7a8167de3398162f9567cbd405aae60e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Friday, 4/15/16, Day 2 Essential Skill: Explicitly assess information and draw conclusions 1 -Congressional Committees and Support Agencies 2 - “Mr. Smith Goes to Washington”
Friday, 4/15/16, Day 2 Essential Skill: Explicitly assess information and draw conclusions 1 -Congressional Committees and Support Agencies 2 - “Mr. Smith Goes to Washington”
 Congressional Committees and Support Agencies
Congressional Committees and Support Agencies
 1 -What are three purposes of committees in the House and Senate? 1 -It allows members of Congress to divide their work among smaller groups. 2 -From the large number of bills that are introduced in each Congress, committees select those few that are to receive further consideration. 3 - By holding public hearings and investigations, committees help the public learn about key problems and issues that face the nation [organized crime, prescription drug safety, hunger, airline safety. .
1 -What are three purposes of committees in the House and Senate? 1 -It allows members of Congress to divide their work among smaller groups. 2 -From the large number of bills that are introduced in each Congress, committees select those few that are to receive further consideration. 3 - By holding public hearings and investigations, committees help the public learn about key problems and issues that face the nation [organized crime, prescription drug safety, hunger, airline safety. .
 2 -Explain the general responsibility of each type of committee: Standing committees: Permanent committees that oversee bills that deal with certain kinds of issues. They continue from one Congress to the next.
2 -Explain the general responsibility of each type of committee: Standing committees: Permanent committees that oversee bills that deal with certain kinds of issues. They continue from one Congress to the next.
 2 -Explain the general responsibility of each type of committee Standing committees: Permanent committees that oversee bills that deal with certain kinds of issues. They continue from one Congress to the next.
2 -Explain the general responsibility of each type of committee Standing committees: Permanent committees that oversee bills that deal with certain kinds of issues. They continue from one Congress to the next.
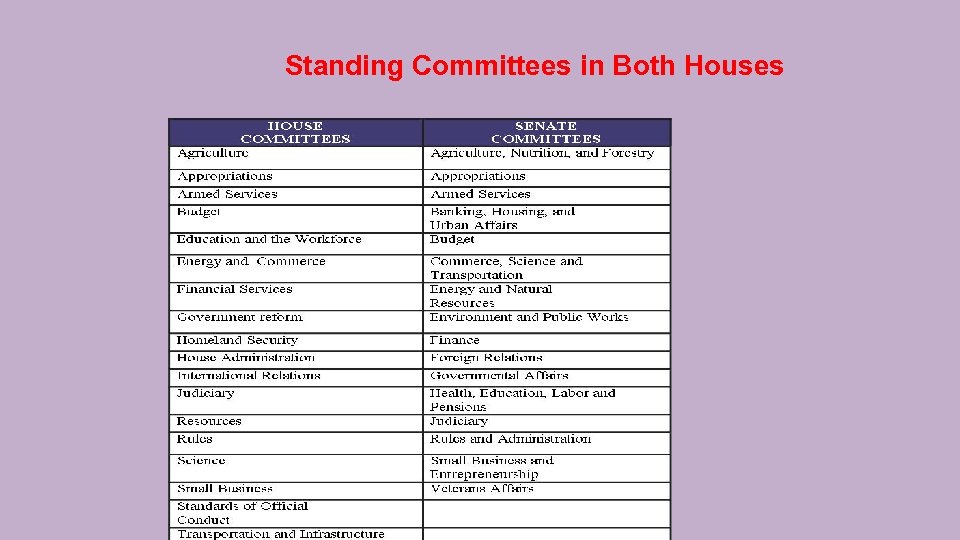 Standing Committees in Both Houses
Standing Committees in Both Houses
 Who controls the standing committees? Majority party: it selects the chairperson; has more members
Who controls the standing committees? Majority party: it selects the chairperson; has more members
 Subcommittees: Subdivisions of standing committees. Each specializes in a subcategory of its standing committee’s responsibility. Standing Committee: Ways and Means Subcommittees • Health • Income Security and Family Support • Oversight • Social Security • Trade
Subcommittees: Subdivisions of standing committees. Each specializes in a subcategory of its standing committee’s responsibility. Standing Committee: Ways and Means Subcommittees • Health • Income Security and Family Support • Oversight • Social Security • Trade
 Select committees: Temporary committees that study one specific issue and report their findings to the House or Senate. [gas prices, health matters. . ] Does not submit bills.
Select committees: Temporary committees that study one specific issue and report their findings to the House or Senate. [gas prices, health matters. . ] Does not submit bills.
 Joint committees: Made up of members of both house; they can be temporary or permanent. Act as a study group that reports back to the House or Senate on a topic or a bill [Joint Economic Committee might report on the economic impact of a particular war; or income trends for average Americans. ] Does not deal directly with bills or propose laws.
Joint committees: Made up of members of both house; they can be temporary or permanent. Act as a study group that reports back to the House or Senate on a topic or a bill [Joint Economic Committee might report on the economic impact of a particular war; or income trends for average Americans. ] Does not deal directly with bills or propose laws.
 Conference committees: A bill cannot be signed into law by the president until both houses have passed an identical law. A temporary committee that is set up when the House and Senate have passed different versions of the same bill. They resolve the differences between the two versions.
Conference committees: A bill cannot be signed into law by the president until both houses have passed an identical law. A temporary committee that is set up when the House and Senate have passed different versions of the same bill. They resolve the differences between the two versions.
 3 -What are some of the advantages to being on some committees? 1 -Membership on certain committees can increase a lawmakers chances for reelection because it puts a congressperson in a position to act on bills that are important to their constituents [farm state: House Committee on Agriculture] 2 -Membership on some committees mean that a lawmaker can influence national policies: education, health, judiciary, foreign affairs
3 -What are some of the advantages to being on some committees? 1 -Membership on certain committees can increase a lawmakers chances for reelection because it puts a congressperson in a position to act on bills that are important to their constituents [farm state: House Committee on Agriculture] 2 -Membership on some committees mean that a lawmaker can influence national policies: education, health, judiciary, foreign affairs
 4 -Who assigns members of both houses to committees? The Parties
4 -Who assigns members of both houses to committees? The Parties
 5 -What is the seniority system? The majority party member with the longest uninterrupted service on a committee was appointed leader of that committees. Some newer members viewed this as unfair.
5 -What is the seniority system? The majority party member with the longest uninterrupted service on a committee was appointed leader of that committees. Some newer members viewed this as unfair.
 6 -How has the seniority system changed since 1971? Chairpersons of committees are selected by secret ballot.
6 -How has the seniority system changed since 1971? Chairpersons of committees are selected by secret ballot.
 7 -Explain the functions of these support agencies: Library of Congress: Administrates the copyright law; Congressional Research Service [CRS] answers thousands of requests for information from lawmakers, congressional staff and committees. Congressional members use the CRS to research matters related to bills and requests from voters.
7 -Explain the functions of these support agencies: Library of Congress: Administrates the copyright law; Congressional Research Service [CRS] answers thousands of requests for information from lawmakers, congressional staff and committees. Congressional members use the CRS to research matters related to bills and requests from voters.
![Congressional Budget Office [CBO]: • coordinates the budget work of Congress. • studies budget Congressional Budget Office [CBO]: • coordinates the budget work of Congress. • studies budget](https://present5.com/presentation/7a8167de3398162f9567cbd405aae60e/image-17.jpg) Congressional Budget Office [CBO]: • coordinates the budget work of Congress. • studies budget proposals put forward by the president. • projects the costs of proposed programs. • study economic trends. • tracks committee spending. • reports on the budget and calculates how budget decisions might affect the economy
Congressional Budget Office [CBO]: • coordinates the budget work of Congress. • studies budget proposals put forward by the president. • projects the costs of proposed programs. • study economic trends. • tracks committee spending. • reports on the budget and calculates how budget decisions might affect the economy
![Government Accountability Office [GAO] • Watches how funds appropriated by Congress are spent. • Government Accountability Office [GAO] • Watches how funds appropriated by Congress are spent. •](https://present5.com/presentation/7a8167de3398162f9567cbd405aae60e/image-18.jpg) Government Accountability Office [GAO] • Watches how funds appropriated by Congress are spent. • Review financial management of government programs created by Congress. • Answers requests about specific programs from lawmakers and committees. • Prepares reports on federal programs from lawmakers. • Develop questions for committees during hearings. • Provide legal opinions on bills under consideration.
Government Accountability Office [GAO] • Watches how funds appropriated by Congress are spent. • Review financial management of government programs created by Congress. • Answers requests about specific programs from lawmakers and committees. • Prepares reports on federal programs from lawmakers. • Develop questions for committees during hearings. • Provide legal opinions on bills under consideration.
![Government Printing Office [GPO] Provides printing for the entire federal government. Publishes the Congressional Government Printing Office [GPO] Provides printing for the entire federal government. Publishes the Congressional](https://present5.com/presentation/7a8167de3398162f9567cbd405aae60e/image-19.jpg) Government Printing Office [GPO] Provides printing for the entire federal government. Publishes the Congressional Record [daily record of bills, speeches. . ] Published the Statistical Abstract of the United States: published by the Bureau of Census, provides information on: population statistics; government expenditures; average personal income, levels of education; elections. Used by Congress and public.
Government Printing Office [GPO] Provides printing for the entire federal government. Publishes the Congressional Record [daily record of bills, speeches. . ] Published the Statistical Abstract of the United States: published by the Bureau of Census, provides information on: population statistics; government expenditures; average personal income, levels of education; elections. Used by Congress and public.


