cc9018d621717f3a4bf8fd0e27360f7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 From Stonehenge to Keck: Architecture and Astronomy C. G. De Pree RARE CATS Green Bank, WV June 2002
From Stonehenge to Keck: Architecture and Astronomy C. G. De Pree RARE CATS Green Bank, WV June 2002
 Questions Why have societies observed the heavens since ancient times? n What sort of structures have been associated with observing the sky? n How have these structures changed with time? n
Questions Why have societies observed the heavens since ancient times? n What sort of structures have been associated with observing the sky? n How have these structures changed with time? n
 Overview Ancient Observatories n 16 th and 17 th Century Observatories n Early Modern (19 th century) Observatories n Modern Observatories n
Overview Ancient Observatories n 16 th and 17 th Century Observatories n Early Modern (19 th century) Observatories n Modern Observatories n
 Ancient Observatories Stonehenge/Newgrange n Chichen Itza, Caracol Tower n Locations n – Horizon line n Uses – Religious – Timekeeping – Ceremonial
Ancient Observatories Stonehenge/Newgrange n Chichen Itza, Caracol Tower n Locations n – Horizon line n Uses – Religious – Timekeeping – Ceremonial
 Newgrange (3200 BCE) Aligned to winter solstice (light interior) n One of thousands of sites in Europe n – Stonehenge
Newgrange (3200 BCE) Aligned to winter solstice (light interior) n One of thousands of sites in Europe n – Stonehenge
 Caracol (Snail) Tower Location: Chichen Itza, Northern Yucatan n Period: Mayan, c. 1000 AD n Interior: 16. 7 m-diameter tower with spiral staircase and four doorways aligned with cardinal directions n Upper room: 7 openings aligned with the equinoxes and the S transit of Venus n
Caracol (Snail) Tower Location: Chichen Itza, Northern Yucatan n Period: Mayan, c. 1000 AD n Interior: 16. 7 m-diameter tower with spiral staircase and four doorways aligned with cardinal directions n Upper room: 7 openings aligned with the equinoxes and the S transit of Venus n
 Caracol Tower at Chichen Itza
Caracol Tower at Chichen Itza
 Caracol Tower Astronomical function: solstice and equinox alignments, some star alignments n Religious function: apparent alignments with Venus n – Mayan tablets mention the rising of Venus – Worship of the wind god Ehecatl
Caracol Tower Astronomical function: solstice and equinox alignments, some star alignments n Religious function: apparent alignments with Venus n – Mayan tablets mention the rising of Venus – Worship of the wind god Ehecatl
 16 th to 18 th Century Observatories Uraniborg/Stjarneborg (Tycho Brahe) n L’Observatoire de Paris n – Louis XIV n Royal Greenwich Observatory – Flamsteed, Astronomer Royal
16 th to 18 th Century Observatories Uraniborg/Stjarneborg (Tycho Brahe) n L’Observatoire de Paris n – Louis XIV n Royal Greenwich Observatory – Flamsteed, Astronomer Royal
 Uraniborg Castle Location: Island of Hven n Date: 1576 -1580 (pre-telescope) n Complex included: castle, observatory, papermill, earthworks, dams and ponds n Subsidized by Danish State (~1% of national budget) n Purpose: determine accurate planetary positions n
Uraniborg Castle Location: Island of Hven n Date: 1576 -1580 (pre-telescope) n Complex included: castle, observatory, papermill, earthworks, dams and ponds n Subsidized by Danish State (~1% of national budget) n Purpose: determine accurate planetary positions n
 Uraniborg: Grounds and Interior Castle too small n Mounts unstable n
Uraniborg: Grounds and Interior Castle too small n Mounts unstable n
 Stjarneborg Observatory Funded by Danish king Frederick II n Lost funding under Christian IV (1596) n Brahe came under patronage of the German emperor Rudolf II n Relocated to Observatory near Prague (1599) n
Stjarneborg Observatory Funded by Danish king Frederick II n Lost funding under Christian IV (1596) n Brahe came under patronage of the German emperor Rudolf II n Relocated to Observatory near Prague (1599) n
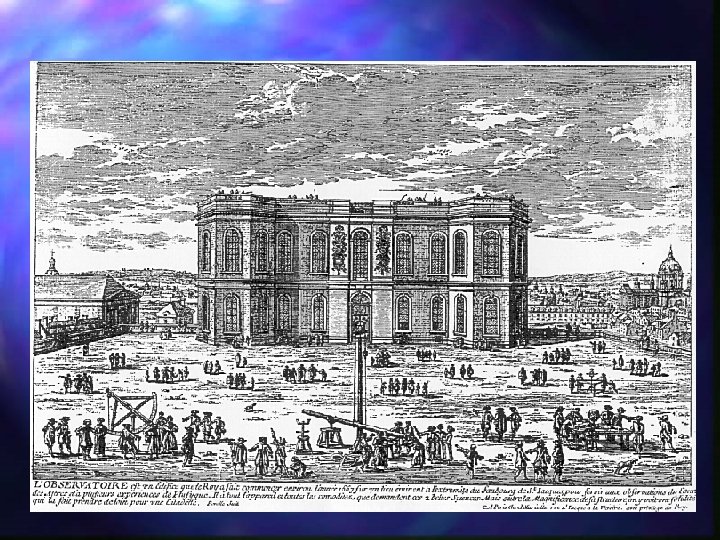 Paris Observatory Louis XIV funds `l'Observatoire Royal’ n Architect: Claude Perrault (ded. 1672) n Oriented with the cardinal points of the compass (in 1667) n Paris latitude: Latitude of the south face n n Paris longitude: Meridian line passing through building center
Paris Observatory Louis XIV funds `l'Observatoire Royal’ n Architect: Claude Perrault (ded. 1672) n Oriented with the cardinal points of the compass (in 1667) n Paris latitude: Latitude of the south face n n Paris longitude: Meridian line passing through building center
 Paris Observatory--Planned Uses Offices for astronomers/academics n Lecture hall and laboratories n n Instruments dedicated to the astronomical observations
Paris Observatory--Planned Uses Offices for astronomers/academics n Lecture hall and laboratories n n Instruments dedicated to the astronomical observations
 Old Greenwich Royal Observatory Location: Greenwich, England n Founded: 22 June, 1675 by King Charles II n Primary purpose: To solve the problem of finding longitude n John Flamsteed, Astronomer Royal n n Observatory added functions over time
Old Greenwich Royal Observatory Location: Greenwich, England n Founded: 22 June, 1675 by King Charles II n Primary purpose: To solve the problem of finding longitude n John Flamsteed, Astronomer Royal n n Observatory added functions over time
 17 -18 th Century Interiors Observing/Reception Room Flamsteed Apartment
17 -18 th Century Interiors Observing/Reception Room Flamsteed Apartment
 Meridian Building Houses a ten-foot transit instrument, installed in 1816 n Bradley's original transit instrument is shown n
Meridian Building Houses a ten-foot transit instrument, installed in 1816 n Bradley's original transit instrument is shown n
 Airy Transit Circle Sir George Biddell Airy (7 th Astronomer Royal) designed a transit instrument, installed in 1850 n Transit circle: special type of telescope moves in a vertical circle n Transit circles used to accurately measure stellar positions n
Airy Transit Circle Sir George Biddell Airy (7 th Astronomer Royal) designed a transit instrument, installed in 1850 n Transit circle: special type of telescope moves in a vertical circle n Transit circles used to accurately measure stellar positions n
 Altazimuth Pavilion n The Altazimuth Pavilion (1899) n Named after the altaz telescope originally installed in its dome n Dome now contains a 'photoheliograph’ (solar projection) n Weather vane over the dome represents Halley's Comet as seen in the Bayeux tapestry
Altazimuth Pavilion n The Altazimuth Pavilion (1899) n Named after the altaz telescope originally installed in its dome n Dome now contains a 'photoheliograph’ (solar projection) n Weather vane over the dome represents Halley's Comet as seen in the Bayeux tapestry
 The South Building Originally called the New Physical Building (1899) n Astronomer Royal, William Christie (architect William Crisp) n 4 wings housed branches: magnetic and meteorological, astro-photography, time, and library n The dome originally accommodated a 30 -inch (76. 2 cm) reflecting telescope n
The South Building Originally called the New Physical Building (1899) n Astronomer Royal, William Christie (architect William Crisp) n 4 wings housed branches: magnetic and meteorological, astro-photography, time, and library n The dome originally accommodated a 30 -inch (76. 2 cm) reflecting telescope n
 Jantar Mantar: five observatories built by Sawai Jai Singh II n Locations: New Delhi, Jaipur, Varanasi, Ujjain and Mathura. n Built AD 1724– 1730 n
Jantar Mantar: five observatories built by Sawai Jai Singh II n Locations: New Delhi, Jaipur, Varanasi, Ujjain and Mathura. n Built AD 1724– 1730 n
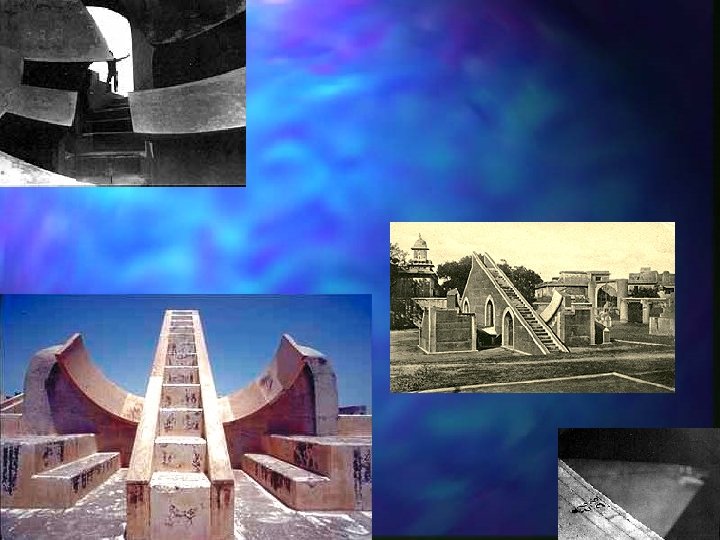

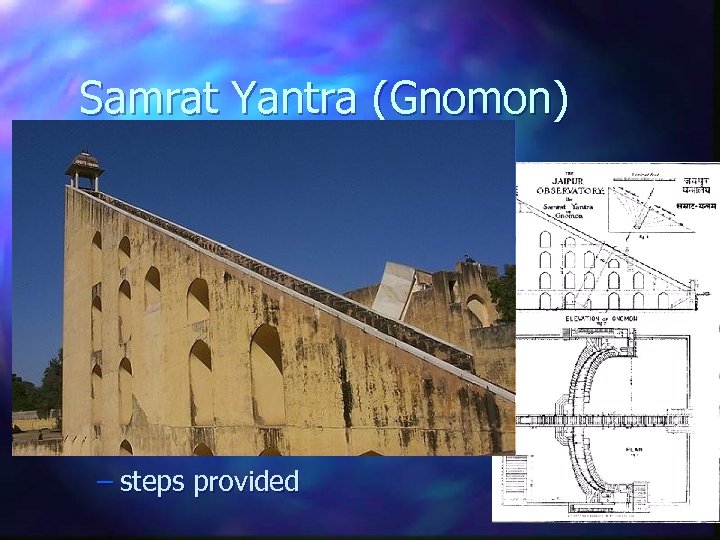 Samrat Yantra (Gnomon) Gnomon 90 feet high, points toward Polaris n Used to find time and declination and hour angle of stars and planets n Either side of the gnomon is a masonry quadrant n – to read time – steps provided
Samrat Yantra (Gnomon) Gnomon 90 feet high, points toward Polaris n Used to find time and declination and hour angle of stars and planets n Either side of the gnomon is a masonry quadrant n – to read time – steps provided
 Early Modern Observatories (19 th C) More remote locations (outside cities) n Still show integration of observing structure, teaching space and research space n e. g. Yerkes Observatory, University of Chicago (1897) n
Early Modern Observatories (19 th C) More remote locations (outside cities) n Still show integration of observing structure, teaching space and research space n e. g. Yerkes Observatory, University of Chicago (1897) n
 Yerkes Architect: Henry Ives Cobb n Funded: Charles Yerkes (Chicago streetcars) n Astronmer: George Ellery Hale (U. Chicago) n Exterior: Animals, signs of the Zodiac, phases of the Moon n Architecture and technology of late 19 th century, 77 -acre site n
Yerkes Architect: Henry Ives Cobb n Funded: Charles Yerkes (Chicago streetcars) n Astronmer: George Ellery Hale (U. Chicago) n Exterior: Animals, signs of the Zodiac, phases of the Moon n Architecture and technology of late 19 th century, 77 -acre site n
 1893 Columbian Exposition in Chicago/Installation
1893 Columbian Exposition in Chicago/Installation
 Yerkes: 40 in Refractor
Yerkes: 40 in Refractor
 Yerkes: Architectural Detail
Yerkes: Architectural Detail
 Modern Observatories n Separation between observing structure and office/research structure – Mt Wilson Telescopes/Cal Tech – Keck I and Keck II/Waimea headquarters/Cal Tech – Very Large Array/Array Operations Center/NRAO – HST/NGST/NASA/STSc. I
Modern Observatories n Separation between observing structure and office/research structure – Mt Wilson Telescopes/Cal Tech – Keck I and Keck II/Waimea headquarters/Cal Tech – Very Large Array/Array Operations Center/NRAO – HST/NGST/NASA/STSc. I
 Palomar Observatory George Ellery Hale (Yerkes) n Grants from Carnegie Institution of Washington n Mount Wilson 60 -inch reflector first completed (1908) n Harlow Shapley measures the size of the MW and our position in it n n 1928, $6 million grant from Rockefeller
Palomar Observatory George Ellery Hale (Yerkes) n Grants from Carnegie Institution of Washington n Mount Wilson 60 -inch reflector first completed (1908) n Harlow Shapley measures the size of the MW and our position in it n n 1928, $6 million grant from Rockefeller
 n Mt. Wilson 100 -in & 200 -in telescopes
n Mt. Wilson 100 -in & 200 -in telescopes
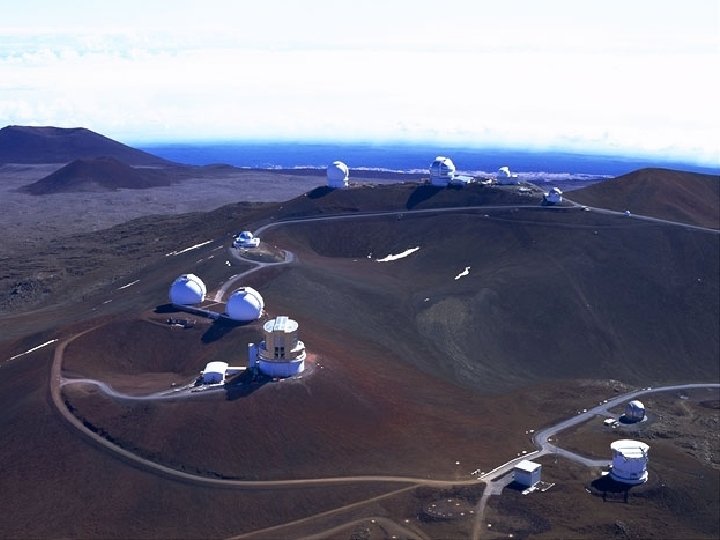 Keck Headquarters n Located in Waimea n Telescopes are 48 miles from HQ n Most employees work at headquarters n 20 -25 technicians and engineers commute daily to summit n Annual budget $11 million
Keck Headquarters n Located in Waimea n Telescopes are 48 miles from HQ n Most employees work at headquarters n 20 -25 technicians and engineers commute daily to summit n Annual budget $11 million
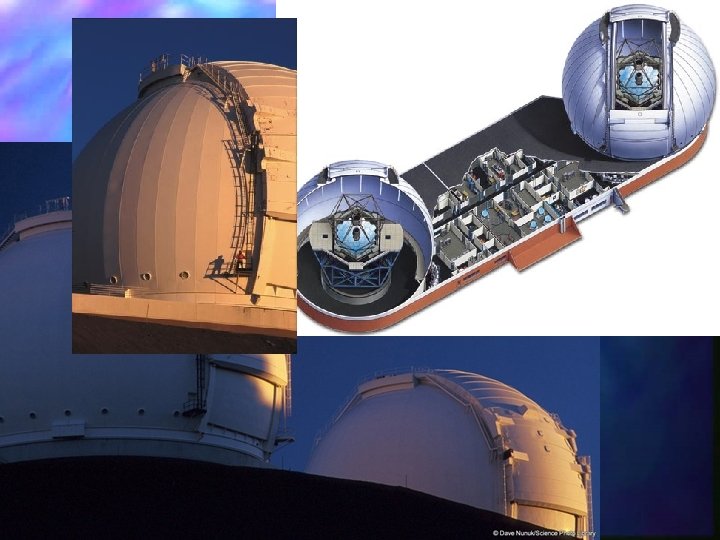 Keck Telescope
Keck Telescope
 Keck Control Room
Keck Control Room
 Very Large Array
Very Large Array
 VLA (view looking South)
VLA (view looking South)
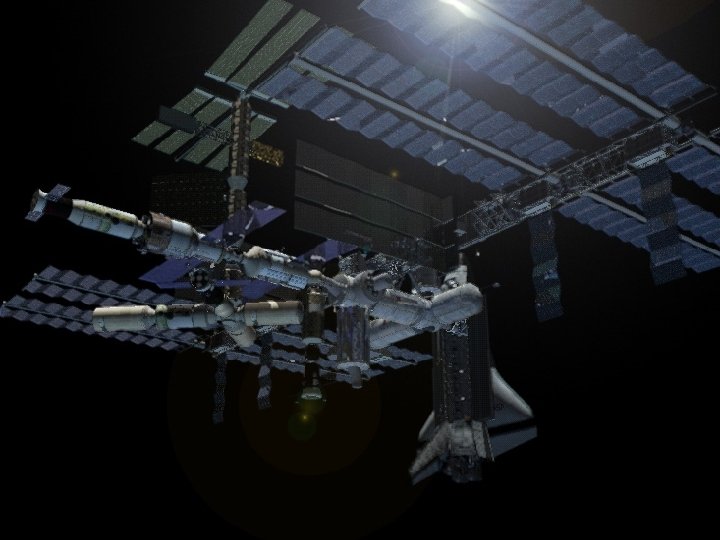
 Orbiting Observatories Hubble Space Telescope (HST) n Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST) n Space Telescope Science Institute (STSc. I) n
Orbiting Observatories Hubble Space Telescope (HST) n Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST) n Space Telescope Science Institute (STSc. I) n

 Reflections Astronomical architecture has evolved along with astronomical technology n Telescopes and the structures that house them are becoming more and more remote from most people n From earliest times, there alignments with cardinal points n Growing separation between instruments and observers n
Reflections Astronomical architecture has evolved along with astronomical technology n Telescopes and the structures that house them are becoming more and more remote from most people n From earliest times, there alignments with cardinal points n Growing separation between instruments and observers n



