Fritz Albert Lipmann (June 12, 1899 – July


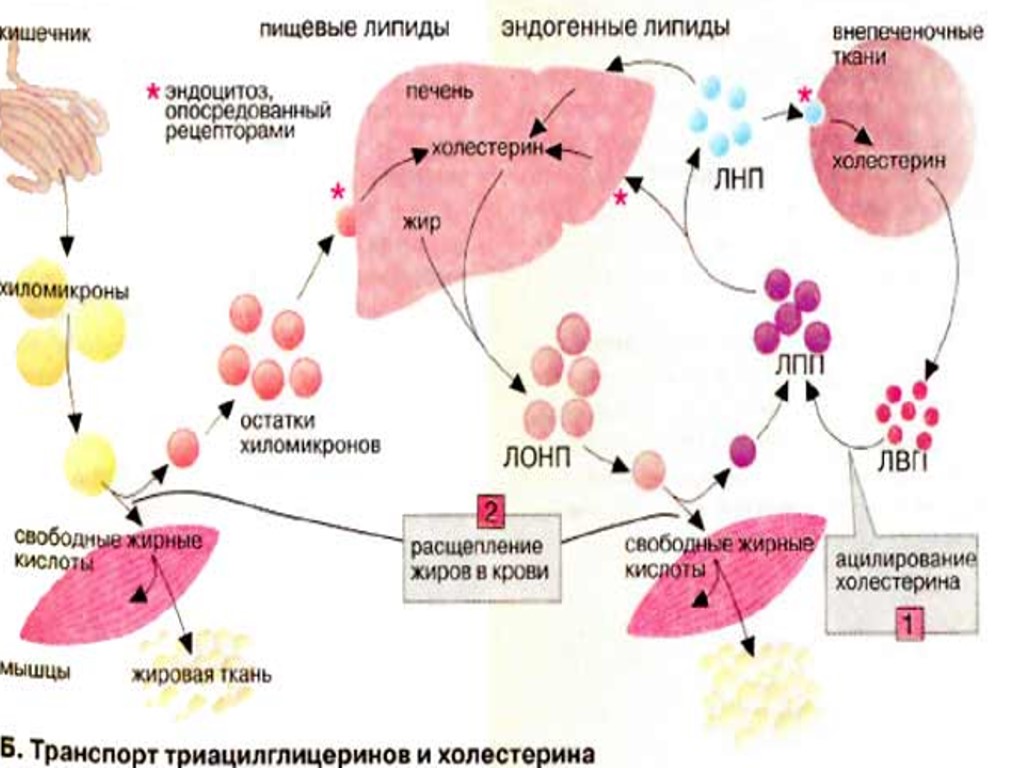
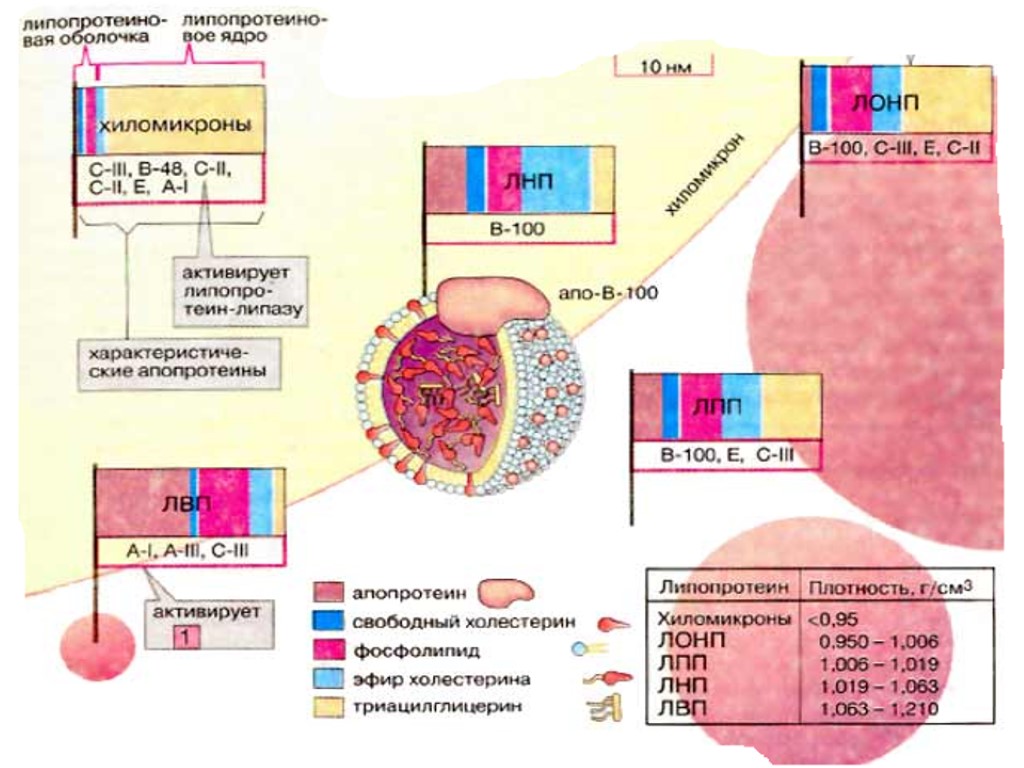
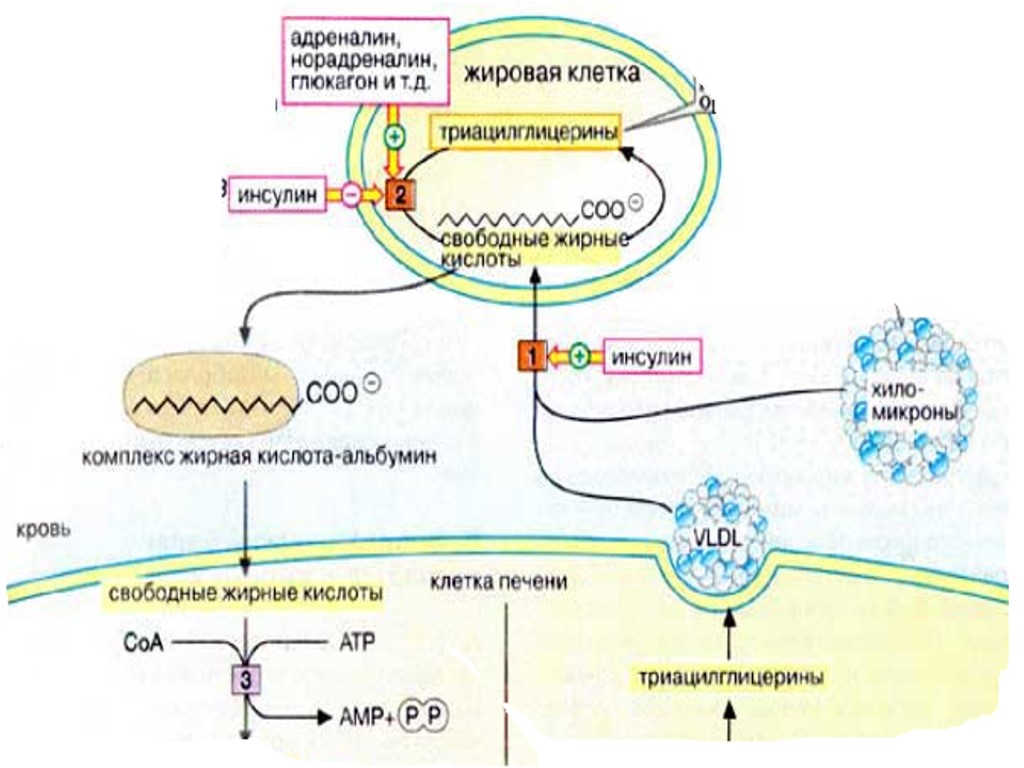
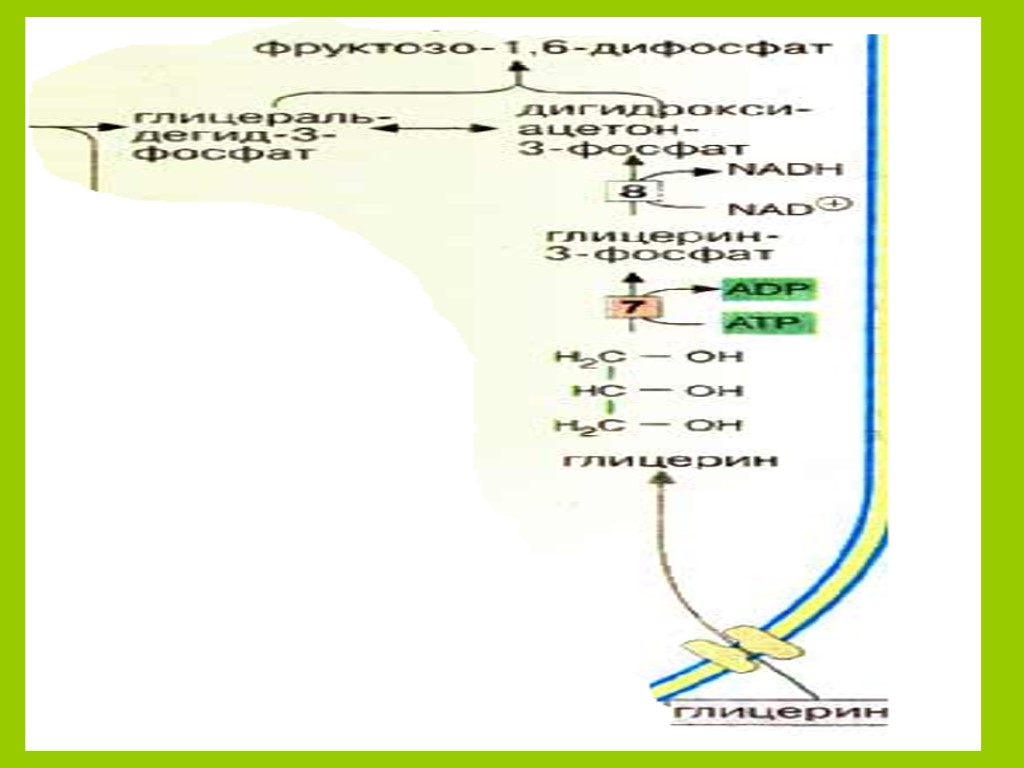


Fritz Albert Lipmann (June 12, 1899 – July 24, 1986) German-American biochemist and a co-discoverer in 1945 of coenzyme A. For this, together with other research on coenzyme A, he was awarded half the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1953 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953

Fritz Albert Lipmann (June 12, 1899 – July 24, 1986) German-American biochemist and a co-discoverer in 1945 of coenzyme A. For this, together with other research on coenzyme A, he was awarded half the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1953

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1964 "for their discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of the cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism"

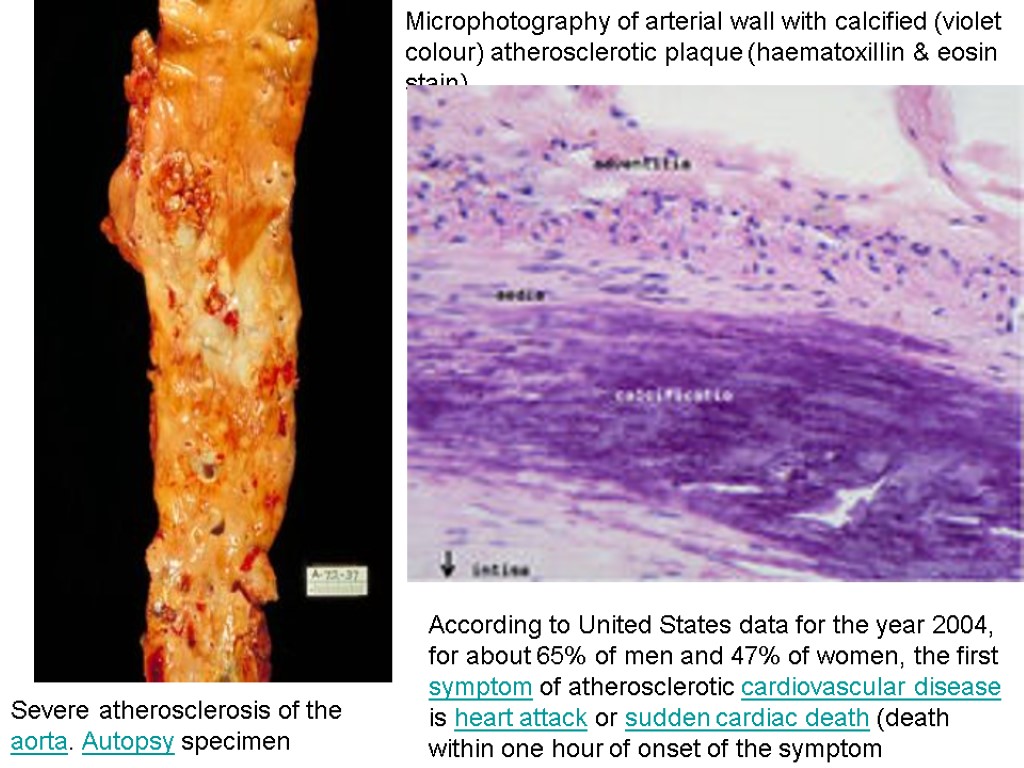
Severe atherosclerosis of the aorta. Autopsy specimen Microphotography of arterial wall with calcified (violet colour) atherosclerotic plaque (haematoxillin & eosin stain). According to United States data for the year 2004, for about 65% of men and 47% of women, the first symptom of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is heart attack or sudden cardiac death (death within one hour of onset of the symptom

Physiologic factors that increase risk Various anatomic, physiological & behavioral risk factors for atherosclerosis are known. These can be divided into various categories: congenital vs acquired, modifiable or not, classical or non-classical. The points labelled '+' in the following list form the core components of "metabolic syndrome": Advanced age , Male sex Having Diabetes or Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) + Dyslipidemia (elevated serum cholesterol or triglyceride levels): + High serum concentration of low density lipoprotein (LDL, "bad cholesterol"), Lipoprotein(a) (a variant of LDL), and / or very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles, i.e. "lipoprotein subclass analysis" Low serum concentration of functioning high density lipoprotein (HDL, "good cholesterol") particles, i.e. "lipoprotein subclass analysis" Tobacco smoking . Having high blood pressure + Being obese (in particular central obesity, also referred to as abdominal or male-type obesity) + A sedentary lifestyle Having close relatives who have had some complication of atherosclerosis (eg. coronary heart disease or stroke) Elevated serum levels of homocysteine Elevated serum levels of uric acid (also responsible for gout) Elevated serum fibrinogen concentrations + Chronic systemic inflammation as reflected by upper normal WBC concentrations, elevated hs-CRP and many other blood chemistry markers, most only research level at present, not clinically done.[2] Stress or symptoms of clinical depression Hypothyroidism (a slow-acting thyroid) High intake of trans-fats and saturated fats in diet
presentation_06.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

