830b4cf694b7381b2567adf7ec4ad361.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 FTII Introducing Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF) and its programs to bridge the digital divide Idris F. Sulaiman, Ph. D International Cooperation Advisor, (IITF ~ Federasi Teknologi Informasi Indonesia, FTII)
FTII Introducing Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF) and its programs to bridge the digital divide Idris F. Sulaiman, Ph. D International Cooperation Advisor, (IITF ~ Federasi Teknologi Informasi Indonesia, FTII)
 Introduction • In early 2003, an exciting development took place in the IT industry with the consolidation of a federation by four IT industry associations — Internet Service Providers Association (APJII), Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO), Telematic Software Association (ASPILUKI), and Association of Animators (ANIMA) • The federation was needed to bring about § a greater coordination in IT and Communications convergence and to produce a better synergy § a greater cooperation through a ‘single point of contact’ for domestic and international relations.
Introduction • In early 2003, an exciting development took place in the IT industry with the consolidation of a federation by four IT industry associations — Internet Service Providers Association (APJII), Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO), Telematic Software Association (ASPILUKI), and Association of Animators (ANIMA) • The federation was needed to bring about § a greater coordination in IT and Communications convergence and to produce a better synergy § a greater cooperation through a ‘single point of contact’ for domestic and international relations.
 FTII n n Founding Members Indonesia Telematics Software Association (ASPILUKI Asosiasi Peranti Lunak Telematika Indonesia) Indonesia Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO Asosiasi Pengusaha Komputer Indonesia) Internet Services Providers Association of Indonesia (APJII Asosiasi Penyelenggara Jasa Internet Indonesia) Animators Association of Indonesia (ANIMA - Asosiasi Animasi Indonesia) ASPILUKI
FTII n n Founding Members Indonesia Telematics Software Association (ASPILUKI Asosiasi Peranti Lunak Telematika Indonesia) Indonesia Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO Asosiasi Pengusaha Komputer Indonesia) Internet Services Providers Association of Indonesia (APJII Asosiasi Penyelenggara Jasa Internet Indonesia) Animators Association of Indonesia (ANIMA - Asosiasi Animasi Indonesia) ASPILUKI
 Other members FTII n n Cellular Phone Association of Indonesia (ATSI - Asosiasi Telepon Seluler Indonesia) Internet Kiosk Association of Indonesia (AWARI - Asosiasi Warnet Indonesia) Telephone Kiosk Association of Indonesia (APWI - Asosiasi Pengusaha Wartel Indonesia) Indonesia Satellite Association (ASSI - Asosiasi Satelit Indonesia)
Other members FTII n n Cellular Phone Association of Indonesia (ATSI - Asosiasi Telepon Seluler Indonesia) Internet Kiosk Association of Indonesia (AWARI - Asosiasi Warnet Indonesia) Telephone Kiosk Association of Indonesia (APWI - Asosiasi Pengusaha Wartel Indonesia) Indonesia Satellite Association (ASSI - Asosiasi Satelit Indonesia)
 VISION Indonesia now has a thriving Information Technology industry which potentially can maximize all kinds of contributions to the development of the nation and state 1. By improving productivity, national competitiveness, and the welfare of the nation. 2. By enhancing and maintaining national unity. 3. By facilitating the convergence between various segments of the Information Technology, Computing and Communications industries.
VISION Indonesia now has a thriving Information Technology industry which potentially can maximize all kinds of contributions to the development of the nation and state 1. By improving productivity, national competitiveness, and the welfare of the nation. 2. By enhancing and maintaining national unity. 3. By facilitating the convergence between various segments of the Information Technology, Computing and Communications industries.
 Mission n n To translate the Common Vision into practical, up-to-date and relevant programs to include Information Technology as an integral part of the National Development Strategy To take an active role as a partner of government agencies , other industry, educational and civil society organizations in the development of Information Technology To provide strategic recommendations for policy formulation, regulation and development strategy of the Information Technology industry To concretely prepare the Information Technology industry to face the opening of markets and free competition by developing the potential domestic as well as global markets
Mission n n To translate the Common Vision into practical, up-to-date and relevant programs to include Information Technology as an integral part of the National Development Strategy To take an active role as a partner of government agencies , other industry, educational and civil society organizations in the development of Information Technology To provide strategic recommendations for policy formulation, regulation and development strategy of the Information Technology industry To concretely prepare the Information Technology industry to face the opening of markets and free competition by developing the potential domestic as well as global markets
 Executives - 2003 Chairperson Secretary General Deputy Treasurer Deputy Vice Chair - Infrastructure Deputy Vice Chair - Application Deputy Vice Chair - HRD Deputy : Teddy Sukardi : Heru Nugroho : Teguh Anantawikrama : Soegiharto Santoso : Shanti Poesposoecipto : Andre Ludya Liap : Bambang Lusmiadi : Djarot Subiantoro : Daniel Haryanto : Sutiono Gunadi : Eko K Budiardjo
Executives - 2003 Chairperson Secretary General Deputy Treasurer Deputy Vice Chair - Infrastructure Deputy Vice Chair - Application Deputy Vice Chair - HRD Deputy : Teddy Sukardi : Heru Nugroho : Teguh Anantawikrama : Soegiharto Santoso : Shanti Poesposoecipto : Andre Ludya Liap : Bambang Lusmiadi : Djarot Subiantoro : Daniel Haryanto : Sutiono Gunadi : Eko K Budiardjo
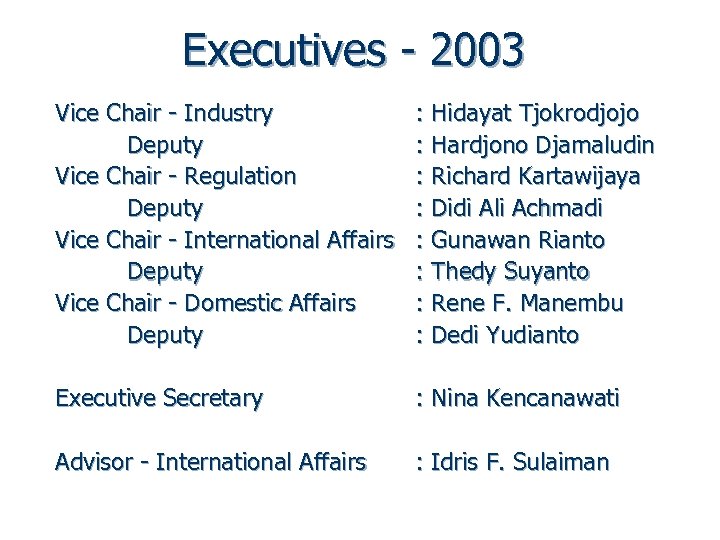 Executives - 2003 Vice Chair - Industry Deputy Vice Chair - Regulation Deputy Vice Chair - International Affairs Deputy Vice Chair - Domestic Affairs Deputy : Hidayat Tjokrodjojo : Hardjono Djamaludin : Richard Kartawijaya : Didi Ali Achmadi : Gunawan Rianto : Thedy Suyanto : Rene F. Manembu : Dedi Yudianto Executive Secretary : Nina Kencanawati Advisor - International Affairs : Idris F. Sulaiman
Executives - 2003 Vice Chair - Industry Deputy Vice Chair - Regulation Deputy Vice Chair - International Affairs Deputy Vice Chair - Domestic Affairs Deputy : Hidayat Tjokrodjojo : Hardjono Djamaludin : Richard Kartawijaya : Didi Ali Achmadi : Gunawan Rianto : Thedy Suyanto : Rene F. Manembu : Dedi Yudianto Executive Secretary : Nina Kencanawati Advisor - International Affairs : Idris F. Sulaiman
 Information Technology and Convergence n n Information Technology (IT) is rapidly converging with Communications and Computing Technologies such that a new agglomerated industry has emerged. It is interchangably called just “IT”, IT & Communications (ITC in the European Union) or Information Communications Technology (ICT in the United States), “Telematika” or “Infokom” in the Indonesian language. ITs are now essential tools for competitiveness in the business world and commerce (e-commerce), for improving a better delivery of government services and for achieving good governance for private and government agencies (e-government).
Information Technology and Convergence n n Information Technology (IT) is rapidly converging with Communications and Computing Technologies such that a new agglomerated industry has emerged. It is interchangably called just “IT”, IT & Communications (ITC in the European Union) or Information Communications Technology (ICT in the United States), “Telematika” or “Infokom” in the Indonesian language. ITs are now essential tools for competitiveness in the business world and commerce (e-commerce), for improving a better delivery of government services and for achieving good governance for private and government agencies (e-government).
 Information Society is both a description and an aspiration n “For we live today in an era in which information is omnipresent, through newspapers, radio, television and the Internet; in which information is n n transforming the ways we live, learn, work and relate Indispensable–for health, agriculture, education and trade, and for cultivating the engaged and learned citizenry that is essential for democracy to work. ” “Description turns to aspiration when we consider what to do with the masses of information and knowledge increasingly at our disposal–how to make it serve some greater purpose, be it peace, development, human rights, global harmony or all these together. ” “What is new today are the technologies are dramatically accelerating its global dissemination. These technologies are a tremendous force for creating opportunities, and for integrating people and nations into the global economy. ”
Information Society is both a description and an aspiration n “For we live today in an era in which information is omnipresent, through newspapers, radio, television and the Internet; in which information is n n transforming the ways we live, learn, work and relate Indispensable–for health, agriculture, education and trade, and for cultivating the engaged and learned citizenry that is essential for democracy to work. ” “Description turns to aspiration when we consider what to do with the masses of information and knowledge increasingly at our disposal–how to make it serve some greater purpose, be it peace, development, human rights, global harmony or all these together. ” “What is new today are the technologies are dramatically accelerating its global dissemination. These technologies are a tremendous force for creating opportunities, and for integrating people and nations into the global economy. ”
 Information Society and the Digital Divide n n “But too many of the world’s people remain untouched by the information revolution. ” “A <
Information Society and the Digital Divide n n “But too many of the world’s people remain untouched by the information revolution. ” “A <
 Indonesia shows potential in realizing the Information Society n n “The growing gap between the information-rich and the information-poor can only be bridged by concrete interventions. Pure declarations of goodwill not be enough. The World Summit Award (WSA) is the first attempt within the global information society to evaluate and honour the best multimedia realisations from all over the world. ” Prof. Peter A. Bruck, a distinguished researcher and the catalyst for WSA at the ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) event at the first WSIS. Among 40 Best Products in 8 Catagories from 136 Countries and 803 Entries, the Indonesian product “ORISINAL: Morning Sunshine” was chosen in the e. Entertainment category which was showcased at the gala event in the WSIS, Geneva, December 2003 (see www. wsis-award. org)
Indonesia shows potential in realizing the Information Society n n “The growing gap between the information-rich and the information-poor can only be bridged by concrete interventions. Pure declarations of goodwill not be enough. The World Summit Award (WSA) is the first attempt within the global information society to evaluate and honour the best multimedia realisations from all over the world. ” Prof. Peter A. Bruck, a distinguished researcher and the catalyst for WSA at the ICT for Development (ICT 4 D) event at the first WSIS. Among 40 Best Products in 8 Catagories from 136 Countries and 803 Entries, the Indonesian product “ORISINAL: Morning Sunshine” was chosen in the e. Entertainment category which was showcased at the gala event in the WSIS, Geneva, December 2003 (see www. wsis-award. org)
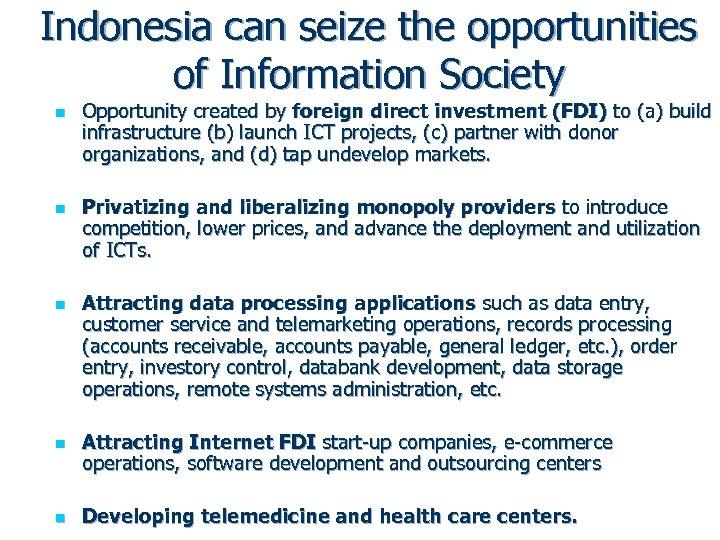 Indonesia can seize the opportunities of Information Society n n n Opportunity created by foreign direct investment (FDI) to (a) build infrastructure (b) launch ICT projects, (c) partner with donor organizations, and (d) tap undevelop markets. Privatizing and liberalizing monopoly providers to introduce competition, lower prices, and advance the deployment and utilization of ICTs. Attracting data processing applications such as data entry, customer service and telemarketing operations, records processing (accounts receivable, accounts payable, general ledger, etc. ), order entry, investory control, databank development, data storage operations, remote systems administration, etc. Attracting Internet FDI start-up companies, e-commerce operations, software development and outsourcing centers Developing telemedicine and health care centers.
Indonesia can seize the opportunities of Information Society n n n Opportunity created by foreign direct investment (FDI) to (a) build infrastructure (b) launch ICT projects, (c) partner with donor organizations, and (d) tap undevelop markets. Privatizing and liberalizing monopoly providers to introduce competition, lower prices, and advance the deployment and utilization of ICTs. Attracting data processing applications such as data entry, customer service and telemarketing operations, records processing (accounts receivable, accounts payable, general ledger, etc. ), order entry, investory control, databank development, data storage operations, remote systems administration, etc. Attracting Internet FDI start-up companies, e-commerce operations, software development and outsourcing centers Developing telemedicine and health care centers.
 Indonesia can seize the opportunities of Information Society Using ICTs for distance learning, education, unemployment n n n n database and workforce skills. Using ICTs for agri-business and agriculture information and industry sector support. Attracting light manufacturing operations. Modernizing the financial sector. Fostering the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to spur job creation, innovation, flexibility and competitiveness. Reforming and automating court administration and case management and availability of judicial information. Developing effective networks in Indonesia with security and affordability free from virus, spam and post 9/11 concerns. Each of these opportunities is dependent upon the development of the public policy, legal and regulatory framework to support the above activities. They form the underlying foundation of government support for ICTs and a favorable business environment.
Indonesia can seize the opportunities of Information Society Using ICTs for distance learning, education, unemployment n n n n database and workforce skills. Using ICTs for agri-business and agriculture information and industry sector support. Attracting light manufacturing operations. Modernizing the financial sector. Fostering the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to spur job creation, innovation, flexibility and competitiveness. Reforming and automating court administration and case management and availability of judicial information. Developing effective networks in Indonesia with security and affordability free from virus, spam and post 9/11 concerns. Each of these opportunities is dependent upon the development of the public policy, legal and regulatory framework to support the above activities. They form the underlying foundation of government support for ICTs and a favorable business environment.
 Programs of FTII Examples of our key activities in public policy, legal and regulatory framework development: n n Participation in the activities of the Inter-Governmental Committee on the preparation of the Draft Bill on Information and Electronic Transaction (RUU-ITE). Participation in the public-private discussion on policy issues on the ICT Coordinating Team (TKTI) and on the ICT Security Task Force (coordinated by Min. Comm. & Information) Working with industry and government counterparts to rally their support for the annual ICT Month of Promotion (usually for the month of August when the Independence was declared). Advocacy work for a favorable IT business environment in various IT and IT-users’ industry and government forums.
Programs of FTII Examples of our key activities in public policy, legal and regulatory framework development: n n Participation in the activities of the Inter-Governmental Committee on the preparation of the Draft Bill on Information and Electronic Transaction (RUU-ITE). Participation in the public-private discussion on policy issues on the ICT Coordinating Team (TKTI) and on the ICT Security Task Force (coordinated by Min. Comm. & Information) Working with industry and government counterparts to rally their support for the annual ICT Month of Promotion (usually for the month of August when the Independence was declared). Advocacy work for a favorable IT business environment in various IT and IT-users’ industry and government forums.
 Main Programs on ICT 4 D Examples of our ICT for Development and Education to bridge the digital divide programs: n n n “PC Ownership Initiative (PCOI)” - to provide localassembled and low-cost computers for poverty alleviation (APKOMINDO) “Regional Innovation Center for Excellence (RICE)” - involving the establishment of software incubation center in collaboration with PT Inti, Bandung, and, the “Regional Center for IT Assisted Learning “ (RECITAL)” Initiative to accelerate E-learning in RECITAL Rural Areas (ASPILUKI) “School 2000” and “RT-RW Net” - to set up low-cost fixedline/wireless connections to schools (APJIIIndo. WLI) as well as to neighborhoods (AWARI)
Main Programs on ICT 4 D Examples of our ICT for Development and Education to bridge the digital divide programs: n n n “PC Ownership Initiative (PCOI)” - to provide localassembled and low-cost computers for poverty alleviation (APKOMINDO) “Regional Innovation Center for Excellence (RICE)” - involving the establishment of software incubation center in collaboration with PT Inti, Bandung, and, the “Regional Center for IT Assisted Learning “ (RECITAL)” Initiative to accelerate E-learning in RECITAL Rural Areas (ASPILUKI) “School 2000” and “RT-RW Net” - to set up low-cost fixedline/wireless connections to schools (APJIIIndo. WLI) as well as to neighborhoods (AWARI)
 Main Programs on ICT 4 D n n Other programs on ICT for Development to close the digital gap are: “Women & Community Tele-Center (WCTC)” in West Java and North Sumatra (Community Tele-Center
Main Programs on ICT 4 D n n Other programs on ICT for Development to close the digital gap are: “Women & Community Tele-Center (WCTC)” in West Java and North Sumatra (Community Tele-Center
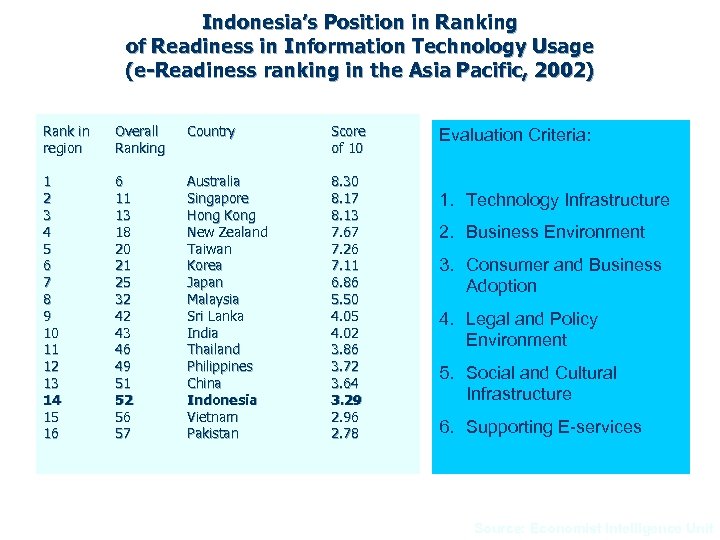 Indonesia’s Position in Ranking of Readiness in Information Technology Usage (e-Readiness ranking in the Asia Pacific, 2002) Rank in region Overall Ranking Country Score of 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 6 11 13 18 20 21 25 32 42 43 46 49 51 52 56 57 Australia Singapore Hong Kong New Zealand Taiwan Korea Japan Malaysia Sri Lanka India Thailand Philippines China Indonesia Vietnam Pakistan 8. 30 8. 17 8. 13 7. 67 7. 26 7. 11 6. 86 5. 50 4. 05 4. 02 3. 86 3. 72 3. 64 3. 29 2. 96 2. 78 Evaluation Criteria: 1. Technology Infrastructure 2. Business Environment 3. Consumer and Business Adoption 4. Legal and Policy Environment 5. Social and Cultural Infrastructure 6. Supporting E-services Source: Economist Intelligence Unit
Indonesia’s Position in Ranking of Readiness in Information Technology Usage (e-Readiness ranking in the Asia Pacific, 2002) Rank in region Overall Ranking Country Score of 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 6 11 13 18 20 21 25 32 42 43 46 49 51 52 56 57 Australia Singapore Hong Kong New Zealand Taiwan Korea Japan Malaysia Sri Lanka India Thailand Philippines China Indonesia Vietnam Pakistan 8. 30 8. 17 8. 13 7. 67 7. 26 7. 11 6. 86 5. 50 4. 05 4. 02 3. 86 3. 72 3. 64 3. 29 2. 96 2. 78 Evaluation Criteria: 1. Technology Infrastructure 2. Business Environment 3. Consumer and Business Adoption 4. Legal and Policy Environment 5. Social and Cultural Infrastructure 6. Supporting E-services Source: Economist Intelligence Unit
 Key Issues in Indonesia n Development of Supporting Infrastructure n n Development of Human Resources n n To raise awareness and motivation on the best use information technology To develop National IT Competency Standards as reference for industry, educational sector, training and to issue certification and accreditation To develop integrated programs to accelerate the development of human resources Electronic Transaction Law and Cybercrime Law n n Ratio per capita: Computer use, Internet subscription and use, tele-density Affordability and infrastructure cost: new fixed-line connections, data network and infrastructure cost Conducive regulatory framework which supports transparency, free competition and improved efficiency To raise awareness and assist with the development of an appropriate legal framework for all activities relating to information technology including cybersecurity and cybercrime Creation of Conducive Domestic Market Place n n To improve the Rule of Law To bring about a healthy business and investment environment by, for example, initiating and supporting programs that can create an “investment-friendly” business climate to develop information technologies (such as modern licensing procedures, fiscal incentives and others)
Key Issues in Indonesia n Development of Supporting Infrastructure n n Development of Human Resources n n To raise awareness and motivation on the best use information technology To develop National IT Competency Standards as reference for industry, educational sector, training and to issue certification and accreditation To develop integrated programs to accelerate the development of human resources Electronic Transaction Law and Cybercrime Law n n Ratio per capita: Computer use, Internet subscription and use, tele-density Affordability and infrastructure cost: new fixed-line connections, data network and infrastructure cost Conducive regulatory framework which supports transparency, free competition and improved efficiency To raise awareness and assist with the development of an appropriate legal framework for all activities relating to information technology including cybersecurity and cybercrime Creation of Conducive Domestic Market Place n n To improve the Rule of Law To bring about a healthy business and investment environment by, for example, initiating and supporting programs that can create an “investment-friendly” business climate to develop information technologies (such as modern licensing procedures, fiscal incentives and others)
 For further information, please contact: Idris F. Sulaiman, Ph. D International Cooperation Advisor, Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF/FTII) Cyber-Elektrindo Building, 11 th Floor Jl Kuningan Barat No. 8, Jakarta 12710 Indonesia Phone: +62 -811 -111 -312, +62 (0)21 5296 -0634 Fax: +62 (0)21 5296 -0635 Email: idriss@indo. net. id, secretariat@ftii. or. id @indo. net. id, Website: http: //www. ftii. or. id (under re-construction)
For further information, please contact: Idris F. Sulaiman, Ph. D International Cooperation Advisor, Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF/FTII) Cyber-Elektrindo Building, 11 th Floor Jl Kuningan Barat No. 8, Jakarta 12710 Indonesia Phone: +62 -811 -111 -312, +62 (0)21 5296 -0634 Fax: +62 (0)21 5296 -0635 Email: idriss@indo. net. id, secretariat@ftii. or. id @indo. net. id, Website: http: //www. ftii. or. id (under re-construction)
 For further information on associations: Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF) consists of: 1) Indonesian Telematics Software Association (ASPILUKI) n n n n n Secretariat : Jl. Taman Gandaria No. A-7 Jakarta 12240, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 72792201 - 02 Fax. : +62 (0)21 72792203 Email : aspiluki@telkom. net Web : http: //www. aspiluki. or. id (under re-construction) President : Mr. Djarot Subiantoro Email : djarot_subiantoro@sigma. co. id 2) Indonesia Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO): Secretariat : Glodok Plaza Lt. 3 No. 28 -30 Jl. Pinangsia Raya No. 1 Jakarta 11180, Indonesia n Telp. : +62 (0)21 62302935 n Fax. : +62 (0)21 62302936 n Website: http: //www. apkomindo. or. id n President : Mr. G. Hidayat Tjokrodjojo n Email : ghidayat@realta. co. id
For further information on associations: Indonesia Information Technology Federation (IITF) consists of: 1) Indonesian Telematics Software Association (ASPILUKI) n n n n n Secretariat : Jl. Taman Gandaria No. A-7 Jakarta 12240, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 72792201 - 02 Fax. : +62 (0)21 72792203 Email : aspiluki@telkom. net Web : http: //www. aspiluki. or. id (under re-construction) President : Mr. Djarot Subiantoro Email : djarot_subiantoro@sigma. co. id 2) Indonesia Computer Business Association (APKOMINDO): Secretariat : Glodok Plaza Lt. 3 No. 28 -30 Jl. Pinangsia Raya No. 1 Jakarta 11180, Indonesia n Telp. : +62 (0)21 62302935 n Fax. : +62 (0)21 62302936 n Website: http: //www. apkomindo. or. id n President : Mr. G. Hidayat Tjokrodjojo n Email : ghidayat@realta. co. id
 For further information on associations: n 3) Internet Service Providers Association of Indonesia (APJII): n Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 5296 0634 Fax. : +62 (0)21 5296 0635 Website: http: //www. apjii. or. id Secretary General : Mr. Heru Nugroho Email : sekjen@apjii. or. id n 4) Indonesia Association of Animators (ANIMA): n n n Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 5296 0634 Fax. : +62 (0)21 5296 0635 Website: http: //www. anima. or. id (under re-construction) President : Mr. (Tatong) Teguh Ananto W. Email : sekretariat@ftii. or. id
For further information on associations: n 3) Internet Service Providers Association of Indonesia (APJII): n Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 5296 0634 Fax. : +62 (0)21 5296 0635 Website: http: //www. apjii. or. id Secretary General : Mr. Heru Nugroho Email : sekjen@apjii. or. id n 4) Indonesia Association of Animators (ANIMA): n n n Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 5296 0634 Fax. : +62 (0)21 5296 0635 Website: http: //www. anima. or. id (under re-construction) President : Mr. (Tatong) Teguh Ananto W. Email : sekretariat@ftii. or. id
 For further information on associations: n n n n 5) Wireless LAN Association of Indonesia (WLI Indonesia): Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 721 0503 Fax. : +62 (0)21 Website: http: //www. indowli. or. id Secretary General : Mr. Barata Wardhana Email : barata@indosat. net. id 6) Internet Kiosks Association of Indonesia (AWARI): http: //www. awari. or. id Secretariat : Vila Indah Padjadjaran, Jl. Raya Pajajaran 88 F Bogor Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)25 133 7555 Fax. : +62 (0)25 ? ? ? Website: http: //www. awari. or. id Presidium Member : Mr. Michael S. Sunggiardi Email : michael@sunggiardi. com
For further information on associations: n n n n 5) Wireless LAN Association of Indonesia (WLI Indonesia): Secretariat : Cyber-Elektrindo Building Jl. Kuningan Barat No. 8 Jakarta 12710, Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)21 721 0503 Fax. : +62 (0)21 Website: http: //www. indowli. or. id Secretary General : Mr. Barata Wardhana Email : barata@indosat. net. id 6) Internet Kiosks Association of Indonesia (AWARI): http: //www. awari. or. id Secretariat : Vila Indah Padjadjaran, Jl. Raya Pajajaran 88 F Bogor Indonesia Telp. : +62 (0)25 133 7555 Fax. : +62 (0)25 ? ? ? Website: http: //www. awari. or. id Presidium Member : Mr. Michael S. Sunggiardi Email : michael@sunggiardi. com
 For further information on associations: n 7) Post and Telephone Kiosks Association of Indonesia (APWI) n Secretariat : Taman Buaran Indah Blok U-225, Jl. KRT Rajiman Widyodiningrat, Jakarta, Indonesia Tel. : +62 (0)21 8660 4428 Fax. : +62 (0)21 8660 4428 Website: http: //www. apwi. or. id (under re-construction) Secretary General : Mr. Srijanto Tjokrosudarmo Email : srijanto@indosat. net. id n 8) Indonesia Satellite Association (ASSI): n n n n Secretariat : Jl. Cisanggarung No. 2, 2 F, Room 3536 Bandung 40115, Indonesia Tel. : +62 (0)22 452 1657 -8 Fax. : +62 (0)22 422 0610 Website: http: //assi. indointernet. com/ Secretary General : Mr. Arifin Nugroho Email : arifin_nugroho@attglobal. net
For further information on associations: n 7) Post and Telephone Kiosks Association of Indonesia (APWI) n Secretariat : Taman Buaran Indah Blok U-225, Jl. KRT Rajiman Widyodiningrat, Jakarta, Indonesia Tel. : +62 (0)21 8660 4428 Fax. : +62 (0)21 8660 4428 Website: http: //www. apwi. or. id (under re-construction) Secretary General : Mr. Srijanto Tjokrosudarmo Email : srijanto@indosat. net. id n 8) Indonesia Satellite Association (ASSI): n n n n Secretariat : Jl. Cisanggarung No. 2, 2 F, Room 3536 Bandung 40115, Indonesia Tel. : +62 (0)22 452 1657 -8 Fax. : +62 (0)22 422 0610 Website: http: //assi. indointernet. com/ Secretary General : Mr. Arifin Nugroho Email : arifin_nugroho@attglobal. net


