43fdf67b9ecd1db137f5909e3a33e095.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
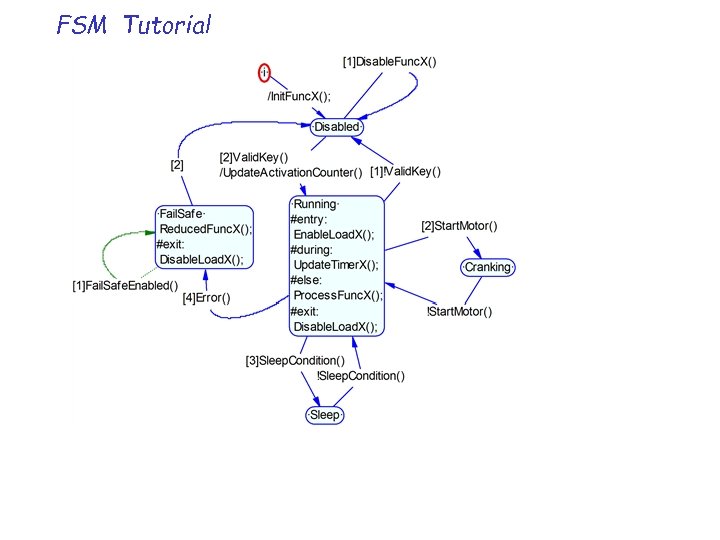 FSM Tutorial
FSM Tutorial
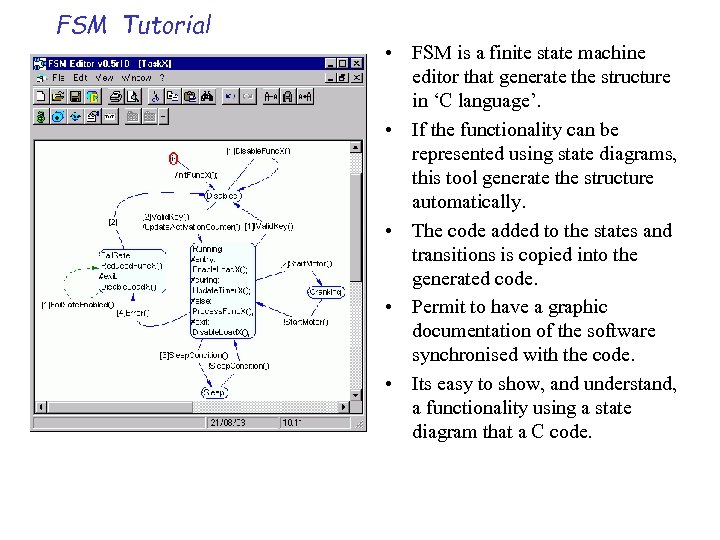 FSM Tutorial • FSM is a finite state machine editor that generate the structure in ‘C language’. • If the functionality can be represented using state diagrams, this tool generate the structure automatically. • The code added to the states and transitions is copied into the generated code. • Permit to have a graphic documentation of the software synchronised with the code. • Its easy to show, and understand, a functionality using a state diagram that a C code.
FSM Tutorial • FSM is a finite state machine editor that generate the structure in ‘C language’. • If the functionality can be represented using state diagrams, this tool generate the structure automatically. • The code added to the states and transitions is copied into the generated code. • Permit to have a graphic documentation of the software synchronised with the code. • Its easy to show, and understand, a functionality using a state diagram that a C code.
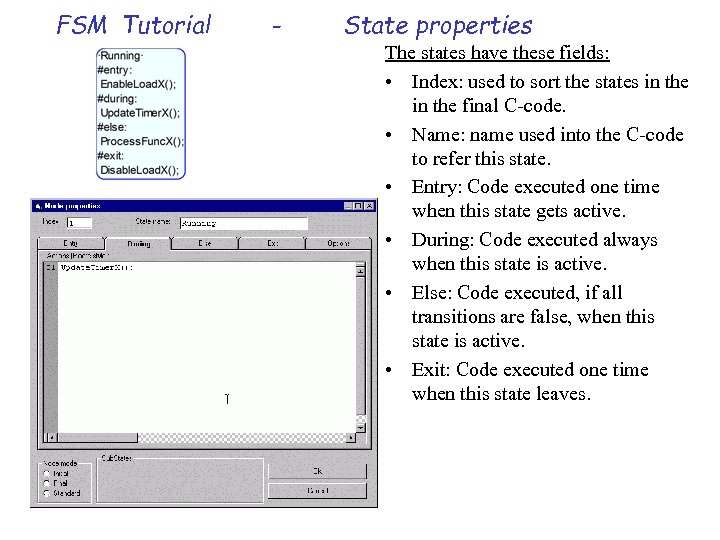 FSM Tutorial - State properties The states have these fields: • Index: used to sort the states in the final C-code. • Name: name used into the C-code to refer this state. • Entry: Code executed one time when this state gets active. • During: Code executed always when this state is active. • Else: Code executed, if all transitions are false, when this state is active. • Exit: Code executed one time when this state leaves.
FSM Tutorial - State properties The states have these fields: • Index: used to sort the states in the final C-code. • Name: name used into the C-code to refer this state. • Entry: Code executed one time when this state gets active. • During: Code executed always when this state is active. • Else: Code executed, if all transitions are false, when this state is active. • Exit: Code executed one time when this state leaves.
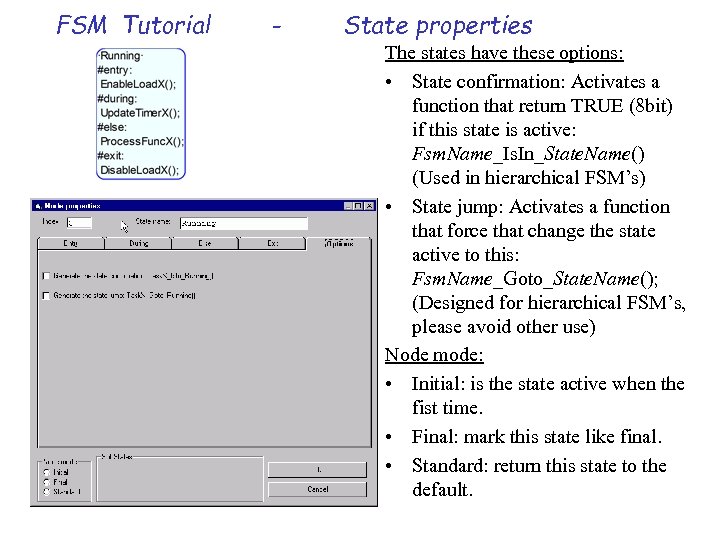 FSM Tutorial - State properties The states have these options: • State confirmation: Activates a function that return TRUE (8 bit) if this state is active: Fsm. Name_Is. In_State. Name() (Used in hierarchical FSM’s) • State jump: Activates a function that force that change the state active to this: Fsm. Name_Goto_State. Name(); (Designed for hierarchical FSM’s, please avoid other use) Node mode: • Initial: is the state active when the fist time. • Final: mark this state like final. • Standard: return this state to the default.
FSM Tutorial - State properties The states have these options: • State confirmation: Activates a function that return TRUE (8 bit) if this state is active: Fsm. Name_Is. In_State. Name() (Used in hierarchical FSM’s) • State jump: Activates a function that force that change the state active to this: Fsm. Name_Goto_State. Name(); (Designed for hierarchical FSM’s, please avoid other use) Node mode: • Initial: is the state active when the fist time. • Final: mark this state like final. • Standard: return this state to the default.
 FSM Tutorial - Transition properties Transitions have these fields&options: • Priority: is the priority used to analyse the transitions, if a more priority condition (lower number) is true the rest of conditions won’t be analysed. • Transition condition: test condition that had to be true to modify the state active. If it’s empty it use ‘ 1’. • Transition action: Code executed one when the condition is true. • This Self-transition cause exitentry: let us to decide if a selftransition had to cause these actions. (only valid for self. Trans. ) • Last transition: Ensure that even if we add new transitions this will be the last one.
FSM Tutorial - Transition properties Transitions have these fields&options: • Priority: is the priority used to analyse the transitions, if a more priority condition (lower number) is true the rest of conditions won’t be analysed. • Transition condition: test condition that had to be true to modify the state active. If it’s empty it use ‘ 1’. • Transition action: Code executed one when the condition is true. • This Self-transition cause exitentry: let us to decide if a selftransition had to cause these actions. (only valid for self. Trans. ) • Last transition: Ensure that even if we add new transitions this will be the last one.
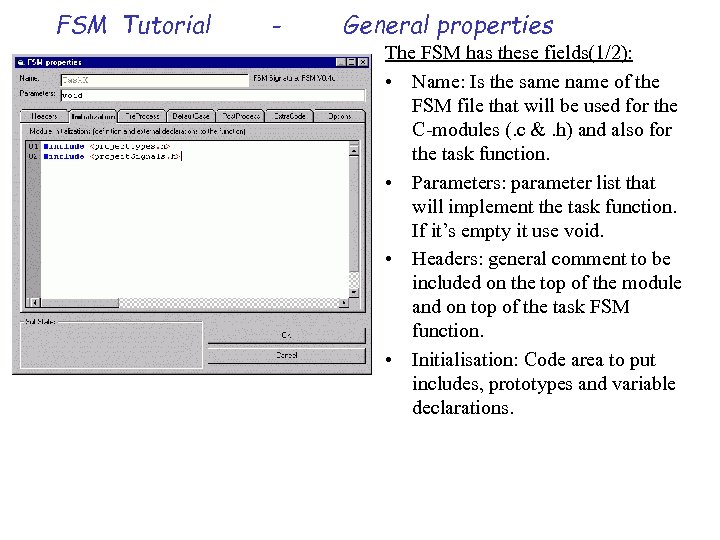 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these fields(1/2): • Name: Is the same name of the FSM file that will be used for the C-modules (. c &. h) and also for the task function. • Parameters: parameter list that will implement the task function. If it’s empty it use void. • Headers: general comment to be included on the top of the module and on top of the task FSM function. • Initialisation: Code area to put includes, prototypes and variable declarations.
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these fields(1/2): • Name: Is the same name of the FSM file that will be used for the C-modules (. c &. h) and also for the task function. • Parameters: parameter list that will implement the task function. If it’s empty it use void. • Headers: general comment to be included on the top of the module and on top of the task FSM function. • Initialisation: Code area to put includes, prototypes and variable declarations.
 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these fields(2/2): • Pre. Process: Code executed always before call the state dispatcher. Can include local variable declarations. • Default. Case: Code executed if the dispatcher index don’t match wit a valid state. This can happens only if we manipulate this index. Only is used whit generation models based on “switch cases”. • Prost. Process: Code executed always after call the state dispatcher. • Extra Code: Code area to implement optionally C-functions.
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these fields(2/2): • Pre. Process: Code executed always before call the state dispatcher. Can include local variable declarations. • Default. Case: Code executed if the dispatcher index don’t match wit a valid state. This can happens only if we manipulate this index. Only is used whit generation models based on “switch cases”. • Prost. Process: Code executed always after call the state dispatcher. • Extra Code: Code area to implement optionally C-functions.
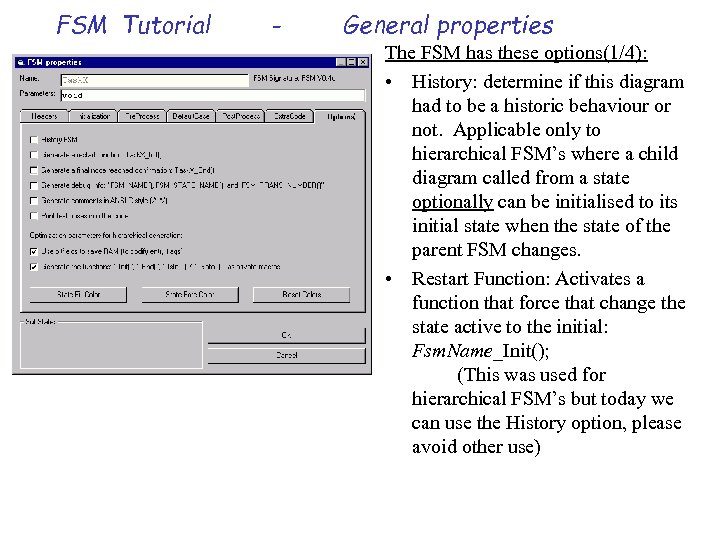 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(1/4): • History: determine if this diagram had to be a historic behaviour or not. Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s where a child diagram called from a state optionally can be initialised to its initial state when the state of the parent FSM changes. • Restart Function: Activates a function that force that change the state active to the initial: Fsm. Name_Init(); (This was used for hierarchical FSM’s but today we can use the History option, please avoid other use)
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(1/4): • History: determine if this diagram had to be a historic behaviour or not. Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s where a child diagram called from a state optionally can be initialised to its initial state when the state of the parent FSM changes. • Restart Function: Activates a function that force that change the state active to the initial: Fsm. Name_Init(); (This was used for hierarchical FSM’s but today we can use the History option, please avoid other use)
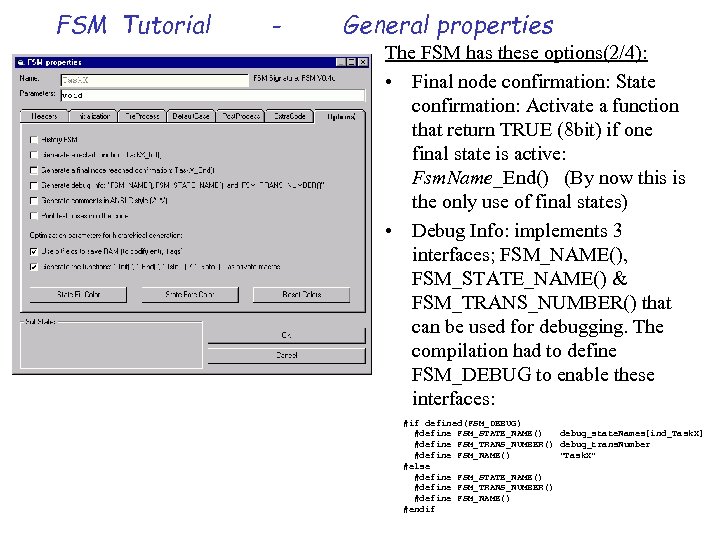 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(2/4): • Final node confirmation: State confirmation: Activate a function that return TRUE (8 bit) if one final state is active: Fsm. Name_End() (By now this is the only use of final states) • Debug Info: implements 3 interfaces; FSM_NAME(), FSM_STATE_NAME() & FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() that can be used for debugging. The compilation had to define FSM_DEBUG to enable these interfaces: #if defined(FSM_DEBUG) #define FSM_STATE_NAME() debug_state. Names[ind_Task. X] #define FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() debug_trans. Number #define FSM_NAME() "Task. X" #else #define FSM_STATE_NAME() #define FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() #define FSM_NAME() #endif
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(2/4): • Final node confirmation: State confirmation: Activate a function that return TRUE (8 bit) if one final state is active: Fsm. Name_End() (By now this is the only use of final states) • Debug Info: implements 3 interfaces; FSM_NAME(), FSM_STATE_NAME() & FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() that can be used for debugging. The compilation had to define FSM_DEBUG to enable these interfaces: #if defined(FSM_DEBUG) #define FSM_STATE_NAME() debug_state. Names[ind_Task. X] #define FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() debug_trans. Number #define FSM_NAME() "Task. X" #else #define FSM_STATE_NAME() #define FSM_TRANS_NUMBER() #define FSM_NAME() #endif
 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(3/4): • Ansi-C comments: The generator convert all lines that have // ~~~ comment to /* ~~~ */. • Print Text Boxes: The text boxes (comments) are also printed like C - comments in the bottom of the ‘. c file’. (This feature must be enhanced in future versions) • Use bitfields: Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s compiled with the format hierarchical switch case. This format join all fsm’s (parent & child-diagrams) in a single file, then all entry flags variables can be packed in a bit structure.
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(3/4): • Ansi-C comments: The generator convert all lines that have // ~~~ comment to /* ~~~ */. • Print Text Boxes: The text boxes (comments) are also printed like C - comments in the bottom of the ‘. c file’. (This feature must be enhanced in future versions) • Use bitfields: Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s compiled with the format hierarchical switch case. This format join all fsm’s (parent & child-diagrams) in a single file, then all entry flags variables can be packed in a bit structure.
 FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(4/4): • Implement interfaces like macros: Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s compiled with the format hierarchical switch case. This format join all fsm’s (parent & child-diagrams) in a single file. Here all interfaces, that originally were developed to improve the hierarchical navigability, can be declared like macros. This encapsulate more the code and optimise the execution. • Color buttons: Let us to modify the state colors. Note you can create a template with your favourite colors.
FSM Tutorial - General properties The FSM has these options(4/4): • Implement interfaces like macros: Applicable only to hierarchical FSM’s compiled with the format hierarchical switch case. This format join all fsm’s (parent & child-diagrams) in a single file. Here all interfaces, that originally were developed to improve the hierarchical navigability, can be declared like macros. This encapsulate more the code and optimise the execution. • Color buttons: Let us to modify the state colors. Note you can create a template with your favourite colors.
 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Buttons: • New, Open, Save & Generate C-Code (using the predefined method). • Print & Print Preview. • Cut, Copy, Paste: (Copy & paste work only with remark boxes). • Find Text: Find and optionally replace text. • Undo last action & Redo last undo. • Reduce Font, Change Font, Enlarge Font. • Lock & Unlock diagram, • Insert. Mode: Change the editor between insert mode and select mode. • Auto. Size: Set if the state size can be adjusted automatically or manually. • Properties edit: Opens the properties menu (equivalent to do a double click in the diagram) • Insert Remark: Inserts a new remark box. • Open Parent diagram & Open child diagram (hierarchical navigation)
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Buttons: • New, Open, Save & Generate C-Code (using the predefined method). • Print & Print Preview. • Cut, Copy, Paste: (Copy & paste work only with remark boxes). • Find Text: Find and optionally replace text. • Undo last action & Redo last undo. • Reduce Font, Change Font, Enlarge Font. • Lock & Unlock diagram, • Insert. Mode: Change the editor between insert mode and select mode. • Auto. Size: Set if the state size can be adjusted automatically or manually. • Properties edit: Opens the properties menu (equivalent to do a double click in the diagram) • Insert Remark: Inserts a new remark box. • Open Parent diagram & Open child diagram (hierarchical navigation)
 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - File(1/2): • New: opens a new diagram. • New Child opens a new diagram into a subdirectory. (this directory is named like the parent). • Open opens a existent diagram (only fsm format). • Close closes the diagram. • Save saves the diagram. • Save As… saves the diagram with a new name. • Save All saves all open diagrams. • Save As enhanced metafile… saves the diagram like a metafile. • Save As HTML File… saves the diagram like HTML. • Generate List… saves the diagram info in a list.
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - File(1/2): • New: opens a new diagram. • New Child opens a new diagram into a subdirectory. (this directory is named like the parent). • Open opens a existent diagram (only fsm format). • Close closes the diagram. • Save saves the diagram. • Save As… saves the diagram with a new name. • Save All saves all open diagrams. • Save As enhanced metafile… saves the diagram like a metafile. • Save As HTML File… saves the diagram like HTML. • Generate List… saves the diagram info in a list.
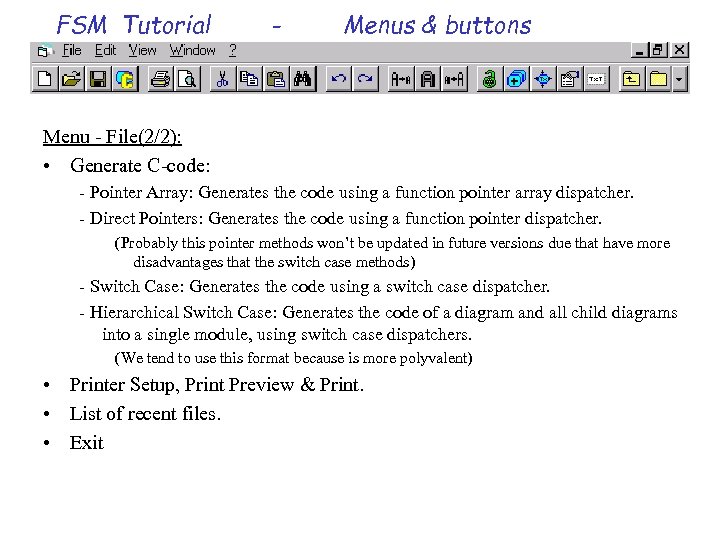 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - File(2/2): • Generate C-code: - Pointer Array: Generates the code using a function pointer array dispatcher. - Direct Pointers: Generates the code using a function pointer dispatcher. (Probably this pointer methods won’t be updated in future versions due that have more disadvantages that the switch case methods) - Switch Case: Generates the code using a switch case dispatcher. - Hierarchical Switch Case: Generates the code of a diagram and all child diagrams into a single module, using switch case dispatchers. (We tend to use this format because is more polyvalent) • Printer Setup, Print Preview & Print. • List of recent files. • Exit
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - File(2/2): • Generate C-code: - Pointer Array: Generates the code using a function pointer array dispatcher. - Direct Pointers: Generates the code using a function pointer dispatcher. (Probably this pointer methods won’t be updated in future versions due that have more disadvantages that the switch case methods) - Switch Case: Generates the code using a switch case dispatcher. - Hierarchical Switch Case: Generates the code of a diagram and all child diagrams into a single module, using switch case dispatchers. (We tend to use this format because is more polyvalent) • Printer Setup, Print Preview & Print. • List of recent files. • Exit
 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - Edit(1/2): • FSM Properties: Opens the properties menu (equivalent to do a double click in the diagram) • Insert Remark: Inserts a new remark box. • Font - Change: Menu to edit font parameters - Fixed Pitch: Let us to select fixed or non fixed pitch fonts. • • • Find: Find and optionally replace text. Undo: Undo last action. Redo: Redo last undo. Cut, Copy & Paste: (Copy & paste work only with remark boxes). Delete. Export as Enhanced Metafile: Puts the selected items into clipboard.
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - Edit(1/2): • FSM Properties: Opens the properties menu (equivalent to do a double click in the diagram) • Insert Remark: Inserts a new remark box. • Font - Change: Menu to edit font parameters - Fixed Pitch: Let us to select fixed or non fixed pitch fonts. • • • Find: Find and optionally replace text. Undo: Undo last action. Redo: Redo last undo. Cut, Copy & Paste: (Copy & paste work only with remark boxes). Delete. Export as Enhanced Metafile: Puts the selected items into clipboard.
 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - Edit(2/2): • Select All: Select all items (states, transitions & Remark boxes) • Select Mode: Change the editor between insert mode and select mode. • Autosize Nodes: Set if the state size can be adjusted automatically. • Locked: Lock & Unlock diagram.
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - Edit(2/2): • Select All: Select all items (states, transitions & Remark boxes) • Select Mode: Change the editor between insert mode and select mode. • Autosize Nodes: Set if the state size can be adjusted automatically. • Locked: Lock & Unlock diagram.
 FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - View: • Toolbar: Hide or show the toolbar. • Status Bar : Hide or show the status bar. • Hide Comments ‘//’ : Hide all comment lines that star with //. • Grid - Show grid - Snap to grid - Grid Size (60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360). • Zoom: 150%, 100% (&Normal), 75%, 50%, 25%, Fit in Window • Zoom Window
FSM Tutorial - Menus & buttons Menu - View: • Toolbar: Hide or show the toolbar. • Status Bar : Hide or show the status bar. • Hide Comments ‘//’ : Hide all comment lines that star with //. • Grid - Show grid - Snap to grid - Grid Size (60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360). • Zoom: 150%, 100% (&Normal), 75%, 50%, 25%, Fit in Window • Zoom Window
 FSM Tutorial Menu - Window: • Window • Cascade • Tile Horizontally • Tile Vertically • Reorganise Menu - ? : • Help • About - Menus & buttons
FSM Tutorial Menu - Window: • Window • Cascade • Tile Horizontally • Tile Vertically • Reorganise Menu - ? : • Help • About - Menus & buttons
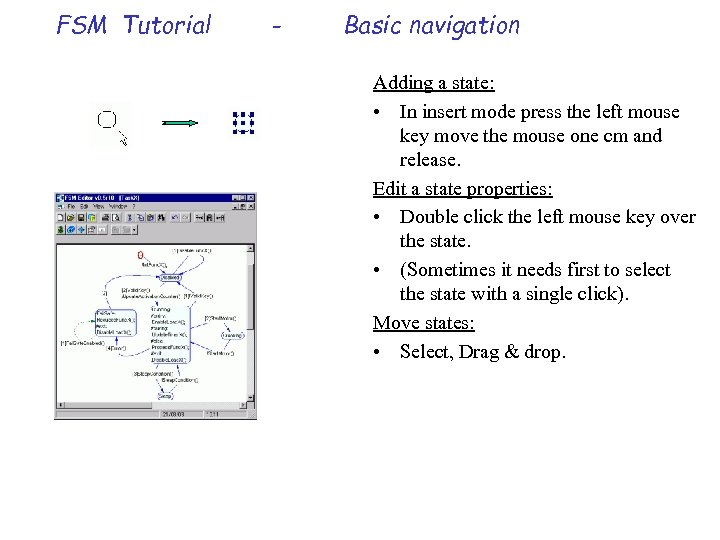 FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Adding a state: • In insert mode press the left mouse key move the mouse one cm and release. Edit a state properties: • Double click the left mouse key over the state. • (Sometimes it needs first to select the state with a single click). Move states: • Select, Drag & drop.
FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Adding a state: • In insert mode press the left mouse key move the mouse one cm and release. Edit a state properties: • Double click the left mouse key over the state. • (Sometimes it needs first to select the state with a single click). Move states: • Select, Drag & drop.
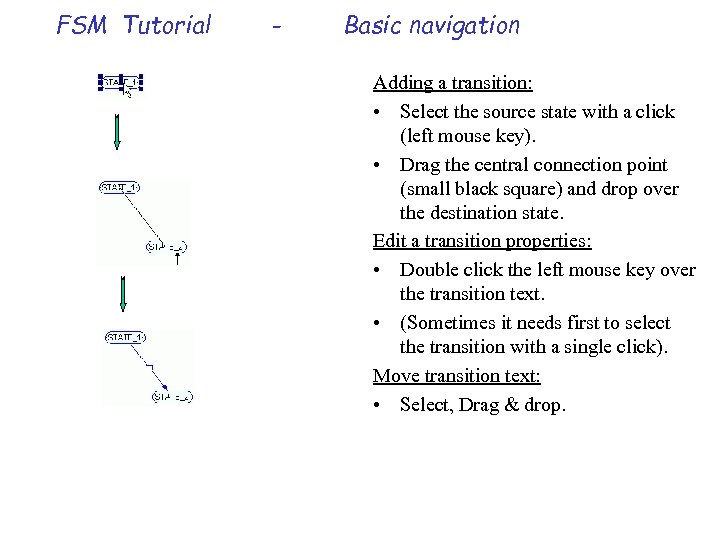 FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Adding a transition: • Select the source state with a click (left mouse key). • Drag the central connection point (small black square) and drop over the destination state. Edit a transition properties: • Double click the left mouse key over the transition text. • (Sometimes it needs first to select the transition with a single click). Move transition text: • Select, Drag & drop.
FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Adding a transition: • Select the source state with a click (left mouse key). • Drag the central connection point (small black square) and drop over the destination state. Edit a transition properties: • Double click the left mouse key over the transition text. • (Sometimes it needs first to select the transition with a single click). Move transition text: • Select, Drag & drop.
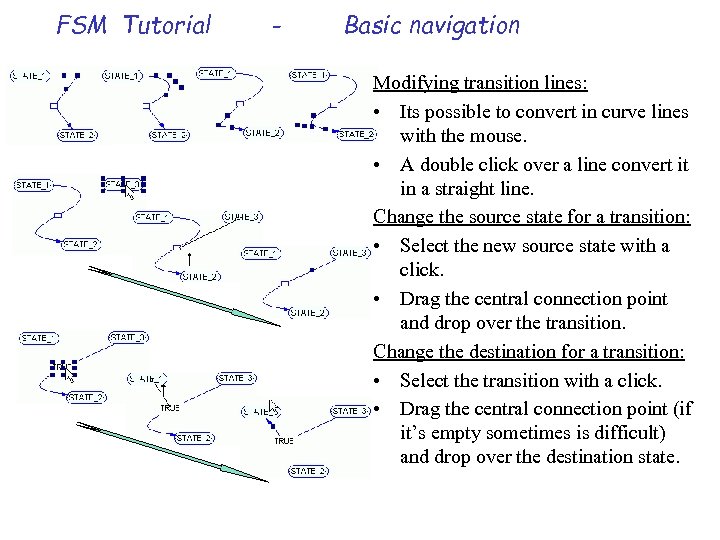 FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Modifying transition lines: • Its possible to convert in curve lines with the mouse. • A double click over a line convert it in a straight line. Change the source state for a transition: • Select the new source state with a click. • Drag the central connection point and drop over the transition. Change the destination for a transition: • Select the transition with a click. • Drag the central connection point (if it’s empty sometimes is difficult) and drop over the destination state.
FSM Tutorial - Basic navigation Modifying transition lines: • Its possible to convert in curve lines with the mouse. • A double click over a line convert it in a straight line. Change the source state for a transition: • Select the new source state with a click. • Drag the central connection point and drop over the transition. Change the destination for a transition: • Select the transition with a click. • Drag the central connection point (if it’s empty sometimes is difficult) and drop over the destination state.
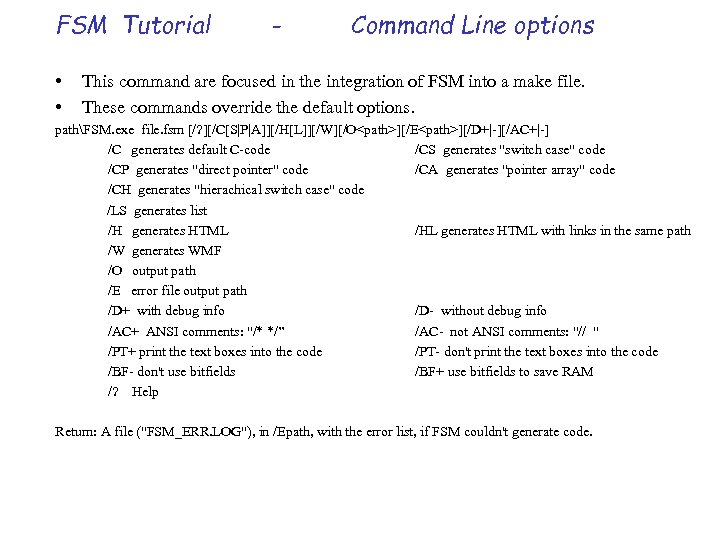 FSM Tutorial • • - Command Line options This command are focused in the integration of FSM into a make file. These commands override the default options. pathFSM. exe file. fsm [/? ][/C[S|P|A]][/H[L]][/W][/O
FSM Tutorial • • - Command Line options This command are focused in the integration of FSM into a make file. These commands override the default options. pathFSM. exe file. fsm [/? ][/C[S|P|A]][/H[L]][/W][/O
 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Basic concepts about Hierarchical implementations : • Are useful to divide a problem into small sub-problems. – Example of a three level hierarchy: • The first level decides if the functionality is “disabled”, “running” or “sleep”. • The second level implement the “running” main lines: “On”, “Off”, “waiting inputs”, etc. • The third level does the basic functions. E. g: if “On” handle a intermittent output, a child-FSM of “On” can control the flashing of the output timings. • Are built nesting one or more child-FSM into other parent-FSM. The child -FSM is a function called into a “during” or “else” action of a parent. FSM. • A child-FSM file should be found into a subdirectory called like their parent. This enables the editor automatic hierarchical capabilities. – Task. X. fsm – Task. XProcess. Func. X. fsm – now “Process. Func. X. fsm” will be a child of “Task. X. fsm” if Process. Func. X() is called from a ”during” or “else” action of Task. X().
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Basic concepts about Hierarchical implementations : • Are useful to divide a problem into small sub-problems. – Example of a three level hierarchy: • The first level decides if the functionality is “disabled”, “running” or “sleep”. • The second level implement the “running” main lines: “On”, “Off”, “waiting inputs”, etc. • The third level does the basic functions. E. g: if “On” handle a intermittent output, a child-FSM of “On” can control the flashing of the output timings. • Are built nesting one or more child-FSM into other parent-FSM. The child -FSM is a function called into a “during” or “else” action of a parent. FSM. • A child-FSM file should be found into a subdirectory called like their parent. This enables the editor automatic hierarchical capabilities. – Task. X. fsm – Task. XProcess. Func. X. fsm – now “Process. Func. X. fsm” will be a child of “Task. X. fsm” if Process. Func. X() is called from a ”during” or “else” action of Task. X().
 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files History concept: • A child-FSM can have a historical behaviour if only is started to its initial state on a program reset. • A child-FSM can have a standard behaviour if is initialized (the state index points to the initial state again) when the parent-FSM state changes. • A
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files History concept: • A child-FSM can have a historical behaviour if only is started to its initial state on a program reset. • A child-FSM can have a standard behaviour if is initialized (the state index points to the initial state again) when the parent-FSM state changes. • A
 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • The implementation of a transition is easy if the source and destination are in the same level. This means in the same diagram. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM(): note: the child is standard (not historical) then on every Switch. Off()+Switch. On() the child will start in Load. On state again.
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • The implementation of a transition is easy if the source and destination are in the same level. This means in the same diagram. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM(): note: the child is standard (not historical) then on every Switch. Off()+Switch. On() the child will start in Load. On state again.
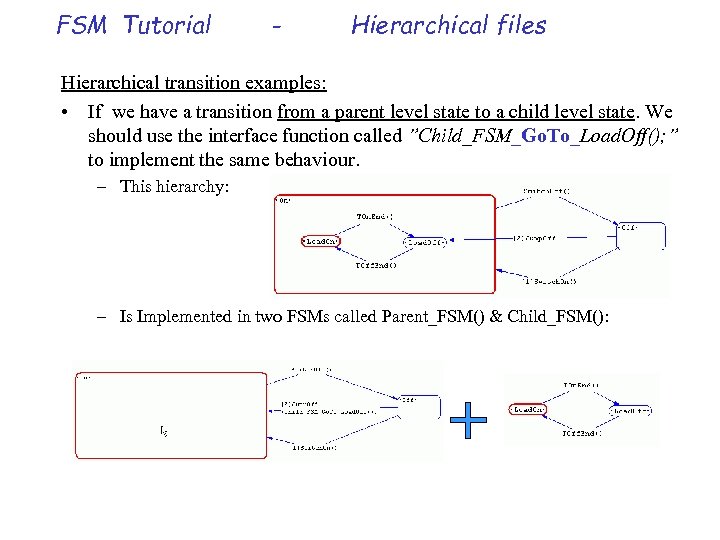 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • If we have a transition from a parent level state to a child level state. We should use the interface function called ”Child_FSM_Go. To_Load. Off(); ” to implement the same behaviour. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM():
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • If we have a transition from a parent level state to a child level state. We should use the interface function called ”Child_FSM_Go. To_Load. Off(); ” to implement the same behaviour. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM():
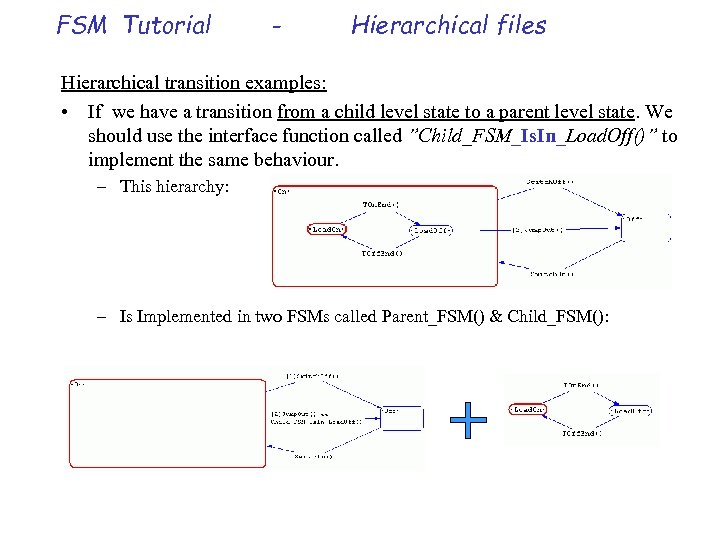 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • If we have a transition from a child level state to a parent level state. We should use the interface function called ”Child_FSM_Is. In_Load. Off()” to implement the same behaviour. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM():
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Hierarchical transition examples: • If we have a transition from a child level state to a parent level state. We should use the interface function called ”Child_FSM_Is. In_Load. Off()” to implement the same behaviour. – This hierarchy: – Is Implemented in two FSMs called Parent_FSM() & Child_FSM():
 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Execution sequence on every call to a two level diagram if the child-FSM is called into a “else action”: • Parent-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active state on last call). • Parent-state “during action”. • Parent-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. – If a transition condition is valid: • Parent-state “exit action”. • Parent-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). • END • Parent-state “else action” (here is the call to the child-Fsm). – Child-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active child-state on last call). – Child-state “during action”. – Child-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. • If a transition condition is valid: – Child-state “exit action”. – Child-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). – END
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Execution sequence on every call to a two level diagram if the child-FSM is called into a “else action”: • Parent-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active state on last call). • Parent-state “during action”. • Parent-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. – If a transition condition is valid: • Parent-state “exit action”. • Parent-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). • END • Parent-state “else action” (here is the call to the child-Fsm). – Child-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active child-state on last call). – Child-state “during action”. – Child-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. • If a transition condition is valid: – Child-state “exit action”. – Child-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). – END
 FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Execution sequence on every call to a two level diagram if the child-FSM is called into a “during action”: • Parent-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active state on last call). • Parent-state “during action” (here is the call to the child-Fsm). – Child-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active child-state on last call). – Child-state “during action”. – Child-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. • If a transition condition is valid: – Child-state “exit action”. – Child-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). – END • Parent-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. – If a transition condition is valid: • Parent-state “exit action”. • Parent-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). • END • Parent-state “else action”.
FSM Tutorial - Hierarchical files Execution sequence on every call to a two level diagram if the child-FSM is called into a “during action”: • Parent-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active state on last call). • Parent-state “during action” (here is the call to the child-Fsm). – Child-state “entry action” (if it wasn’t the active child-state on last call). – Child-state “during action”. – Child-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. • If a transition condition is valid: – Child-state “exit action”. – Child-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). – END • Parent-state “transition conditions” analysis in sequence. – If a transition condition is valid: • Parent-state “exit action”. • Parent-state “transition action” (of the accepted transition). • END • Parent-state “else action”.


