578e1cd4076c2b143da5ed9ab6601e0e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 From Revolution to Constitution Creating our Government
From Revolution to Constitution Creating our Government
 Articles of Confederation government) (Our first national • Reflected the two main fears of colonists… • Fear of strong national government • Fear that some states would dominate others • Articles established a “league of friendship” among the states • Each state retains sovereignty (power, authority) But, there were numerous weaknesses…
Articles of Confederation government) (Our first national • Reflected the two main fears of colonists… • Fear of strong national government • Fear that some states would dominate others • Articles established a “league of friendship” among the states • Each state retains sovereignty (power, authority) But, there were numerous weaknesses…
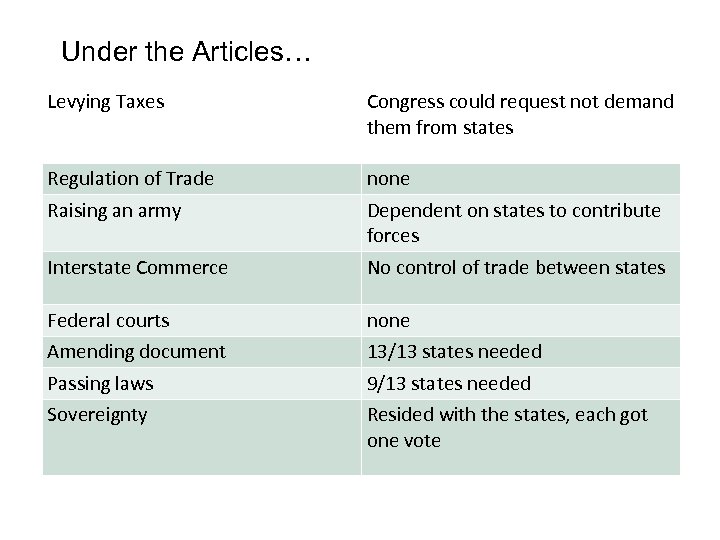 Under the Articles… Levying Taxes Congress could request not demand them from states Regulation of Trade Raising an army none Dependent on states to contribute forces Interstate Commerce No control of trade between states Federal courts Amending document none 13/13 states needed Passing laws Sovereignty 9/13 states needed Resided with the states, each got one vote
Under the Articles… Levying Taxes Congress could request not demand them from states Regulation of Trade Raising an army none Dependent on states to contribute forces Interstate Commerce No control of trade between states Federal courts Amending document none 13/13 states needed Passing laws Sovereignty 9/13 states needed Resided with the states, each got one vote
 Critical Period • Weaknesses of Articles led to economic and political problems • • • States in conflict (taxes, trade) States don’t support central gov’t States printed own money / made own laws Can’t pay off debt Shay’s Rebellion • Showed that to survive the United States needed a stronger national government “We are one nation today and 13 tomorrow. Who will treat us on such terms? ”
Critical Period • Weaknesses of Articles led to economic and political problems • • • States in conflict (taxes, trade) States don’t support central gov’t States printed own money / made own laws Can’t pay off debt Shay’s Rebellion • Showed that to survive the United States needed a stronger national government “We are one nation today and 13 tomorrow. Who will treat us on such terms? ”
 Constitutional Convention Summer of 1787 in Philadelphia • 12 of 13 states (no Rhode Island) • 55 delegates make up Framers of Constitution • Worked in total secrecy • Originally called to revise the Articles then decided to create a new government
Constitutional Convention Summer of 1787 in Philadelphia • 12 of 13 states (no Rhode Island) • 55 delegates make up Framers of Constitution • Worked in total secrecy • Originally called to revise the Articles then decided to create a new government
 Federalist Papers Background • Constitutional Convention • Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists • Federalist Papers • 85 essays • Publius (“the people”) • Hamilton, Madison, Jay
Federalist Papers Background • Constitutional Convention • Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists • Federalist Papers • 85 essays • Publius (“the people”) • Hamilton, Madison, Jay
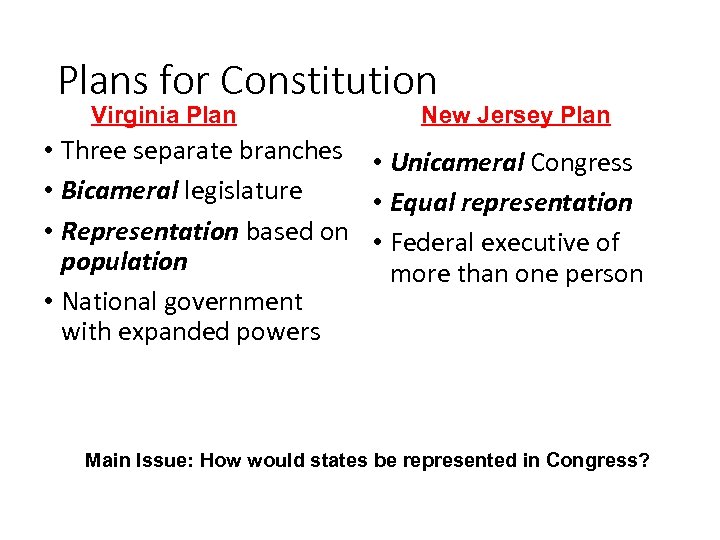 Plans for Constitution Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan • Three separate branches • Unicameral Congress • Bicameral legislature • Equal representation • Representation based on • Federal executive of population more than one person • National government with expanded powers Main Issue: How would states be represented in Congress?
Plans for Constitution Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan • Three separate branches • Unicameral Congress • Bicameral legislature • Equal representation • Representation based on • Federal executive of population more than one person • National government with expanded powers Main Issue: How would states be represented in Congress?
 Great Compromise • Connecticut Compromise • Bicameral Congress • Senate states represented equally • House of Representatives represented based on population
Great Compromise • Connecticut Compromise • Bicameral Congress • Senate states represented equally • House of Representatives represented based on population
 Slave Question Three-Fifths Compromise • slaves counted as 3/5 for representation, but states paid federal taxes for 3/5 as well • Congress can’t interfere with slave trade until 1808 • Congress could regulate commerce
Slave Question Three-Fifths Compromise • slaves counted as 3/5 for representation, but states paid federal taxes for 3/5 as well • Congress can’t interfere with slave trade until 1808 • Congress could regulate commerce
 Constitution Information • Written in 1787 • Took effect 1789 • New Hampshire 9 th state • New York and Virginia (40% of population) • North Carolina and Rhode Island (all 13 only with addition of Bill of Rights) • “Supreme Law of the Land” • Lays out basic framework and procedures of our government Less than 7, 000 words, but able to guide the country through two centuries!
Constitution Information • Written in 1787 • Took effect 1789 • New Hampshire 9 th state • New York and Virginia (40% of population) • North Carolina and Rhode Island (all 13 only with addition of Bill of Rights) • “Supreme Law of the Land” • Lays out basic framework and procedures of our government Less than 7, 000 words, but able to guide the country through two centuries!
 How did the Constitution address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? Levying Taxes Regulation of Trade Raising an army Congress could levy on individuals Yes yes Interstate Commerce yes Federal courts Amending document yes 2/3 of both houses of Congress plus ¾ of state legislatures 50% + 1 of both houses plus Pres. approval Const. supreme law of the land Passing laws Sovereignty
How did the Constitution address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? Levying Taxes Regulation of Trade Raising an army Congress could levy on individuals Yes yes Interstate Commerce yes Federal courts Amending document yes 2/3 of both houses of Congress plus ¾ of state legislatures 50% + 1 of both houses plus Pres. approval Const. supreme law of the land Passing laws Sovereignty
 U. S. Constitution Section • • Subject Preamble Article III Article IV Article VI • • Article VII • 27 Amendments Purpose Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch Relations among Sts. Amending the Const. Nt. Debts, supremacy of national law, oaths • Ratifying Constitution • Changes to Constitution
U. S. Constitution Section • • Subject Preamble Article III Article IV Article VI • • Article VII • 27 Amendments Purpose Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch Relations among Sts. Amending the Const. Nt. Debts, supremacy of national law, oaths • Ratifying Constitution • Changes to Constitution
 Purpose of Govt Outlined in the Preamble • Form a more perfect union • Establish justice • Insure domestic tranquility • Provide for the common defense • Promote the general welfare • Secure the blessings of liberty
Purpose of Govt Outlined in the Preamble • Form a more perfect union • Establish justice • Insure domestic tranquility • Provide for the common defense • Promote the general welfare • Secure the blessings of liberty
 Reflect On the piece of paper from the beginning of class, reflect on how the Constitution answered the problems of the Articles of Confederation. Give at least two examples.
Reflect On the piece of paper from the beginning of class, reflect on how the Constitution answered the problems of the Articles of Confederation. Give at least two examples.
 The Six Basic Principles of the Constitution
The Six Basic Principles of the Constitution
 Popular Sovereignty • The people are sovereign (have supreme authority) • Government only with the ‘consent of the governed” “We the People…”
Popular Sovereignty • The people are sovereign (have supreme authority) • Government only with the ‘consent of the governed” “We the People…”
 Limited Government • Government may do ONLY what the people give it power to do • It is not all powerful • Rule of Law / Constitutionalism: Leaders are never above the law
Limited Government • Government may do ONLY what the people give it power to do • It is not all powerful • Rule of Law / Constitutionalism: Leaders are never above the law
 Judicial Review • One of the checks and balances • Courts may rule that a law or an action of an government is unconstitutional
Judicial Review • One of the checks and balances • Courts may rule that a law or an action of an government is unconstitutional
 Federalism • Power divided b/w national gov’t and state govt’s • All powers not explicitly granted to the national gov’t are reserved to the states
Federalism • Power divided b/w national gov’t and state govt’s • All powers not explicitly granted to the national gov’t are reserved to the states
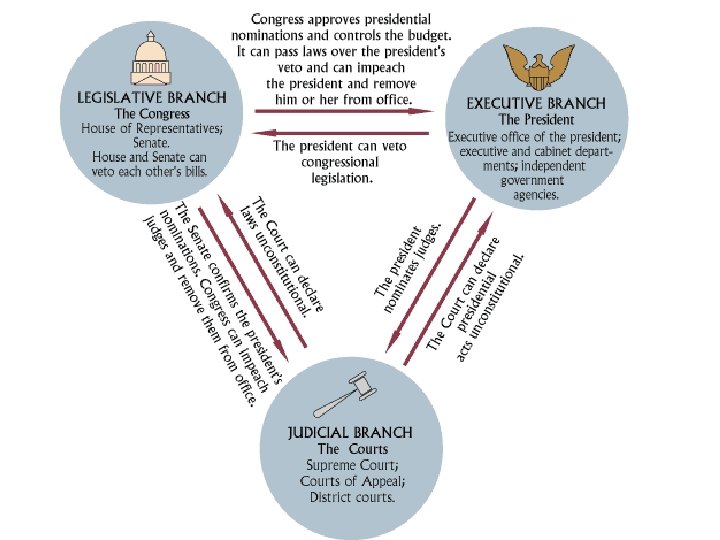
 Separation of Powers • Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary powers separated into distinct branches • Congress • President • Supreme Court What powers does each branch hold?
Separation of Powers • Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary powers separated into distinct branches • Congress • President • Supreme Court What powers does each branch hold?
 Checks and Balances “Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. ” • Each branch subject to restraints by the other branches; each branch may check the workings of the others • makes compromise necessary • intended to prevent tyranny of majority What is an example of a check held by one branch over another?
Checks and Balances “Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. ” • Each branch subject to restraints by the other branches; each branch may check the workings of the others • makes compromise necessary • intended to prevent tyranny of majority What is an example of a check held by one branch over another?
 Amendment Game • Directions: • Take out your Amendment Graphic Organizer • Clear all other materials off of your desk
Amendment Game • Directions: • Take out your Amendment Graphic Organizer • Clear all other materials off of your desk
 Amendment Pictionary • Rules and Guidelines: • • No words No numbers (or something that leads to counting) No acting out / dramatizations Other teams may not distract / disrupt the groups
Amendment Pictionary • Rules and Guidelines: • • No words No numbers (or something that leads to counting) No acting out / dramatizations Other teams may not distract / disrupt the groups
 Amendment Pictionary • Rules and Guidelines: • One artist from a team will be chosen to come up at a time to draw a representation of an amendment • All Teams will use their amendment graphic organizers to guess the amendment • Each team will get up to 1 minute to correctly ID an amendment (once you have the answer quietly write it on your white board) • Each team that gets it right gets 1 pt • The artist’s team that gets it right gets 2 pts
Amendment Pictionary • Rules and Guidelines: • One artist from a team will be chosen to come up at a time to draw a representation of an amendment • All Teams will use their amendment graphic organizers to guess the amendment • Each team will get up to 1 minute to correctly ID an amendment (once you have the answer quietly write it on your white board) • Each team that gets it right gets 1 pt • The artist’s team that gets it right gets 2 pts


