0310ec6d5dde08ce2ee3560fcedcd447.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

 Gaining Access & Vehicle Extrication The Role of EMS During Patient Extrication or Rescue
Gaining Access & Vehicle Extrication The Role of EMS During Patient Extrication or Rescue
 Introduction h. The number of transportation, agricultural, environmental and residential accidents are increasing throughout the world, resulting in higher numbers of serious injuries and deaths.
Introduction h. The number of transportation, agricultural, environmental and residential accidents are increasing throughout the world, resulting in higher numbers of serious injuries and deaths.
 Introduction Con’t h. In Manitoba we have a vast area to cover as EMS providers. With accidents increasing we as EMS providers should be concerned. Being prepared when accidents occur throughout our province takes preparation and dedication from members of rural EMS.
Introduction Con’t h. In Manitoba we have a vast area to cover as EMS providers. With accidents increasing we as EMS providers should be concerned. Being prepared when accidents occur throughout our province takes preparation and dedication from members of rural EMS.
 Introduction Cont’d h. Develop loosely defined roles for responding EMS crew to assess accident scene and confirm level of response needed. h. EMS crews should be aware of any responding agencies roles and responsabilities.
Introduction Cont’d h. Develop loosely defined roles for responding EMS crew to assess accident scene and confirm level of response needed. h. EMS crews should be aware of any responding agencies roles and responsabilities.
 Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
 Objectives h. Stabilization h. Access to patient h. Disentanglement of patient h. Patient removal h. Post call
Objectives h. Stabilization h. Access to patient h. Disentanglement of patient h. Patient removal h. Post call
 Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
 Extrication The removal of a person from a building, vehicle or area of danger. More specifically the removal from a damaged vehicle, collapsed structure, or other position of entrapment.
Extrication The removal of a person from a building, vehicle or area of danger. More specifically the removal from a damaged vehicle, collapsed structure, or other position of entrapment.
 Simple Definition: Removal of a trapped patient
Simple Definition: Removal of a trapped patient
 Goal of Extrication
Goal of Extrication
 Goal of Extrication To remove the victim from entrapment without further injury or unnecessary movement.
Goal of Extrication To remove the victim from entrapment without further injury or unnecessary movement.
 Primary EMS Unit h. Crew members responsibilities: • Safety first for themselves and their partner • Secondly safety to the patient • Determine need for addition resources • Plan of action to complete goals
Primary EMS Unit h. Crew members responsibilities: • Safety first for themselves and their partner • Secondly safety to the patient • Determine need for addition resources • Plan of action to complete goals
 Crew Safety h PPE. p Rescue Helmet p. Eye protection p. Protective clothing (Jacket, Gloves) p Position of vehicle(s) in relation to traffic
Crew Safety h PPE. p Rescue Helmet p. Eye protection p. Protective clothing (Jacket, Gloves) p Position of vehicle(s) in relation to traffic
 Hazards!! h h h h Fire Fuel Leaks Downed Power Lines Hazardous Materials Unstable Vehicle/Structure Traffic Crowds
Hazards!! h h h h Fire Fuel Leaks Downed Power Lines Hazardous Materials Unstable Vehicle/Structure Traffic Crowds
 Communications h. Communications: • Interagency communications must be available • Important to asses and update potential resources (Fire Dept. , Additional EMS units, ER. Dept, Law Enforcement) • Communication between agencies is of the utmost importance
Communications h. Communications: • Interagency communications must be available • Important to asses and update potential resources (Fire Dept. , Additional EMS units, ER. Dept, Law Enforcement) • Communication between agencies is of the utmost importance
 Communications h. Communications con’t: • Messages, whether sent via radio or in conversation, must be clear, concise and to the point • During major incidents members may be required to change to a different frequency on their radios so as not to hamper radio transmissions on a department’s primary channel. Secondary and tertiary channels should be established before or on arrival at the scene • Special codes or radio language should be common between all members (e. g. 10 codes)
Communications h. Communications con’t: • Messages, whether sent via radio or in conversation, must be clear, concise and to the point • During major incidents members may be required to change to a different frequency on their radios so as not to hamper radio transmissions on a department’s primary channel. Secondary and tertiary channels should be established before or on arrival at the scene • Special codes or radio language should be common between all members (e. g. 10 codes)
 Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
Objectives h. Define extrication and goals h. Roles of agencies at scene h. Placement of vehicles at scene h. Scene assessment / Scene size-up
 Different Agencies h. Law Enforcement h. Fire Department h. Rescue h. Hazmat h. Hydro h. Gas (Natural Gas / Propane)
Different Agencies h. Law Enforcement h. Fire Department h. Rescue h. Hazmat h. Hydro h. Gas (Natural Gas / Propane)
 Role of Law Enforcement d. Investigation of incident d. Traffic control d. Crowd control d. Preserve scene for reconstruction and investigation
Role of Law Enforcement d. Investigation of incident d. Traffic control d. Crowd control d. Preserve scene for reconstruction and investigation
 Role of Fire Dept. f. Extinguishing fires f. Preventing fires f. Handling spills or leaks f. Vehicle safety f. Energy absorbing bumpers f. Electrical system f. Fuel system f. Stabilization f. Assist police and EMS
Role of Fire Dept. f. Extinguishing fires f. Preventing fires f. Handling spills or leaks f. Vehicle safety f. Energy absorbing bumpers f. Electrical system f. Fuel system f. Stabilization f. Assist police and EMS
 Role of EMS h h h h (That’s us) Patient contact throughout incident Patient assessment(s) Triage Patient care Assess need for disentanglement Advise rescue of entrapment conditions Packaging of injuries / patients Transport patient
Role of EMS h h h h (That’s us) Patient contact throughout incident Patient assessment(s) Triage Patient care Assess need for disentanglement Advise rescue of entrapment conditions Packaging of injuries / patients Transport patient
 Role of Rescue may be performed by a separate agency or may be a part of Fire Dept or EMS Duties. h Establish incident/scene command h Assess rescue needs/ ext’n techniques h Provide patient access h Disentanglement h Assist EMS h Scene safety
Role of Rescue may be performed by a separate agency or may be a part of Fire Dept or EMS Duties. h Establish incident/scene command h Assess rescue needs/ ext’n techniques h Provide patient access h Disentanglement h Assist EMS h Scene safety
 Role of Hazmat >Advise command of risk / hazards >Secure scene >Evacuation of area >Removal of patients at contaminated scene >Decontamination of patients
Role of Hazmat >Advise command of risk / hazards >Secure scene >Evacuation of area >Removal of patients at contaminated scene >Decontamination of patients
 Role of Hydro / Gas ~Advise command of risk / hazards ~Assist in securing scene
Role of Hydro / Gas ~Advise command of risk / hazards ~Assist in securing scene
 Scene Size-up Consists of two surveys. h Outer circle survey h Inner circle survey
Scene Size-up Consists of two surveys. h Outer circle survey h Inner circle survey
 Scene Size-up h. Outer Circle Survey h. Starts when arriving, includes ambulance parking. h. Assess hazards h. Medical Needs p. Number of patients p. Location of patients • Trapped or not h. Rollover - search 300 ft or more for additional patients
Scene Size-up h. Outer Circle Survey h. Starts when arriving, includes ambulance parking. h. Assess hazards h. Medical Needs p. Number of patients p. Location of patients • Trapped or not h. Rollover - search 300 ft or more for additional patients
 Scene Size-up h. Assess Rescue needs. Require: p. Forcible entry p. Tools for disentanglement p. Tools for patients egress p. Additional lighting h. Additional Manpower h. Call in other agencies h. Vehicle size-up
Scene Size-up h. Assess Rescue needs. Require: p. Forcible entry p. Tools for disentanglement p. Tools for patients egress p. Additional lighting h. Additional Manpower h. Call in other agencies h. Vehicle size-up
 Inner circle survey h Close up look at crash h Initial patient contact p Approach patient from in front h Identify patient condition(s) h Identify degree of entrapment h Find hidden hazards (Airbags/Bumpers) h. Assess need for stabilization
Inner circle survey h Close up look at crash h Initial patient contact p Approach patient from in front h Identify patient condition(s) h Identify degree of entrapment h Find hidden hazards (Airbags/Bumpers) h. Assess need for stabilization
 Stabilization h Stabilization: • Safety before approaching the vehicle. (is the vehicle still running, on fire, hazardous chemicals present, HYDRO lines downed etc. ) • Vehicle should be stabilized before personnel enter vehicle using wooden blocks and deflating the tires, vetter mats, or using jacks • Personnel should be aware of possible undeployed airbags • Traffic hazards
Stabilization h Stabilization: • Safety before approaching the vehicle. (is the vehicle still running, on fire, hazardous chemicals present, HYDRO lines downed etc. ) • Vehicle should be stabilized before personnel enter vehicle using wooden blocks and deflating the tires, vetter mats, or using jacks • Personnel should be aware of possible undeployed airbags • Traffic hazards
 h Stabilization Con’t: • How many vehicles involved • Scene may require light - if so use intrinsically safe devices if available • Make use of vehicles own safety features such as placing vehicle in park or applying the emergency brake
h Stabilization Con’t: • How many vehicles involved • Scene may require light - if so use intrinsically safe devices if available • Make use of vehicles own safety features such as placing vehicle in park or applying the emergency brake
 Where airbags? h Driver side (steering wheel) h Passenger side (above glove box)
Where airbags? h Driver side (steering wheel) h Passenger side (above glove box)
 Where airbags? h Side impact p p In side of seat In ‘B’ post Tubular across window Curtain (guillotine)
Where airbags? h Side impact p p In side of seat In ‘B’ post Tubular across window Curtain (guillotine)
 Where airbags? h Side impact A Post B Post C Post
Where airbags? h Side impact A Post B Post C Post
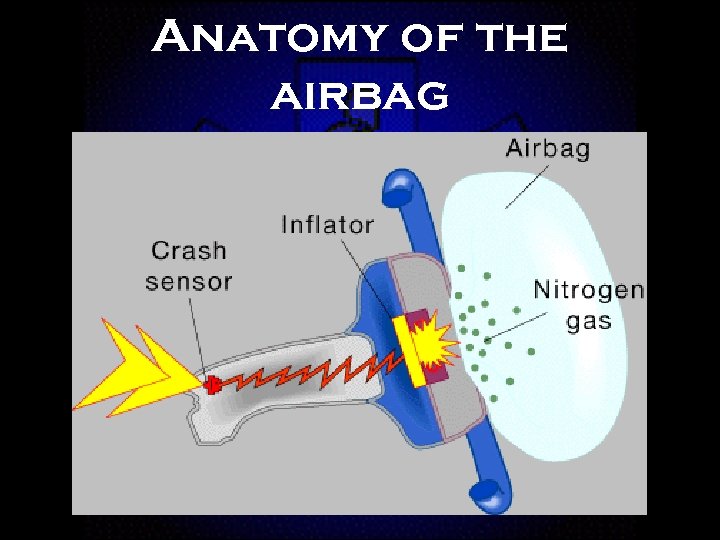 Anatomy of the airbag
Anatomy of the airbag
 Control Zones h. Hot, Warm, Cold h h h Reduce congestion More efficient Less confusion Circular Size depends on accident scene
Control Zones h. Hot, Warm, Cold h h h Reduce congestion More efficient Less confusion Circular Size depends on accident scene
 Hot Zone Closest to extrication Access only to those performing Patient care Extrication Keep unused equipment out of hot zone
Hot Zone Closest to extrication Access only to those performing Patient care Extrication Keep unused equipment out of hot zone
 Warm Zone Just outside of hot zone Access only to those Helping workers in hot zone Handling charged lines Handling scene lighting Treating patients Treat patients prior to transport in warm zone if safe to do so
Warm Zone Just outside of hot zone Access only to those Helping workers in hot zone Handling charged lines Handling scene lighting Treating patients Treat patients prior to transport in warm zone if safe to do so
 Cold Zone Outer circle Where equipment and manpower staged Command post Cordoned off
Cold Zone Outer circle Where equipment and manpower staged Command post Cordoned off
 Patient Access h. When safe access the patient h If possible make the car safer / easier to access p Secure the keys p Remove or cut seatbelt if safe p Unlock doors and roll down windows h Assess patient injuries and entrapment h Cover patient
Patient Access h. When safe access the patient h If possible make the car safer / easier to access p Secure the keys p Remove or cut seatbelt if safe p Unlock doors and roll down windows h Assess patient injuries and entrapment h Cover patient
 Patient Access “Try before you pry!” First try simple access: attempt access without using tools. Open a door or go through an open window. If this doesn’t work, you must try complex access.
Patient Access “Try before you pry!” First try simple access: attempt access without using tools. Open a door or go through an open window. If this doesn’t work, you must try complex access.
 Complex Access Tools are required to access patient h Break a window, open a door h Break a window, crawl in h Use hand tools to make a pathway through wreckage to patient h Have TOOL personnel create a pathway using hand tools or heavy hydraulics (jaws of life)
Complex Access Tools are required to access patient h Break a window, open a door h Break a window, crawl in h Use hand tools to make a pathway through wreckage to patient h Have TOOL personnel create a pathway using hand tools or heavy hydraulics (jaws of life)
 Laminated glass h Formed of a layer of plastic between 2 layers of glass h Shatters, but glass stays in place h Found on vehicle windshields (front)
Laminated glass h Formed of a layer of plastic between 2 layers of glass h Shatters, but glass stays in place h Found on vehicle windshields (front)
 Tempered glass h Single piece of hardened glass h Shatters into thousands of small pieces h Found on vehicle side and rear windows
Tempered glass h Single piece of hardened glass h Shatters into thousands of small pieces h Found on vehicle side and rear windows
 Removing Laminated Glass h Try pulling out rubber seal around window, remove window intact h Cut windshield with saw, axe, or specialized tool h If cutting, USE DUST MASKS ON RESCUERS AND PATIENT! Let patient and other rescuers know you are “CUTTING GLASS!”
Removing Laminated Glass h Try pulling out rubber seal around window, remove window intact h Cut windshield with saw, axe, or specialized tool h If cutting, USE DUST MASKS ON RESCUERS AND PATIENT! Let patient and other rescuers know you are “CUTTING GLASS!”
 Removing Tempered Glass h Try rolling down side windows, try pulling rubber out around rear windows h Break window with a center punch (bottom corner) or pointed object h When possible, use farthest window h Pull glass out, possibly into tarp or sheet, then roll it up h Make sure patient and rescuers know you are “BREAKING GLASS!”, cover Pt.
Removing Tempered Glass h Try rolling down side windows, try pulling rubber out around rear windows h Break window with a center punch (bottom corner) or pointed object h When possible, use farthest window h Pull glass out, possibly into tarp or sheet, then roll it up h Make sure patient and rescuers know you are “BREAKING GLASS!”, cover Pt.
 Disentanglement h. Always use soft and hard protection h. EMS must maintain patient contact h. EMS must maintain contact with rescuers h. Continue re-assessing patient h. Treat patient accordingly, Ccollar, KED, Splints, etc.
Disentanglement h. Always use soft and hard protection h. EMS must maintain patient contact h. EMS must maintain contact with rescuers h. Continue re-assessing patient h. Treat patient accordingly, Ccollar, KED, Splints, etc.
 Extrication h What’s happening around you! h. Dash roll / dash lift / steering wheel lift h Cut steering wheel h Roof removal / Roof flap h Side takedown h “Pop” doors
Extrication h What’s happening around you! h. Dash roll / dash lift / steering wheel lift h Cut steering wheel h Roof removal / Roof flap h Side takedown h “Pop” doors
 Side Flap
Side Flap
 Roof Removal Dash Lift
Roof Removal Dash Lift
 Caring For The Patient h Safety while treating the patient is paramount. If available, a safety officer should be established along with the IC. Safety can also be another roll the IC and his crew members, leaving the IC with the overall command. h Personnel should establish direct communication link between EMS involved with Pt. care and those performing extrication. h Always communicate to ensure safety of all involved
Caring For The Patient h Safety while treating the patient is paramount. If available, a safety officer should be established along with the IC. Safety can also be another roll the IC and his crew members, leaving the IC with the overall command. h Personnel should establish direct communication link between EMS involved with Pt. care and those performing extrication. h Always communicate to ensure safety of all involved
 Caring For The Patient h Once the EMS has gained access, he or she acts as the eyes and ears. He or she must communicate with the extrication members, Pt. , and additional EMS resources during extrication. h EMS also decides (and must recognize) load and go situations or stay and play situations.
Caring For The Patient h Once the EMS has gained access, he or she acts as the eyes and ears. He or she must communicate with the extrication members, Pt. , and additional EMS resources during extrication. h EMS also decides (and must recognize) load and go situations or stay and play situations.
 Caring For The Patient h For patient safety, here a few tips: » » » » Ensure the Pt’s airway and control C-spine Assess the Pt’s breathing and pulse Establish the Pt’s L. O. C. and re-evaluate Scan the Pt. starting at the head Control hemorrhage as you encounter severe bleeding Treat for shock Provide emotional first aid as well as physical first aid » Personnel should explain what is happening around the Pt. (e. g. we are going to be breaking the window across from you)
Caring For The Patient h For patient safety, here a few tips: » » » » Ensure the Pt’s airway and control C-spine Assess the Pt’s breathing and pulse Establish the Pt’s L. O. C. and re-evaluate Scan the Pt. starting at the head Control hemorrhage as you encounter severe bleeding Treat for shock Provide emotional first aid as well as physical first aid » Personnel should explain what is happening around the Pt. (e. g. we are going to be breaking the window across from you)
 Patient removal h May require more disassembly, distortion, displacement or severing h Communicate with rescue team h Communicate with patient h Maintain spinal immobilization
Patient removal h May require more disassembly, distortion, displacement or severing h Communicate with rescue team h Communicate with patient h Maintain spinal immobilization
 Patient removal h Out door, feet first onto long board h Out door, head first onto long board h Out top, tilt seat back slide patient up onto long board h Improvise! h Secure to board h Treat patient h. Advise receiving facility of Pt. condition
Patient removal h Out door, feet first onto long board h Out door, head first onto long board h Out top, tilt seat back slide patient up onto long board h Improvise! h Secure to board h Treat patient h. Advise receiving facility of Pt. condition
 Post call h Determine need for CISM h Collect equipment, pick up people you left behind h Clean, test and restock equipment h Critique
Post call h Determine need for CISM h Collect equipment, pick up people you left behind h Clean, test and restock equipment h Critique
 Some info on non powered hand tools h Screwdrivers can be used to break glass, open trunks & remove vehicle’s cosmetics. h Socket set w/ratchet to remove nuts & bolts that hold seats, doors, etc. h Pliers to cut wires, remove cosmetics or pull valve stems. h Spring loaded center punch to break glass. h Bolt cutters to cut bolt & steering wheel ring. h Long & short board for pt’s protection, stabilization & packaging.
Some info on non powered hand tools h Screwdrivers can be used to break glass, open trunks & remove vehicle’s cosmetics. h Socket set w/ratchet to remove nuts & bolts that hold seats, doors, etc. h Pliers to cut wires, remove cosmetics or pull valve stems. h Spring loaded center punch to break glass. h Bolt cutters to cut bolt & steering wheel ring. h Long & short board for pt’s protection, stabilization & packaging.
 Non powered tools (continued) Pike pole to help flop the roof Pry bar to make a purchase point & force doors Flat headed axe to cut windshield Halligen to make a purchase point, remove trunk locks & break tempered glass h Pry axle can opener to cut windshield, make purchase point & cut sheet metal h 2 X 4 & 4 X 4 cribbing & wedges to stabilize vehicle (used with come along) h Come along with chains to pull dashes & seats, displace doors, pull roof & stabilize vehicle h h
Non powered tools (continued) Pike pole to help flop the roof Pry bar to make a purchase point & force doors Flat headed axe to cut windshield Halligen to make a purchase point, remove trunk locks & break tempered glass h Pry axle can opener to cut windshield, make purchase point & cut sheet metal h 2 X 4 & 4 X 4 cribbing & wedges to stabilize vehicle (used with come along) h Come along with chains to pull dashes & seats, displace doors, pull roof & stabilize vehicle h h
 Non powered tools (continued) h Chains to wrap dashboard & seats, pull roof or displace doors h Pneumatic tools (air powered) to cut roof, make relief cuts, third door conversion & cut windshield h Air bags used for lifting, pulling & stabilizing h Reciprocating electric or air operated saw h Hand operated hydraulic tools h Spreader used to force doors, seats & pedals h Cutter used to cut posts, make relief cuts, cut steering wheel & roof.
Non powered tools (continued) h Chains to wrap dashboard & seats, pull roof or displace doors h Pneumatic tools (air powered) to cut roof, make relief cuts, third door conversion & cut windshield h Air bags used for lifting, pulling & stabilizing h Reciprocating electric or air operated saw h Hand operated hydraulic tools h Spreader used to force doors, seats & pedals h Cutter used to cut posts, make relief cuts, cut steering wheel & roof.


