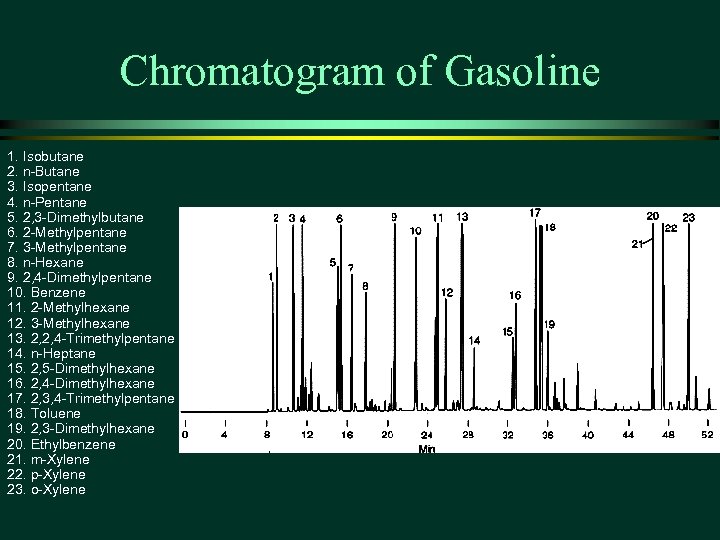 Chromatogram of Gasoline 1. Isobutane 2. n-Butane 3. Isopentane 4. n-Pentane 5. 2, 3 -Dimethylbutane 6. 2 -Methylpentane 7. 3 -Methylpentane 8. n-Hexane 9. 2, 4 -Dimethylpentane 10. Benzene 11. 2 -Methylhexane 12. 3 -Methylhexane 13. 2, 2, 4 -Trimethylpentane 14. n-Heptane 15. 2, 5 -Dimethylhexane 16. 2, 4 -Dimethylhexane 17. 2, 3, 4 -Trimethylpentane 18. Toluene 19. 2, 3 -Dimethylhexane 20. Ethylbenzene 21. m-Xylene 22. p-Xylene 23. o-Xylene
Chromatogram of Gasoline 1. Isobutane 2. n-Butane 3. Isopentane 4. n-Pentane 5. 2, 3 -Dimethylbutane 6. 2 -Methylpentane 7. 3 -Methylpentane 8. n-Hexane 9. 2, 4 -Dimethylpentane 10. Benzene 11. 2 -Methylhexane 12. 3 -Methylhexane 13. 2, 2, 4 -Trimethylpentane 14. n-Heptane 15. 2, 5 -Dimethylhexane 16. 2, 4 -Dimethylhexane 17. 2, 3, 4 -Trimethylpentane 18. Toluene 19. 2, 3 -Dimethylhexane 20. Ethylbenzene 21. m-Xylene 22. p-Xylene 23. o-Xylene
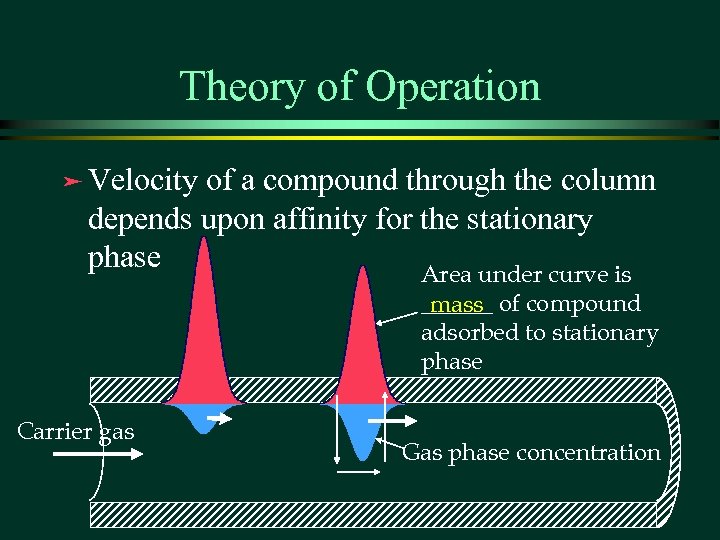 Theory of Operation ä Velocity of a compound through the column depends upon affinity for the stationary phase Area under curve is ______ of compound mass adsorbed to stationary phase Carrier gas Gas phase concentration
Theory of Operation ä Velocity of a compound through the column depends upon affinity for the stationary phase Area under curve is ______ of compound mass adsorbed to stationary phase Carrier gas Gas phase concentration
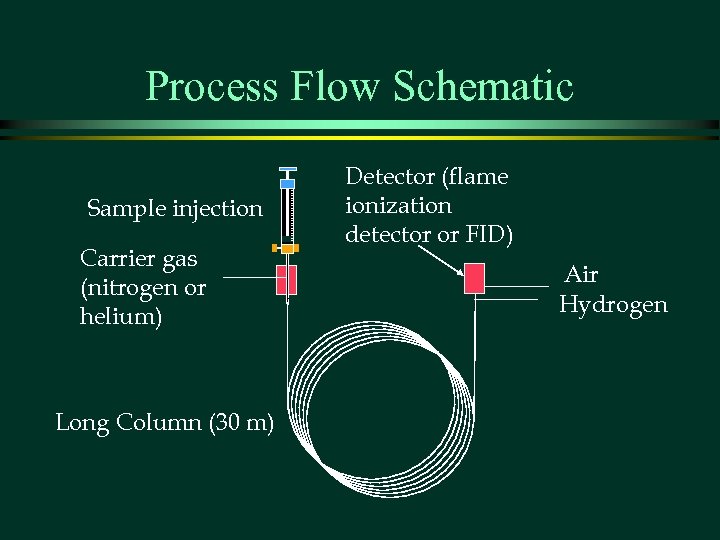 Process Flow Schematic Sample injection Carrier gas (nitrogen or helium) Long Column (30 m) Detector (flame ionization detector or FID) Air Hydrogen
Process Flow Schematic Sample injection Carrier gas (nitrogen or helium) Long Column (30 m) Detector (flame ionization detector or FID) Air Hydrogen
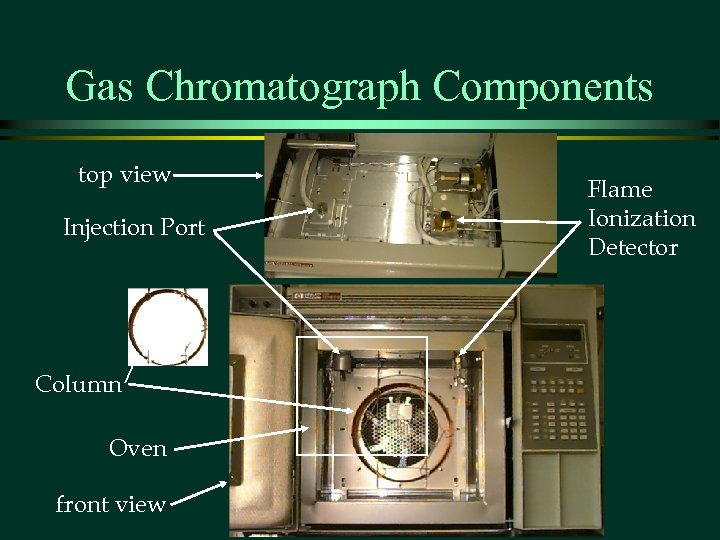 Gas Chromatograph Components top view Injection Port Column Oven front view Flame Ionization Detector
Gas Chromatograph Components top view Injection Port Column Oven front view Flame Ionization Detector
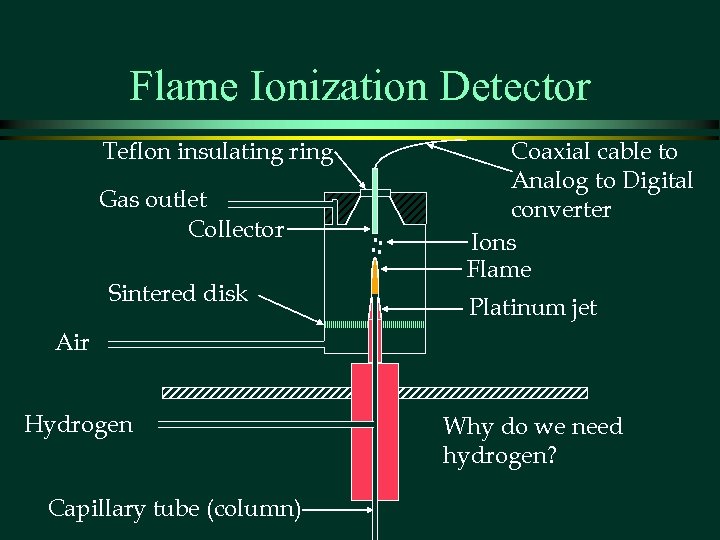 Flame Ionization Detector Teflon insulating ring Gas outlet Collector Sintered disk Coaxial cable to Analog to Digital converter Ions Flame Platinum jet Air Hydrogen Capillary tube (column) Why do we need hydrogen?
Flame Ionization Detector Teflon insulating ring Gas outlet Collector Sintered disk Coaxial cable to Analog to Digital converter Ions Flame Platinum jet Air Hydrogen Capillary tube (column) Why do we need hydrogen?
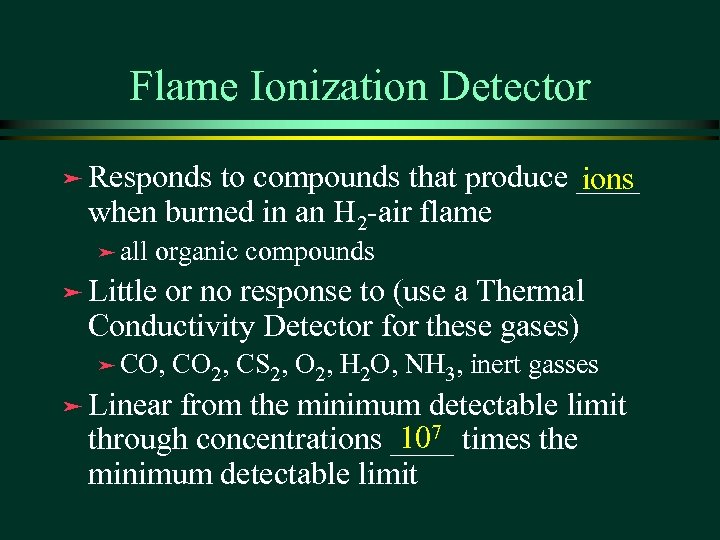 Flame Ionization Detector ä Responds to compounds that produce ____ ions when burned in an H 2 -air flame ä all organic compounds ä Little or no response to (use a Thermal Conductivity Detector for these gases) ä CO, ä Linear CO 2, CS 2, O 2, H 2 O, NH 3, inert gasses from the minimum detectable limit 107 through concentrations ____ times the minimum detectable limit
Flame Ionization Detector ä Responds to compounds that produce ____ ions when burned in an H 2 -air flame ä all organic compounds ä Little or no response to (use a Thermal Conductivity Detector for these gases) ä CO, ä Linear CO 2, CS 2, O 2, H 2 O, NH 3, inert gasses from the minimum detectable limit 107 through concentrations ____ times the minimum detectable limit
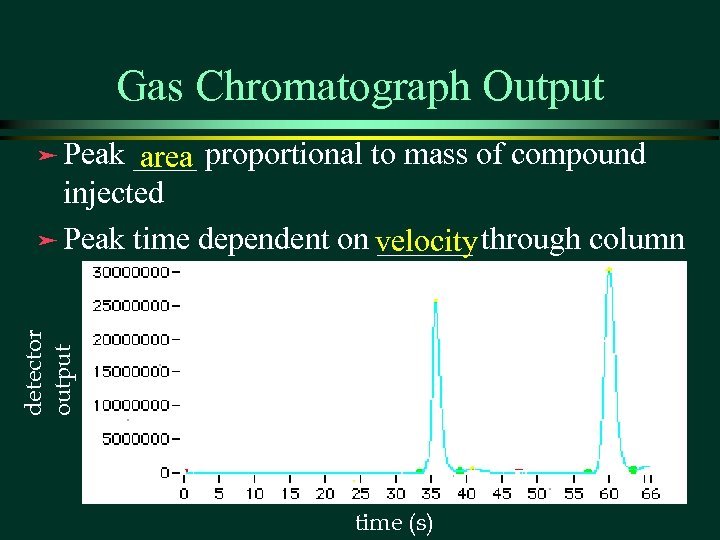 Gas Chromatograph Output ____ proportional to mass of compound area injected ä Peak time dependent on velocity through column ______ detector output ä Peak time (s)
Gas Chromatograph Output ____ proportional to mass of compound area injected ä Peak time dependent on velocity through column ______ detector output ä Peak time (s)
 Other Detectors ä Thermal Conductivity Detector ä Difference in thermal conductivity between the carrier gas and sample gas causes a voltage output ä Ideal carrier gas has a very ____ thermal low conductivity (He) ä Electron Capture Detector ä Specific for halogenated organics
Other Detectors ä Thermal Conductivity Detector ä Difference in thermal conductivity between the carrier gas and sample gas causes a voltage output ä Ideal carrier gas has a very ____ thermal low conductivity (He) ä Electron Capture Detector ä Specific for halogenated organics
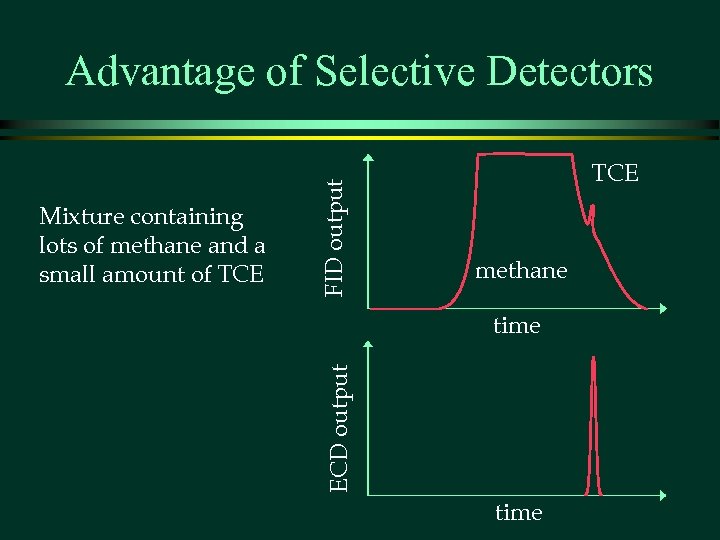 TCE methane time ECD output Mixture containing lots of methane and a small amount of TCE FID output Advantage of Selective Detectors time
TCE methane time ECD output Mixture containing lots of methane and a small amount of TCE FID output Advantage of Selective Detectors time
 Mass Spectrophotometer Uses the difference in mass-to-charge ratio (m/e) of ionized atoms or molecules to separate them from each other. ä Molecules have distinctive fragmentation patterns that provide structural information to identify structural components. ä The general operation of a mass spectrometer is: ä create pure gas-phase ions ( Gas chromatograph ) _________ ä separate the ions in space or time based on their mass-to -charge ratio ä measure the quantity of ions of each mass-to-charge ratio ä
Mass Spectrophotometer Uses the difference in mass-to-charge ratio (m/e) of ionized atoms or molecules to separate them from each other. ä Molecules have distinctive fragmentation patterns that provide structural information to identify structural components. ä The general operation of a mass spectrometer is: ä create pure gas-phase ions ( Gas chromatograph ) _________ ä separate the ions in space or time based on their mass-to -charge ratio ä measure the quantity of ions of each mass-to-charge ratio ä
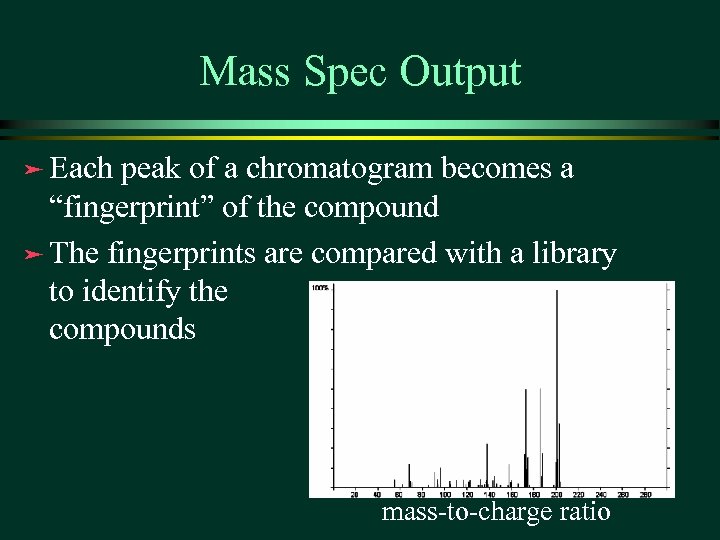 Mass Spec Output ä Each peak of a chromatogram becomes a “fingerprint” of the compound ä The fingerprints are compared with a library to identify the compounds mass-to-charge ratio
Mass Spec Output ä Each peak of a chromatogram becomes a “fingerprint” of the compound ä The fingerprints are compared with a library to identify the compounds mass-to-charge ratio
 Purge and Trap Way to measure dilute samples by concentration of constituents ä Trap constituents under low temperature ä Heat trap to release constituents and send to GC column ä N 2 Trap
Purge and Trap Way to measure dilute samples by concentration of constituents ä Trap constituents under low temperature ä Heat trap to release constituents and send to GC column ä N 2 Trap
 Techniques to Speed Analysis ä Problem: some components of a mixture may have very high velocities and others extremely low velocities. ä slow down fast components so they can be separated ä speed up slow components so analysis doesn’t take forever ä Solution…
Techniques to Speed Analysis ä Problem: some components of a mixture may have very high velocities and others extremely low velocities. ä slow down fast components so they can be separated ä speed up slow components so analysis doesn’t take forever ä Solution…
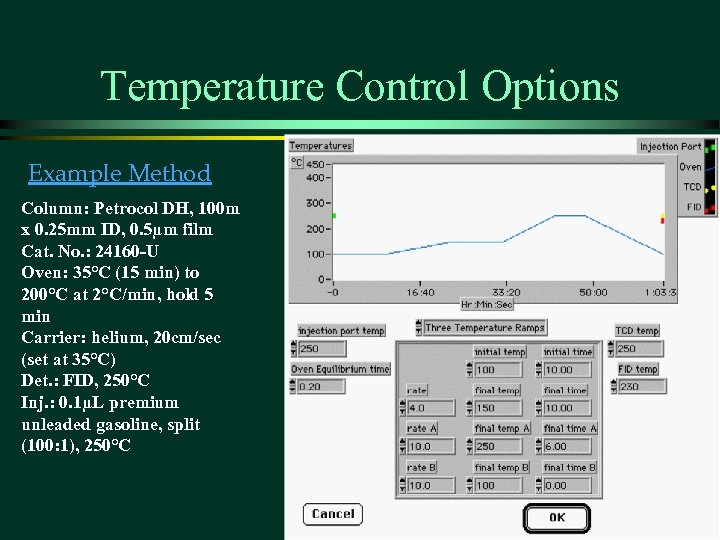 Temperature Control Options Example Method Column: Petrocol DH, 100 m x 0. 25 mm ID, 0. 5µm film Cat. No. : 24160 -U Oven: 35°C (15 min) to 200°C at 2°C/min, hold 5 min Carrier: helium, 20 cm/sec (set at 35°C) Det. : FID, 250°C Inj. : 0. 1µL premium unleaded gasoline, split (100: 1), 250°C
Temperature Control Options Example Method Column: Petrocol DH, 100 m x 0. 25 mm ID, 0. 5µm film Cat. No. : 24160 -U Oven: 35°C (15 min) to 200°C at 2°C/min, hold 5 min Carrier: helium, 20 cm/sec (set at 35°C) Det. : FID, 250°C Inj. : 0. 1µL premium unleaded gasoline, split (100: 1), 250°C


