Visual perception_lecture2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

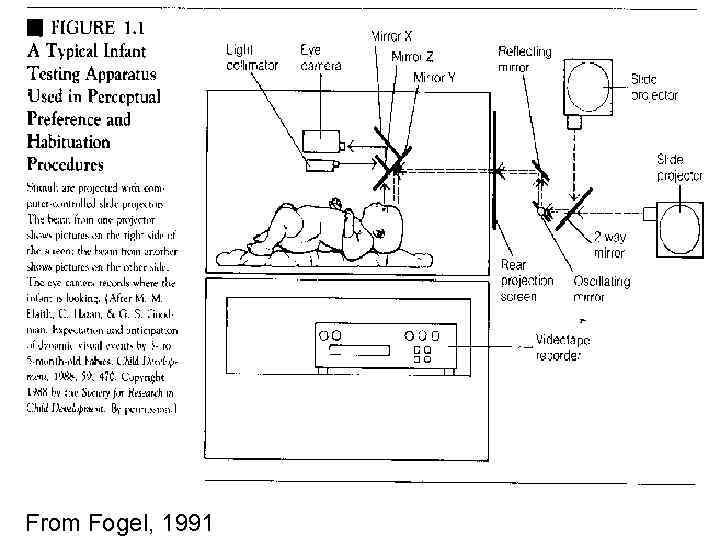
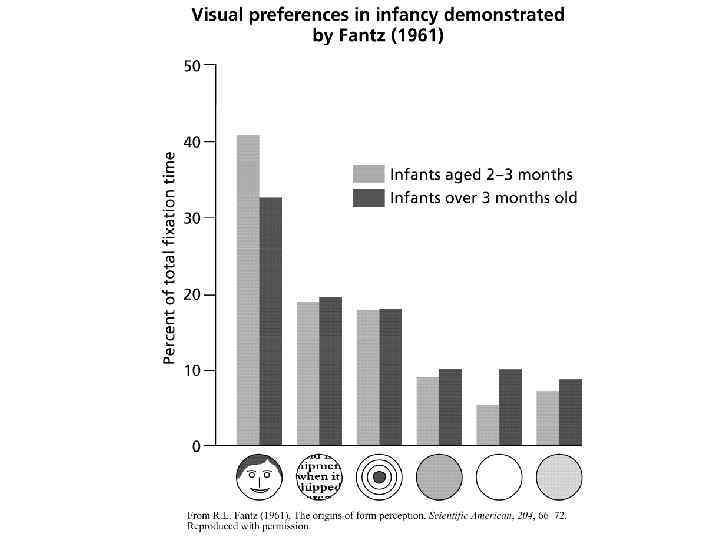
From Fogel, 1991


Visual perception • Newborns – Can discriminate between stripes and a uniform surface – Fixed focal length – 21 cm
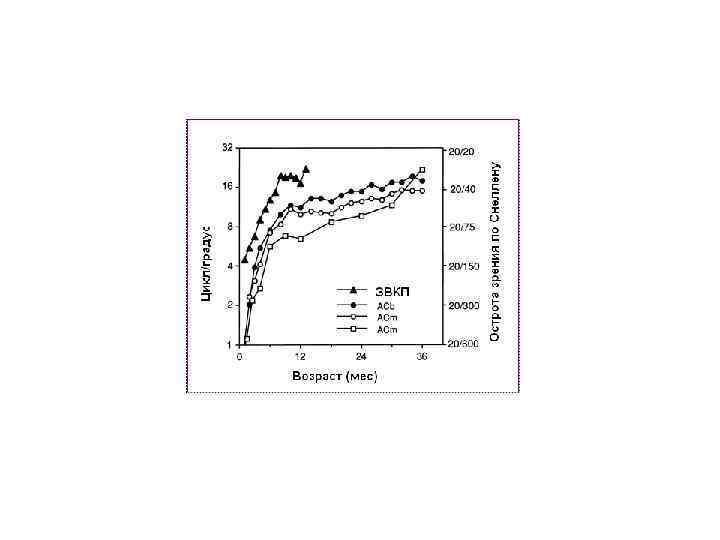
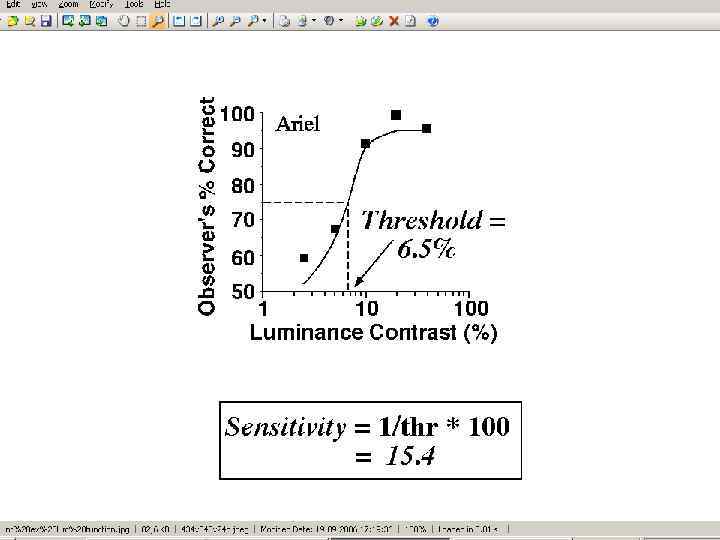

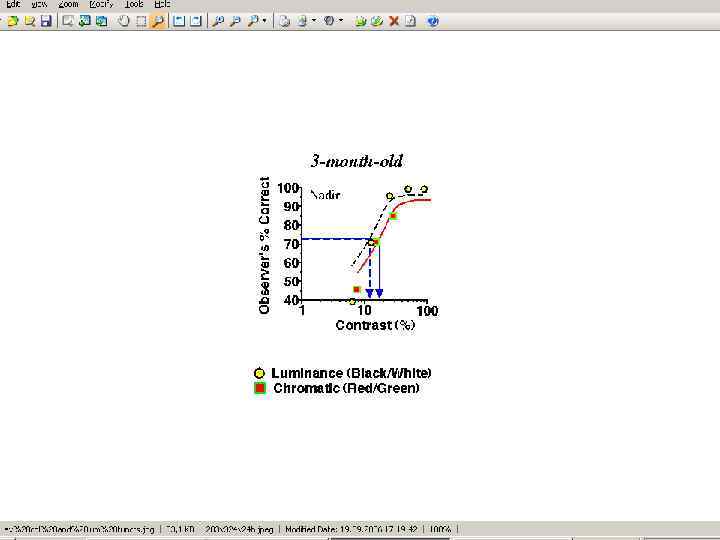
Visual Acuity Newborn 4 weeks 8 weeks 3 months 6 months

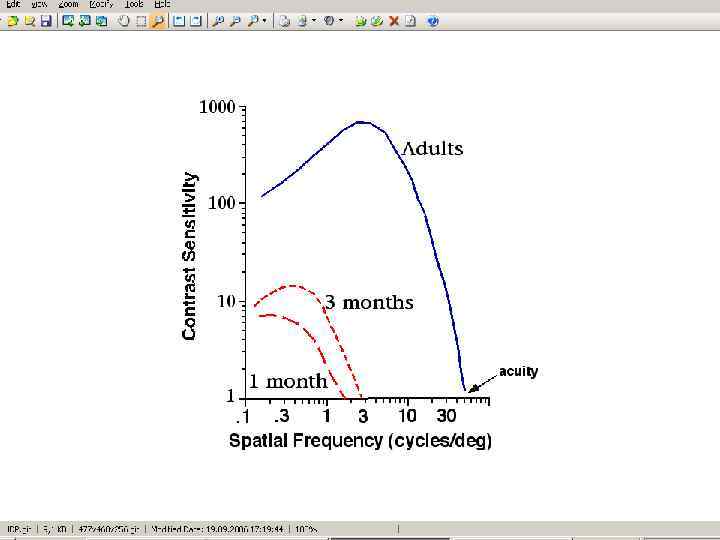
v Immature (coarse) spacing: photoreceptors take up a lot of room (since they are fat!), do not resolve well v So overall resolution (acuity) is poor Adult Infant
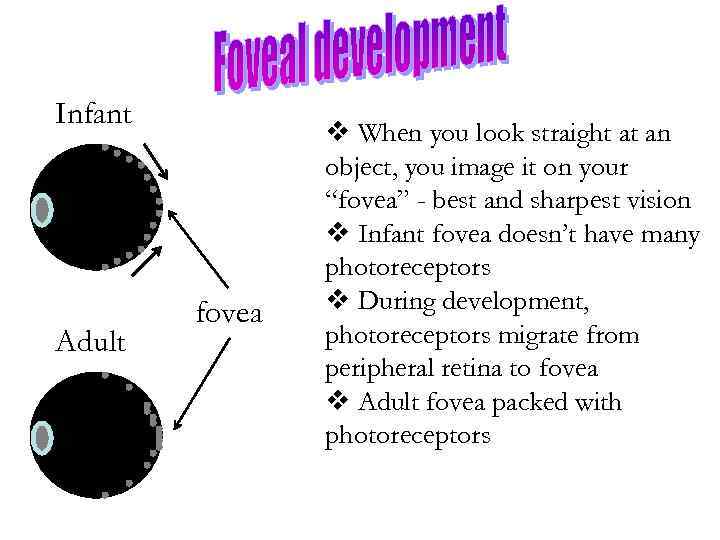
Infant Adult fovea v When you look straight at an object, you image it on your “fovea” - best and sharpest vision v Infant fovea doesn’t have many photoreceptors v During development, photoreceptors migrate from peripheral retina to fovea v Adult fovea packed with photoreceptors
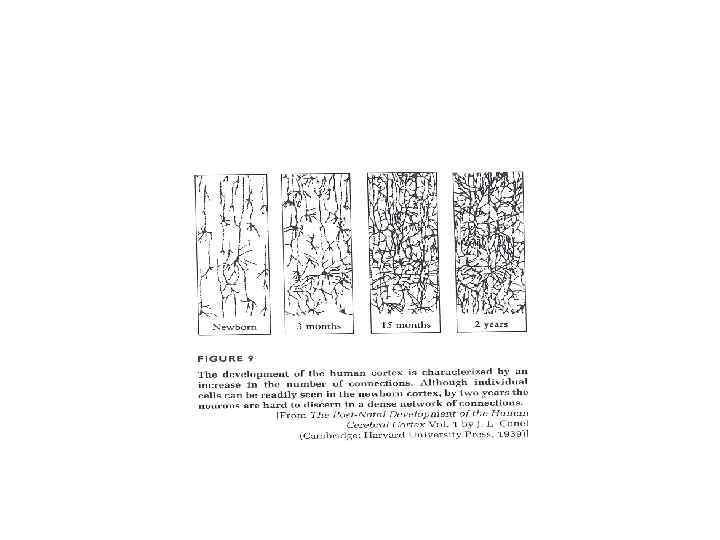
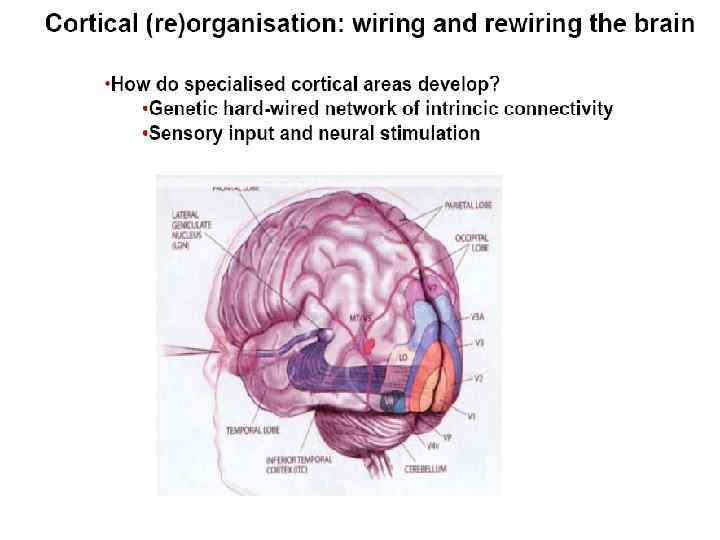
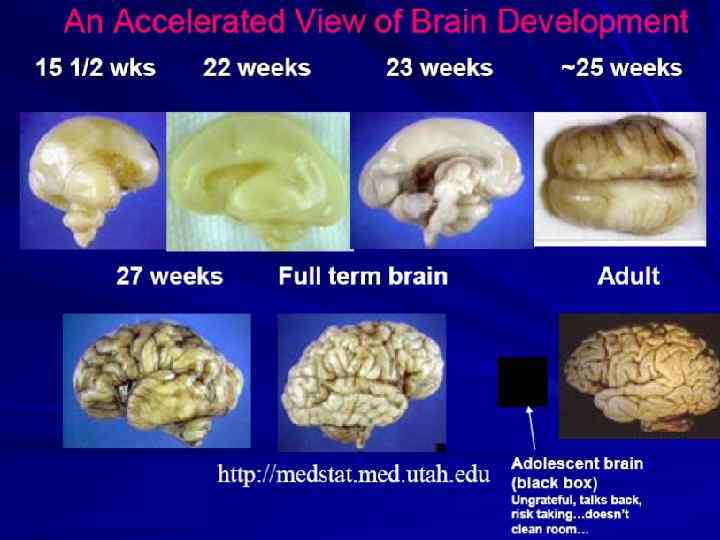
Human Brain Development: Connection Density
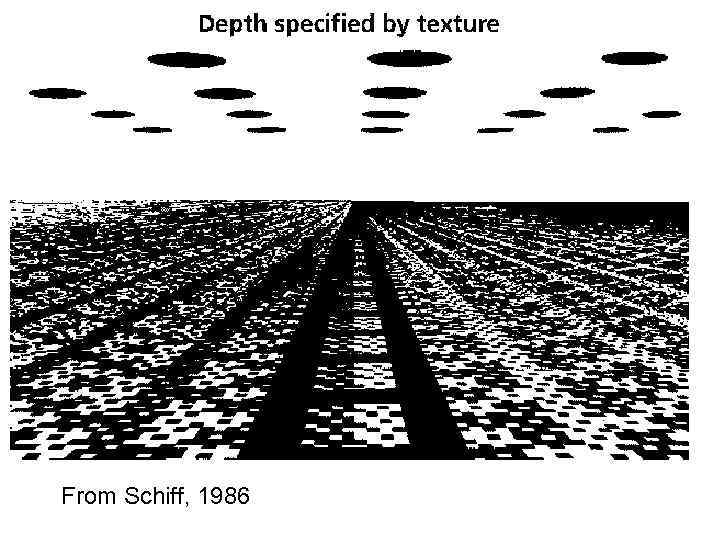
From Schiff, 1986


What difference am I suggesting between color and form perception? • Preprogrammed maturation is predominant in color perception, compared to form perception, where proper stimulation in early sensitive periods is crucial. • Early deprivation seems not to result in irreversible loss of aspects of color vision. (No critical periods are apparent in the development of color perception. ) • In many cases, color perception supports form perception and object recognition. This happens in both sighted and newly sighted subjects. • (Motion perception is similar in this respect. It is present immediately after operation, and it also supports form perception. Example: static drawings of the Necker cube do not pop into 3 D for the newly sighted, whereas rotating versions do: kinetic depth effect, Fine et al. , 2003)






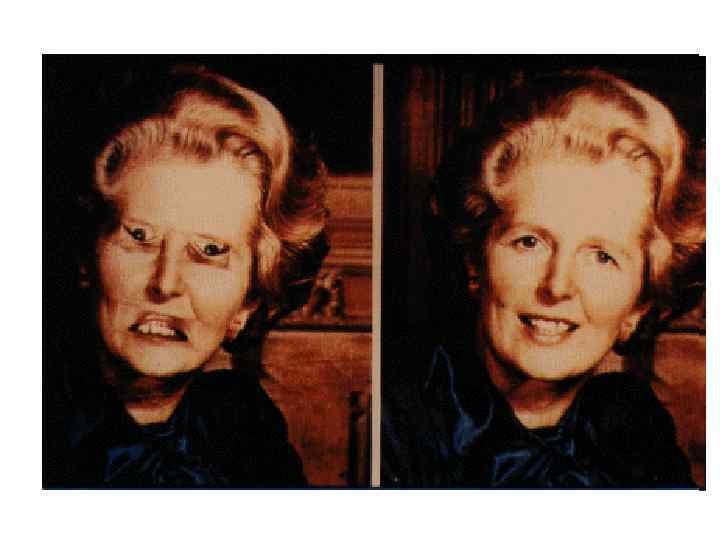
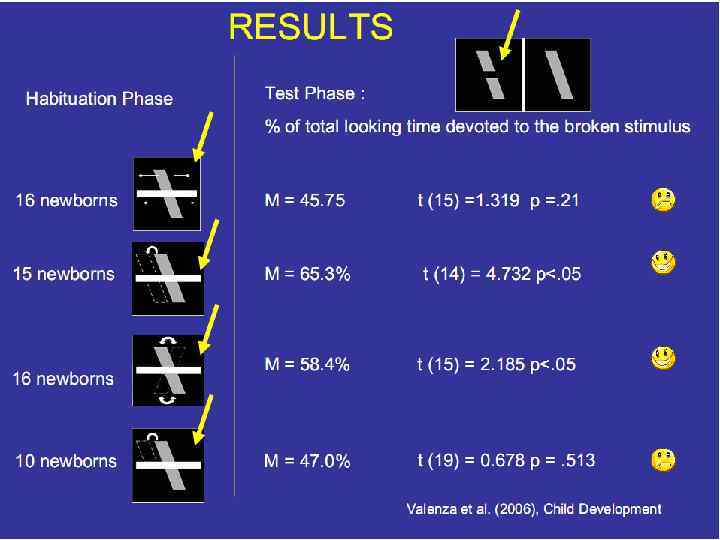
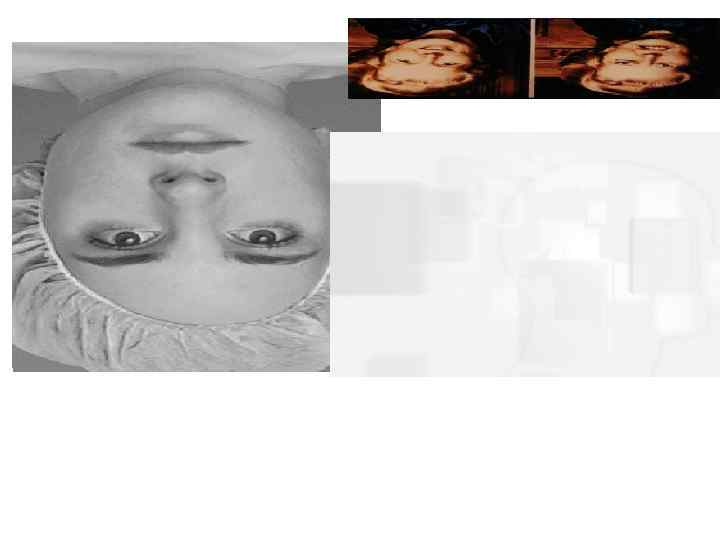
1. Inversion, Rotation Recognition drops dramatically for inverted human faces. Rotation, too, disturbs recognition.



Research Participants Needed RESEARCH PARTICIPANTS NEEDED

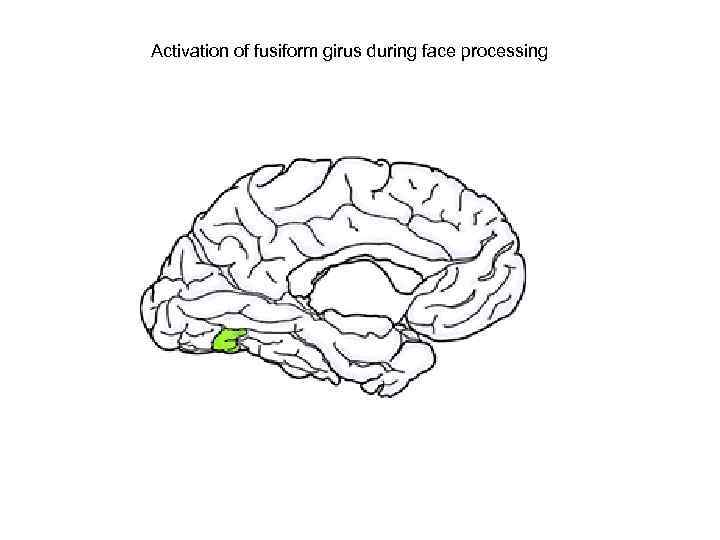
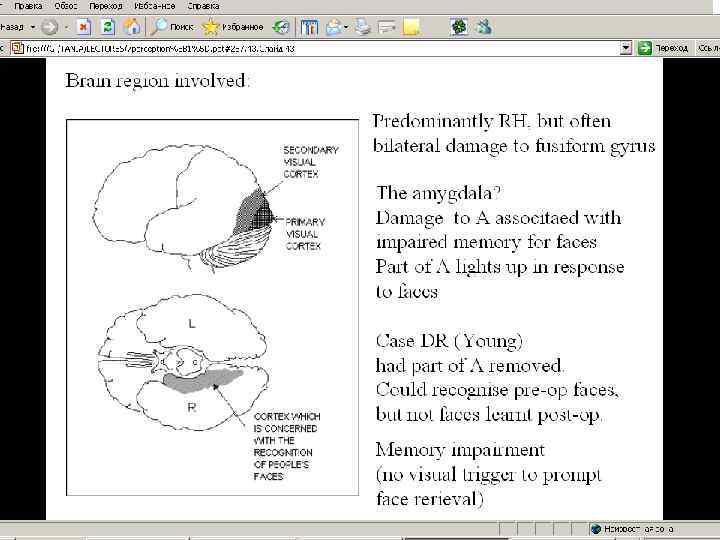
Activation of fusiform girus during face processing

Most interesting to infants
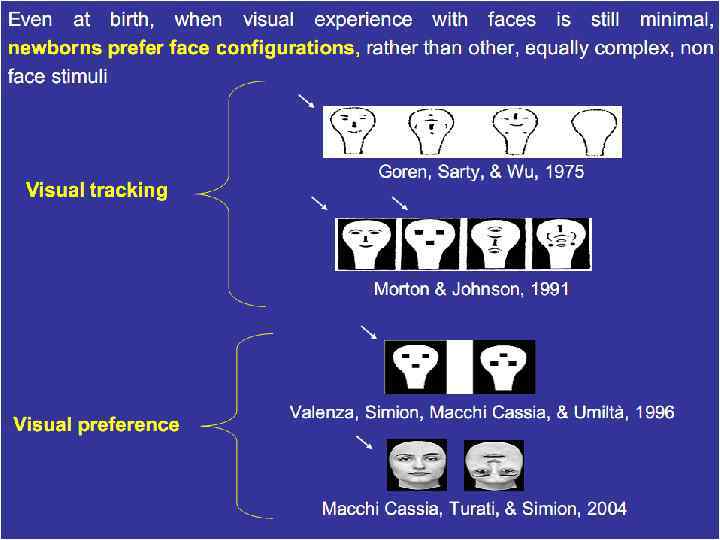
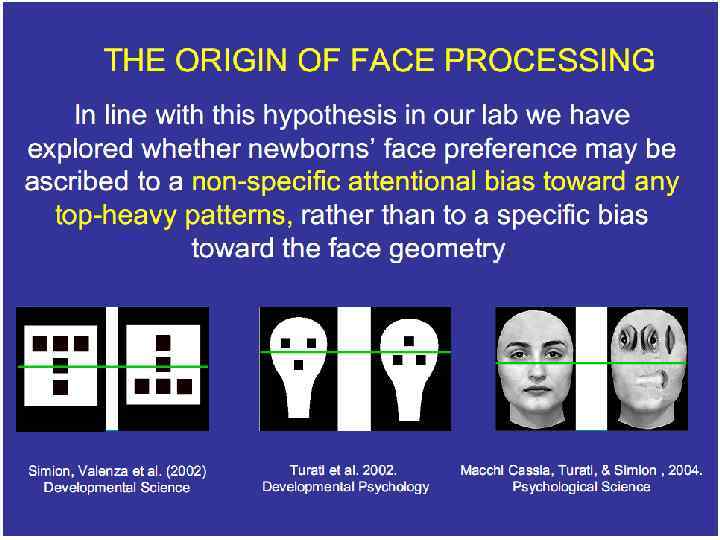




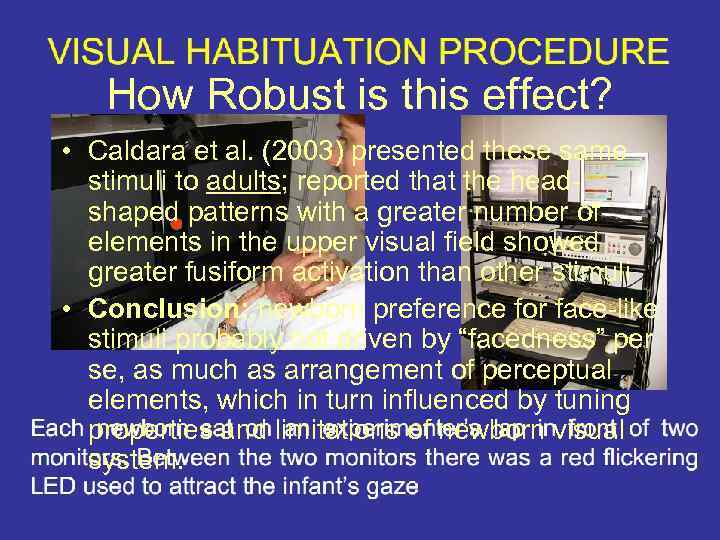
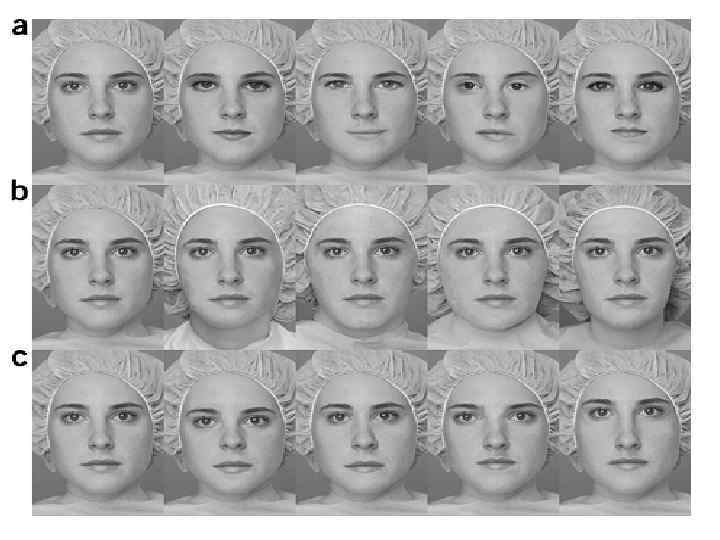
How Robust is this effect? • Caldara et al. (2003) presented these same stimuli to adults; reported that the headshaped patterns with a greater number of elements in the upper visual field showed greater fusiform activation than other stimuli • Conclusion: newborn preference for face-like stimuli probably not driven by “facedness” per se, as much as arrangement of perceptual elements, which in turn influenced by tuning properties and limitations of newborn visual system.

Behavioral Studies – Older Infants • Archival Data: Fagan (1972) demonstrated that around 4 months, infants begin to show facial inversion effect, pointing to development of face “schema. ” • Modern Data: is rapid improvement in face processing skills >4 -6 months. Examples: Infants <1 year can categorize facial gender, some facial expressions. However, no evidence of categorizing negative facial expressions till 1 -2 years; furthermore, recognition of negative facial expressions still lags behind adult levels through (at least) middle childhood.

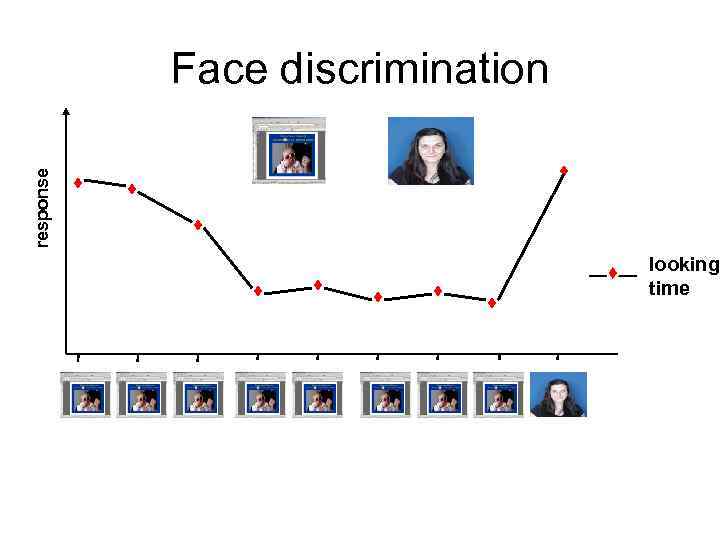
response Face discrimination looking time

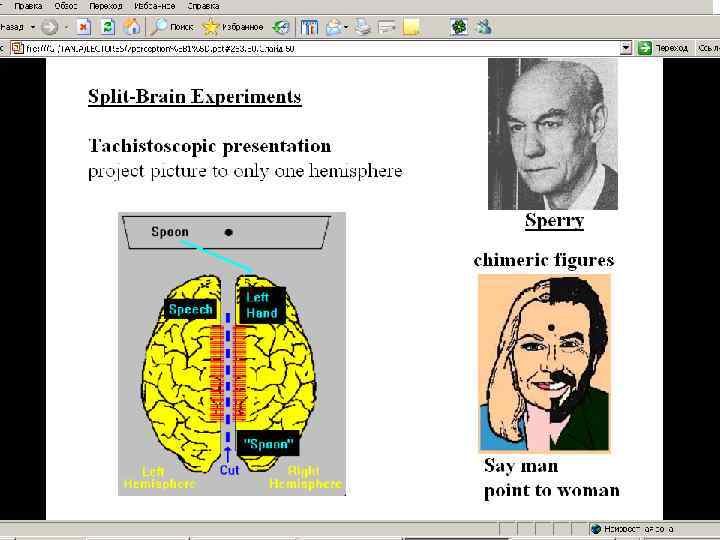
Neuropsychological Studies § de Schonen and her colleagues have demonstrated that 4 - to 9 -month-old infants show a right hemisphere (left visual field; LVF) bias towards processing faces, similar to what is observed in the adult (i. e. , is long history of research using divided field presentations, and more recent f. MRI studies, point to right>left hemisphere specialization)
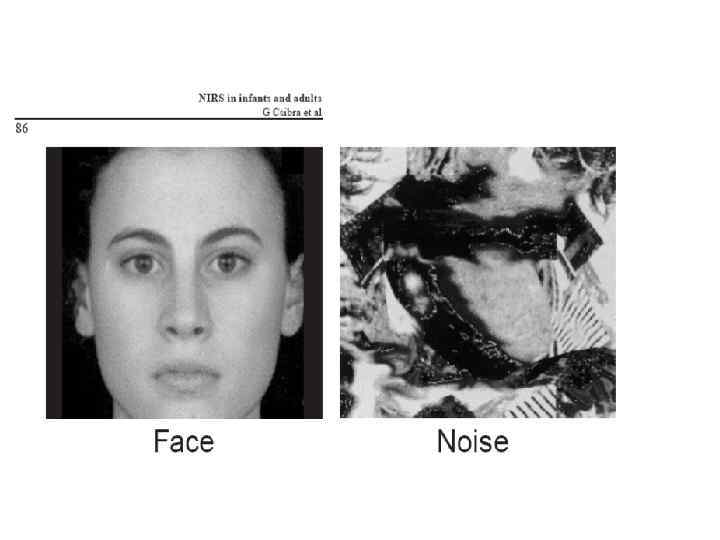
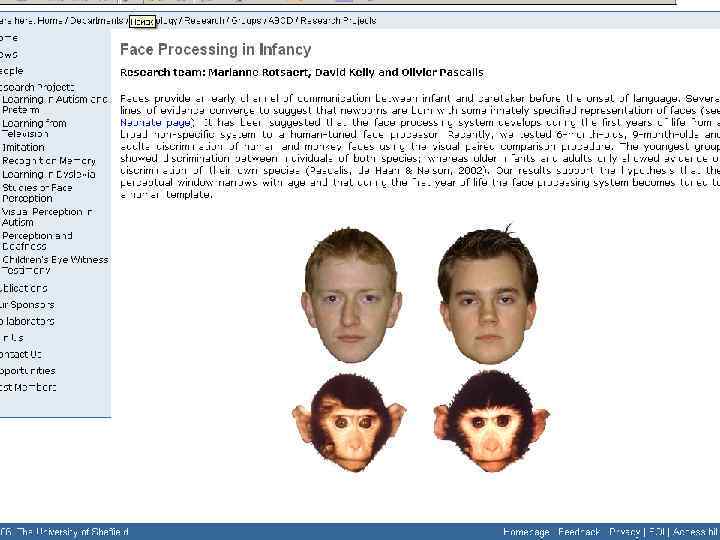
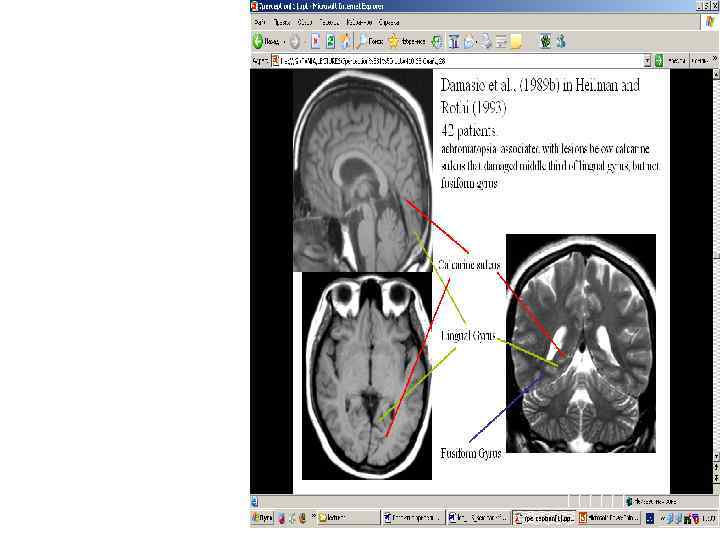
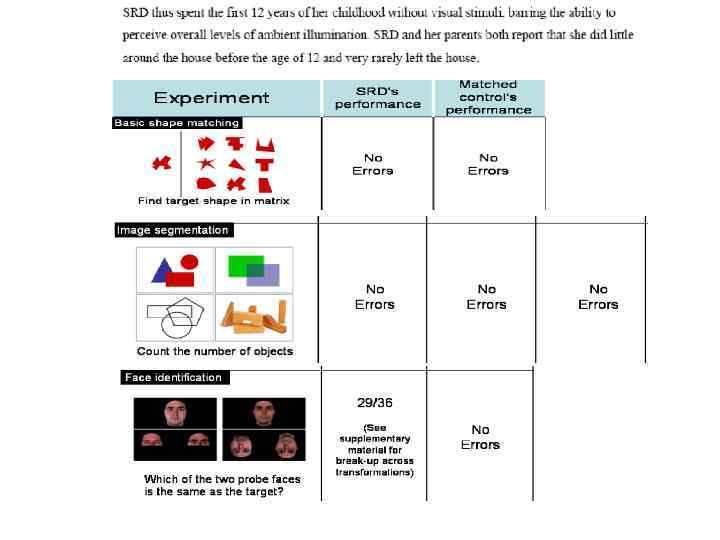


Visual perception_lecture2011.ppt