7d13a1fa6b93e7ac71ca554af0abcd56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Fundamentals of Computer Science Part i 2 Lecture 2 I/O devices and networks 1
Fundamentals of Computer Science Part i 2 Lecture 2 I/O devices and networks 1
 Topics for this lecture • Memory – primary, cache • Storage devices – disks, CD-ROMs, … • Input/Output – terminals, mice, printers, . . . • Networks – LANs, WANs, MANs, WLANs 2
Topics for this lecture • Memory – primary, cache • Storage devices – disks, CD-ROMs, … • Input/Output – terminals, mice, printers, . . . • Networks – LANs, WANs, MANs, WLANs 2
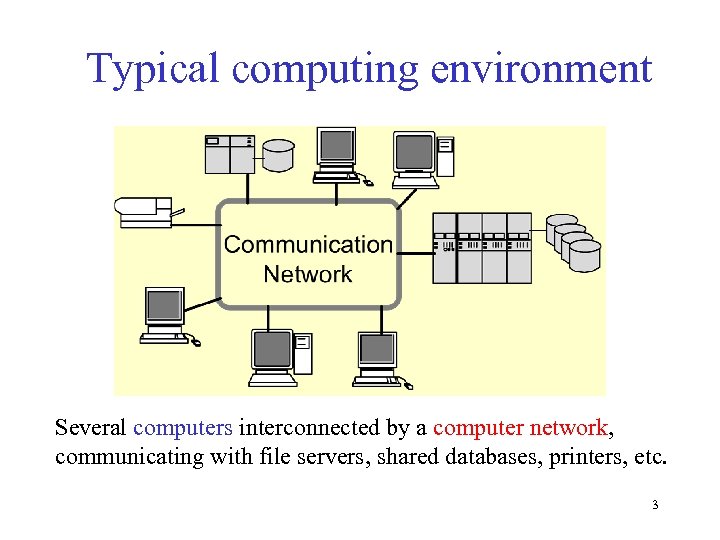 Typical computing environment Several computers interconnected by a computer network, communicating with file servers, shared databases, printers, etc. 3
Typical computing environment Several computers interconnected by a computer network, communicating with file servers, shared databases, printers, etc. 3
 Memory • Primary memory – RAM (Random Access) – stores data and program • Cache memory – fast, to improve speed 4
Memory • Primary memory – RAM (Random Access) – stores data and program • Cache memory – fast, to improve speed 4
 Primary memory • N cells • Addresses 0. . N-1 • Each cell has k bits, hence 2 k distinct bit sequences that can be stored Ways of organising 96 bit memory. . . 5
Primary memory • N cells • Addresses 0. . N-1 • Each cell has k bits, hence 2 k distinct bit sequences that can be stored Ways of organising 96 bit memory. . . 5
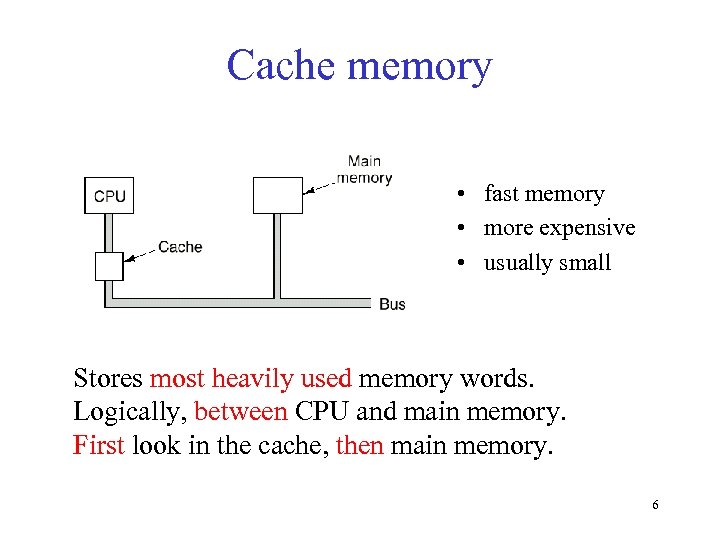 Cache memory • fast memory • more expensive • usually small Stores most heavily used memory words. Logically, between CPU and main memory. First look in the cache, then main memory. 6
Cache memory • fast memory • more expensive • usually small Stores most heavily used memory words. Logically, between CPU and main memory. First look in the cache, then main memory. 6
 Storage devices • High speed & cost, small size • Low speed & cost, large size Magnetic disks: hard, floppy, scuzzy, . . . Optical disks: CD-ROM, CD-Writeable, DVD, . . . 7
Storage devices • High speed & cost, small size • Low speed & cost, large size Magnetic disks: hard, floppy, scuzzy, . . . Optical disks: CD-ROM, CD-Writeable, DVD, . . . 7
 Magnetic disks • • Platter rotates under a head; magnetic coating reacts. Bits stored in tracks (concentric circles), split into sectors. Can be hard or flexible (floppy disk, diskette). SCSI (scuzzy) disks have high transfer rates. 8
Magnetic disks • • Platter rotates under a head; magnetic coating reacts. Bits stored in tracks (concentric circles), split into sectors. Can be hard or flexible (floppy disk, diskette). SCSI (scuzzy) disks have high transfer rates. 8
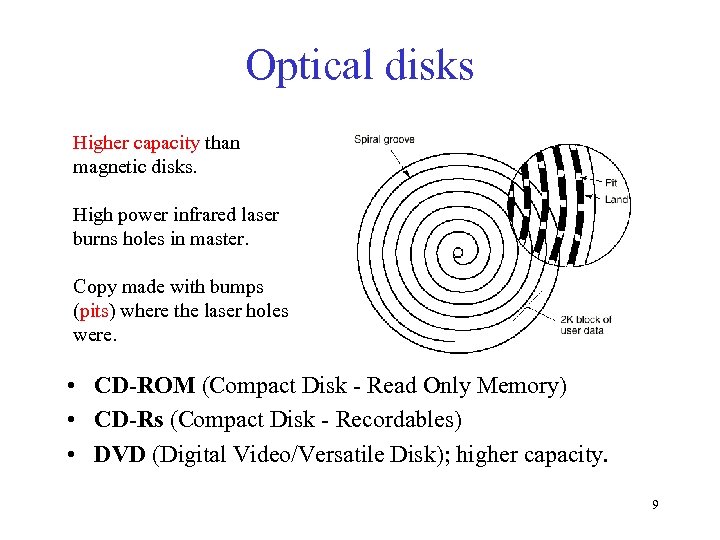 Optical disks Higher capacity than magnetic disks. High power infrared laser burns holes in master. Copy made with bumps (pits) where the laser holes were. • CD-ROM (Compact Disk - Read Only Memory) • CD-Rs (Compact Disk - Recordables) • DVD (Digital Video/Versatile Disk); higher capacity. 9
Optical disks Higher capacity than magnetic disks. High power infrared laser burns holes in master. Copy made with bumps (pits) where the laser holes were. • CD-ROM (Compact Disk - Read Only Memory) • CD-Rs (Compact Disk - Recordables) • DVD (Digital Video/Versatile Disk); higher capacity. 9
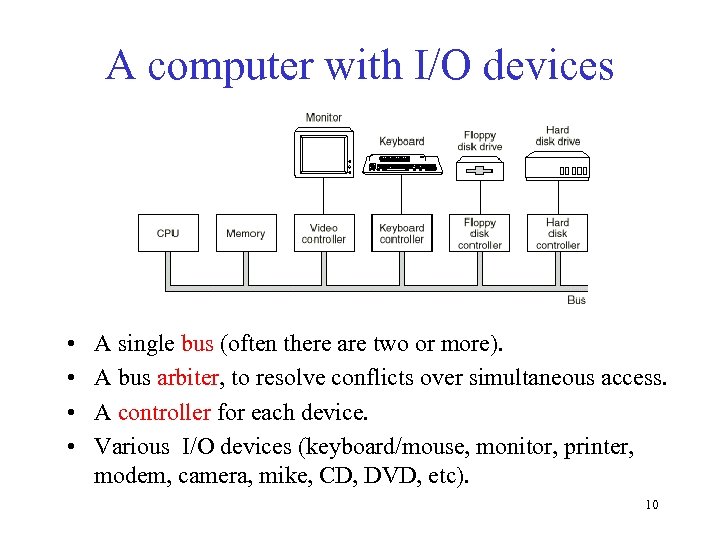 A computer with I/O devices • • A single bus (often there are two or more). A bus arbiter, to resolve conflicts over simultaneous access. A controller for each device. Various I/O devices (keyboard/mouse, monitor, printer, modem, camera, mike, CD, DVD, etc). 10
A computer with I/O devices • • A single bus (often there are two or more). A bus arbiter, to resolve conflicts over simultaneous access. A controller for each device. Various I/O devices (keyboard/mouse, monitor, printer, modem, camera, mike, CD, DVD, etc). 10
 Types of Computer Networks • LANs (Local Area Networks) – technology suitable for small area, usually wire/fibre • WANs (Wide Area Networks) – large distances, inter-city/country/continental – the Internet • MANs (Metropolitan Area Networks) – intra-city, cable based, multimedia • Wireless networks – WLANs, WPANs 11
Types of Computer Networks • LANs (Local Area Networks) – technology suitable for small area, usually wire/fibre • WANs (Wide Area Networks) – large distances, inter-city/country/continental – the Internet • MANs (Metropolitan Area Networks) – intra-city, cable based, multimedia • Wireless networks – WLANs, WPANs 11
 LANs • Local Area Networks – within an institution, home, etc • High bandwith (total amount of data per unit of time) • Low latency (time taken for the first bit to reach destination) • Technology – predominantly Ethernet, now 100/1000 Mbps 12
LANs • Local Area Networks – within an institution, home, etc • High bandwith (total amount of data per unit of time) • Low latency (time taken for the first bit to reach destination) • Technology – predominantly Ethernet, now 100/1000 Mbps 12
 WANs • Low bandwith, high latency • Satellite/wire/cable • Routers introduce delays MANs • Wire/cable • Range of technologies (ATM, Ethernet) 13
WANs • Low bandwith, high latency • Satellite/wire/cable • Routers introduce delays MANs • Wire/cable • Range of technologies (ATM, Ethernet) 13
 The Internet & WWW • The Internet – large, heterogeneous and open-ended WAN – connects home users and businesses • World-wide Web: resource sharing over the Internet • Based on technologies: – HTML (Hyper. Text Markup Language) – URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – client-server architecture 14
The Internet & WWW • The Internet – large, heterogeneous and open-ended WAN – connects home users and businesses • World-wide Web: resource sharing over the Internet • Based on technologies: – HTML (Hyper. Text Markup Language) – URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – client-server architecture 14
 The future is mobile. . . Internet Host intranet Wireless LAN Printer Camera Mobile phone Laptop WAP gateway Home intranet Host site 15
The future is mobile. . . Internet Host intranet Wireless LAN Printer Camera Mobile phone Laptop WAP gateway Home intranet Host site 15
 The future is home intranet. . . • Wireless LANs (WLANs) – connectivity for portable devices (laptops, PDAs, mobile phones, video/dig. cameras, …) • Home intranet – devices embedded in home appliances (hi-fi, washing machines, …) – universal ‘remote control’ + communication 16
The future is home intranet. . . • Wireless LANs (WLANs) – connectivity for portable devices (laptops, PDAs, mobile phones, video/dig. cameras, …) • Home intranet – devices embedded in home appliances (hi-fi, washing machines, …) – universal ‘remote control’ + communication 16
 Summary • Conventional I/O devices – memory and external storage – increasing variety of I/O devices (multimedia sound, video, etc) • Networks for sharing and communication • Current & future developments – increasing of personal & mobile devices – growth of home intranets 17
Summary • Conventional I/O devices – memory and external storage – increasing variety of I/O devices (multimedia sound, video, etc) • Networks for sharing and communication • Current & future developments – increasing of personal & mobile devices – growth of home intranets 17


