400e6069bf3c72a83377ea6043313f29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance 2 nd NATIONAL EXPORT FORUM 2008 Steven C. M. Wong* Institute of Strategic and International Studies (ISIS) Malaysia * The opinions expressed are solely those of the speaker
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance 2 nd NATIONAL EXPORT FORUM 2008 Steven C. M. Wong* Institute of Strategic and International Studies (ISIS) Malaysia * The opinions expressed are solely those of the speaker
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance OUTLINE Present status • Short-term outlook • Medium- to longer-term horizon • Conclusions
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance OUTLINE Present status • Short-term outlook • Medium- to longer-term horizon • Conclusions
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance PRESENT STATUS • Strong growth in export value since 2001 • Manufactured products account for more than 75%, and electrical and electronics about 45%, of total exports • ASEAN countries, particularly Singapore, Thailand, Indonesia and Vietnam, represent a quarter of the total export market • The US is the largest single market (16%), followed by the EU countries (13%) and Mainland China (9%) and Japan (9%) • Fastest growing markets have been those of ASEAN, Northeast Asia and the South • Exports to US, comprising mainly E&E products, have been tapering off and begun to show decline
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance PRESENT STATUS • Strong growth in export value since 2001 • Manufactured products account for more than 75%, and electrical and electronics about 45%, of total exports • ASEAN countries, particularly Singapore, Thailand, Indonesia and Vietnam, represent a quarter of the total export market • The US is the largest single market (16%), followed by the EU countries (13%) and Mainland China (9%) and Japan (9%) • Fastest growing markets have been those of ASEAN, Northeast Asia and the South • Exports to US, comprising mainly E&E products, have been tapering off and begun to show decline
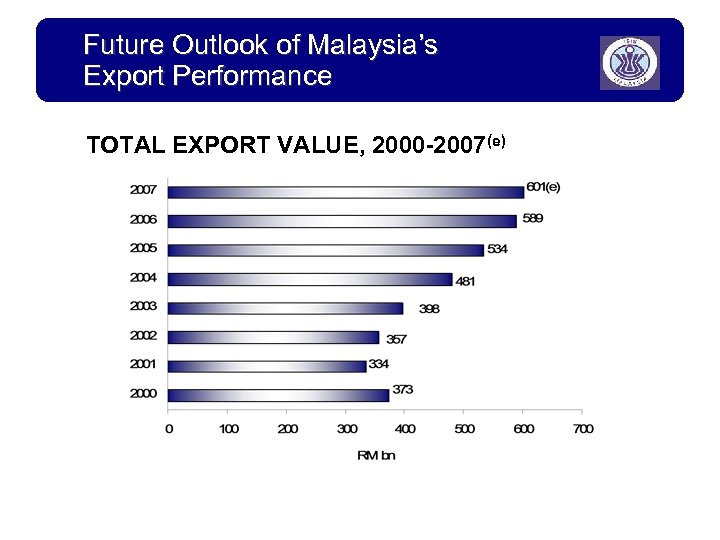 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance TOTAL EXPORT VALUE, 2000 -2007(e)
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance TOTAL EXPORT VALUE, 2000 -2007(e)
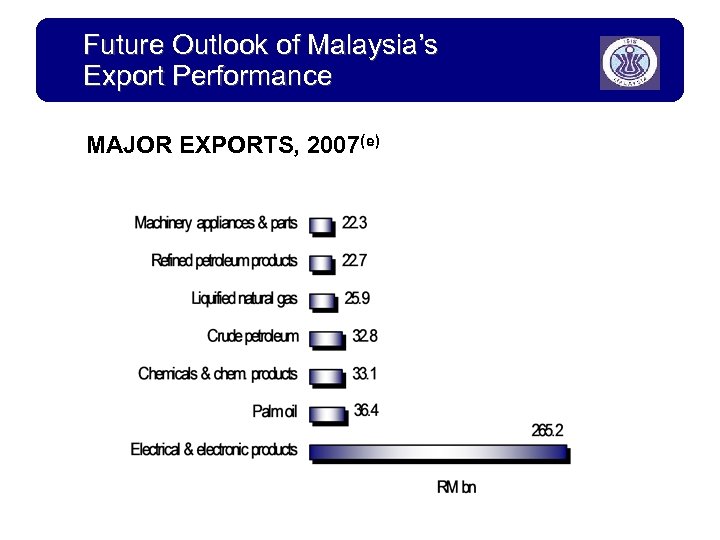 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MAJOR EXPORTS, 2007(e)
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MAJOR EXPORTS, 2007(e)
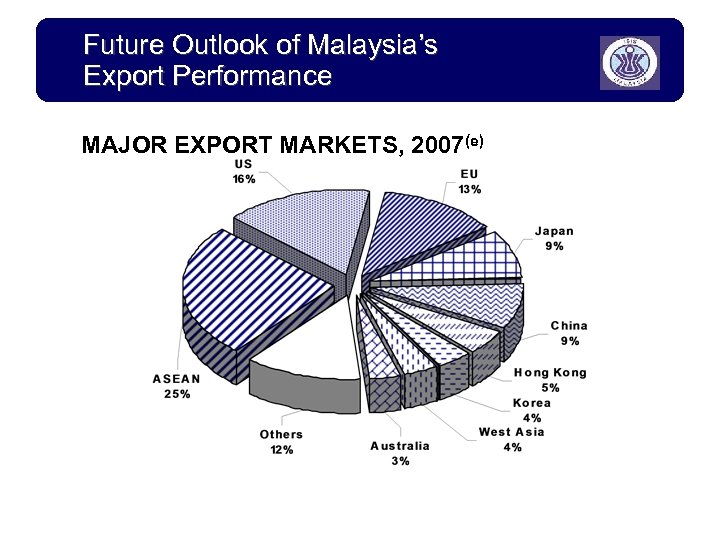 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MAJOR EXPORT MARKETS, 2007(e)
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MAJOR EXPORT MARKETS, 2007(e)
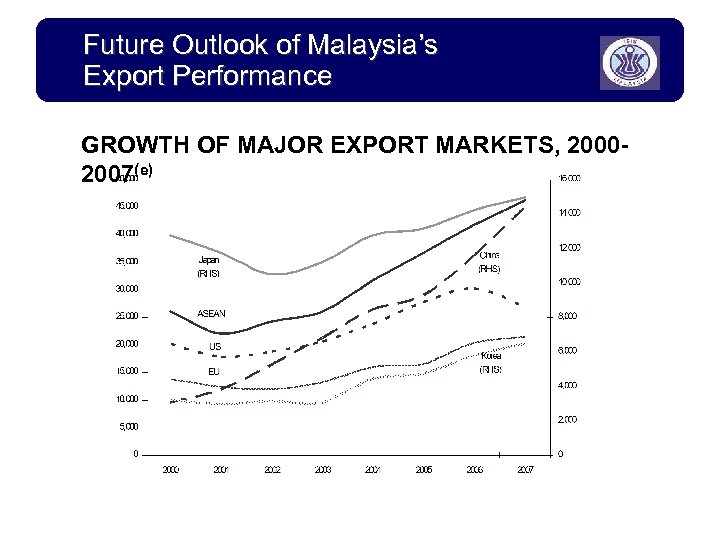 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance GROWTH OF MAJOR EXPORT MARKETS, 20002007(e)
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance GROWTH OF MAJOR EXPORT MARKETS, 20002007(e)
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Exports to the US look increasingly vulnerable, with high risks (not certainty) of an economic recession • The combined impact on Malaysian exports could be substantial taking into account parts & component (P & C) trade with the US as the final destination market • Compounding the uncertainty is the price-quantity effect of appreciated Asian currencies on US demand • De-coupling scenarios only work if domestic absorption is substantially and simultaneously increased in the Rest of the World • East Asian countries are investing too much and consuming too little Economic integration of East Asia is production-oriented and not consumption-based.
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Exports to the US look increasingly vulnerable, with high risks (not certainty) of an economic recession • The combined impact on Malaysian exports could be substantial taking into account parts & component (P & C) trade with the US as the final destination market • Compounding the uncertainty is the price-quantity effect of appreciated Asian currencies on US demand • De-coupling scenarios only work if domestic absorption is substantially and simultaneously increased in the Rest of the World • East Asian countries are investing too much and consuming too little Economic integration of East Asia is production-oriented and not consumption-based.
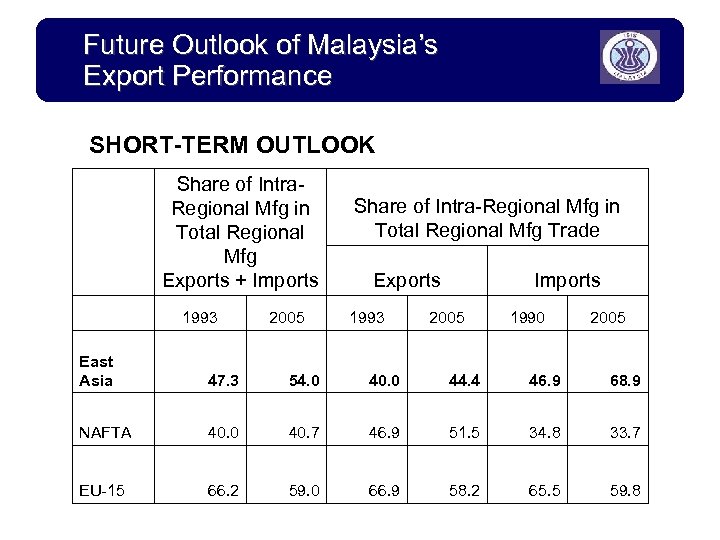 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Share of Intra. Regional Mfg in Total Regional Mfg Exports + Imports 1993 2005 Share of Intra-Regional Mfg in Total Regional Mfg Trade Exports 1993 Imports 2005 1990 2005 East Asia 47. 3 54. 0 40. 0 44. 4 46. 9 68. 9 NAFTA 40. 0 40. 7 46. 9 51. 5 34. 8 33. 7 EU-15 66. 2 59. 0 66. 9 58. 2 65. 5 59. 8
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Share of Intra. Regional Mfg in Total Regional Mfg Exports + Imports 1993 2005 Share of Intra-Regional Mfg in Total Regional Mfg Trade Exports 1993 Imports 2005 1990 2005 East Asia 47. 3 54. 0 40. 0 44. 4 46. 9 68. 9 NAFTA 40. 0 40. 7 46. 9 51. 5 34. 8 33. 7 EU-15 66. 2 59. 0 66. 9 58. 2 65. 5 59. 8
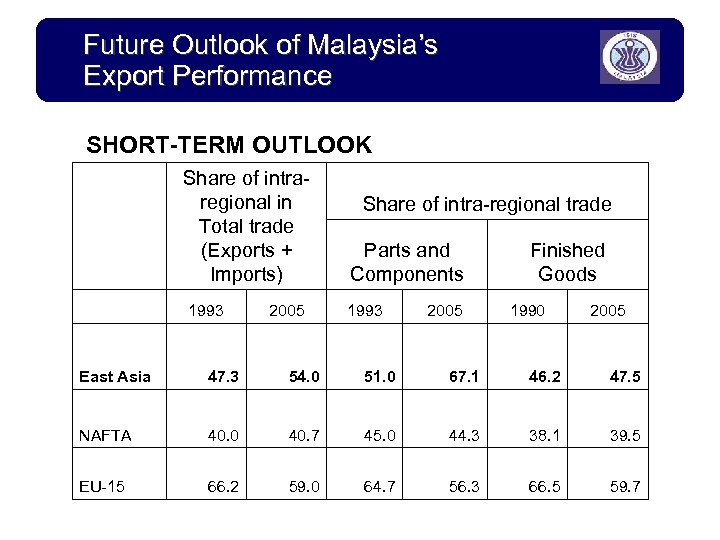 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Share of intraregional in Total trade (Exports + Imports) 1993 2005 Share of intra-regional trade Parts and Components 1993 2005 Finished Goods 1990 2005 East Asia 47. 3 54. 0 51. 0 67. 1 46. 2 47. 5 NAFTA 40. 0 40. 7 45. 0 44. 3 38. 1 39. 5 EU-15 66. 2 59. 0 64. 7 56. 3 66. 5 59. 7
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK Share of intraregional in Total trade (Exports + Imports) 1993 2005 Share of intra-regional trade Parts and Components 1993 2005 Finished Goods 1990 2005 East Asia 47. 3 54. 0 51. 0 67. 1 46. 2 47. 5 NAFTA 40. 0 40. 7 45. 0 44. 3 38. 1 39. 5 EU-15 66. 2 59. 0 64. 7 56. 3 66. 5 59. 7
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK • Intra-regional trade is concentrated. Just 30 exports account for 50% of total trade, primarily office machinery, telecommunications, electronics, textiles and clothing. • Intra-regional trade is parts and components-driven and Chinacentred. International production sharing has driven intra-regional trade, with Japan, Korea and Taiwan being major suppliers and China being the production platform. • Studies show before there is a sharp increase of East Asian exports to the US, intra-regional trade rises. An increase in Japanese exports to the region also leads to higher exports to the US.
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK • Intra-regional trade is concentrated. Just 30 exports account for 50% of total trade, primarily office machinery, telecommunications, electronics, textiles and clothing. • Intra-regional trade is parts and components-driven and Chinacentred. International production sharing has driven intra-regional trade, with Japan, Korea and Taiwan being major suppliers and China being the production platform. • Studies show before there is a sharp increase of East Asian exports to the US, intra-regional trade rises. An increase in Japanese exports to the region also leads to higher exports to the US.
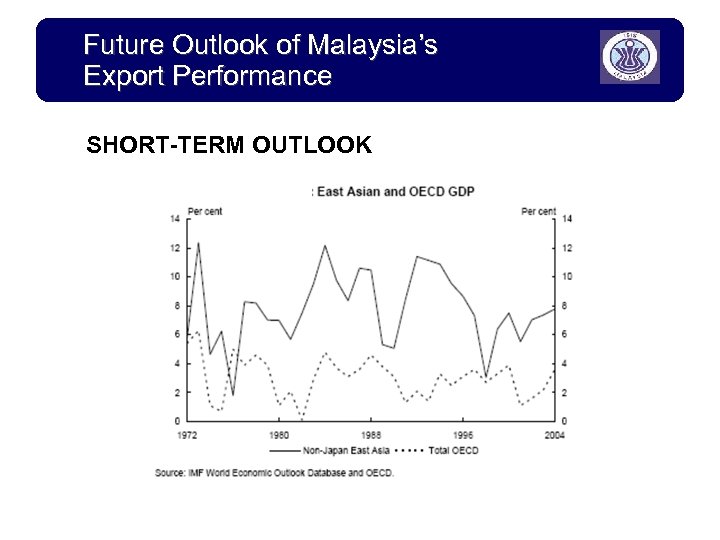 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance SHORT-TERM OUTLOOK
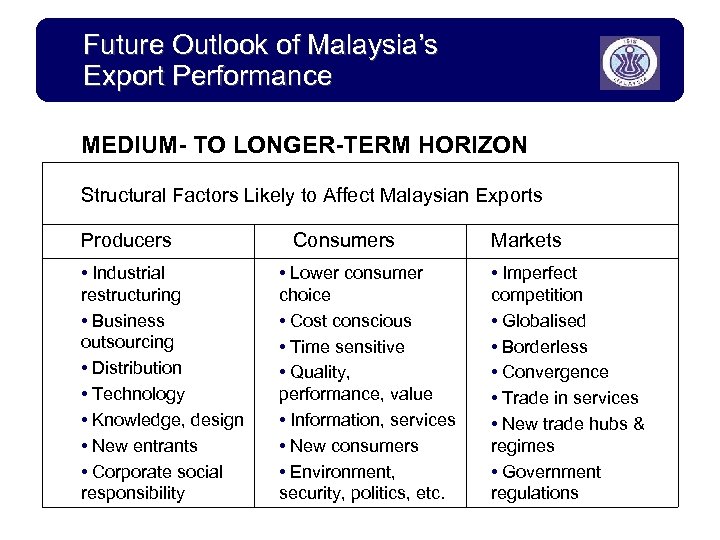 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Structural Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports Producers • Industrial restructuring • Business outsourcing • Distribution • Technology • Knowledge, design • New entrants • Corporate social responsibility Consumers • Lower consumer choice • Cost conscious • Time sensitive • Quality, performance, value • Information, services • New consumers • Environment, security, politics, etc. Markets • Imperfect competition • Globalised • Borderless • Convergence • Trade in services • New trade hubs & regimes • Government regulations
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Structural Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports Producers • Industrial restructuring • Business outsourcing • Distribution • Technology • Knowledge, design • New entrants • Corporate social responsibility Consumers • Lower consumer choice • Cost conscious • Time sensitive • Quality, performance, value • Information, services • New consumers • Environment, security, politics, etc. Markets • Imperfect competition • Globalised • Borderless • Convergence • Trade in services • New trade hubs & regimes • Government regulations
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Specific Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports – (1) • Trade creation from China, India, Vietnam & other rapidly growing economies (+ve) • Regional economic integration via Asean Economic Community and Plus One (and possibly Plus Three, Plus Six) countries (+ve) • Displacement effects in third markets as a result of competition from emerging economies (-ve) • Spill-over/exclusion effects from third-party regional trading arrangements (? ) • Stable exchange rate and macroeconomic regime (+ve) • Integration of export-sector with domestic economy
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Specific Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports – (1) • Trade creation from China, India, Vietnam & other rapidly growing economies (+ve) • Regional economic integration via Asean Economic Community and Plus One (and possibly Plus Three, Plus Six) countries (+ve) • Displacement effects in third markets as a result of competition from emerging economies (-ve) • Spill-over/exclusion effects from third-party regional trading arrangements (? ) • Stable exchange rate and macroeconomic regime (+ve) • Integration of export-sector with domestic economy
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Specific Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports – (2) • Generating investments in targeted growth areas (IMP 3) • Integrating Malaysian companies into regional and global networks (IMP 3) • Sustaining the contribution of manufacturing sector to growth (IMP 3) • Positioning services as a major source of growth (IMP 3) • Facilitating development and application of knowledge-intensive technologies (IMP 3) • Developing innovative and creative human capital (IMP 3) • Creating a more competitive business-operating environment (IMP 3)
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Specific Factors Likely to Affect Malaysian Exports – (2) • Generating investments in targeted growth areas (IMP 3) • Integrating Malaysian companies into regional and global networks (IMP 3) • Sustaining the contribution of manufacturing sector to growth (IMP 3) • Positioning services as a major source of growth (IMP 3) • Facilitating development and application of knowledge-intensive technologies (IMP 3) • Developing innovative and creative human capital (IMP 3) • Creating a more competitive business-operating environment (IMP 3)
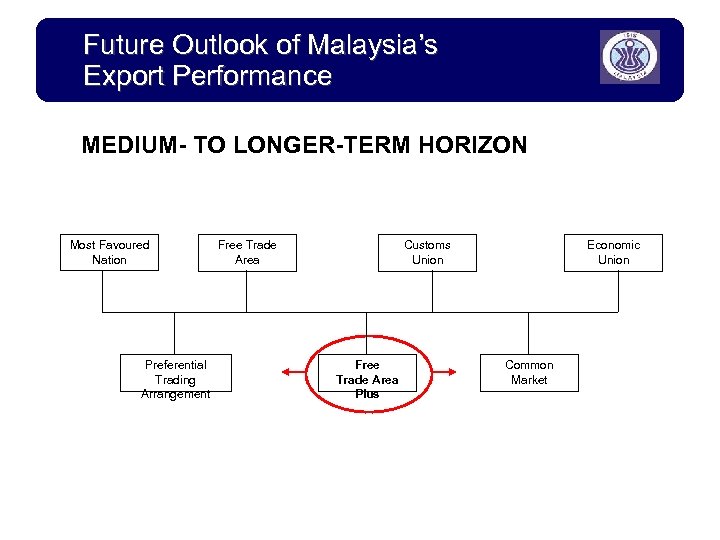 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Most Favoured Nation Preferential Trading Arrangement Free Trade Area Customs Union Free Trade Area Plus Economic Union Common Market
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Most Favoured Nation Preferential Trading Arrangement Free Trade Area Customs Union Free Trade Area Plus Economic Union Common Market
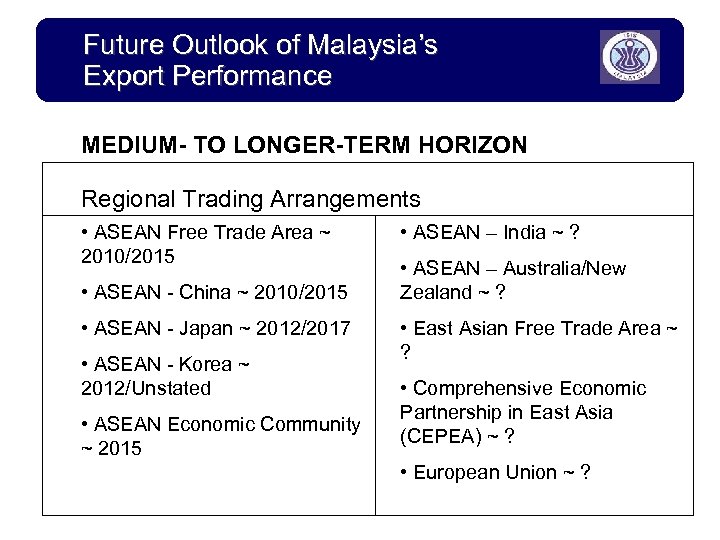 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Regional Trading Arrangements • ASEAN Free Trade Area ~ 2010/2015 • ASEAN - China ~ 2010/2015 • ASEAN - Japan ~ 2012/2017 • ASEAN - Korea ~ 2012/Unstated • ASEAN Economic Community ~ 2015 • ASEAN – India ~ ? • ASEAN – Australia/New Zealand ~ ? • East Asian Free Trade Area ~ ? • Comprehensive Economic Partnership in East Asia (CEPEA) ~ ? • European Union ~ ?
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance MEDIUM- TO LONGER-TERM HORIZON Regional Trading Arrangements • ASEAN Free Trade Area ~ 2010/2015 • ASEAN - China ~ 2010/2015 • ASEAN - Japan ~ 2012/2017 • ASEAN - Korea ~ 2012/Unstated • ASEAN Economic Community ~ 2015 • ASEAN – India ~ ? • ASEAN – Australia/New Zealand ~ ? • East Asian Free Trade Area ~ ? • Comprehensive Economic Partnership in East Asia (CEPEA) ~ ? • European Union ~ ?
 Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance CONCLUSIONS • Challenging short-term environment • Total de-coupling scenario is unlikely • Exact depth and duration of impact will depend on individual & collective actions • Longer-term structural changes also require attention • National and regional supply-side strategies and initiatives are in place and hinge on implementation effectiveness • The extent to which they respond to demand-side changes, including those of importing country governments, remain to be seen • Given speed of change, policy action deficits should be felt quickly on national welfare
Future Outlook of Malaysia’s Export Performance CONCLUSIONS • Challenging short-term environment • Total de-coupling scenario is unlikely • Exact depth and duration of impact will depend on individual & collective actions • Longer-term structural changes also require attention • National and regional supply-side strategies and initiatives are in place and hinge on implementation effectiveness • The extent to which they respond to demand-side changes, including those of importing country governments, remain to be seen • Given speed of change, policy action deficits should be felt quickly on national welfare


