81bd02036f37a9f59c30eb5d88552aa9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 From Digital Divide to Digital Inclusion Are we REDI? Jorge-A. Sanchez-P. & Nikos Vogiatzis based on the EARNEST/GEANT 2 Foresight Study http: //www. terena. org/activities/earnest/geog. html Presented By: Jorge-A. Sanchez-P. General Manager and Co-Founder, JNPartners Co. Director, Strategy, Corallia Clusters Initiative j. sanchez@corallia. org Bruges, 21 May 2008
From Digital Divide to Digital Inclusion Are we REDI? Jorge-A. Sanchez-P. & Nikos Vogiatzis based on the EARNEST/GEANT 2 Foresight Study http: //www. terena. org/activities/earnest/geog. html Presented By: Jorge-A. Sanchez-P. General Manager and Co-Founder, JNPartners Co. Director, Strategy, Corallia Clusters Initiative j. sanchez@corallia. org Bruges, 21 May 2008
 Research and Education Networking Digital Divide and Index (REDI) A way to quantify and measure “the uneven distribution, difference or gap in regular and effective access to and usage of digital resources and technologies” … between scientists, researchers, students, etc* attached to research and education networks … due to infrastructural, social, economic, educational, regulatory and other causes, including but not limited to, unavailability of, difficulty in accessing, unawareness of the availability and/or capabilities of, lack of understanding of how to access and/or use such digital resources and technologies. * Conclusions should be able to be deducted for organizations, campuses, and geographic areas attached to research and education networks.
Research and Education Networking Digital Divide and Index (REDI) A way to quantify and measure “the uneven distribution, difference or gap in regular and effective access to and usage of digital resources and technologies” … between scientists, researchers, students, etc* attached to research and education networks … due to infrastructural, social, economic, educational, regulatory and other causes, including but not limited to, unavailability of, difficulty in accessing, unawareness of the availability and/or capabilities of, lack of understanding of how to access and/or use such digital resources and technologies. * Conclusions should be able to be deducted for organizations, campuses, and geographic areas attached to research and education networks.
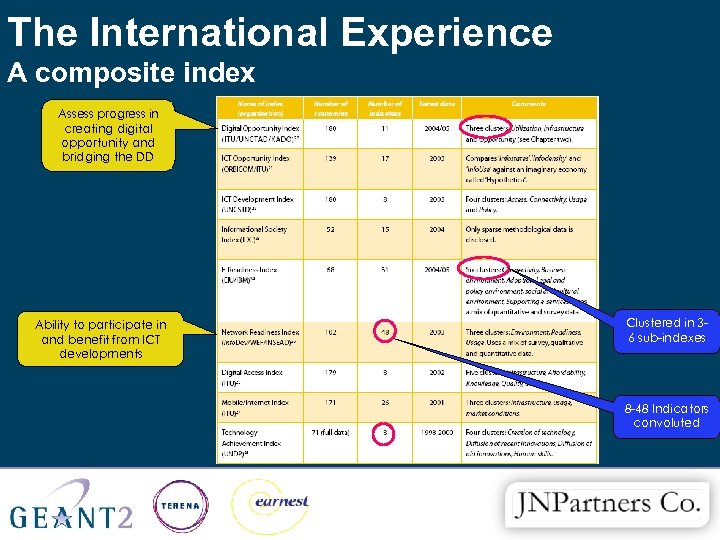 The International Experience A composite index Assess progress in creating digital opportunity and bridging the DD Ability to participate in and benefit from ICT developments Clustered in 36 sub-indexes 8 -48 Indicators convoluted
The International Experience A composite index Assess progress in creating digital opportunity and bridging the DD Ability to participate in and benefit from ICT developments Clustered in 36 sub-indexes 8 -48 Indicators convoluted
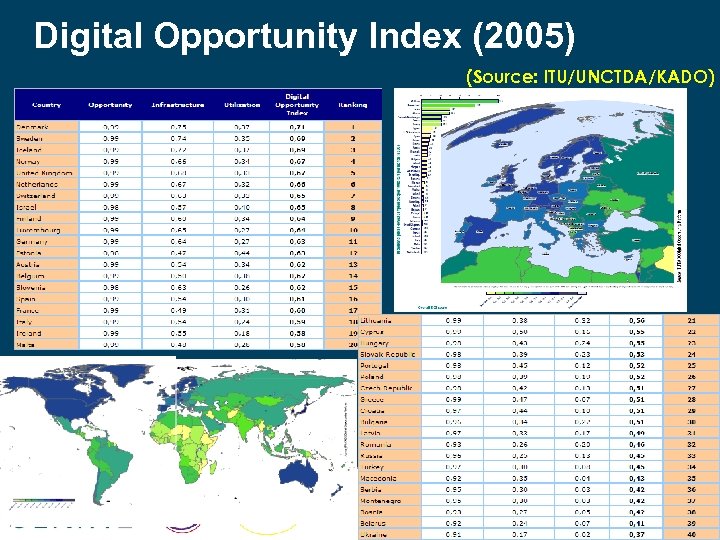 Digital Opportunity Index (2005) (Source: ITU/UNCTDA/KADO)
Digital Opportunity Index (2005) (Source: ITU/UNCTDA/KADO)
 A composite index for REN: The REDI Framework – Covers a large number of countries – Modular structure • can be grouped in logical classifications/clusters/categories/areas with special interest (e. g. enabling factors/opportunity, infrastructure, usage, etc) – Straightforward methodology • Raw ingredients are separate indicators that can be measured relatively easily. • Can be convoluted into a single Index (RENDDI) – Objective criteria and measurable indicators • Data collected via high-quality sources, e. g. the Compendium or other databases from the ITU, World. Bank, Euro. Stat, etc, and processed via robust statistical methods. – Standardized indicators • Allows for consistent and periodical measurements and assessments • Permits comparisons of the Digital Divide evolution (whether it is diminishing and at what speed)—both changes in absolute scores, as well as changes in rankings. – Captures the causes as well as the effects of the Digital Divide • exposing both the readiness as well as the intensity of use of digital resources and technologies
A composite index for REN: The REDI Framework – Covers a large number of countries – Modular structure • can be grouped in logical classifications/clusters/categories/areas with special interest (e. g. enabling factors/opportunity, infrastructure, usage, etc) – Straightforward methodology • Raw ingredients are separate indicators that can be measured relatively easily. • Can be convoluted into a single Index (RENDDI) – Objective criteria and measurable indicators • Data collected via high-quality sources, e. g. the Compendium or other databases from the ITU, World. Bank, Euro. Stat, etc, and processed via robust statistical methods. – Standardized indicators • Allows for consistent and periodical measurements and assessments • Permits comparisons of the Digital Divide evolution (whether it is diminishing and at what speed)—both changes in absolute scores, as well as changes in rankings. – Captures the causes as well as the effects of the Digital Divide • exposing both the readiness as well as the intensity of use of digital resources and technologies
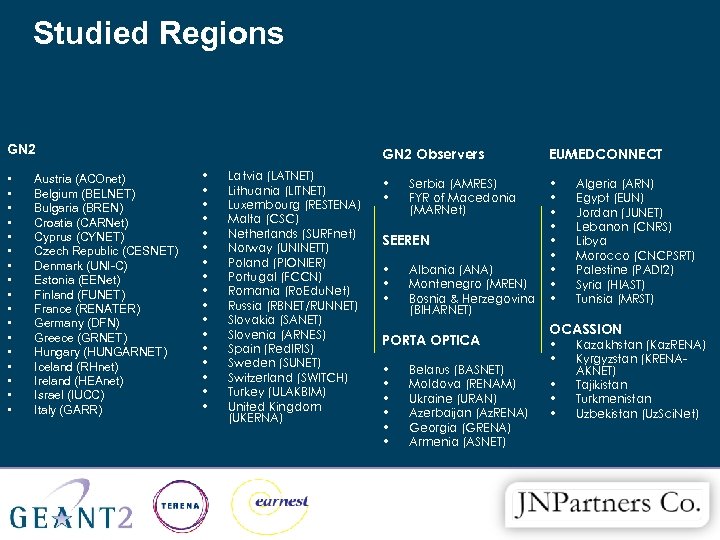 Studied Regions GN 2 • • • • • Austria (ACOnet) Belgium (BELNET) Bulgaria (BREN) Croatia (CARNet) Cyprus (CYNET) Czech Republic (CESNET) Denmark (UNI-C) Estonia (EENet) Finland (FUNET) France (RENATER) Germany (DFN) Greece (GRNET) Hungary (HUNGARNET) Iceland (RHnet) Ireland (HEAnet) Israel (IUCC) Italy (GARR) GN 2 Observers • • • • • Latvia (LATNET) Lithuania (LITNET) Luxembourg (RESTENA) Malta (CSC) Netherlands (SURFnet) Norway (UNINETT) Poland (PIONIER) Portugal (FCCN) Romania (Ro. Edu. Net) Russia (RBNET/RUNNET) Slovakia (SANET) Slovenia (ARNES) Spain (Red. IRIS) Sweden (SUNET) Switzerland (SWITCH) Turkey (ULAKBIM) United Kingdom (UKERNA) EUMEDCONNECT • • • Serbia (AMRES) FYR of Macedonia (MARNet) SEEREN • • • Albania (ANA) Montenegro (MREN) Bosnia & Herzegovina (BIHARNET) PORTA OPTICA • • • Belarus (BASNET) Moldova (RENAM) Ukraine (URAN) Azerbaijan (Az. RENA) Georgia (GRENA) Armenia (ASNET) Algeria (ARN) Egypt (EUN) Jordan (JUNET) Lebanon (CNRS) Libya Morocco (CNCPSRT) Palestine (PADI 2) Syria (HIAST) Tunisia (MRST) OCASSION • • • Kazakhstan (Kaz. RENA) Kyrgyzstan (KRENAAKNET) Tajikistan Turkmenistan Uzbekistan (Uz. Sci. Net)
Studied Regions GN 2 • • • • • Austria (ACOnet) Belgium (BELNET) Bulgaria (BREN) Croatia (CARNet) Cyprus (CYNET) Czech Republic (CESNET) Denmark (UNI-C) Estonia (EENet) Finland (FUNET) France (RENATER) Germany (DFN) Greece (GRNET) Hungary (HUNGARNET) Iceland (RHnet) Ireland (HEAnet) Israel (IUCC) Italy (GARR) GN 2 Observers • • • • • Latvia (LATNET) Lithuania (LITNET) Luxembourg (RESTENA) Malta (CSC) Netherlands (SURFnet) Norway (UNINETT) Poland (PIONIER) Portugal (FCCN) Romania (Ro. Edu. Net) Russia (RBNET/RUNNET) Slovakia (SANET) Slovenia (ARNES) Spain (Red. IRIS) Sweden (SUNET) Switzerland (SWITCH) Turkey (ULAKBIM) United Kingdom (UKERNA) EUMEDCONNECT • • • Serbia (AMRES) FYR of Macedonia (MARNet) SEEREN • • • Albania (ANA) Montenegro (MREN) Bosnia & Herzegovina (BIHARNET) PORTA OPTICA • • • Belarus (BASNET) Moldova (RENAM) Ukraine (URAN) Azerbaijan (Az. RENA) Georgia (GRENA) Armenia (ASNET) Algeria (ARN) Egypt (EUN) Jordan (JUNET) Lebanon (CNRS) Libya Morocco (CNCPSRT) Palestine (PADI 2) Syria (HIAST) Tunisia (MRST) OCASSION • • • Kazakhstan (Kaz. RENA) Kyrgyzstan (KRENAAKNET) Tajikistan Turkmenistan Uzbekistan (Uz. Sci. Net)
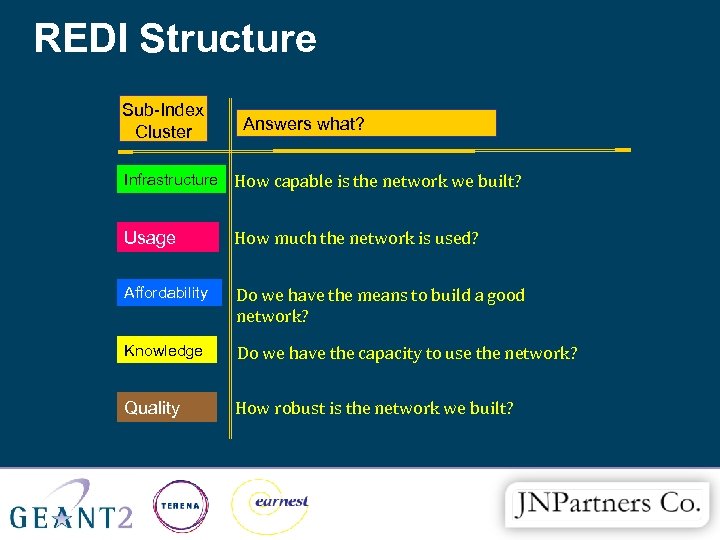 REDI Structure Sub-Index Cluster Answers what? Infrastructure How capable is the network we built? Usage How much the network is used? Affordability Do we have the means to build a good network? Knowledge Do we have the capacity to use the network? Quality How robust is the network we built?
REDI Structure Sub-Index Cluster Answers what? Infrastructure How capable is the network we built? Usage How much the network is used? Affordability Do we have the means to build a good network? Knowledge Do we have the capacity to use the network? Quality How robust is the network we built?
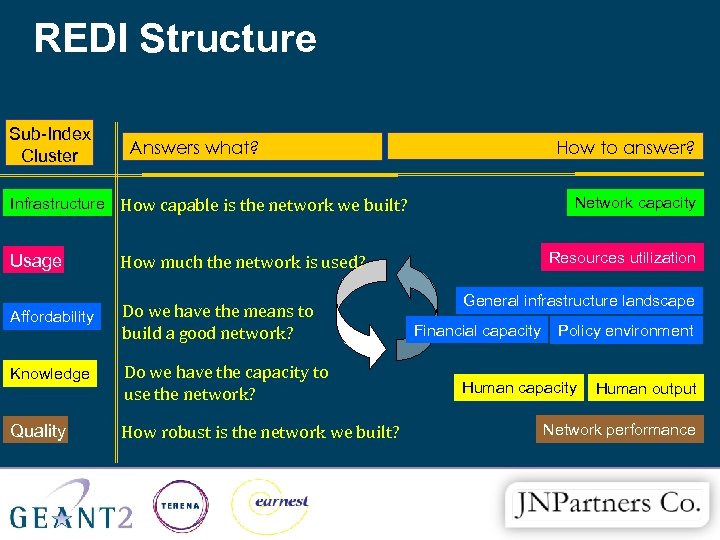 REDI Structure Sub-Index Cluster How to answer? Answers what? Network capacity Infrastructure How capable is the network we built? Usage Affordability Do we have the means to build a good network? Knowledge Do we have the capacity to use the network? Quality How robust is the network we built? Resources utilization How much the network is used? General infrastructure landscape Financial capacity Policy environment Human capacity Human output Network performance
REDI Structure Sub-Index Cluster How to answer? Answers what? Network capacity Infrastructure How capable is the network we built? Usage Affordability Do we have the means to build a good network? Knowledge Do we have the capacity to use the network? Quality How robust is the network we built? Resources utilization How much the network is used? General infrastructure landscape Financial capacity Policy environment Human capacity Human output Network performance
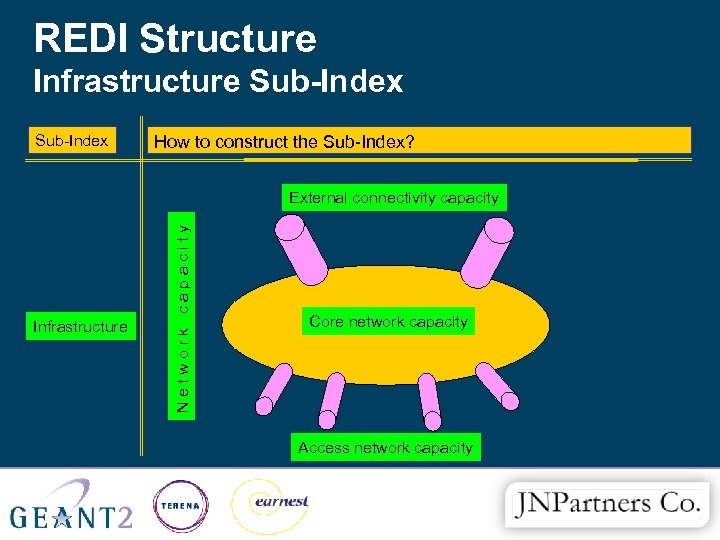 REDI Structure Infrastructure Sub-Index Category How to construct the Sub-Index? Sub-category Infrastructure Network capacity External connectivity capacity Core network capacity Access network capacity
REDI Structure Infrastructure Sub-Index Category How to construct the Sub-Index? Sub-category Infrastructure Network capacity External connectivity capacity Core network capacity Access network capacity
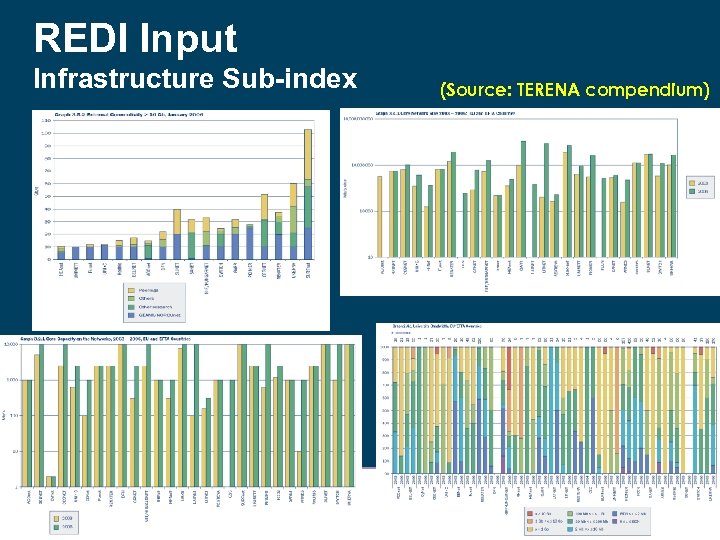 REDI Input Infrastructure Sub-index (Source: TERENA compendium)
REDI Input Infrastructure Sub-index (Source: TERENA compendium)
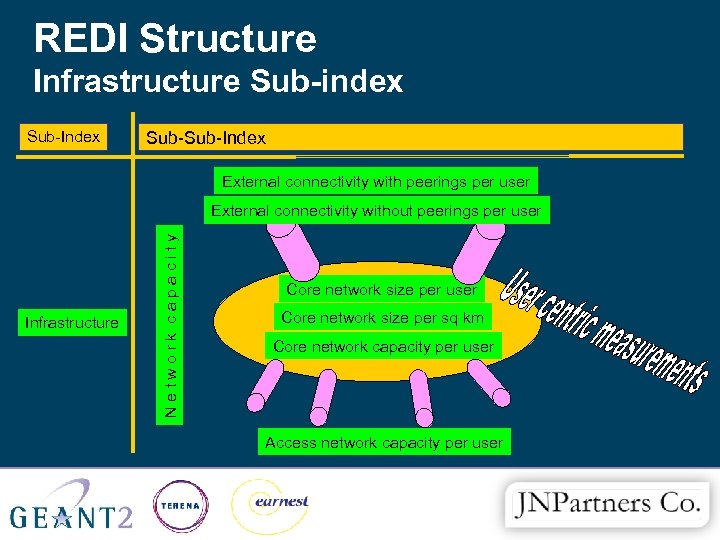 REDI Structure Infrastructure Sub-index Sub-Index Category Sub-Index Sub-category External connectivity with peerings per user Infrastructure Network capacity External connectivity without peerings per user Core network size per sq km Core network capacity per user Access network capacity per user
REDI Structure Infrastructure Sub-index Sub-Index Category Sub-Index Sub-category External connectivity with peerings per user Infrastructure Network capacity External connectivity without peerings per user Core network size per sq km Core network capacity per user Access network capacity per user
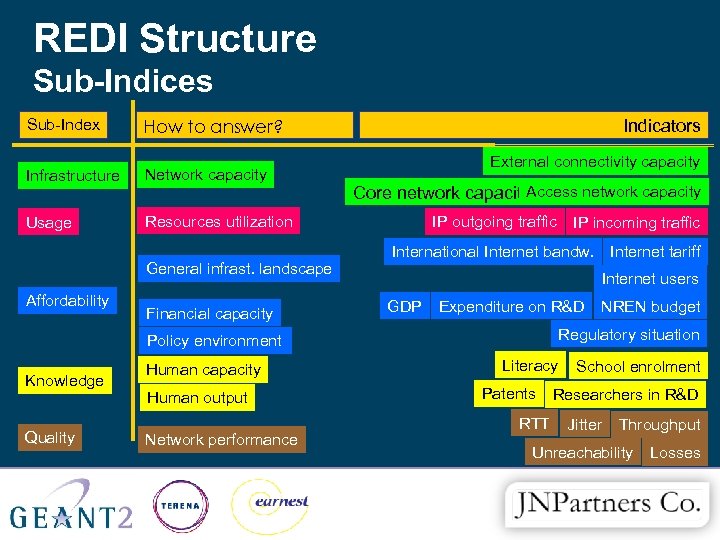 REDI Structure Sub-Indices Sub-Index Category How to answer? Infrastructure Network capacity Usage Indicators External connectivity capacity Resources utilization General infrast. landscape Affordability Financial capacity Access network capacity Core network capacity IP outgoing traffic International Internet bandw. Internet tariff Internet users GDP Expenditure on R&D Knowledge Quality Human output Network performance NREN budget Regulatory situation Policy environment Human capacity IP incoming traffic Literacy Patents RTT School enrolment Researchers in R&D Jitter Throughput Unreachability Losses
REDI Structure Sub-Indices Sub-Index Category How to answer? Infrastructure Network capacity Usage Indicators External connectivity capacity Resources utilization General infrast. landscape Affordability Financial capacity Access network capacity Core network capacity IP outgoing traffic International Internet bandw. Internet tariff Internet users GDP Expenditure on R&D Knowledge Quality Human output Network performance NREN budget Regulatory situation Policy environment Human capacity IP incoming traffic Literacy Patents RTT School enrolment Researchers in R&D Jitter Throughput Unreachability Losses
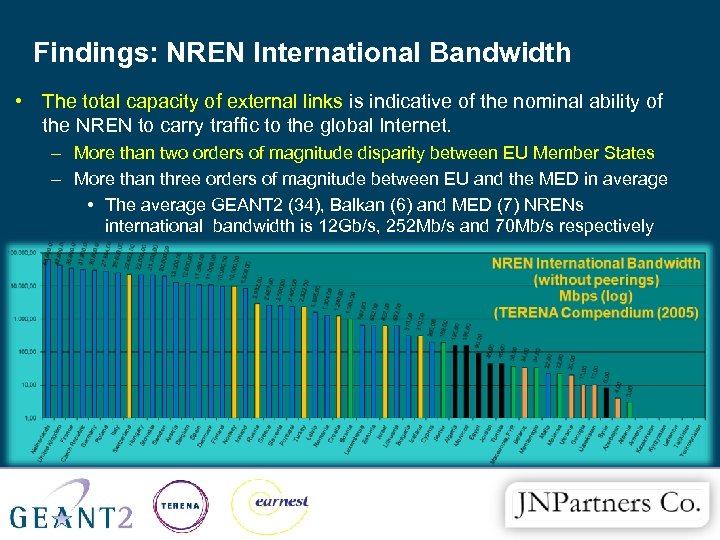 Findings: NREN International Bandwidth • The total capacity of external links is indicative of the nominal ability of the NREN to carry traffic to the global Internet. – More than two orders of magnitude disparity between EU Member States – More than three orders of magnitude between EU and the MED in average • The average GEANT 2 (34), Balkan (6) and MED (7) NRENs international bandwidth is 12 Gb/s, 252 Mb/s and 70 Mb/s respectively
Findings: NREN International Bandwidth • The total capacity of external links is indicative of the nominal ability of the NREN to carry traffic to the global Internet. – More than two orders of magnitude disparity between EU Member States – More than three orders of magnitude between EU and the MED in average • The average GEANT 2 (34), Balkan (6) and MED (7) NRENs international bandwidth is 12 Gb/s, 252 Mb/s and 70 Mb/s respectively
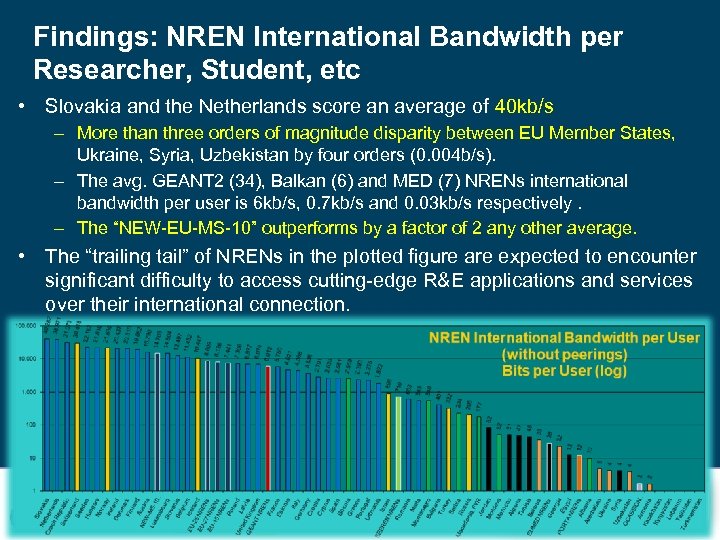 Findings: NREN International Bandwidth per Researcher, Student, etc • Slovakia and the Netherlands score an average of 40 kb/s – More than three orders of magnitude disparity between EU Member States, Ukraine, Syria, Uzbekistan by four orders (0. 004 b/s). – The avg. GEANT 2 (34), Balkan (6) and MED (7) NRENs international bandwidth per user is 6 kb/s, 0. 7 kb/s and 0. 03 kb/s respectively. – The “NEW-EU-MS-10” outperforms by a factor of 2 any other average. • The “trailing tail” of NRENs in the plotted figure are expected to encounter significant difficulty to access cutting-edge R&E applications and services over their international connection.
Findings: NREN International Bandwidth per Researcher, Student, etc • Slovakia and the Netherlands score an average of 40 kb/s – More than three orders of magnitude disparity between EU Member States, Ukraine, Syria, Uzbekistan by four orders (0. 004 b/s). – The avg. GEANT 2 (34), Balkan (6) and MED (7) NRENs international bandwidth per user is 6 kb/s, 0. 7 kb/s and 0. 03 kb/s respectively. – The “NEW-EU-MS-10” outperforms by a factor of 2 any other average. • The “trailing tail” of NRENs in the plotted figure are expected to encounter significant difficulty to access cutting-edge R&E applications and services over their international connection.
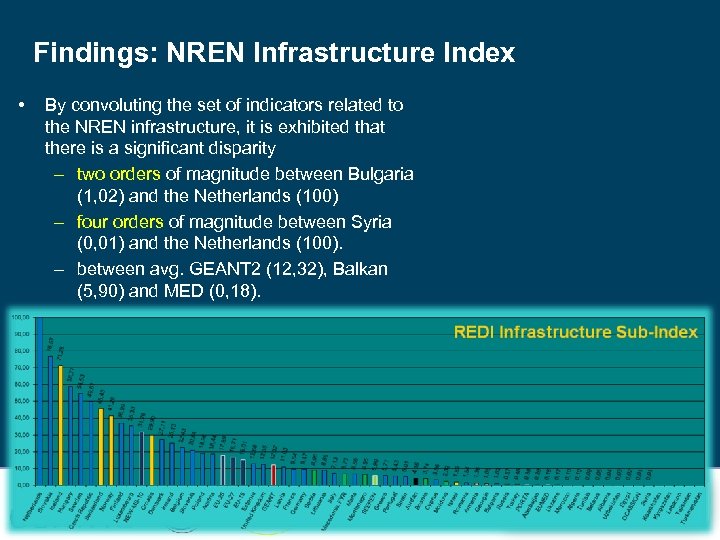 Findings: NREN Infrastructure Index • By convoluting the set of indicators related to the NREN infrastructure, it is exhibited that there is a significant disparity – two orders of magnitude between Bulgaria (1, 02) and the Netherlands (100) – four orders of magnitude between Syria (0, 01) and the Netherlands (100). – between avg. GEANT 2 (12, 32), Balkan (5, 90) and MED (0, 18).
Findings: NREN Infrastructure Index • By convoluting the set of indicators related to the NREN infrastructure, it is exhibited that there is a significant disparity – two orders of magnitude between Bulgaria (1, 02) and the Netherlands (100) – four orders of magnitude between Syria (0, 01) and the Netherlands (100). – between avg. GEANT 2 (12, 32), Balkan (5, 90) and MED (0, 18).
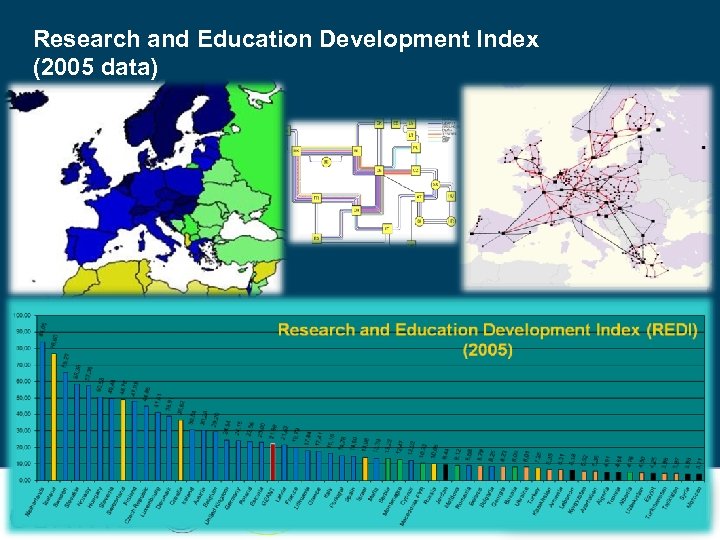 Research and Education Development Index (2005 data)
Research and Education Development Index (2005 data)
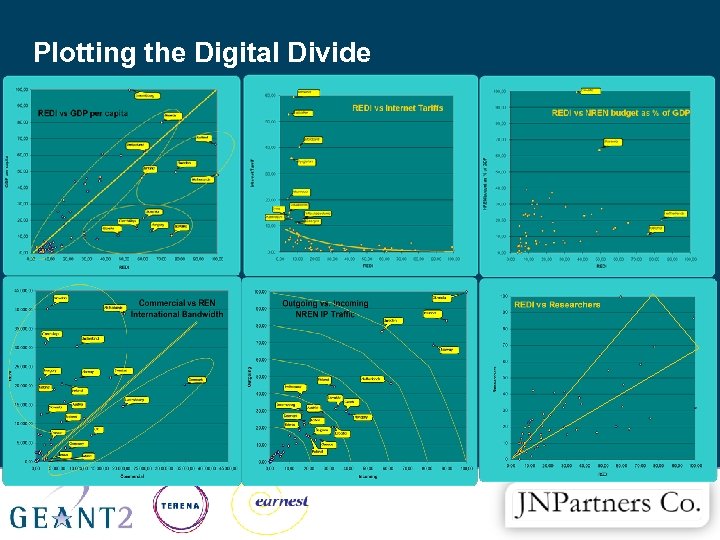 Plotting the Digital Divide
Plotting the Digital Divide
 Recommendations 1. GÉANT extensions in developing regions. 2. NRENs’ institutional role. 3. Predictability, fair competition, and deregulation of (telecom) markets. 4. EC special support action for low REDI performers (e-RED Initiative). 5. Member States’ R&E roadmaps in sync and in tune. 6. Education and training programmes for accessing and utilizing e-Infrastructures. 7. Monitor periodically progress towards sustainability through the REDI. 8. Policy Statement - Declaration of Solidarity for diminishing the digital divide.
Recommendations 1. GÉANT extensions in developing regions. 2. NRENs’ institutional role. 3. Predictability, fair competition, and deregulation of (telecom) markets. 4. EC special support action for low REDI performers (e-RED Initiative). 5. Member States’ R&E roadmaps in sync and in tune. 6. Education and training programmes for accessing and utilizing e-Infrastructures. 7. Monitor periodically progress towards sustainability through the REDI. 8. Policy Statement - Declaration of Solidarity for diminishing the digital divide.
 Future Work • Further validate raw input from databases • Assess and improve convolution methods and weights • Identify data for the Quality Index and include in measurements • Run the Index for 2007 and potentially on an annual basis for a 3 -5 year period • Endorsement by Stakeholders: – – – National Research and Education Networks Management of research institutes, universities and other research organizations Governments and research funding bodies European Commission / DG INFSO and other DGs European Parliament / STOA
Future Work • Further validate raw input from databases • Assess and improve convolution methods and weights • Identify data for the Quality Index and include in measurements • Run the Index for 2007 and potentially on an annual basis for a 3 -5 year period • Endorsement by Stakeholders: – – – National Research and Education Networks Management of research institutes, universities and other research organizations Governments and research funding bodies European Commission / DG INFSO and other DGs European Parliament / STOA
 Acknowledgements • TERENA Compendium team • EARNEST panel members • Geographic Issues Study Advisory Board • Pinger team • ITU / World. Bank / WEF / OECD - workgroups and studies
Acknowledgements • TERENA Compendium team • EARNEST panel members • Geographic Issues Study Advisory Board • Pinger team • ITU / World. Bank / WEF / OECD - workgroups and studies


