4365401264b5af956c2f3ca2980d4b64.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Future Skills Needs of Enterprise Marie Bourke EGFSN Head of Secretarial 30 th September 2014

About The Expert Group on Future Skills Needs

About the EGFSN • Government Advisory Group established in 1997 in response to developing skills shortage in ICT. Remit has broadened significantly sinception • Reports to Minister for Jobs, Enterprise, & Innovation and Minister for Education & Skills • Day to day management, research and analysis are undertaken by Forfás in conjunction with the Skills and Labour Market Unit, SOLAS • EGFSN meets 4 times a year. Sub-groups oversee individual projects • Funding from the National Training Fund (employer contribution, 0. 7% salaries).

Role of the EGFSN Projected skills requirements at national & sectoral levels & recommendations • Priority education & training requirements • Skills that must be met through inward migration • Developments in overseas content & delivery systems & adaptations to Irish training provision • Recommend how existing systems & delivery mechanisms might be adapted • Convey views on programmes supported by the NTF to the Minister • Ensure that recommendations are assessed by stakeholders & inform on implementation • Provide information to assist labour market justification for new & existing programmes

EGFSN Membership Employers, Unions, Education & Training Providers & Government Departments q Business (Facebook, Openet, Cook Medical, ICE Group) q Employee (ICTU) & Employer (IBEC, ISME) reps, q Higher & Further Education (CDETB, NALA, Skillnets, CIT, IUA, HEA, SOLAS) q Enterprise Development Agencies, (IDA, EI, Forfas) q Guidance Counsellors (IGC) q Government Depts. – Education & Skills - Jobs, Enterprise & Innovation - Public Expenditure & Reform

EGFSN & National Enterprise Policy Work of EGFSN linked to Enterprise Developments, National Policy Objectives & Strategies Ø Action Plan for Jobs - 2012, 2013, 2014 Ø ICT Skills Action Plan, 2014 Ø Strategy for the Manufacturing Sector to 2020 Ø Trade Tourism & Investment Strategy to 2015 Ø Food Harvest 2020 Ø Green Economy Strategy Ø LM Activation – ICT Conversion, Springboard, Momentum, Skillnets

Identified Areas of Future Skills Needs

National Skills Bulletin 2014 • • • National labour market overview Sectoral employment trends and outlook Occupational analysis: o Employment trends and profiles for 135 occupations o Unemployment trends and profiles o Labour market transitions o Vacancies o Sourcing from outside the EEA o Indication of skills and labour shortages Objective - To inform policy design in the areas of: • Education and training provision • Active labour market policies • Immigration • Career guidance

Areas of Skills Shortage • • • ICT (software developers (web, mobile, cloud, IT project management and business analysis, testing and troubleshooting), databases/big data, specific product knowledge, IT security, technical support, networking and infrastructure Engineering (production and process engineering; quality and validation; product development and design (chemicals, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, ICT, food and medical devices); energy; telecommunications; project management and production planning Science (R&D, science & business; science & sales) Business & finance (accountants (financial, tax, compliance, solvency and rationalisation); quantitative analysts (e. g. financial analysts, statisticians, economists, actuaries, risk analysts); management consultants Health (doctors (GPs and non-consultant hospital doctors), nurses (intensive care, theatre, oncology, paediatrics, geriatric care), radiographers (CT, MRI), sonographers Sales (technical sales (B 2 B and B 2 C), multilingual customer support, online sales and marketing) Craft (tool making, welding (TIG, MIG)) Transport (multilingual supply chain and logistics managers, HGV and forklift drivers) Clerical (multilingual credit control/debt collection, supply chain & logistics)

Manufacturing • • • • Sector currently employs around 200, 000 people Replacement demand in the region of 4, 000 to 5, 000 persons p. a. regardless of whether employment expands or not Employment outlook depends on addressing domestic competitiveness & a favourable international trading environment Increasing demand for higher skills, skilled operative jobs replacing elementary jobs & employment of qualified technicians & STEM professionals continuing to increase as a proportion of total employment A small no. of skills shortages but critical at an operational level to the technical expertise in the sector - toolmaking, machinists, supervisors, polymer technicians and across a number of engineering disciplines 3 rd level role in upskilling requirements for employees through CPD / in company programmes Scenario of up to 20, 000 additional jobs in the sector to 2016

High Level ICT skills • • • Strong demand for people with high level ICT skills across the economy Potential 44, 500 new job openings (expansion & replacement demand) over next 6 yrs 68, 280 ICT professionals working within the ICT sector & across other sectors Forecast average 5% pa growth for these high-level ICT skills to 2018 Increasing the employment of ICT professionals to 91, 000 by 2018 Specifically Honours, masters & some Phd level graduates from – Computing courses (computing software, computer programming & multi-media gaming with a substantial computing content) – Electronic & electrical engineering (communications, mechatronics & electronic/ computing engineering). ICT Skills Action Plan – doubling graduate output, plus Conversion & Springboard Flexible learning & CPD for employees to upskill for these roles e. g. EMC, Intel, IBM, VMware with 3 rd level
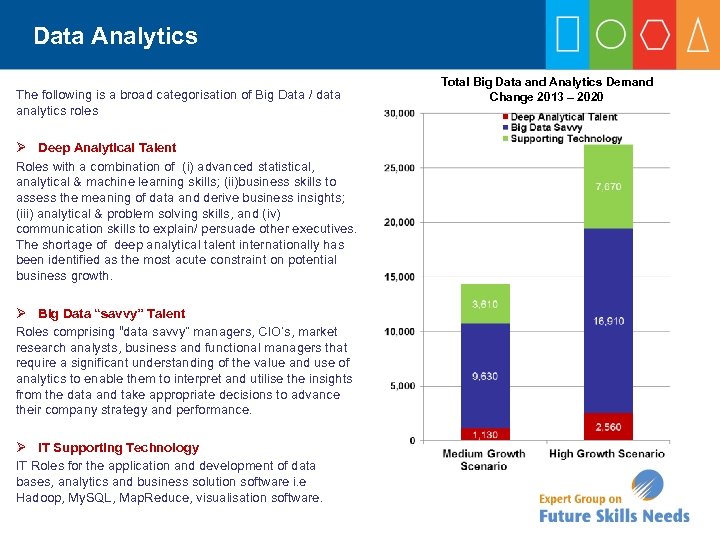
Data Analytics The following is a broad categorisation of Big Data / data analytics roles Ø Deep Analytical Talent Roles with a combination of (i) advanced statistical, analytical & machine learning skills; (ii)business skills to assess the meaning of data and derive business insights; (iii) analytical & problem solving skills, and (iv) communication skills to explain/ persuade other executives. The shortage of deep analytical talent internationally has been identified as the most acute constraint on potential business growth. Ø Big Data “savvy” Talent Roles comprising “data savvy” managers, CIO’s, market research analysts, business and functional managers that require a significant understanding of the value and use of analytics to enable them to interpret and utilise the insights from the data and take appropriate decisions to advance their company strategy and performance. Ø IT Supporting Technology IT Roles for the application and development of data bases, analytics and business solution software i. e Hadoop, My. SQL, Map. Reduce, visualisation software. Total Big Data and Analytics Demand Change 2013 – 2020

Foreign Languages & International Selling Foreign languages • Boosting the uptake of modern foreign languages at 3 rd level • Aligning assessment of foreign language proficiency to CEFR • Focusing Erasmus students placements towards study and work in non-English speaking markets. HEA should set placement targets International Selling • International sales module on 3 rd level general business & marketing courses – focus on B 2 B; B 2 G, Technical Sales content in courses – infrastructure & large systems • Post graduate diploma courses in international sales with foreign languages e. g German, French, Spanish • International Sales Degree programme - with active engagement & support of cos • Strengthen focus within business & marketing programmes on the potential value and use of E-commerce and social media applications

Ireland’s Skills Supply
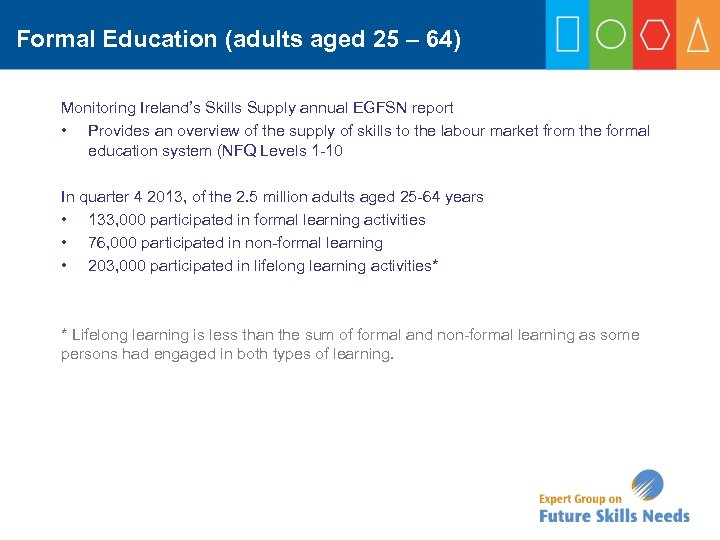
Formal Education (adults aged 25 – 64) Monitoring Ireland’s Skills Supply annual EGFSN report • Provides an overview of the supply of skills to the labour market from the formal education system (NFQ Levels 1 -10 In quarter 4 2013, of the 2. 5 million adults aged 25 -64 years • 133, 000 participated in formal learning activities • 76, 000 participated in non-formal learning • 203, 000 participated in lifelong learning activities* * Lifelong learning is less than the sum of formal and non-formal learning as some persons had engaged in both types of learning.
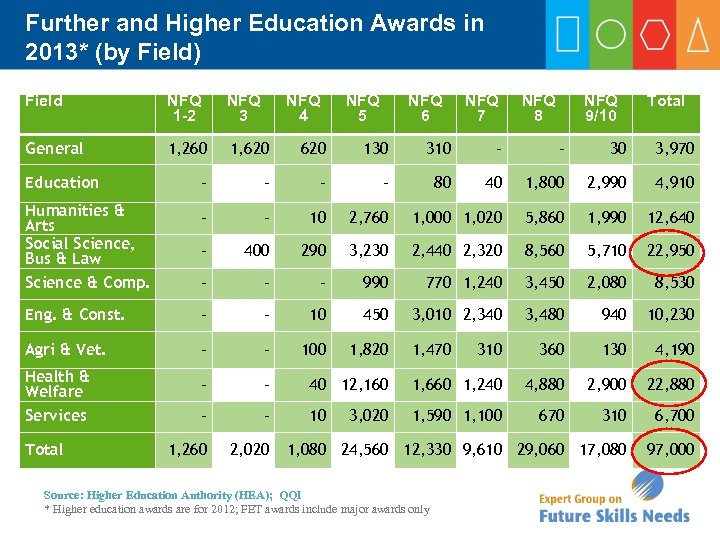
Further and Higher Education Awards in 2013* (by Field) Field NFQ 1 -2 NFQ 3 General 1, 260 1, 620 130 310 - - 30 3, 970 Education - - 80 40 1, 800 2, 990 4, 910 Humanities & Arts Social Science, Bus & Law - - 10 2, 760 1, 000 1, 020 5, 860 1, 990 12, 640 - 400 290 3, 230 2, 440 2, 320 8, 560 5, 710 22, 950 Science & Comp. - - - 990 770 1, 240 3, 450 2, 080 8, 530 Eng. & Const. - - 10 450 3, 010 2, 340 3, 480 940 10, 230 Agri & Vet. - - 100 1, 820 310 360 130 4, 190 Health & Welfare - - 40 12, 160 1, 660 1, 240 4, 880 2, 900 22, 880 Services - - 10 1, 590 1, 100 670 310 6, 700 1, 260 2, 020 1, 080 24, 560 12, 330 9, 610 29, 060 17, 080 97, 000 Total NFQ 4 NFQ 5 NFQ 6 3, 020 1, 470 Source: Higher Education Authority (HEA); QQI * Higher education awards are for 2012; FET awards include major awards only NFQ 7 NFQ 8 NFQ 9/10 Total

What is being done to address skills needs?

Recurring Themes in EGFSN research • • Adding to/adjusting course or programme e. g. Pharma – bioinformatics, Business, Science - data analytics, project management tools, Construction engineering – Building Information Modelling Creation of new programmes - post grad diplomas/certs, Benefits of more interdisciplinary projects Increasing the no. of graduates for particular sectors (ICT programmers, engineers) The need for more/better work placement experience (HEIs) Enhanced industry & HEI engagement at local level, programme design & content, delivery, especially with SMEs Progression outcomes from programmes Promotion/awareness of various job opportunities, skills requirements e. g. STEM, languages, work experience, generic skills

Further Education and Training Strategy Strategic Goals: • • • Planning and Funding - provision will be planned and funded on the basis of objective analysis of needs and evidence of impact Active Inclusion, Literacy and Numeracy Strategy - provision will support the active inclusion of all citizens with special reference to literacy and numeracy Quality Provision - provision will meet appropriate national and international quality standards Employer Engagement - linked to labour market needs and will contribute to national economic development Standing of FET – reposition FET as a high-status learning path leading to worthwhile career options

Aligning Labour Market Activation initiatives with Future Skills Needs of Employers Springboard & ICT Conversion The EGFSN Guidance document summarises the skills in demand across various sectors in the economy. Each year it accompanies the Government funded call for up to 6, 000 places on part-time HE courses for jobseekers with the aim of progressing them to employment Priorities for Springboard / ICT Conversion 2014: 1. ICT Skills – all sectors 2. Manufacturing – engineering, biopharma-pharmachem, medical devices, food & beverages, consumer goods & ICT hardware 3. Skills to Trade Internationally – all sectors 4. International Financial Services 5. Cross-Enterprise Skills – big-data savvy roles, 6. entrepreneurship, creativity-design-innovation, business & finance, core management, people skills 7. Construction – BIM, Green, Management

ICT Skills Action Plan EGFSN Report , Nov 2013 Continuing strong demand for people with honours degree level+ (NFQ 8 & 9) ICT skills across the economy could lead to 44, 500 new job openings arising from expansion & replacement demand over the next 6 years Government’s ICT Skills Action Plan (Published 14 March 2014) • Graduates from HE supply over 60% of the demand & this plan will boost graduate numbers to meet approx. 74% by 2018 by enhancing core provision, improved retention, conversion programmes & awareness raising, especially for females on ICT careers. • Inward migration will always play a key role in meeting the demand for high-level ICT skills with the issue of up to 2, 000 work permits for ICT professionals in 2014

Employment Permits (Amendment) Bill 2014 Objectives of Bill • Bill extends and amends the Employment Permits Acts of 2003 and 2006 to: – provide flexibility to deal with changing labour market, work patterns and economic development needs – provide for a robust employment permits regime which will provide clarity and certainty to potential investors and employers, both indigenous and multinational, to better enable their business planning and HR decision-making; and – address recent deficiencies identified by the High Court in Younis case (defence for employee, can take case for civil remedy)

Employment Permit Types Provides a legislative basis for the following new EP types: 1. Critical Skills EP (formerly Green Card) – To attract highly skilled people into the labour market to fill our critical skill shortages – Labour Market Needs Test is not required – Can apply for immediate family reunification from INIS – Can apply for residency from INIS upon completion of the Green Card’s duration (i. e. 2 yrs, so no renewals). 2. Dependant/Civil Partner/Spouse EP – To support the attractiveness of Ireland as a location of employment for Critical Skills EP holders and Researchers – Can apply for all occupations – Can apply with a salary of less than € 30 k. – No labour market test – No fee 3. Intra-Company Transfer EP – To facilitate the transfer of senior management, key personnel or trainees who are foreign nationals from an overseas branch of a multinational corporation to its Irish branch – Employees can stay on the foreign payroll – No labour market test – Salary of € 40, 000 or € 30, 000 (Trainee)
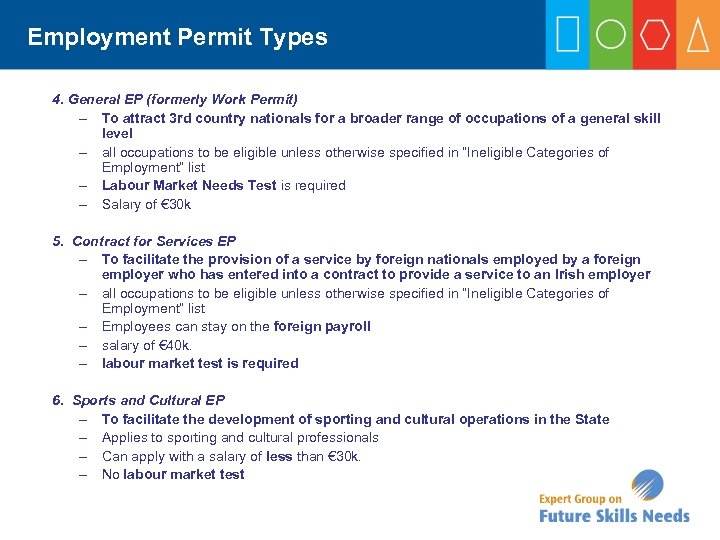
Employment Permit Types 4. General EP (formerly Work Permit) – To attract 3 rd country nationals for a broader range of occupations of a general skill level – all occupations to be eligible unless otherwise specified in “Ineligible Categories of Employment“ list – Labour Market Needs Test is required – Salary of € 30 k 5. Contract for Services EP – To facilitate the provision of a service by foreign nationals employed by a foreign employer who has entered into a contract to provide a service to an Irish employer – all occupations to be eligible unless otherwise specified in “Ineligible Categories of Employment“ list – Employees can stay on the foreign payroll – salary of € 40 k. – labour market test is required 6. Sports and Cultural EP – To facilitate the development of sporting and cultural operations in the State – Applies to sporting and cultural professionals – Can apply with a salary of less than € 30 k. – No labour market test

Employment Permit Types 7. Reactivation EP – for those who had fallen out of the employment permits system through no fault of their own and who have DJE permission to apply for an EP – Can apply for all occupations – Can apply with a salary of less than € 30 k. – No labour market test 8. Internship EP – To facilitate non-EEA students who are undertaking a Degree Programme outside the State to undertake an internship in the State – Can apply for occupations on the highly skilled list – Can apply with a salary of less than € 30 k. – No labour market test 9. Exchange Agreement EP – To facilitate exchanges between Irish and international bodies e. g. fulbright commission – Can apply with a salary of less than € 30 k. – No labour market test

Employer Engagement & Collaboration • • • Work placements Design of courses – to meet competencies required in the job Programme Reviews - Course content & 5 year course reviews Delivery of modules – where expertise is in industry Use of projects for research – post grad & undergrad Awareness raising re careers – profiling careers, careers fairs Data sets for data analytics Research CPD for employees Summer schools – tasters for courses

Thank you! Expert Group on Future Skills Needs www. skillsireland. com
4365401264b5af956c2f3ca2980d4b64.ppt