9288c40df23e8ab53a6f739e1fe5a9ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Further Shell Scripting Michael Griffiths Corporate Information and Computing Services The University of Sheffield Email m. griffiths@sheffield. ac. uk
Further Shell Scripting Michael Griffiths Corporate Information and Computing Services The University of Sheffield Email m. griffiths@sheffield. ac. uk
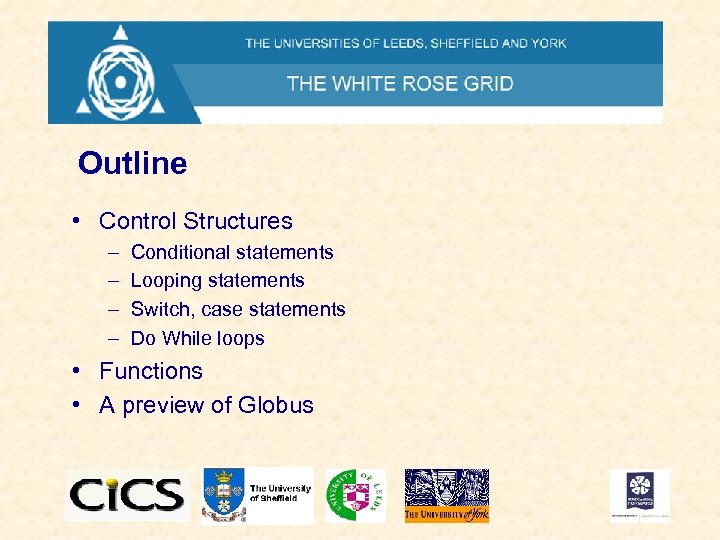 Outline • Control Structures – – Conditional statements Looping statements Switch, case statements Do While loops • Functions • A preview of Globus
Outline • Control Structures – – Conditional statements Looping statements Switch, case statements Do While loops • Functions • A preview of Globus
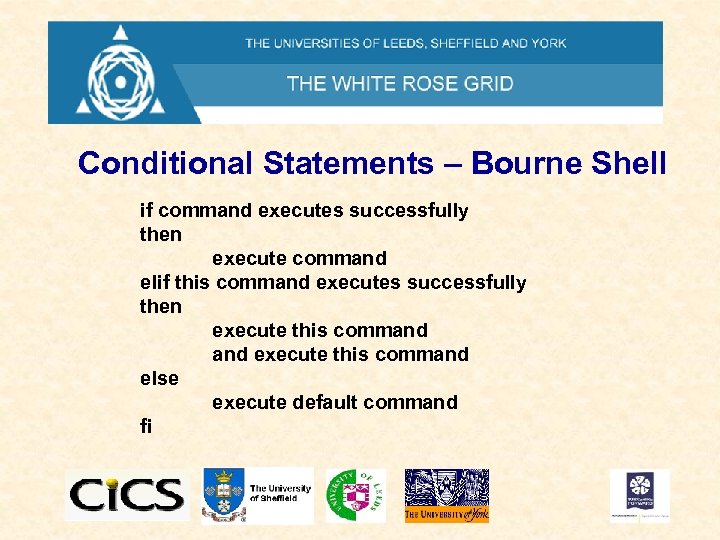 Conditional Statements – Bourne Shell if command executes successfully then execute command elif this command executes successfully then execute this command else execute default command fi
Conditional Statements – Bourne Shell if command executes successfully then execute command elif this command executes successfully then execute this command else execute default command fi
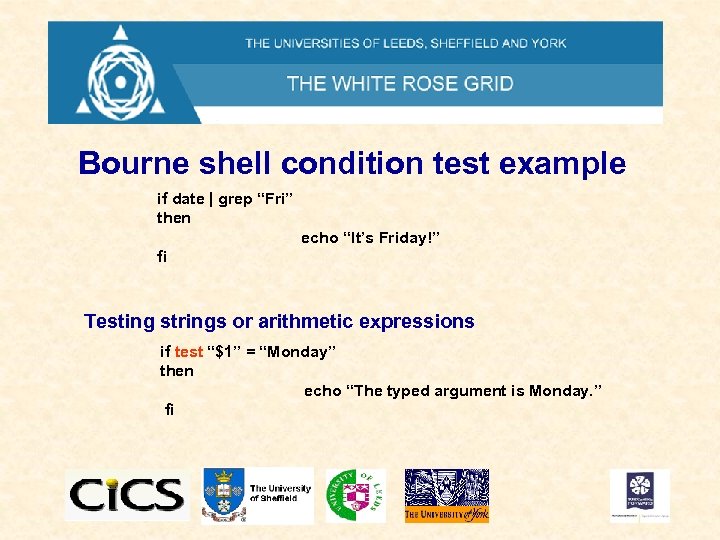 Bourne shell condition test example if date | grep “Fri” then echo “It’s Friday!” fi Testing strings or arithmetic expressions if test “$1” = “Monday” then echo “The typed argument is Monday. ” fi
Bourne shell condition test example if date | grep “Fri” then echo “It’s Friday!” fi Testing strings or arithmetic expressions if test “$1” = “Monday” then echo “The typed argument is Monday. ” fi
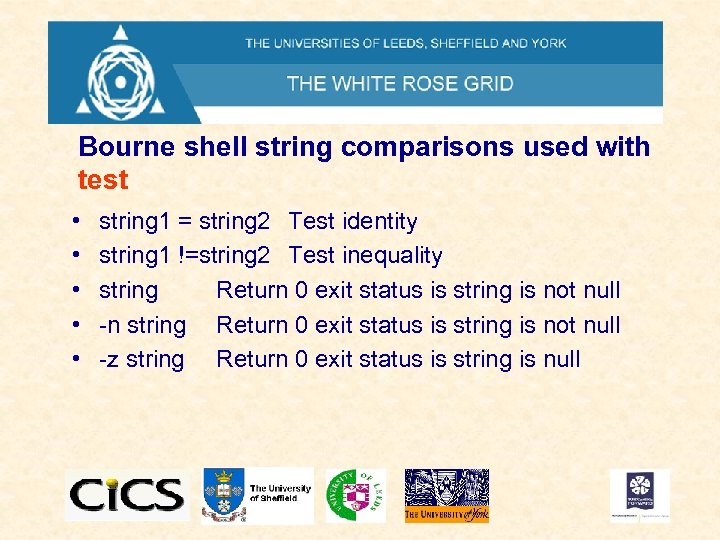 Bourne shell string comparisons used with test • • • string 1 = string 2 Test identity string 1 !=string 2 Test inequality string Return 0 exit status is string is not null -n string Return 0 exit status is string is not null -z string Return 0 exit status is string is null
Bourne shell string comparisons used with test • • • string 1 = string 2 Test identity string 1 !=string 2 Test inequality string Return 0 exit status is string is not null -n string Return 0 exit status is string is not null -z string Return 0 exit status is string is null
 Bourne shell arithmetic comparison operations used with test • • • int 1 –eq int 2 int 1 –ne int 2 int 1 –lt int 2 int 1 –gt int 2 int 1 –le int 2 int 1 –ge int 2 Test identity Test inequality Less than Greater than Less than or equal Greater than or equal
Bourne shell arithmetic comparison operations used with test • • • int 1 –eq int 2 int 1 –ne int 2 int 1 –lt int 2 int 1 –gt int 2 int 1 –le int 2 int 1 –ge int 2 Test identity Test inequality Less than Greater than Less than or equal Greater than or equal
 Bourne shell combining tests using logical operators || (or) and && (and) if date | grep “Fri” && test `date +’%H’` -gt 17 then echo “It’s Friday, it’s hometime!!!” fi
Bourne shell combining tests using logical operators || (or) and && (and) if date | grep “Fri” && test `date +’%H’` -gt 17 then echo “It’s Friday, it’s hometime!!!” fi
 Conditional statements c-shell if (condition(s)) then command group 1 else command group 2 endif Example: if( -e $ifile) then nedit $ifile else echo The file $ifile does not exist! endif
Conditional statements c-shell if (condition(s)) then command group 1 else command group 2 endif Example: if( -e $ifile) then nedit $ifile else echo The file $ifile does not exist! endif
 Arithmetic comparison example for the cshell if ( ( ($1 % 5) == 0) && ( ($1 % 3) == 0) ) then echo You entered a multiple of 3 and 5! else if( ( $1 % 5) == 0)then echo You entered a multiple of 5! else if ( ($1 % 3)== 0) then echo You entered a multiple of 3! else echo Not divisible by 3 or 5 endif
Arithmetic comparison example for the cshell if ( ( ($1 % 5) == 0) && ( ($1 % 3) == 0) ) then echo You entered a multiple of 3 and 5! else if( ( $1 % 5) == 0)then echo You entered a multiple of 5! else if ( ($1 % 3)== 0) then echo You entered a multiple of 3! else echo Not divisible by 3 or 5 endif
 File enquiry operations with the bourne shell and c-shell -d file -f file -s file -r file -w file -x file -o file -e file -z file Test if file is a directory Test if file is not a directory Test if the file has non zero length Test if the file is readable Test if the file is writable Test if the file is executable Test if the file is owned by the user Test if the file exists Test if the file has zero length
File enquiry operations with the bourne shell and c-shell -d file -f file -s file -r file -w file -x file -o file -e file -z file Test if file is a directory Test if file is not a directory Test if the file has non zero length Test if the file is readable Test if the file is writable Test if the file is executable Test if the file is owned by the user Test if the file exists Test if the file has zero length
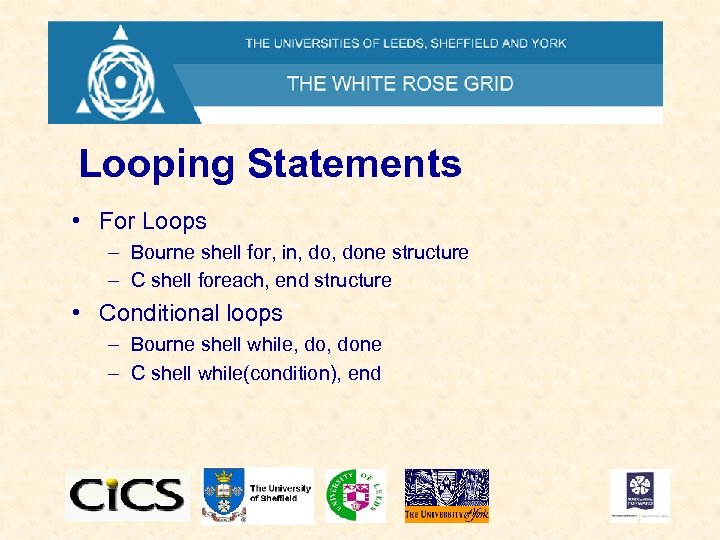 Looping Statements • For Loops – Bourne shell for, in, done structure – C shell foreach, end structure • Conditional loops – Bourne shell while, done – C shell while(condition), end
Looping Statements • For Loops – Bourne shell for, in, done structure – C shell foreach, end structure • Conditional loops – Bourne shell while, done – C shell while(condition), end
 For loop – Bourne shell for name in name_1 name_2 name_3 …. . name_n do command(s). . . done Example: for i in 3 7 do echo " $i * 5 is `expr $i * 5` " done
For loop – Bourne shell for name in name_1 name_2 name_3 …. . name_n do command(s). . . done Example: for i in 3 7 do echo " $i * 5 is `expr $i * 5` " done
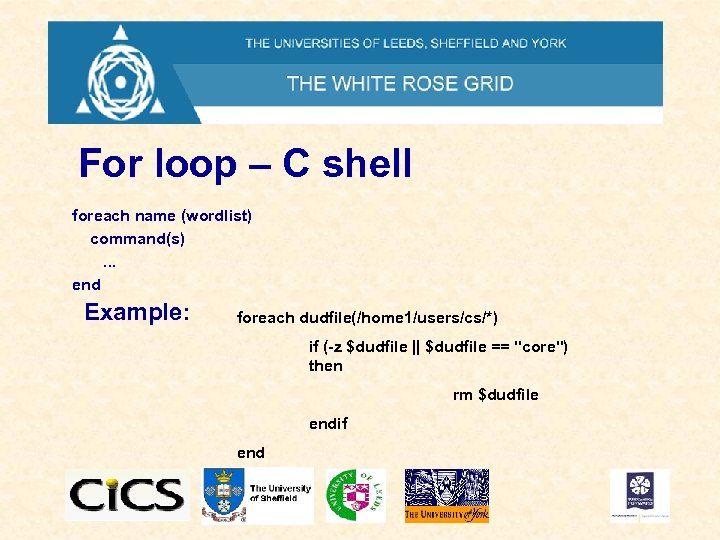 For loop – C shell foreach name (wordlist) command(s). . . end Example: foreach dudfile(/home 1/users/cs/*) if (-z $dudfile || $dudfile == "core") then rm $dudfile endif end
For loop – C shell foreach name (wordlist) command(s). . . end Example: foreach dudfile(/home 1/users/cs/*) if (-z $dudfile || $dudfile == "core") then rm $dudfile endif end
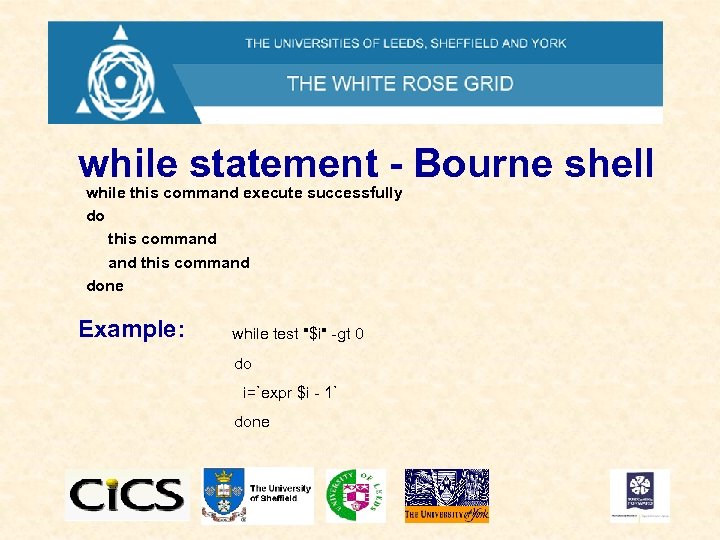 while statement - Bourne shell while this command execute successfully do this command done Example: while test "$i" -gt 0 do i=`expr $i - 1` done
while statement - Bourne shell while this command execute successfully do this command done Example: while test "$i" -gt 0 do i=`expr $i - 1` done
 While – c shell while (condition) statements end Example: while($i > 0 ) echo $i Sent to printer! to a printer set i=`expr $i - 1` end #Might send the file
While – c shell while (condition) statements end Example: while($i > 0 ) echo $i Sent to printer! to a printer set i=`expr $i - 1` end #Might send the file
 Selecting From a List of Possibilities • Switch … case – Bourne shell – c-shell
Selecting From a List of Possibilities • Switch … case – Bourne shell – c-shell
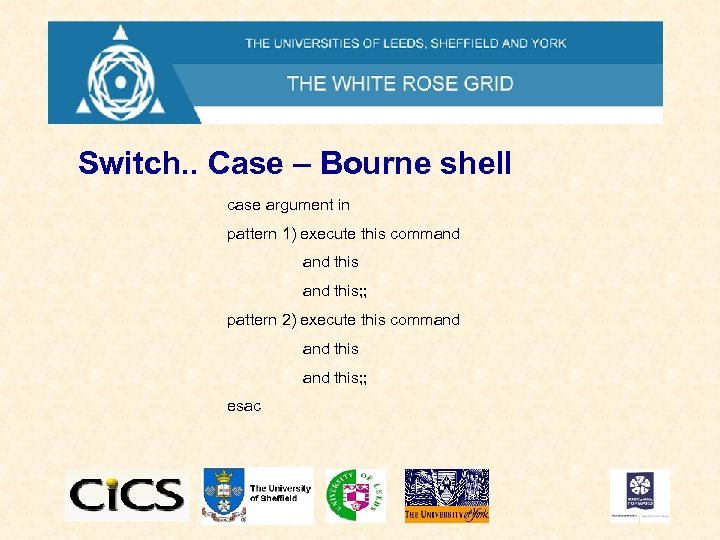 Switch. . Case – Bourne shell case argument in pattern 1) execute this command this; ; pattern 2) execute this command this; ; esac
Switch. . Case – Bourne shell case argument in pattern 1) execute this command this; ; pattern 2) execute this command this; ; esac
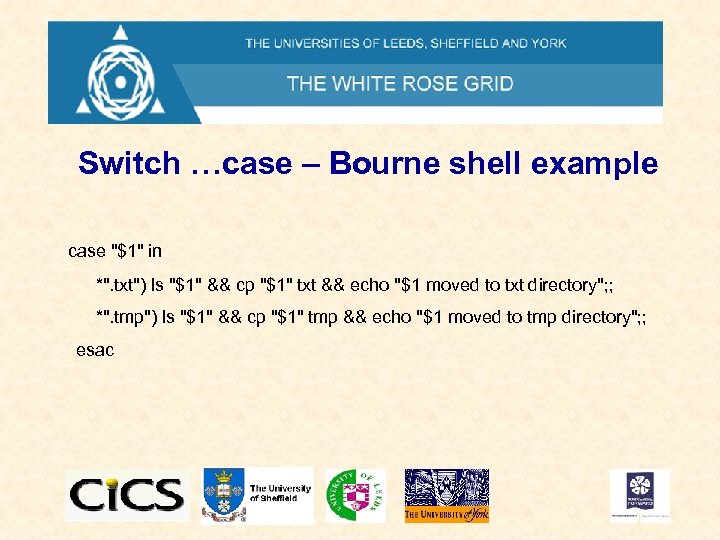 Switch …case – Bourne shell example case "$1" in *". txt") ls "$1" && cp "$1" txt && echo "$1 moved to txt directory"; ; *". tmp") ls "$1" && cp "$1" tmp && echo "$1 moved to tmp directory"; ; esac
Switch …case – Bourne shell example case "$1" in *". txt") ls "$1" && cp "$1" txt && echo "$1 moved to txt directory"; ; *". tmp") ls "$1" && cp "$1" tmp && echo "$1 moved to tmp directory"; ; esac
 Switch … case – c-shell switch($1) case *". txt": ls "$1" && cp "$1" txt && echo "$1 moved to txt directory" breaksw case *". tmp": ls "$1" && cp "$1" tmp && echo "$1 moved to tmp directory" breaksw endsw
Switch … case – c-shell switch($1) case *". txt": ls "$1" && cp "$1" txt && echo "$1 moved to txt directory" breaksw case *". tmp": ls "$1" && cp "$1" tmp && echo "$1 moved to tmp directory" breaksw endsw
 Functions • Functions are declared at the beginning of a shell script and take the format shown below functionname() { function script commands go here }
Functions • Functions are declared at the beginning of a shell script and take the format shown below functionname() { function script commands go here }
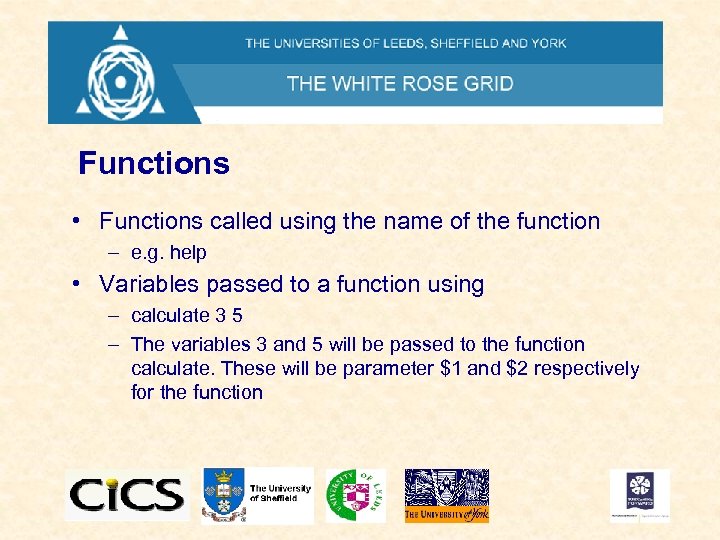 Functions • Functions called using the name of the function – e. g. help • Variables passed to a function using – calculate 3 5 – The variables 3 and 5 will be passed to the function calculate. These will be parameter $1 and $2 respectively for the function
Functions • Functions called using the name of the function – e. g. help • Variables passed to a function using – calculate 3 5 – The variables 3 and 5 will be passed to the function calculate. These will be parameter $1 and $2 respectively for the function
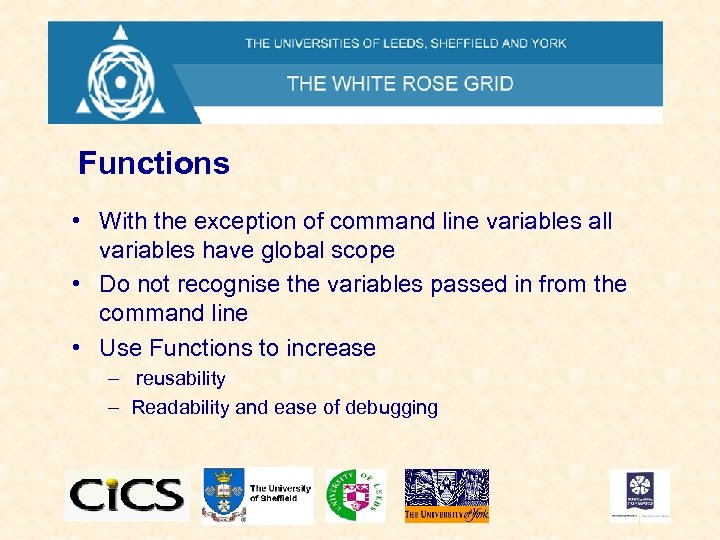 Functions • With the exception of command line variables all variables have global scope • Do not recognise the variables passed in from the command line • Use Functions to increase – reusability – Readability and ease of debugging
Functions • With the exception of command line variables all variables have global scope • Do not recognise the variables passed in from the command line • Use Functions to increase – reusability – Readability and ease of debugging
 A Preview The Globus Toolkit – Middleware for grids • Grid job submission – GRAM (Globus resource allocation manager) • Resource discovery and information – GIS (Grid information service a metacomputiing directory service using LDAP) • Secure Access – Grid security infrastructure • File Management – Grid ftp
A Preview The Globus Toolkit – Middleware for grids • Grid job submission – GRAM (Globus resource allocation manager) • Resource discovery and information – GIS (Grid information service a metacomputiing directory service using LDAP) • Secure Access – Grid security infrastructure • File Management – Grid ftp
 Globus Examples • grid-proxy-init • globus-job-run maxima. leeds. ac. uk /bin/echo Hello world • globus-url-copy gsiftp: //maxima. leeds. ac. uk$LEEDSHOME/$1 file: $PWD/$2 • Use globus commands to create grid shells scripts – Later on
Globus Examples • grid-proxy-init • globus-job-run maxima. leeds. ac. uk /bin/echo Hello world • globus-url-copy gsiftp: //maxima. leeds. ac. uk$LEEDSHOME/$1 file: $PWD/$2 • Use globus commands to create grid shells scripts – Later on
 Staging a Job • Useful for running a series of commands on a remote node • globus-job-run maxima. leeds. ac. uk –s /path/script. sh arguments – Script should not return an exit value
Staging a Job • Useful for running a series of commands on a remote node • globus-job-run maxima. leeds. ac. uk –s /path/script. sh arguments – Script should not return an exit value
 Examples • • Executing UNIX commands on remote nodes Querying Sun Grid engine on remote nodes Starting X-Applications Staging your shell scripts
Examples • • Executing UNIX commands on remote nodes Querying Sun Grid engine on remote nodes Starting X-Applications Staging your shell scripts


