26d933e84049e353757e1693158d0775.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Future Directions in Sensor Data Management: A Panel Discussion Demetris Zeinalipour University of Cyprus Sponsored by : DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Future Directions in Sensor Data Management: A Panel Discussion Demetris Zeinalipour University of Cyprus Sponsored by : DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 Panel Objective • To provide views on the following: – To what extend the vision of applying data management techniques to sensor network research has been successful over the years • e. g. , Adoption of ideas proposed by the community – To examine the significance of recent advances and to identify new directions that can foster research in sensor data management DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Panel Objective • To provide views on the following: – To what extend the vision of applying data management techniques to sensor network research has been successful over the years • e. g. , Adoption of ideas proposed by the community – To examine the significance of recent advances and to identify new directions that can foster research in sensor data management DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 DMSN’ 10 Panelists… Yanlei Diao (Univ. of Massachusetts Amherst, USA) DMSN’ 08 PC Chair Christian S. Jensen (Aarhus University, Denmark) DMSN’ 08 PC Chair Le Gruenwald (National Science Foundation, USA) Kian-Lee Tan (National University of Singapore, Singapore) DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
DMSN’ 10 Panelists… Yanlei Diao (Univ. of Massachusetts Amherst, USA) DMSN’ 08 PC Chair Christian S. Jensen (Aarhus University, Denmark) DMSN’ 08 PC Chair Le Gruenwald (National Science Foundation, USA) Kian-Lee Tan (National University of Singapore, Singapore) DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 Wireless Sensor Networks • We will soon celebrate 10 years of research and developments in the area of sensor networks. – 1999: Kristofer Pister (UCB) introduces the Smartdust vision • – – – “a hypothetical wireless network of tiny microelectromechanical sensors (MEMS), robots, or devices, that can detect (for example) light, temperature, or vibration. ” wikipedia. org 2000: First release of Tiny. OS for Rene – Crossbow partners 2001: Berkeley develops MICA 2002: Tiny. OS in nes. C is released 2003: Tiny. DB launch and 1 st Sen. Sys Conference 2004: First DMSN workshop in Toronto DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Wireless Sensor Networks • We will soon celebrate 10 years of research and developments in the area of sensor networks. – 1999: Kristofer Pister (UCB) introduces the Smartdust vision • – – – “a hypothetical wireless network of tiny microelectromechanical sensors (MEMS), robots, or devices, that can detect (for example) light, temperature, or vibration. ” wikipedia. org 2000: First release of Tiny. OS for Rene – Crossbow partners 2001: Berkeley develops MICA 2002: Tiny. OS in nes. C is released 2003: Tiny. DB launch and 1 st Sen. Sys Conference 2004: First DMSN workshop in Toronto DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 High – – – – – Research Emphasis of DMSN (based on titles since 2004) Query Processing Frameworks Monitoring Energy-efficiency Models Systems Applications Storage …. DMSN Aim: “All important aspects of sensor data management, including data acquisition, processing, and storage in remote wireless networks” Low DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
High – – – – – Research Emphasis of DMSN (based on titles since 2004) Query Processing Frameworks Monitoring Energy-efficiency Models Systems Applications Storage …. DMSN Aim: “All important aspects of sensor data management, including data acquisition, processing, and storage in remote wireless networks” Low DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 Important Research Areas of DMSN (based on citations since 2004) Total Citations since 2004: 778 DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Important Research Areas of DMSN (based on citations since 2004) Total Citations since 2004: 778 DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 What is the current state? • In recent years, we have been witnessing a paradigm shift from the initial target of Sensor Networks that focused on “Low Power Embedded Sensing devices” and “Environmental Monitoring Applications” • Nowadays Sensor Devices are packed with more hardware (e. g. , i-Mote 2) and software capabilities (e. g. , running Linux) • Additionally, even traditional applications are much more diverse (e. g. , using camera boards for urban monitoring, etc. ) DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
What is the current state? • In recent years, we have been witnessing a paradigm shift from the initial target of Sensor Networks that focused on “Low Power Embedded Sensing devices” and “Environmental Monitoring Applications” • Nowadays Sensor Devices are packed with more hardware (e. g. , i-Mote 2) and software capabilities (e. g. , running Linux) • Additionally, even traditional applications are much more diverse (e. g. , using camera boards for urban monitoring, etc. ) DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
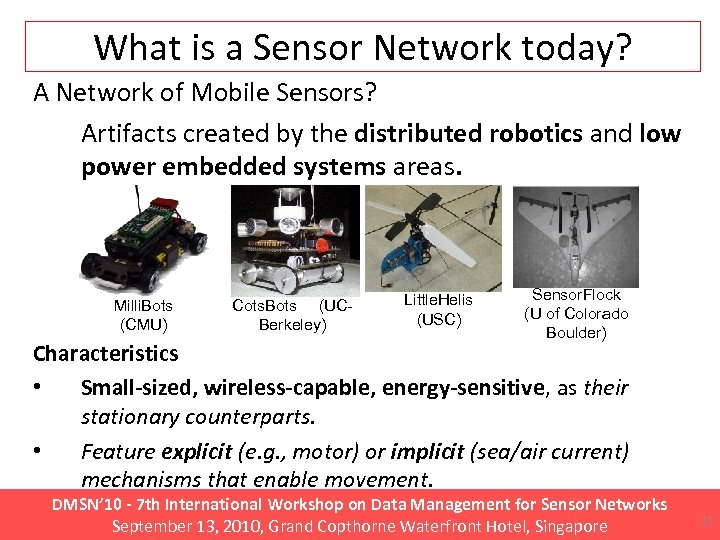 What is a Sensor Network today? A Network of Mobile Sensors? Artifacts created by the distributed robotics and low power embedded systems areas. Milli. Bots (CMU) Cots. Bots (UCBerkeley) Little. Helis (USC) Sensor. Flock (U of Colorado Boulder) Characteristics • Small-sized, wireless-capable, energy-sensitive, as their stationary counterparts. • Feature explicit (e. g. , motor) or implicit (sea/air current) mechanisms that enable movement. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 12
What is a Sensor Network today? A Network of Mobile Sensors? Artifacts created by the distributed robotics and low power embedded systems areas. Milli. Bots (CMU) Cots. Bots (UCBerkeley) Little. Helis (USC) Sensor. Flock (U of Colorado Boulder) Characteristics • Small-sized, wireless-capable, energy-sensitive, as their stationary counterparts. • Feature explicit (e. g. , motor) or implicit (sea/air current) mechanisms that enable movement. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 12
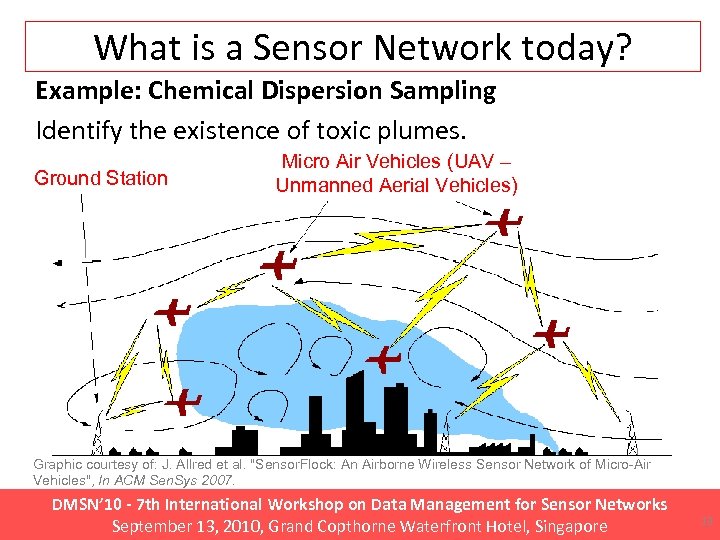 What is a Sensor Network today? Example: Chemical Dispersion Sampling Identify the existence of toxic plumes. Ground Station Micro Air Vehicles (UAV – Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) Graphic courtesy of: J. Allred et al. "Sensor. Flock: An Airborne Wireless Sensor Network of Micro-Air Vehicles", In ACM Sen. Sys 2007. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 13
What is a Sensor Network today? Example: Chemical Dispersion Sampling Identify the existence of toxic plumes. Ground Station Micro Air Vehicles (UAV – Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) Graphic courtesy of: J. Allred et al. "Sensor. Flock: An Airborne Wireless Sensor Network of Micro-Air Vehicles", In ACM Sen. Sys 2007. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 13
 What is a Sensor Network today? • A Network of Smartphones? – Sensor: • • Proximity Sensor (turn off display when getting close to ear) Ambient Light Detector (brighten display when in sunlight) Accelerometer (identify rotation and digital compass) Camera, Microphone, Geo-location on GPS, WIFI, Cellular Towers, … – Network: • Bluetooth: Peer-to-Peer applications / services • WLAN, WCDMA/UMTS(3 G) / HSPA(3. 5 G): broadband access. – Actuators: Notification Light, Speaker. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
What is a Sensor Network today? • A Network of Smartphones? – Sensor: • • Proximity Sensor (turn off display when getting close to ear) Ambient Light Detector (brighten display when in sunlight) Accelerometer (identify rotation and digital compass) Camera, Microphone, Geo-location on GPS, WIFI, Cellular Towers, … – Network: • Bluetooth: Peer-to-Peer applications / services • WLAN, WCDMA/UMTS(3 G) / HSPA(3. 5 G): broadband access. – Actuators: Notification Light, Speaker. DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
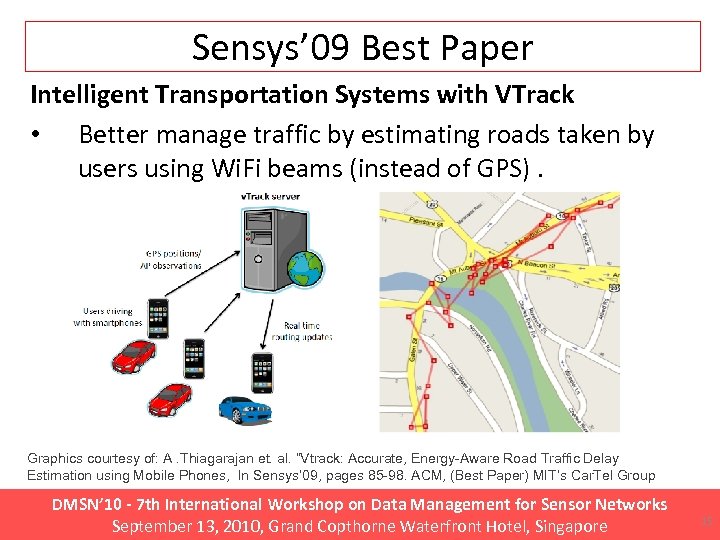 Sensys’ 09 Best Paper Intelligent Transportation Systems with VTrack • Better manage traffic by estimating roads taken by users using Wi. Fi beams (instead of GPS). Graphics courtesy of: A. Thiagarajan et. al. “Vtrack: Accurate, Energy-Aware Road Traffic Delay Estimation using Mobile Phones, In Sensys’ 09, pages 85 -98. ACM, (Best Paper) MIT’s Car. Tel Group DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 15
Sensys’ 09 Best Paper Intelligent Transportation Systems with VTrack • Better manage traffic by estimating roads taken by users using Wi. Fi beams (instead of GPS). Graphics courtesy of: A. Thiagarajan et. al. “Vtrack: Accurate, Energy-Aware Road Traffic Delay Estimation using Mobile Phones, In Sensys’ 09, pages 85 -98. ACM, (Best Paper) MIT’s Car. Tel Group DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore 15
 Complementary Technologies? • Several complementary research fields in the area of data management seek to solve problems similar to those addressed by the DMSN community e. g. , 1. Stream Processors • i. e. , for processing real-time data flows. 2. Cloud Data Analytic Frameworks • e. g. , Map-reduce for analyzing massive data. 3. Semantic Web Technologies • e. g. , Sensorweb for structuring Internet-scale sensor data repositories DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Complementary Technologies? • Several complementary research fields in the area of data management seek to solve problems similar to those addressed by the DMSN community e. g. , 1. Stream Processors • i. e. , for processing real-time data flows. 2. Cloud Data Analytic Frameworks • e. g. , Map-reduce for analyzing massive data. 3. Semantic Web Technologies • e. g. , Sensorweb for structuring Internet-scale sensor data repositories DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
 Complementary Technologies? • Several complementary research fields in the area of data management seek to solve problems similar to or those addressed by the DMSNs f community e. g. , ion 1. Stream Processors ct ire Data flows. • i. e. , for processing real-time data D r t? re so 2. Cloud Data Analytic Frameworks en tu en u FMap-reduce for analyzing massive data. em S ag • e. g. , an 3. Semantic Web Technologies M • e. g. , Sensorweb for structuring Internet-scale sensor data repositories DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore
Complementary Technologies? • Several complementary research fields in the area of data management seek to solve problems similar to or those addressed by the DMSNs f community e. g. , ion 1. Stream Processors ct ire Data flows. • i. e. , for processing real-time data D r t? re so 2. Cloud Data Analytic Frameworks en tu en u FMap-reduce for analyzing massive data. em S ag • e. g. , an 3. Semantic Web Technologies M • e. g. , Sensorweb for structuring Internet-scale sensor data repositories DMSN’ 10 - 7 th International Workshop on Data Management for Sensor Networks September 13, 2010, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore


