759db96b0ba1d133ea9db9a21fb00353.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Gamma-ray generation in strong laser field: QED cascading and laser-solid interaction in QED regime I. Yu. Kostyukov, E. N. Nerush, V. F. Bashmakov Institute of Applied Physics Russian Academy of Sciences, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia 16. 03. 2018 PIF 2013, 9 -11 July 2013, DESY, Hamburg, Germany 1
Gamma-ray generation in strong laser field: QED cascading and laser-solid interaction in QED regime I. Yu. Kostyukov, E. N. Nerush, V. F. Bashmakov Institute of Applied Physics Russian Academy of Sciences, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia 16. 03. 2018 PIF 2013, 9 -11 July 2013, DESY, Hamburg, Germany 1
 Outline • Introduction • Numerical model • Laser-driven QED cascades • Laser-foil interaction • Summary 16. 03. 2018 2
Outline • Introduction • Numerical model • Laser-driven QED cascades • Laser-foil interaction • Summary 16. 03. 2018 2
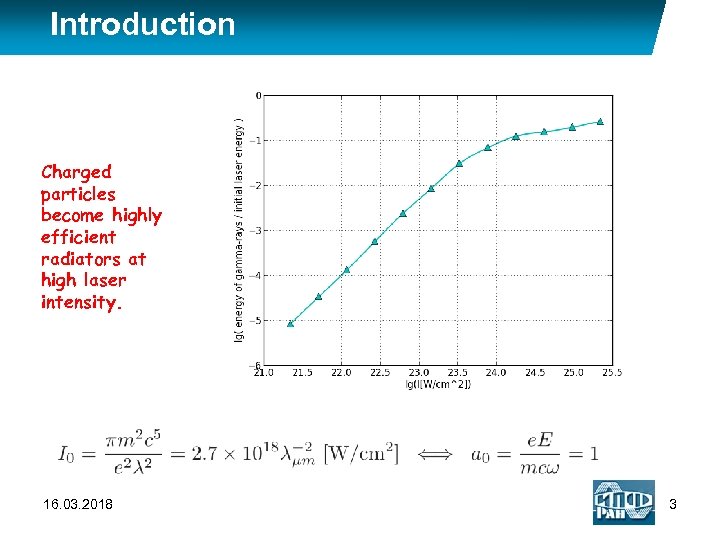 Introduction Charged particles become highly efficient radiators at high laser intensity. 16. 03. 2018 3
Introduction Charged particles become highly efficient radiators at high laser intensity. 16. 03. 2018 3
 Introduction Laser-driven QED cascades A. R. Bell and J. G. Kirk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 200403 (2008). J. G. Kirk et al. , Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51 085008 (2009). A. M. Fedotov et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 080402 (2010). I. V. Sokolov et al. , Phys. Rev. E 81, 036412 (2010). S. S. Bulanov et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 220407 (2010). E. N. Nerush et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 035001 (2011). N. V. Elkina et al. , Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 14, 054401 (2011). E. N. Nerush et al. , NIMA 653 7 (2011). I. V. Sokolov et al. , Phys. Plasmas 18, 093109 (2011). E. N. Nerush et al. , Phys. Plasmas 18, 083107 (2011). S. S. Bulanov et al. , Phys. Rev. A 87, 062110 (2013). B. King et al. , Phys. Rev. A 87, 042117 (2013). QED regime of laser-solid interaction H. Chen et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 015003 (2010) C. P. Ridgers et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 165006 (2012). C. S. Brady et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 245006 (2012). C. P. Ridgers et al. , Phys. Plasmas 20, 056701 (2013); . 16. 03. 2018 4
Introduction Laser-driven QED cascades A. R. Bell and J. G. Kirk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 200403 (2008). J. G. Kirk et al. , Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51 085008 (2009). A. M. Fedotov et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 080402 (2010). I. V. Sokolov et al. , Phys. Rev. E 81, 036412 (2010). S. S. Bulanov et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 220407 (2010). E. N. Nerush et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 035001 (2011). N. V. Elkina et al. , Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 14, 054401 (2011). E. N. Nerush et al. , NIMA 653 7 (2011). I. V. Sokolov et al. , Phys. Plasmas 18, 093109 (2011). E. N. Nerush et al. , Phys. Plasmas 18, 083107 (2011). S. S. Bulanov et al. , Phys. Rev. A 87, 062110 (2013). B. King et al. , Phys. Rev. A 87, 042117 (2013). QED regime of laser-solid interaction H. Chen et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 015003 (2010) C. P. Ridgers et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 165006 (2012). C. S. Brady et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 245006 (2012). C. P. Ridgers et al. , Phys. Plasmas 20, 056701 (2013); . 16. 03. 2018 4
 Numerical model 16. 03. 2018 5
Numerical model 16. 03. 2018 5
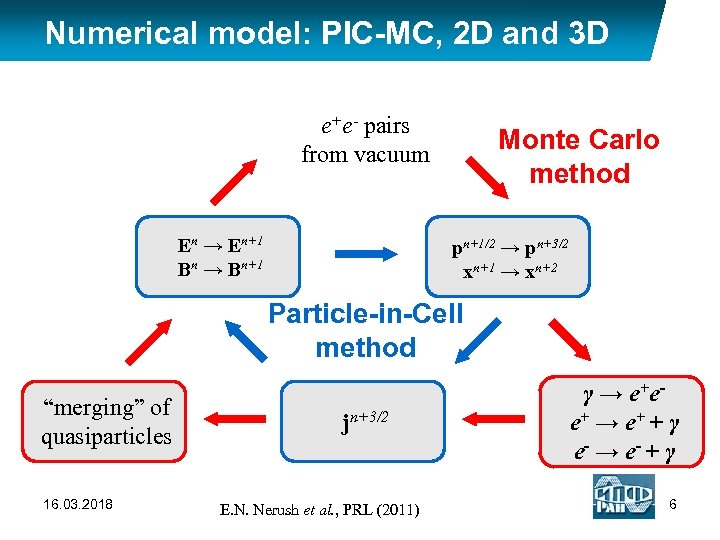 Numerical model: PIC-MC, 2 D and 3 D e+e- pairs from vacuum En → En+1 Bn → Bn+1 Monte Carlo method pn+1/2 → pn+3/2 xn+1 → xn+2 Particle-in-Cell method “merging” of quasiparticles 16. 03. 2018 jn+3/2 E. N. Nerush et al. , PRL (2011) γ → e +e e+ → e+ + γ e- → e- + γ 6
Numerical model: PIC-MC, 2 D and 3 D e+e- pairs from vacuum En → En+1 Bn → Bn+1 Monte Carlo method pn+1/2 → pn+3/2 xn+1 → xn+2 Particle-in-Cell method “merging” of quasiparticles 16. 03. 2018 jn+3/2 E. N. Nerush et al. , PRL (2011) γ → e +e e+ → e+ + γ e- → e- + γ 6
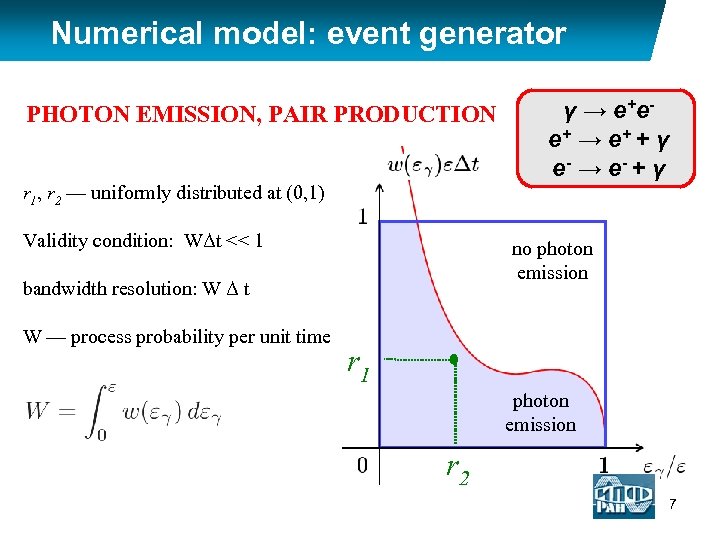 Numerical model: event generator PHOTON EMISSION, PAIR PRODUCTION r 1, r 2 — uniformly distributed at (0, 1) Validity condition: WΔt << 1 no photon emission bandwidth resolution: W Δ t W — process probability per unit time γ → e + ee+ → e + + γ e- → e - + γ r 1 photon emission r 2 7
Numerical model: event generator PHOTON EMISSION, PAIR PRODUCTION r 1, r 2 — uniformly distributed at (0, 1) Validity condition: WΔt << 1 no photon emission bandwidth resolution: W Δ t W — process probability per unit time γ → e + ee+ → e + + γ e- → e - + γ r 1 photon emission r 2 7
 Laser-driven QED cascades 16. 03. 2018 8
Laser-driven QED cascades 16. 03. 2018 8
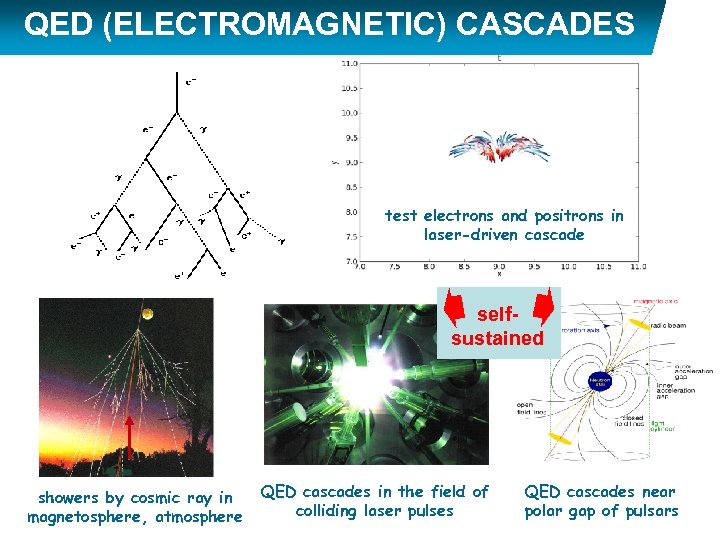 QED (ELECTROMAGNETIC) CASCADES test electrons and positrons in laser-driven cascade selfsustained showers by cosmic ray in magnetosphere, atmosphere QED cascades in the field of colliding laser pulses QED cascades near polar gap of pulsars
QED (ELECTROMAGNETIC) CASCADES test electrons and positrons in laser-driven cascade selfsustained showers by cosmic ray in magnetosphere, atmosphere QED cascades in the field of colliding laser pulses QED cascades near polar gap of pulsars
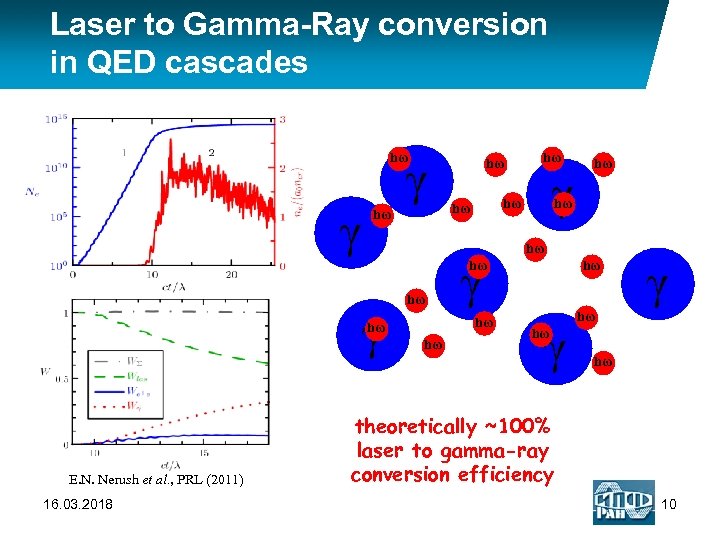 Laser to Gamma-Ray conversion in QED cascades hω γ γ hω hω hω E. N. Nerush et al. , PRL (2011) 16. 03. 2018 hω hω hω γ γ hω hω hω theoretically ~100% laser to gamma-ray conversion efficiency 10
Laser to Gamma-Ray conversion in QED cascades hω γ γ hω hω hω E. N. Nerush et al. , PRL (2011) 16. 03. 2018 hω hω hω γ γ hω hω hω theoretically ~100% laser to gamma-ray conversion efficiency 10
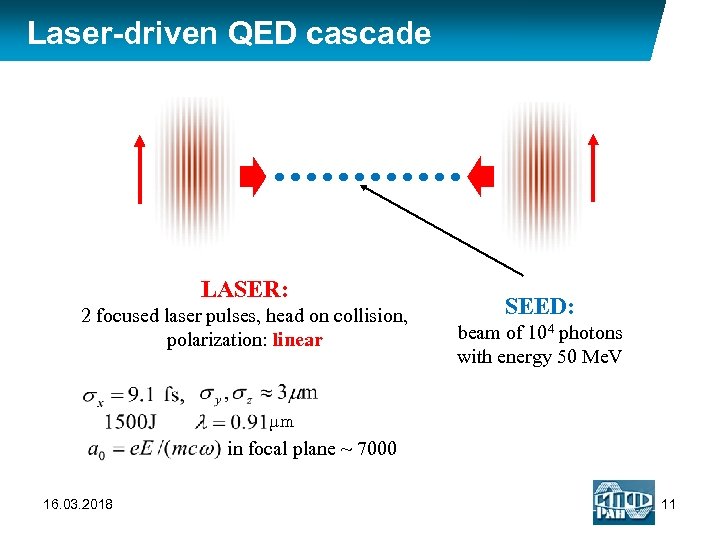 Laser-driven QED cascade LASER: 2 focused laser pulses, head on collision, polarization: linear SEED: beam of 104 photons with energy 50 Me. V µm in focal plane ~ 7000 16. 03. 2018 11
Laser-driven QED cascade LASER: 2 focused laser pulses, head on collision, polarization: linear SEED: beam of 104 photons with energy 50 Me. V µm in focal plane ~ 7000 16. 03. 2018 11
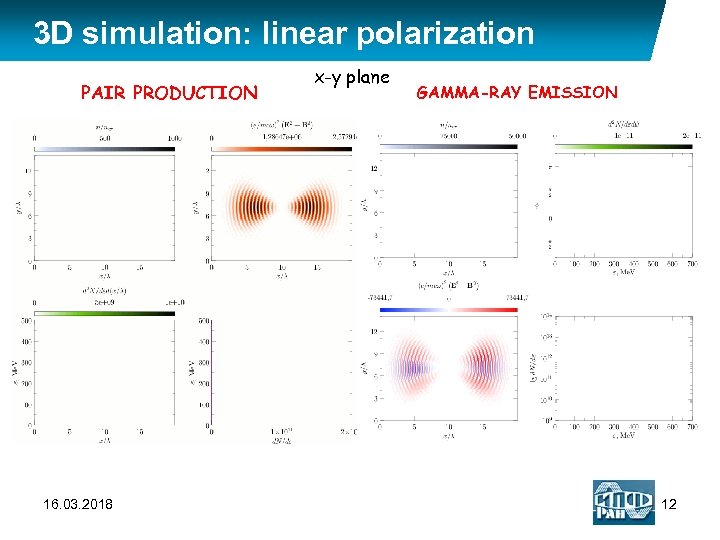 3 D simulation: linear polarization PAIR PRODUCTION 16. 03. 2018 x-y plane GAMMA-RAY EMISSION 12
3 D simulation: linear polarization PAIR PRODUCTION 16. 03. 2018 x-y plane GAMMA-RAY EMISSION 12
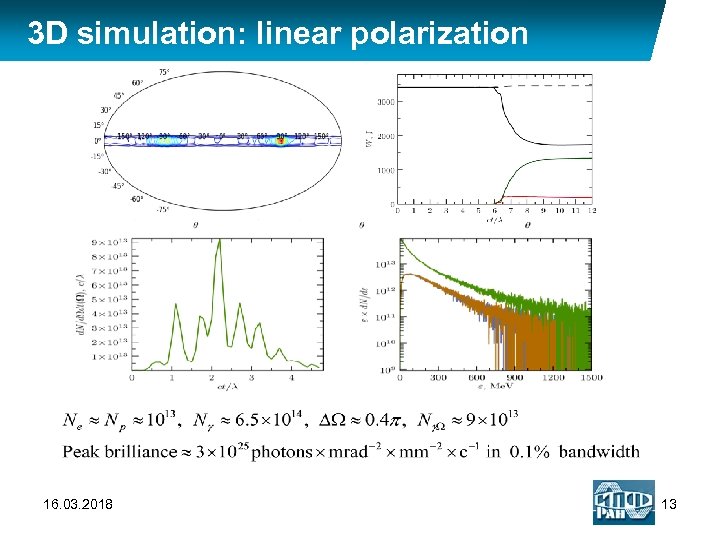 3 D simulation: linear polarization 16. 03. 2018 13
3 D simulation: linear polarization 16. 03. 2018 13
 3 D simulation: circular polarization LASER: 2 focused laser pulses, head on collision, polarization: circular, SEED: beam of 104 photons with energy 50 Me. V in focal plane ~ 5200 16. 03. 2018 14
3 D simulation: circular polarization LASER: 2 focused laser pulses, head on collision, polarization: circular, SEED: beam of 104 photons with energy 50 Me. V in focal plane ~ 5200 16. 03. 2018 14
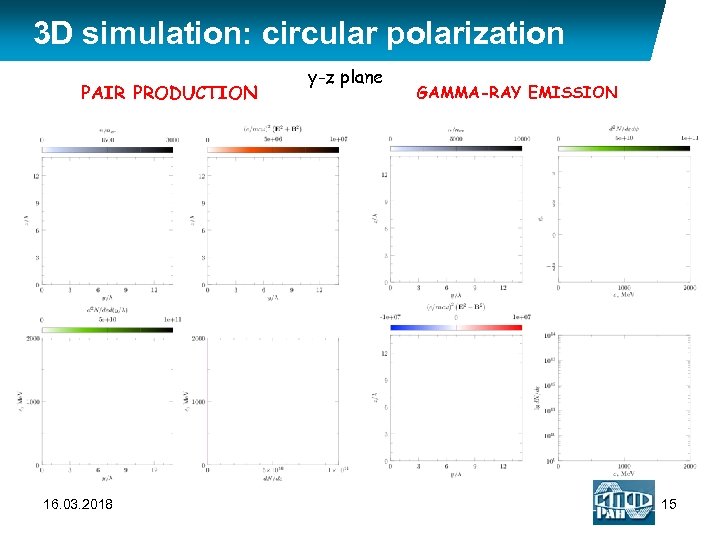 3 D simulation: circular polarization PAIR PRODUCTION 16. 03. 2018 y-z plane GAMMA-RAY EMISSION 15
3 D simulation: circular polarization PAIR PRODUCTION 16. 03. 2018 y-z plane GAMMA-RAY EMISSION 15
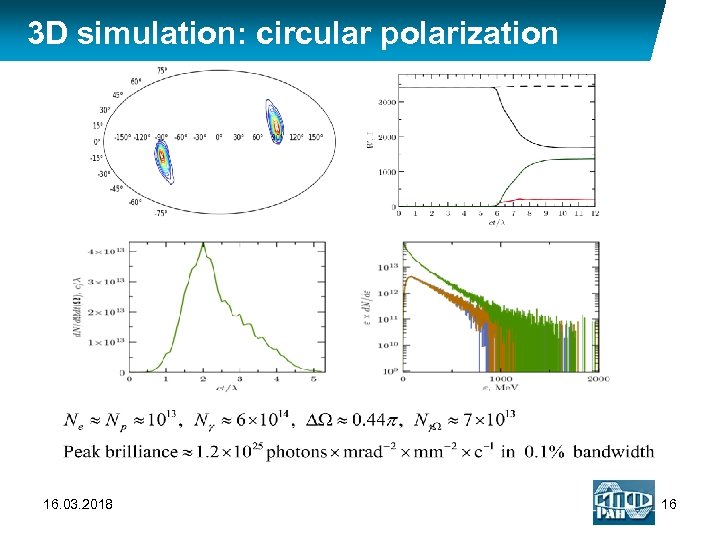 3 D simulation: circular polarization 16. 03. 2018 16
3 D simulation: circular polarization 16. 03. 2018 16
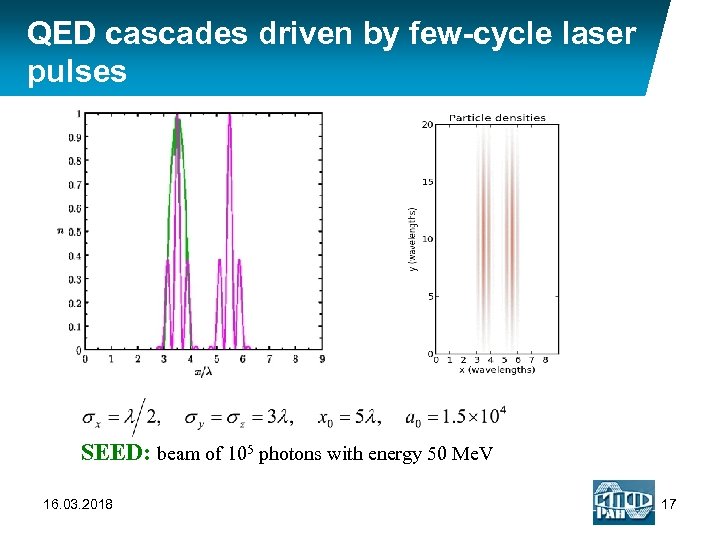 QED cascades driven by few-cycle laser pulses SEED: beam of 105 photons with energy 50 Me. V 16. 03. 2018 17
QED cascades driven by few-cycle laser pulses SEED: beam of 105 photons with energy 50 Me. V 16. 03. 2018 17
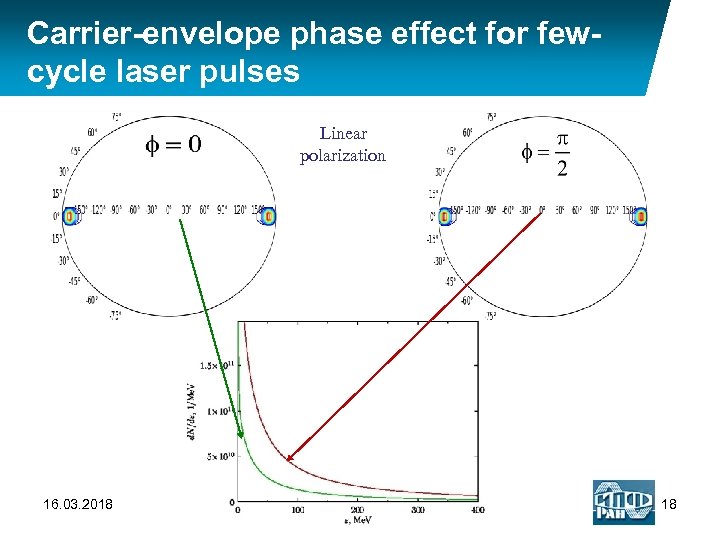 Carrier-envelope phase effect for fewcycle laser pulses Linear polarization 16. 03. 2018 18
Carrier-envelope phase effect for fewcycle laser pulses Linear polarization 16. 03. 2018 18
 Laser-foil interaction 16. 03. 2018 19
Laser-foil interaction 16. 03. 2018 19
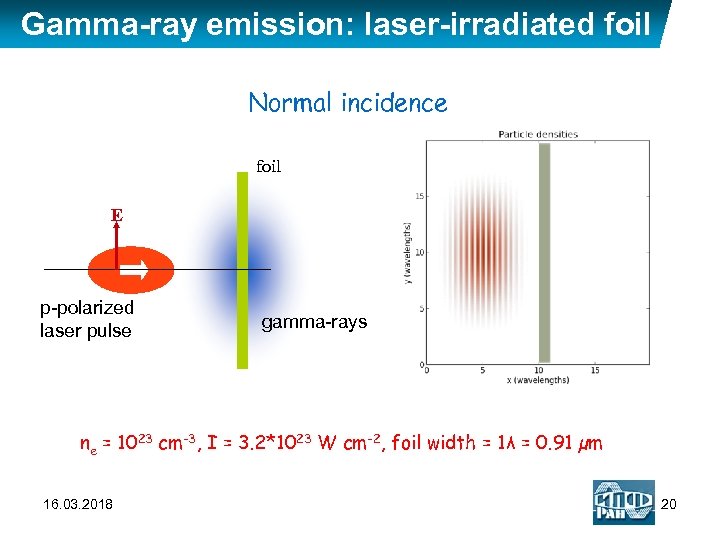 Gamma-ray emission: laser-irradiated foil Normal incidence foil E p-polarized laser pulse gamma-rays ne = 1023 cm-3, I = 3. 2*1023 W cm-2, foil width = 1λ = 0. 91 µm 16. 03. 2018 20
Gamma-ray emission: laser-irradiated foil Normal incidence foil E p-polarized laser pulse gamma-rays ne = 1023 cm-3, I = 3. 2*1023 W cm-2, foil width = 1λ = 0. 91 µm 16. 03. 2018 20
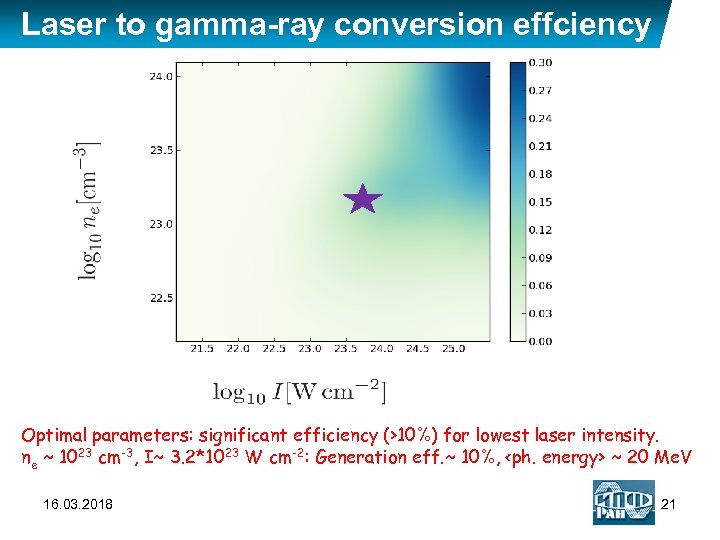 Laser to gamma-ray conversion effciency Optimal parameters: significant efficiency (>10%) for lowest laser intensity. ne ~ 1023 cm-3, I~ 3. 2*1023 W cm-2: Generation eff. ~ 10%,
Laser to gamma-ray conversion effciency Optimal parameters: significant efficiency (>10%) for lowest laser intensity. ne ~ 1023 cm-3, I~ 3. 2*1023 W cm-2: Generation eff. ~ 10%,
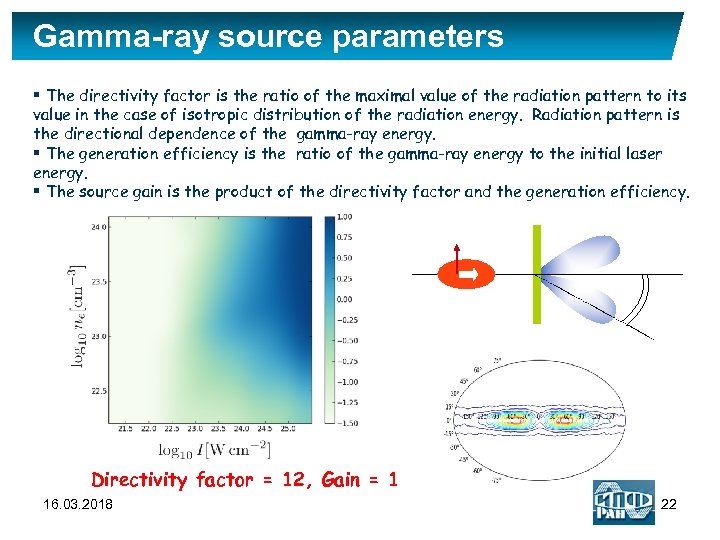 Gamma-ray source parameters § The directivity factor is the ratio of the maximal value of the radiation pattern to its value in the case of isotropic distribution of the radiation energy. Radiation pattern is the directional dependence of the gamma-ray energy. § The generation efficiency is the ratio of the gamma-ray energy to the initial laser energy. § The source gain is the product of the directivity factor and the generation efficiency. Directivity factor = 12, Gain = 1 16. 03. 2018 22
Gamma-ray source parameters § The directivity factor is the ratio of the maximal value of the radiation pattern to its value in the case of isotropic distribution of the radiation energy. Radiation pattern is the directional dependence of the gamma-ray energy. § The generation efficiency is the ratio of the gamma-ray energy to the initial laser energy. § The source gain is the product of the directivity factor and the generation efficiency. Directivity factor = 12, Gain = 1 16. 03. 2018 22
![log(e-density [cm-3]) Physics of laser-foil interaction foil gamma-ray energy ion energy positron energy high log(e-density [cm-3]) Physics of laser-foil interaction foil gamma-ray energy ion energy positron energy high](https://present5.com/presentation/759db96b0ba1d133ea9db9a21fb00353/image-23.jpg) log(e-density [cm-3]) Physics of laser-foil interaction foil gamma-ray energy ion energy positron energy high density, strong reflection low density, transparent foil e+e- pair production at high intensity It can affect ion acceleration. log(Intensity [W/cm 2]) Radiation losses (RL) become significant for electrons oscillating in laser field. Radiation-pressure acceleration (RPA) of ions: electron-ion separation generates electric field which accelerates ions electron density photon density positron density
log(e-density [cm-3]) Physics of laser-foil interaction foil gamma-ray energy ion energy positron energy high density, strong reflection low density, transparent foil e+e- pair production at high intensity It can affect ion acceleration. log(Intensity [W/cm 2]) Radiation losses (RL) become significant for electrons oscillating in laser field. Radiation-pressure acceleration (RPA) of ions: electron-ion separation generates electric field which accelerates ions electron density photon density positron density
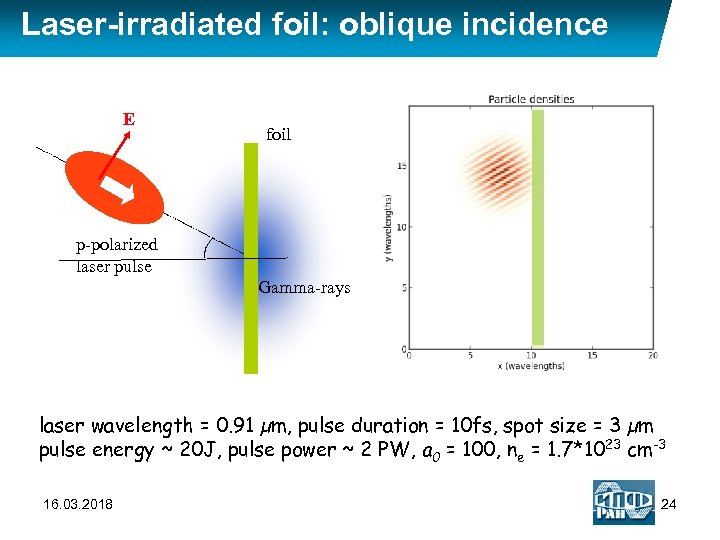 Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence E foil p-polarized laser pulse Gamma-rays laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm, pulse duration = 10 fs, spot size = 3 µm pulse energy ~ 20 J, pulse power ~ 2 PW, a 0 = 100, ne = 1. 7*1023 cm-3 16. 03. 2018 24
Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence E foil p-polarized laser pulse Gamma-rays laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm, pulse duration = 10 fs, spot size = 3 µm pulse energy ~ 20 J, pulse power ~ 2 PW, a 0 = 100, ne = 1. 7*1023 cm-3 16. 03. 2018 24
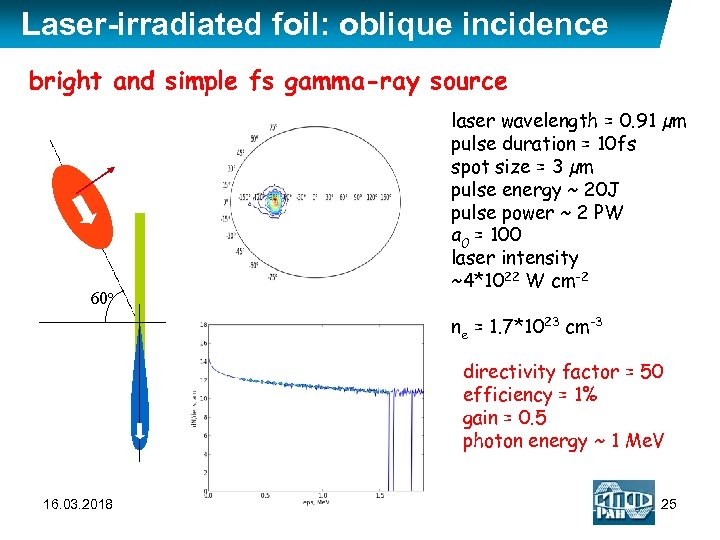 Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence bright and simple fs gamma-ray source 60 o laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm pulse duration = 10 fs spot size = 3 µm pulse energy ~ 20 J pulse power ~ 2 PW a 0 = 100 laser intensity ~4*1022 W cm-2 ne = 1. 7*1023 cm-3 directivity factor = 50 efficiency = 1% gain = 0. 5 photon energy ~ 1 Me. V 16. 03. 2018 25
Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence bright and simple fs gamma-ray source 60 o laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm pulse duration = 10 fs spot size = 3 µm pulse energy ~ 20 J pulse power ~ 2 PW a 0 = 100 laser intensity ~4*1022 W cm-2 ne = 1. 7*1023 cm-3 directivity factor = 50 efficiency = 1% gain = 0. 5 photon energy ~ 1 Me. V 16. 03. 2018 25
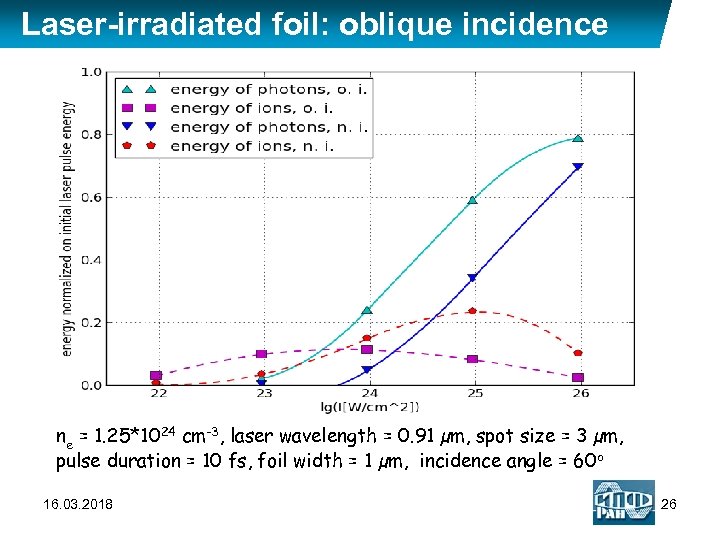 Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence ne = 1. 25*1024 cm-3, laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm, spot size = 3 µm, pulse duration = 10 fs, foil width = 1 µm, incidence angle = 60 o 16. 03. 2018 26
Laser-irradiated foil: oblique incidence ne = 1. 25*1024 cm-3, laser wavelength = 0. 91 µm, spot size = 3 µm, pulse duration = 10 fs, foil width = 1 µm, incidence angle = 60 o 16. 03. 2018 26
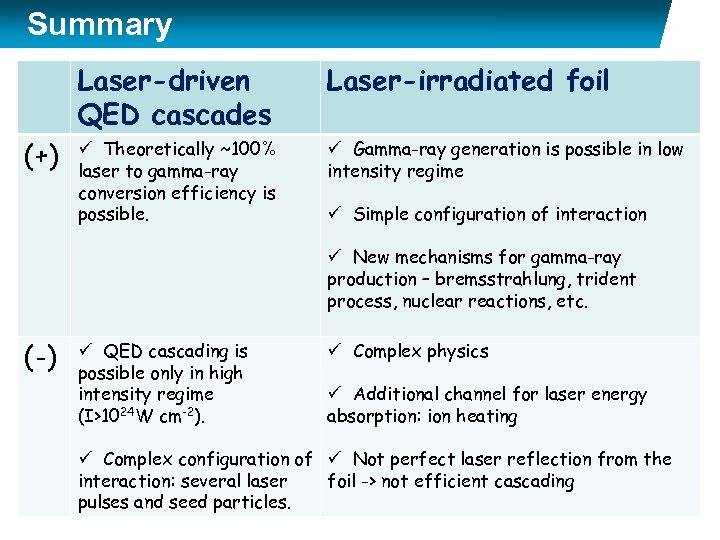 Summary Laser-driven QED cascades (+) Laser-irradiated foil ü Theoretically ~100% laser to gamma-ray conversion efficiency is possible. ü Gamma-ray generation is possible in low intensity regime ü Simple configuration of interaction ü New mechanisms for gamma-ray production – bremsstrahlung, trident process, nuclear reactions, etc. (-) ü QED cascading is possible only in high intensity regime (I>1024 W cm-2). ü Complex physics ü Additional channel for laser energy absorption: ion heating ü Complex configuration of ü Not perfect laser reflection from the interaction: several laser foil -> not efficient cascading pulses and seed particles. 16. 03. 2018
Summary Laser-driven QED cascades (+) Laser-irradiated foil ü Theoretically ~100% laser to gamma-ray conversion efficiency is possible. ü Gamma-ray generation is possible in low intensity regime ü Simple configuration of interaction ü New mechanisms for gamma-ray production – bremsstrahlung, trident process, nuclear reactions, etc. (-) ü QED cascading is possible only in high intensity regime (I>1024 W cm-2). ü Complex physics ü Additional channel for laser energy absorption: ion heating ü Complex configuration of ü Not perfect laser reflection from the interaction: several laser foil -> not efficient cascading pulses and seed particles. 16. 03. 2018
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!


