db8f1aafc755680eebac0bbf27a55e93.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 FY 2001 ONR CIP/SW URI Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing Principal Investigator: Andre Scedrov Institution: University of Pennsylvania URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce STARTED IN MAY 2001 11/19/98 Columbia University
FY 2001 ONR CIP/SW URI Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing Principal Investigator: Andre Scedrov Institution: University of Pennsylvania URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce STARTED IN MAY 2001 11/19/98 Columbia University
 The SPYCE Team l Joan Feigenbaum (Yale) l Joseph Y. Halpern (Cornell) l Patrick D. Lincoln l John C. Mitchell (Stanford) l Andre Scedrov (U Penn) l Jonathan M. Smith (U Penn)
The SPYCE Team l Joan Feigenbaum (Yale) l Joseph Y. Halpern (Cornell) l Patrick D. Lincoln l John C. Mitchell (Stanford) l Andre Scedrov (U Penn) l Jonathan M. Smith (U Penn)
 External Collaborators l Cynthia Dwork (Microsoft) l Tim Griffin (Intel) l Vitaly Shmatikov (SRI) l Paul Syverson (NRL)
External Collaborators l Cynthia Dwork (Microsoft) l Tim Griffin (Intel) l Vitaly Shmatikov (SRI) l Paul Syverson (NRL)
 Postdocs l Bjorn Knutsson, Penn l Ninghui Li, Stanford (till Summer 2003) l Michael Elkin, Yale (since Fall 2003) l 16 Ph. D. Students
Postdocs l Bjorn Knutsson, Penn l Ninghui Li, Stanford (till Summer 2003) l Michael Elkin, Yale (since Fall 2003) l 16 Ph. D. Students
 Project Vision: Diffuse Computing Managing and maintaining a computational infrastucture, distributed among many heterogeneous nodes that do not trust each other completely and may have incentives (needs, priorities).
Project Vision: Diffuse Computing Managing and maintaining a computational infrastucture, distributed among many heterogeneous nodes that do not trust each other completely and may have incentives (needs, priorities).
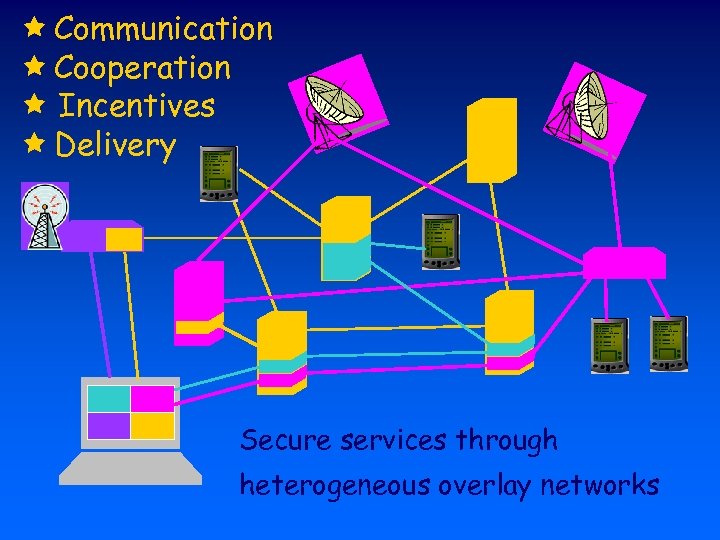 Communication Cooperation Incentives Delivery Secure services through heterogeneous overlay networks
Communication Cooperation Incentives Delivery Secure services through heterogeneous overlay networks
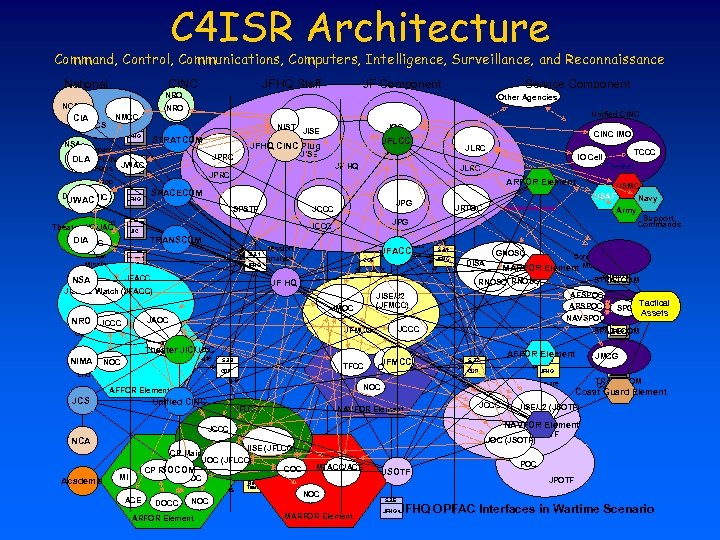 C 4 ISR Architecture Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance National CINC JFHQ Staff JF Component Service Component NRO NCA CIA NSA JCS Prepare ONA Other Agencies NRO NMCC JFHQ Unified CINC NIST JISE STRATCOM w/FDOs Develop Logistics DIA NMJIC Support JWAC JFHQ Collaborative Planning Environment JPG CINC Revise Mission Analysis JFACC 0. 0 JMOC JAOC Develop COAE JFMCC AOC End State 5. 3. 2 CDR TFCC Planning Guidance AFFOR Element JCS JCCC Unified CINC JFLCC COAE JFMCC CVIC/CDC NAVFOR Element CP Main Academia MI ACE DOCC NOC ARFOR Element Red Team Inputs 0. 0 AFFOR Element 5. 3. 7 JMCG 5. 3. 9 CDR Prepare ETO 5. 4 JFHQ JCCC TRANSCOM Command Coast Guard Element JISE/J 2 (JSOTF) JSOTF JOC (JSOTF) JISE (JFLCC) JOC (JFLCC) CP Fwd SOCOM TOC Tactical Assets SPOC NAVFOR Element JCCC NCA 0. 0 JFHQ SPACECOM Select COAE NOC Support Commands JFHQ STRATCOM AFSPOC ARSPOC Compare NAVSPOC Mo. P Analyze 5. 3. 3 CDR CINC Compare Mo. E MARFOR Element 5. 3. 5 JFHQ End Theater JIC/JAC Determine GNOSC DISA RNOSC JFHQ USMC USAF Navy Army JISE/J 2 (JFMCC) 5. 3. 4 JFHQ NIMA NOC Desired 5. 3. 4 JFHQ JF HQ JISE/J 2 ONA (JFACC) Watch JFHQ Project NRO JCCC Future Operations JFHQ Functional Inputs COE JFHQ JFACC NSA Theater JPG JCCC external Functional Inputs 5. 3. 1 TCCC JRTOC JCCC TRANSCOM Task Mission JLRC ARFOR Element SPACECOM JIC DIA JIOC IO Cell JF HQ JPRC SPSTF Sharpen Theater JIC/JAC ONA JLRC JOC JISE JPRC 5. 3. 9 JWAC JFHQ CINC IMO JFLCC JFHQ CINC Plug Prepare CONPLAN DLA NSA JOC 0. 0 Red Team COC MTACC/ACE NOC JSOTF 5. 3. 8 5. 3. 6 CDR JFHQ MARFOR Element POC JPOTF JFHQ OPFAC Interfaces in Wartime Scenario
C 4 ISR Architecture Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance National CINC JFHQ Staff JF Component Service Component NRO NCA CIA NSA JCS Prepare ONA Other Agencies NRO NMCC JFHQ Unified CINC NIST JISE STRATCOM w/FDOs Develop Logistics DIA NMJIC Support JWAC JFHQ Collaborative Planning Environment JPG CINC Revise Mission Analysis JFACC 0. 0 JMOC JAOC Develop COAE JFMCC AOC End State 5. 3. 2 CDR TFCC Planning Guidance AFFOR Element JCS JCCC Unified CINC JFLCC COAE JFMCC CVIC/CDC NAVFOR Element CP Main Academia MI ACE DOCC NOC ARFOR Element Red Team Inputs 0. 0 AFFOR Element 5. 3. 7 JMCG 5. 3. 9 CDR Prepare ETO 5. 4 JFHQ JCCC TRANSCOM Command Coast Guard Element JISE/J 2 (JSOTF) JSOTF JOC (JSOTF) JISE (JFLCC) JOC (JFLCC) CP Fwd SOCOM TOC Tactical Assets SPOC NAVFOR Element JCCC NCA 0. 0 JFHQ SPACECOM Select COAE NOC Support Commands JFHQ STRATCOM AFSPOC ARSPOC Compare NAVSPOC Mo. P Analyze 5. 3. 3 CDR CINC Compare Mo. E MARFOR Element 5. 3. 5 JFHQ End Theater JIC/JAC Determine GNOSC DISA RNOSC JFHQ USMC USAF Navy Army JISE/J 2 (JFMCC) 5. 3. 4 JFHQ NIMA NOC Desired 5. 3. 4 JFHQ JF HQ JISE/J 2 ONA (JFACC) Watch JFHQ Project NRO JCCC Future Operations JFHQ Functional Inputs COE JFHQ JFACC NSA Theater JPG JCCC external Functional Inputs 5. 3. 1 TCCC JRTOC JCCC TRANSCOM Task Mission JLRC ARFOR Element SPACECOM JIC DIA JIOC IO Cell JF HQ JPRC SPSTF Sharpen Theater JIC/JAC ONA JLRC JOC JISE JPRC 5. 3. 9 JWAC JFHQ CINC IMO JFLCC JFHQ CINC Plug Prepare CONPLAN DLA NSA JOC 0. 0 Red Team COC MTACC/ACE NOC JSOTF 5. 3. 8 5. 3. 6 CDR JFHQ MARFOR Element POC JPOTF JFHQ OPFAC Interfaces in Wartime Scenario
 Diffuse Computing l Paradigm developing rapidly as a result of - commercial computing markets - now-recognized potential of peer -to-peer computing and grid computing - the need for distributed network-centric systems l Raises challenges for - system design - software production - the development of mechanisms ensuring stable equilibria of diffuse systems
Diffuse Computing l Paradigm developing rapidly as a result of - commercial computing markets - now-recognized potential of peer -to-peer computing and grid computing - the need for distributed network-centric systems l Raises challenges for - system design - software production - the development of mechanisms ensuring stable equilibria of diffuse systems
 Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. SPYCE Objective: Scalable Distributed Assurance Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Pervasive ‘ 00 s Develop fundamental understanding, models, algorithms, and network testbed, in order to reduce cost, improve performance, and provide higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks. Incentives, Privacy, and Anonymity Protocol Design and Analysis Network Architecture Trust Management
Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. SPYCE Objective: Scalable Distributed Assurance Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Pervasive ‘ 00 s Develop fundamental understanding, models, algorithms, and network testbed, in order to reduce cost, improve performance, and provide higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks. Incentives, Privacy, and Anonymity Protocol Design and Analysis Network Architecture Trust Management
 Critical Infrastructure Protection Many critical infrastructures, national and Do. Dspecific, are decentralized systems Computer networks have, in addition, become critical infrastructures Research Question: How to build large-scale, adaptive and robust next-gen. systems? Approach: New Diffuse Computing concept - results with extremely loosely-coupled modules
Critical Infrastructure Protection Many critical infrastructures, national and Do. Dspecific, are decentralized systems Computer networks have, in addition, become critical infrastructures Research Question: How to build large-scale, adaptive and robust next-gen. systems? Approach: New Diffuse Computing concept - results with extremely loosely-coupled modules
 Critical Infrastructure Protection l Many critical infrastructures, national and Do. D-specific, are decentralized l Data sharing essential for operation, but data compromise can be catastrophic l Research Question: How to share data safely, using policies that are easy to formulate, enforce, maintain l Approach: diffuse trust management
Critical Infrastructure Protection l Many critical infrastructures, national and Do. D-specific, are decentralized l Data sharing essential for operation, but data compromise can be catastrophic l Research Question: How to share data safely, using policies that are easy to formulate, enforce, maintain l Approach: diffuse trust management
 Assuring Software Quality l Loose coupling leads to natural “sandboxing” l High decentralization means high autonomy l New way of writing software l Pieces of system more robust in face of: - Failures / Disruptions - Partial Information - Software Engineering for highly decentralized, policy-controlled and networked world
Assuring Software Quality l Loose coupling leads to natural “sandboxing” l High decentralization means high autonomy l New way of writing software l Pieces of system more robust in face of: - Failures / Disruptions - Partial Information - Software Engineering for highly decentralized, policy-controlled and networked world
 Assuring Software Quality l Technology applicable to managing process interaction - Process A delegates rights to process B § For limited purpose, limited time, limited locations - Fine-grained control of process actions - Works for diffuse systems that escape normal controls imposed by localized OSs l Diffuse principle of least privilege
Assuring Software Quality l Technology applicable to managing process interaction - Process A delegates rights to process B § For limited purpose, limited time, limited locations - Fine-grained control of process actions - Works for diffuse systems that escape normal controls imposed by localized OSs l Diffuse principle of least privilege
 FY 2001 CIP/SW URI BAA Topic #9: ASSURING SOFTWARE QUALITY Research Concentration Areas How to reason about the assurance and quality in highly distributed systems? l. Reason about uncertainty in all contexts of distributed agent-mediated information systems l. Develop co-algebraic foundations for expressing the semantics of concurrency l. Express knowledge of interactions building upon a game theoretic semantics - Vitaly Shmatikov poster l. Investigate configuration management in terms of distributed services, policy coordination - John Mitchell talk l. Develop highly dependable self-configuring operating services for net-centric, resource-aware mobile computing - Jonathan Smith talk, Bjorn Knutsson demo l. Investigate real-time/fault tolerant middleware and component integration in hybrid control - Kostas Anagnostakis demo l. Develop collaborative problem solving theories that emphasize computing as mediation l. Express the meaning of software artifacts, interfaces, aspects, and operating environments l. Extract and synthesize computational knowledge about algorithms and protocols - Joe Halpern talk l. Investigate the economics of software technology diffusion into commercial infrastructures - Joan Feigenbaum talk
FY 2001 CIP/SW URI BAA Topic #9: ASSURING SOFTWARE QUALITY Research Concentration Areas How to reason about the assurance and quality in highly distributed systems? l. Reason about uncertainty in all contexts of distributed agent-mediated information systems l. Develop co-algebraic foundations for expressing the semantics of concurrency l. Express knowledge of interactions building upon a game theoretic semantics - Vitaly Shmatikov poster l. Investigate configuration management in terms of distributed services, policy coordination - John Mitchell talk l. Develop highly dependable self-configuring operating services for net-centric, resource-aware mobile computing - Jonathan Smith talk, Bjorn Knutsson demo l. Investigate real-time/fault tolerant middleware and component integration in hybrid control - Kostas Anagnostakis demo l. Develop collaborative problem solving theories that emphasize computing as mediation l. Express the meaning of software artifacts, interfaces, aspects, and operating environments l. Extract and synthesize computational knowledge about algorithms and protocols - Joe Halpern talk l. Investigate the economics of software technology diffusion into commercial infrastructures - Joan Feigenbaum talk
 Do. D Impact l Joint Vision 2010 / Joint Vision 2020 of “Network Centric” operations l Do. D requirements addressed by project: - Agile and rapidly evolving § CING/Active Networks § Proxies - Secure and Robust § *AME A. N. approach - Scalable § Massively populated persistent worlds concepts
Do. D Impact l Joint Vision 2010 / Joint Vision 2020 of “Network Centric” operations l Do. D requirements addressed by project: - Agile and rapidly evolving § CING/Active Networks § Proxies - Secure and Robust § *AME A. N. approach - Scalable § Massively populated persistent worlds concepts
 Do. D Impact l Dynamic coalitions - Partial sharing based on partial trust l Joint Vision 2010 / Joint Vision 2020 of “Network Centric” operations - Can use policy to push data, overcome network bandwidth limitations - Right data to right place at right time
Do. D Impact l Dynamic coalitions - Partial sharing based on partial trust l Joint Vision 2010 / Joint Vision 2020 of “Network Centric” operations - Can use policy to push data, overcome network bandwidth limitations - Right data to right place at right time
 Project Metrics l Criteria by which success of the project should be measured - Good research Strong collaboration Educational impact Relevance to CIP/SW, Do. D, and Industry Transition Potential and Anticipated Impact
Project Metrics l Criteria by which success of the project should be measured - Good research Strong collaboration Educational impact Relevance to CIP/SW, Do. D, and Industry Transition Potential and Anticipated Impact
 Conferences where we publish l l l l Computer Security Foundations Workshop Conference on Computer and Communication Security International Information Security Conference Workshop on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management Conference on Electronic Commerce Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing International Symposium on High-Performance Distributed Computing l Conference on Computer Communications l International Workshop on Web Content Caching and Distribution l International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems
Conferences where we publish l l l l Computer Security Foundations Workshop Conference on Computer and Communication Security International Information Security Conference Workshop on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management Conference on Electronic Commerce Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing International Symposium on High-Performance Distributed Computing l Conference on Computer Communications l International Workshop on Web Content Caching and Distribution l International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems
 Conferences where we publish l l l l Computer Security Foundations Workshop Conference on Computer and Communication Security International Information Security Conference Workshop on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management Conference on Electronic Commerce Keywords Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing Computer International Symposium on High-Performance Distributed Security Computing Distributed l Conference on Computer Communications Communication l International Workshop on Web Content Caching and Distribution l International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems
Conferences where we publish l l l l Computer Security Foundations Workshop Conference on Computer and Communication Security International Information Security Conference Workshop on Security and Privacy in Digital Rights Management Conference on Electronic Commerce Keywords Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing Computer International Symposium on High-Performance Distributed Security Computing Distributed l Conference on Computer Communications Communication l International Workshop on Web Content Caching and Distribution l International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems
 July 2001 Project Themes l Combines 4 complementary thrusts: - Incentive-compatibility in distributed computing Authorization mechanisms Secure data storage and retrieval Communication protocols l Multi-institution experimental platform + systematic, formal treatment of underlying models, algorithms & data structures
July 2001 Project Themes l Combines 4 complementary thrusts: - Incentive-compatibility in distributed computing Authorization mechanisms Secure data storage and retrieval Communication protocols l Multi-institution experimental platform + systematic, formal treatment of underlying models, algorithms & data structures
 Today SPYCE areas of concentration l Market-based computation (incentive compatibility) l Communication and security protocols analysis l Authorization mechanisms (trust management) l Privacy and anonymity l Networking, experimental platform
Today SPYCE areas of concentration l Market-based computation (incentive compatibility) l Communication and security protocols analysis l Authorization mechanisms (trust management) l Privacy and anonymity l Networking, experimental platform
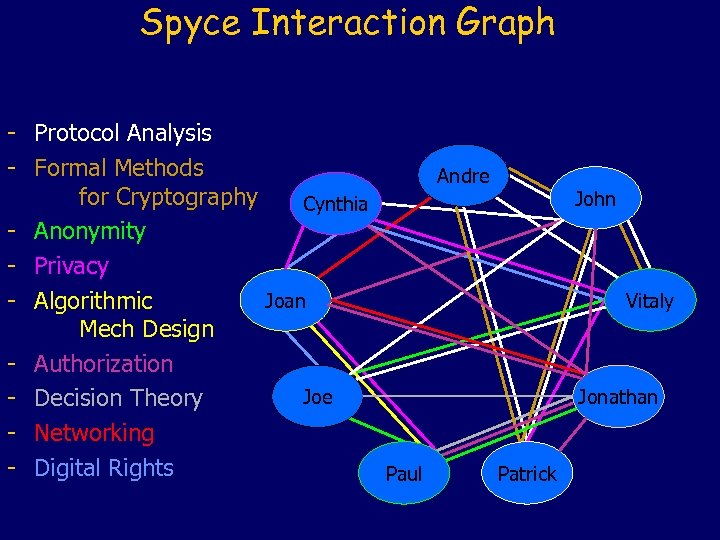 Spyce Interaction Graph - Protocol Analysis - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography John Cynthia - Anonymity - Privacy Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design - Authorization Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory - Networking - Digital Rights Paul Patrick
Spyce Interaction Graph - Protocol Analysis - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography John Cynthia - Anonymity - Privacy Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design - Authorization Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory - Networking - Digital Rights Paul Patrick
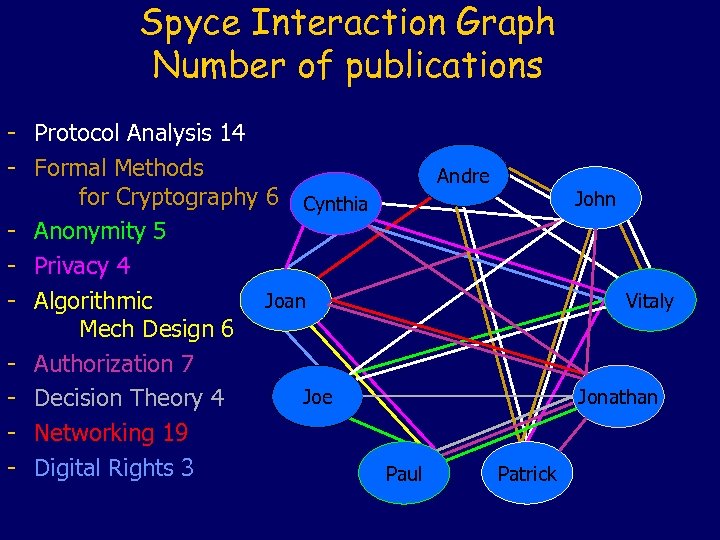 Spyce Interaction Graph Number of publications - Protocol Analysis 14 - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography 6 Cynthia John - Anonymity 5 - Privacy 4 Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design 6 - Authorization 7 Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory 4 - Networking 19 - Digital Rights 3 Paul Patrick
Spyce Interaction Graph Number of publications - Protocol Analysis 14 - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography 6 Cynthia John - Anonymity 5 - Privacy 4 Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design 6 - Authorization 7 Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory 4 - Networking 19 - Digital Rights 3 Paul Patrick
![Sample Accomplishments l Interdomain routing - Path vector protocols [Penn-Yale-Intel] - Local conditions for Sample Accomplishments l Interdomain routing - Path vector protocols [Penn-Yale-Intel] - Local conditions for](https://present5.com/presentation/db8f1aafc755680eebac0bbf27a55e93/image-24.jpg) Sample Accomplishments l Interdomain routing - Path vector protocols [Penn-Yale-Intel] - Local conditions for stable routes [Yale] l Analysis of cryptographic protocols - Formal methods for cryptography [Penn-Stanford] - Kerberos V analysis [Penn-NRL] l l l Logic for reasoning about policies [Cornell-Stanford] SPAM reduction algorithms [Microsoft-Stanford] Privacy in databases [SRI-Microsoft] Anonymity and information hiding [Cornell-NRL] Content transcoding for heterogeneous clients [Penn]
Sample Accomplishments l Interdomain routing - Path vector protocols [Penn-Yale-Intel] - Local conditions for stable routes [Yale] l Analysis of cryptographic protocols - Formal methods for cryptography [Penn-Stanford] - Kerberos V analysis [Penn-NRL] l l l Logic for reasoning about policies [Cornell-Stanford] SPAM reduction algorithms [Microsoft-Stanford] Privacy in databases [SRI-Microsoft] Anonymity and information hiding [Cornell-NRL] Content transcoding for heterogeneous clients [Penn]
 Impact on Education l This grant has enhanced the ability to educate and train students in science and engineering and perform CIP/SW-relevant research l 10 Spyce-related courses taught, including: - Economics and Computation Computer and Network Security E-Commerce Doing Business on the Internet The Internet: Co-Evolution of Technology and Society Sensitive Information in the Wired World Decision Theory Reasoning About Knowledge Mathematical Foundations of Computer Security l Active seminars on computer and information security l New undergraduate major and minor program at Penn in Logic, Information, and Computation including SPYCE-related courses l 16 Students in Degree Program Supported by Project (25% or more FTE) - Penn 4, Cornell 4, Stanford 5 , Yale 3
Impact on Education l This grant has enhanced the ability to educate and train students in science and engineering and perform CIP/SW-relevant research l 10 Spyce-related courses taught, including: - Economics and Computation Computer and Network Security E-Commerce Doing Business on the Internet The Internet: Co-Evolution of Technology and Society Sensitive Information in the Wired World Decision Theory Reasoning About Knowledge Mathematical Foundations of Computer Security l Active seminars on computer and information security l New undergraduate major and minor program at Penn in Logic, Information, and Computation including SPYCE-related courses l 16 Students in Degree Program Supported by Project (25% or more FTE) - Penn 4, Cornell 4, Stanford 5 , Yale 3
 Project Statistics l 1 Transition to Tenure-Track Faculty: Ninghui Li - NYU Ph. D (advisor: Feigenbaum) Stanford postdoc Purdue faculty l 5 Ph. Ds Awarded: - R. Sami: Yale MIT R. Chadha: Penn U. Sussex A. Jaggard: Penn Tulane N. Durgin: Stanford Sandia Livermore Labs Computer Security Group - A. Chander: Stanford NTT Do. Co. Mo US Labs § Proof-carrying-code-based security applications for 4 G wireless product § Direct application to commercial wireless security Sometimes the most effective way to transfer information and technology is to transition people
Project Statistics l 1 Transition to Tenure-Track Faculty: Ninghui Li - NYU Ph. D (advisor: Feigenbaum) Stanford postdoc Purdue faculty l 5 Ph. Ds Awarded: - R. Sami: Yale MIT R. Chadha: Penn U. Sussex A. Jaggard: Penn Tulane N. Durgin: Stanford Sandia Livermore Labs Computer Security Group - A. Chander: Stanford NTT Do. Co. Mo US Labs § Proof-carrying-code-based security applications for 4 G wireless product § Direct application to commercial wireless security Sometimes the most effective way to transfer information and technology is to transition people
 Project Endorsements l Microsoft: Cynthia Dwork l Intel: Tim Griffin l IBM: Ran Canetti l HP: Tomas Sander
Project Endorsements l Microsoft: Cynthia Dwork l Intel: Tim Griffin l IBM: Ran Canetti l HP: Tomas Sander
 Spyce Interaction Graph - Protocol Analysis - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography John Cynthia - Anonymity - Privacy Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design - Authorization Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory - Networking - Digital Rights Paul Patrick
Spyce Interaction Graph - Protocol Analysis - Formal Methods Andre for Cryptography John Cynthia - Anonymity - Privacy Joan Vitaly - Algorithmic Mech Design - Authorization Joe Jonathan - Decision Theory - Networking - Digital Rights Paul Patrick
 Plans for Option l In the first two years - Thoroughly familiarized ourselves with each others areas - Achieved accumulated knowledge of SPYCE l In option - Will take this to the next level - Apply this collective knowledge in the following areas
Plans for Option l In the first two years - Thoroughly familiarized ourselves with each others areas - Achieved accumulated knowledge of SPYCE l In option - Will take this to the next level - Apply this collective knowledge in the following areas
 Plans for Option (1) l Secure, reliable network infrastructure - Combine security mechanism and incentives - Examples: BGP, DNS, NTP, … l General theory of computational mechanism - Mechanism specification and verification - Computational complexity analysis combining network communication and incentives l Discrete information management - Multicentric information delivery and retrieval - Access control, anonymity, and privacy
Plans for Option (1) l Secure, reliable network infrastructure - Combine security mechanism and incentives - Examples: BGP, DNS, NTP, … l General theory of computational mechanism - Mechanism specification and verification - Computational complexity analysis combining network communication and incentives l Discrete information management - Multicentric information delivery and retrieval - Access control, anonymity, and privacy
 Plans for Option (2) l Further investigation of practical protocols l Automating verification l Adding utilities to specifications l Verifying mechanisms - mechanism = set of rules for playing a game, designed to encourage “good” behavior e. g. , tax system, type of auction
Plans for Option (2) l Further investigation of practical protocols l Automating verification l Adding utilities to specifications l Verifying mechanisms - mechanism = set of rules for playing a game, designed to encourage “good” behavior e. g. , tax system, type of auction
 Plans for Option (3) • Combine the study of incentives, privacy, and anonymity • Derive hardness results in diffuse computing • Hardness stems from interplay of computational requirements and incentive-compatibility requirements (as in budget-balanced MCS). • Use hardness as a building block in private algorithmic mechanisms or anonymous algorithmic mechanisms.
Plans for Option (3) • Combine the study of incentives, privacy, and anonymity • Derive hardness results in diffuse computing • Hardness stems from interplay of computational requirements and incentive-compatibility requirements (as in budget-balanced MCS). • Use hardness as a building block in private algorithmic mechanisms or anonymous algorithmic mechanisms.
 Plans for Option (4) l Kostas Anagnostakis Ph. D research: - ITRUST – Incentive TRust for Ultrascale Services and Techniques [P, Y, Columbia] § Ultrascale diffuse approach to distributed anomaly (e. g. , worm) detection § Ultrascale resource (e. g. , file) sharing l Bjorn Knutsson Post-Doctoral research: - Experimental Validation of Massively Populated Persistent Worlds MPPW on Planet. Lab (& new anomaly detection algorithms) - DHARMA – Distributed Home Agent for Reliable Mobile Access (diffuse approach for mobility; advanced adaptive configuration management) l Continuing evolution of SPYCELab
Plans for Option (4) l Kostas Anagnostakis Ph. D research: - ITRUST – Incentive TRust for Ultrascale Services and Techniques [P, Y, Columbia] § Ultrascale diffuse approach to distributed anomaly (e. g. , worm) detection § Ultrascale resource (e. g. , file) sharing l Bjorn Knutsson Post-Doctoral research: - Experimental Validation of Massively Populated Persistent Worlds MPPW on Planet. Lab (& new anomaly detection algorithms) - DHARMA – Distributed Home Agent for Reliable Mobile Access (diffuse approach for mobility; advanced adaptive configuration management) l Continuing evolution of SPYCELab
 Plans for Option (5) l Applications and Transitions - Work with Xr. ML developers on language and algorithm - IBM Privacy Project § Use RT algorithms for EPAL, P 3 P applications - Pursue commercial and DOD applications - Application to large policy sets (social security policies) l Generalize results: RT Datalog PFOL l Improve implementation: RT 0 Datalog PFOL l Policy development environment and tools - User interface, XML-format, interoperability - Testing methodology, analysis methods
Plans for Option (5) l Applications and Transitions - Work with Xr. ML developers on language and algorithm - IBM Privacy Project § Use RT algorithms for EPAL, P 3 P applications - Pursue commercial and DOD applications - Application to large policy sets (social security policies) l Generalize results: RT Datalog PFOL l Improve implementation: RT 0 Datalog PFOL l Policy development environment and tools - User interface, XML-format, interoperability - Testing methodology, analysis methods
 Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. SPYCE Objective: Scalable Distributed Assurance Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Pervasive ‘ 00 s Develop fundamental understanding, models, algorithms, and network testbed, in order to reduce cost, improve performance, and provide higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks. Incentives, Privacy, and Anonymity Protocol Design and Analysis Network Architecture Trust Management
Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. SPYCE Objective: Scalable Distributed Assurance Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Pervasive ‘ 00 s Develop fundamental understanding, models, algorithms, and network testbed, in order to reduce cost, improve performance, and provide higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks. Incentives, Privacy, and Anonymity Protocol Design and Analysis Network Architecture Trust Management
 Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing scedrov@saul. cis. upenn. edu Web URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce/ URI, 2001 Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. October, 2003 URI Objective Algorithms to model diffuse computing and achieve scaleable high assurance Do. D capabilities enhanced Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Reduced cost, improved performance, and higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks Pervasive ‘ 00 s Scientific/technical approach Sample Accomplishments Computing and networking elements diffusing into the environment need: -Local incentive-compatibility in global distributed computing -Scaleable authorization mechanisms -Assured communication -Experimental evidence • Local conditions for stable routes in interdomain routing • SPAM reduction algorithms • Privacy in databases • Content transcoding for heterogeneous clients • Formal methods for cryptography • Logics for reasoning about policies
Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing scedrov@saul. cis. upenn. edu Web URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce/ URI, 2001 Smart devices diffuse into the environment…. October, 2003 URI Objective Algorithms to model diffuse computing and achieve scaleable high assurance Do. D capabilities enhanced Room ‘ 40 s Desktop ‘ 80 s Wearable ‘ 90 s … with control and assurance Reduced cost, improved performance, and higher reliability for networked operations across untrusted networks Pervasive ‘ 00 s Scientific/technical approach Sample Accomplishments Computing and networking elements diffusing into the environment need: -Local incentive-compatibility in global distributed computing -Scaleable authorization mechanisms -Assured communication -Experimental evidence • Local conditions for stable routes in interdomain routing • SPAM reduction algorithms • Privacy in databases • Content transcoding for heterogeneous clients • Formal methods for cryptography • Logics for reasoning about policies
 Project Statistics l Special Awards or Honors - Joan Feigenbaum ACM Fellow, Member NAS Computer Science and Telecommunications Board - Joe Halpern ACM Fellow, AAAI Fellow - Pat Lincoln Member Defense Science Board task force on Science and Technology - John Mitchell Invited Speaker USENIX ‘ 02 - Andre Scedrov Program Co-Chair, International Symposium on Software Security, Tokyo, Japan, 2002 - Jonathan Smith Olga and Alberico Pompa Professorship of Engineering and Applied Science, University of Pennsylvania - Cynthia Dwork SIAM/SIGEST Best Paper 2003 - Paul Syverson Member Board of Directors, International Financial Cryptography Association
Project Statistics l Special Awards or Honors - Joan Feigenbaum ACM Fellow, Member NAS Computer Science and Telecommunications Board - Joe Halpern ACM Fellow, AAAI Fellow - Pat Lincoln Member Defense Science Board task force on Science and Technology - John Mitchell Invited Speaker USENIX ‘ 02 - Andre Scedrov Program Co-Chair, International Symposium on Software Security, Tokyo, Japan, 2002 - Jonathan Smith Olga and Alberico Pompa Professorship of Engineering and Applied Science, University of Pennsylvania - Cynthia Dwork SIAM/SIGEST Best Paper 2003 - Paul Syverson Member Board of Directors, International Financial Cryptography Association
 Project Statistics l 68 Publications - 6 refereed journal articles - 60 refereed conference proceedings - 2 book chapters l 5 Prototypes l 1 Transition to Industry - IBM Privacy Research Institute l Related Sponsored Research includes: - DARPA POSSE, Penn - DARPA Coalitions, Stanford and SRI - NSF ITR PORTIA, Stanford and Yale - DARPA/AFOSR MURI APPeers, UIUC and Stanford - NSF CCR-TC GRIDLOCK, Columbia and Penn and Yale - NSF ITR Networks of strategic agents, Cornell
Project Statistics l 68 Publications - 6 refereed journal articles - 60 refereed conference proceedings - 2 book chapters l 5 Prototypes l 1 Transition to Industry - IBM Privacy Research Institute l Related Sponsored Research includes: - DARPA POSSE, Penn - DARPA Coalitions, Stanford and SRI - NSF ITR PORTIA, Stanford and Yale - DARPA/AFOSR MURI APPeers, UIUC and Stanford - NSF CCR-TC GRIDLOCK, Columbia and Penn and Yale - NSF ITR Networks of strategic agents, Cornell
 Project Interactions l Industry - Microsoft: Cynthia Dwork - Intel: Tim Griffin - IBM Privacy Research Institute l Labs - NRL: Paul Syverson - SRI: Vitaly Shmatikov - Kestrel: Dusko Pavlovic l Other universities - UC Berkeley, Columbia, UIUC
Project Interactions l Industry - Microsoft: Cynthia Dwork - Intel: Tim Griffin - IBM Privacy Research Institute l Labs - NRL: Paul Syverson - SRI: Vitaly Shmatikov - Kestrel: Dusko Pavlovic l Other universities - UC Berkeley, Columbia, UIUC
 FY 2001 ONR CIP/SW URI Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing Principal Investigator: Andre Scedrov Institution: University of Pennsylvania URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce STARTED IN MAY 2001 11/19/98 Columbia University
FY 2001 ONR CIP/SW URI Software Quality and Infrastructure Protection for Diffuse Computing Principal Investigator: Andre Scedrov Institution: University of Pennsylvania URL: http: //www. cis. upenn. edu/spyce STARTED IN MAY 2001 11/19/98 Columbia University


