707633205fbe197480a421c11a9e416e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London
Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
 Issuer Member Anonymous signature Group
Issuer Member Anonymous signature Group
 Issuer Opener Group manager Group signature Group
Issuer Opener Group manager Group signature Group
 Anonymity? • Can group signatures made by the same member be linked? • What happens if somebody loses his secret group membership key, are all his signatures suddenly identifiable? • What happens if somebody gets the opener to trace the signers of selected group signatures? (think chosen ciphertext attack)
Anonymity? • Can group signatures made by the same member be linked? • What happens if somebody loses his secret group membership key, are all his signatures suddenly identifiable? • What happens if somebody gets the opener to trace the signers of selected group signatures? (think chosen ciphertext attack)
 Full anonymity Issuer is corrupt All members’ group signature keys are exposed Opener is honest (otherwise anonymity not possible) but willing to open group signatures • Two honest members’ group signatures on the same message are indistinguishable Unlinkable, key-exposure resilient, CCA-anonymous
Full anonymity Issuer is corrupt All members’ group signature keys are exposed Opener is honest (otherwise anonymity not possible) but willing to open group signatures • Two honest members’ group signatures on the same message are indistinguishable Unlinkable, key-exposure resilient, CCA-anonymous
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
 Previous work • Many papers [ACJT 00, CL 02, CL 04 BBS 04, CG 04, FI 05, KY 05, etc. ] Random oracle model • Boyen, Waters 06, 07 CPA-anonymous • Ateniese, Camenisch, Hohenberger, de Medeiros 06 Key-exposure • Bellare, Micciancio, Warinschi 03 Bellare, Shi, Zhang 05 Groth 06 Fully anonymous inefficient group signatures
Previous work • Many papers [ACJT 00, CL 02, CL 04 BBS 04, CG 04, FI 05, KY 05, etc. ] Random oracle model • Boyen, Waters 06, 07 CPA-anonymous • Ateniese, Camenisch, Hohenberger, de Medeiros 06 Key-exposure • Bellare, Micciancio, Warinschi 03 Bellare, Shi, Zhang 05 Groth 06 Fully anonymous inefficient group signatures
 Our contribution • • Fully anonymous group signature Separate Issuer and Opener Partially dynamic – the group can grow Efficient Group signature is around 2 k. B 50 group elements from elliptic curve • Based on bilinear groups Decisional linear assumption [BBS 04] More efficient schemes exist in the q-Strongrandom oracle model Diffie Hellman assumption [BB 04] q-Unfakeability assumption [ZL 06]
Our contribution • • Fully anonymous group signature Separate Issuer and Opener Partially dynamic – the group can grow Efficient Group signature is around 2 k. B 50 group elements from elliptic curve • Based on bilinear groups Decisional linear assumption [BBS 04] More efficient schemes exist in the q-Strongrandom oracle model Diffie Hellman assumption [BB 04] q-Unfakeability assumption [ZL 06]
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
 New member joining the group Issuer Member Signature key pair: (vk, sk) Issuer’s certificate on vk: cert
New member joining the group Issuer Member Signature key pair: (vk, sk) Issuer’s certificate on vk: cert
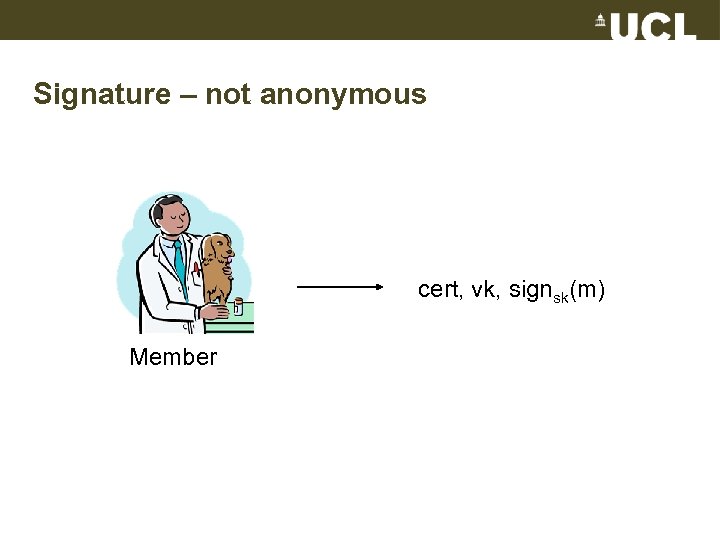 Signature – not anonymous cert, vk, signsk(m) Member
Signature – not anonymous cert, vk, signsk(m) Member
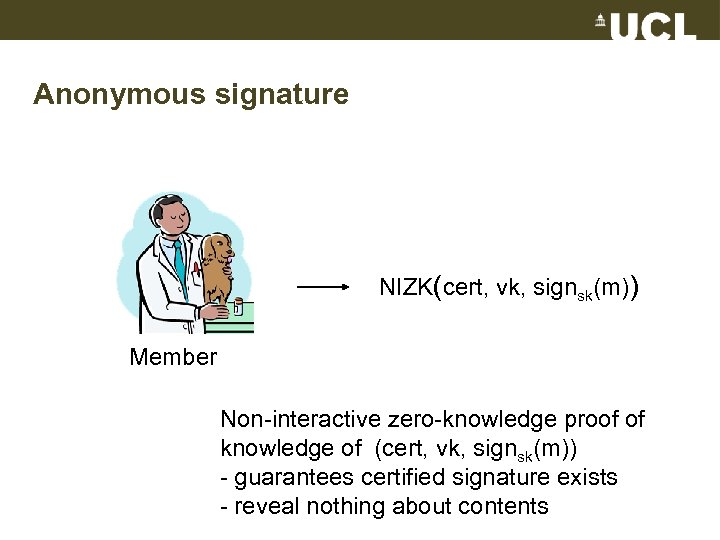 Anonymous signature NIZK(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Non-interactive zero-knowledge proof of knowledge of (cert, vk, signsk(m)) - guarantees certified signature exists - reveal nothing about contents
Anonymous signature NIZK(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Non-interactive zero-knowledge proof of knowledge of (cert, vk, signsk(m)) - guarantees certified signature exists - reveal nothing about contents
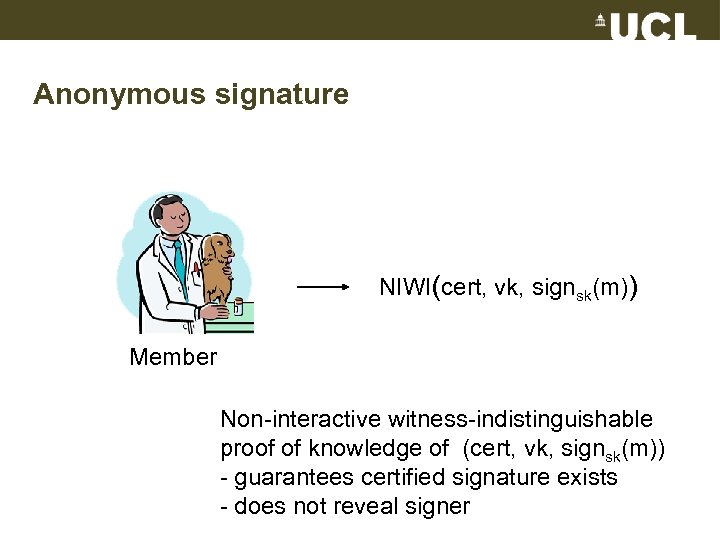 Anonymous signature NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Non-interactive witness-indistinguishable proof of knowledge of (cert, vk, signsk(m)) - guarantees certified signature exists - does not reveal signer
Anonymous signature NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Non-interactive witness-indistinguishable proof of knowledge of (cert, vk, signsk(m)) - guarantees certified signature exists - does not reveal signer
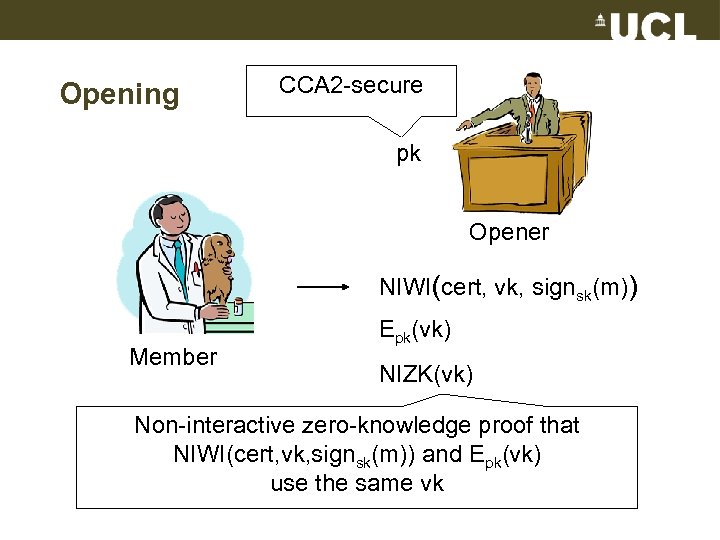 Opening CCA 2 -secure pk Opener NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Epk(vk) NIZK(vk) Non-interactive zero-knowledge proof that NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) and Epk(vk) use the same vk
Opening CCA 2 -secure pk Opener NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) Member Epk(vk) NIZK(vk) Non-interactive zero-knowledge proof that NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)) and Epk(vk) use the same vk
 Group signature vksots NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)sots)) (vk ) Member Epk(vk) NIZK(vk) Signsots(vksots, m, NIWI, E, NIZK) Strong one-time signature on message and everything else
Group signature vksots NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(m)sots)) (vk ) Member Epk(vk) NIZK(vk) Signsots(vksots, m, NIWI, E, NIZK) Strong one-time signature on message and everything else
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
 Bilinear groups • • Prime p Groups G, GT of order p g generates G Bilinear map e: G × G → GT - e(g, g) generates GT - e(ga, gb) = e(g, g)ab • Efficiently computable group operations, group membership, bilinear map, etc.
Bilinear groups • • Prime p Groups G, GT of order p g generates G Bilinear map e: G × G → GT - e(g, g) generates GT - e(ga, gb) = e(g, g)ab • Efficiently computable group operations, group membership, bilinear map, etc.
![GS proofs [Groth, Sahai 06] Efficient NIZK and NIWI proofs for bilinear-group statements Statements GS proofs [Groth, Sahai 06] Efficient NIZK and NIWI proofs for bilinear-group statements Statements](https://present5.com/presentation/707633205fbe197480a421c11a9e416e/image-20.jpg) GS proofs [Groth, Sahai 06] Efficient NIZK and NIWI proofs for bilinear-group statements Statements of the form x, y, z, . . . G φ, θ, . . . Zp e(a, x) e(y, z) = T bφ y 5θ+2 z = t 3φ + 2φθ = 8 mod p Security based on Decisional Linear Assumption
GS proofs [Groth, Sahai 06] Efficient NIZK and NIWI proofs for bilinear-group statements Statements of the form x, y, z, . . . G φ, θ, . . . Zp e(a, x) e(y, z) = T bφ y 5θ+2 z = t 3φ + 2φθ = 8 mod p Security based on Decisional Linear Assumption
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
![Signature BB signature [Boneh, Boyen 04] vk = gsk signsk(m) = g 1/(sk+m) Verify Signature BB signature [Boneh, Boyen 04] vk = gsk signsk(m) = g 1/(sk+m) Verify](https://present5.com/presentation/707633205fbe197480a421c11a9e416e/image-22.jpg) Signature BB signature [Boneh, Boyen 04] vk = gsk signsk(m) = g 1/(sk+m) Verify e(sig, gmvk) = e(g, g) Use BB signature for both vksots, signsots(vk, m, NIWI, E, NIZK) vk, signsk(vksots) Security based on q-Strong Diffie Hellman Assump.
Signature BB signature [Boneh, Boyen 04] vk = gsk signsk(m) = g 1/(sk+m) Verify e(sig, gmvk) = e(g, g) Use BB signature for both vksots, signsots(vk, m, NIWI, E, NIZK) vk, signsk(vksots) Security based on q-Strong Diffie Hellman Assump.
![Certified signature Certificate [Zhou, Lin 06] Public issuer key: f, h G , T Certified signature Certificate [Zhou, Lin 06] Public issuer key: f, h G , T](https://present5.com/presentation/707633205fbe197480a421c11a9e416e/image-23.jpg) Certified signature Certificate [Zhou, Lin 06] Public issuer key: f, h G , T GT Certificate on vk: (a, b) so e(a, hvk) e(f, b) = T Certified in combination with BB Unforgeablesignature Forgeable! signature [Boldyreva, Fischlin, VK = vk 2 h. Hellman and Palacio, Security based on q-Strong Diffie. Warinschi 07] e(a 1/2, h. VK) e(f, b) = T Hard to assumptions q-Unfakeabilityforge both certificate and signature at the same time
Certified signature Certificate [Zhou, Lin 06] Public issuer key: f, h G , T GT Certificate on vk: (a, b) so e(a, hvk) e(f, b) = T Certified in combination with BB Unforgeablesignature Forgeable! signature [Boldyreva, Fischlin, VK = vk 2 h. Hellman and Palacio, Security based on q-Strong Diffie. Warinschi 07] e(a 1/2, h. VK) e(f, b) = T Hard to assumptions q-Unfakeabilityforge both certificate and signature at the same time
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
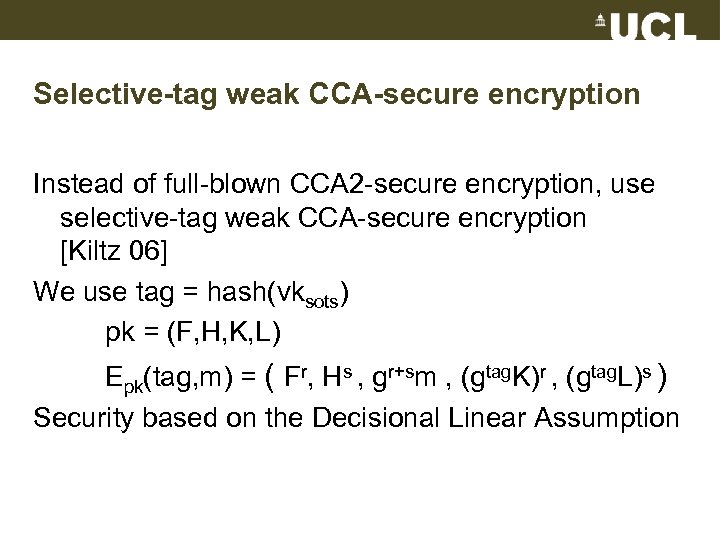 Selective-tag weak CCA-secure encryption Instead of full-blown CCA 2 -secure encryption, use selective-tag weak CCA-secure encryption [Kiltz 06] We use tag = hash(vksots) pk = (F, H, K, L) Epk(tag, m) = ( Fr, Hs , gr+sm , (gtag. K)r , (gtag. L)s ) Security based on the Decisional Linear Assumption
Selective-tag weak CCA-secure encryption Instead of full-blown CCA 2 -secure encryption, use selective-tag weak CCA-secure encryption [Kiltz 06] We use tag = hash(vksots) pk = (F, H, K, L) Epk(tag, m) = ( Fr, Hs , gr+sm , (gtag. K)r , (gtag. L)s ) Security based on the Decisional Linear Assumption
 Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
Agenda • Introduction – Group signatures – Full anonymity – Previous work and our results • Generic construction – – Certified signatures Anonymization through NIZK proofs Opening through CCA 2 -secure encryption Generic group signature • Pairing-based construction – – GS proofs BB signatures and ZL certificates Tag-based CCA 2 -secure encryption Our group signature
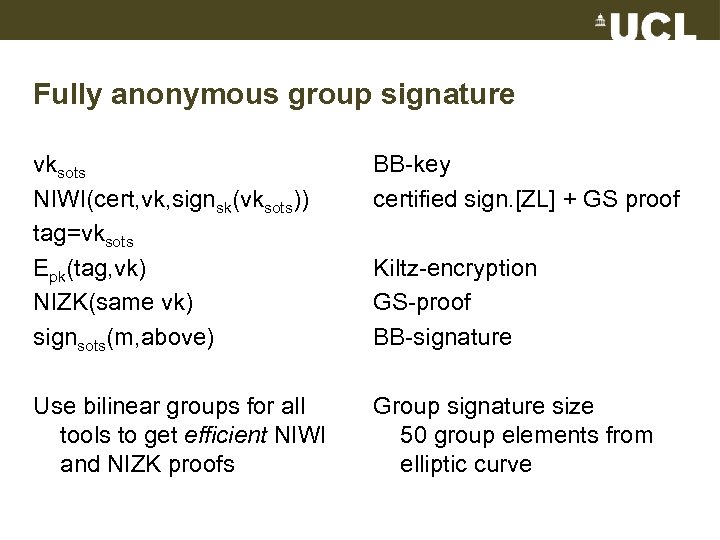 Fully anonymous group signature vksots NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(vksots)) tag=vksots Epk(tag, vk) NIZK(same vk) signsots(m, above) BB-key certified sign. [ZL] + GS proof Use bilinear groups for all tools to get efficient NIWI and NIZK proofs Group signature size 50 group elements from elliptic curve Kiltz-encryption GS-proof BB-signature
Fully anonymous group signature vksots NIWI(cert, vk, signsk(vksots)) tag=vksots Epk(tag, vk) NIZK(same vk) signsots(m, above) BB-key certified sign. [ZL] + GS proof Use bilinear groups for all tools to get efficient NIWI and NIZK proofs Group signature size 50 group elements from elliptic curve Kiltz-encryption GS-proof BB-signature
 Thank you • Conclusion – – – Pairing based group signature Fully anonymous Separate Issuer and Opener Partially dynamic group Size: 50 elements from elliptic curve Standard type cryptographic assumptions (no random oracles)
Thank you • Conclusion – – – Pairing based group signature Fully anonymous Separate Issuer and Opener Partially dynamic group Size: 50 elements from elliptic curve Standard type cryptographic assumptions (no random oracles)


