5bac61fc3c4c17b5748e940551a427f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 French Wars of Religion
French Wars of Religion
 I. Nature of religious wars mid-16 th c. 1. Religious wars engulfed Europe a) intellectuals saw the wisdom in __________ more quickly than the politicians. b) Politiques were rulers who place political unity above ______.
I. Nature of religious wars mid-16 th c. 1. Religious wars engulfed Europe a) intellectuals saw the wisdom in __________ more quickly than the politicians. b) Politiques were rulers who place political unity above ______.
 Keep in Mind: 1. France & Spain = Catholic governments 2. These govs will get together and send armies against Protestant regimes in ______&_________ 3. Before end of Thirty Years’ War (1648) every major Euro nation was directly or indirectly drawn in the war. (We will discuss Thirty Years’ War on Thursday)
Keep in Mind: 1. France & Spain = Catholic governments 2. These govs will get together and send armies against Protestant regimes in ______&_________ 3. Before end of Thirty Years’ War (1648) every major Euro nation was directly or indirectly drawn in the war. (We will discuss Thirty Years’ War on Thursday)
 II. French Wars of Religion 1. _______was the engine that drove the French civil war of the 16 th c. 2. Huguenots a) French Protestants (Calvinists) b) under surveillance b/c of writings c) Came from all levels of society 3. Approx 40 -50% of Fr. Nobility became Huguenots a) Why? 4. Calvinists = 10% of pop. , but they were a wellorganized minority.
II. French Wars of Religion 1. _______was the engine that drove the French civil war of the 16 th c. 2. Huguenots a) French Protestants (Calvinists) b) under surveillance b/c of writings c) Came from all levels of society 3. Approx 40 -50% of Fr. Nobility became Huguenots a) Why? 4. Calvinists = 10% of pop. , but they were a wellorganized minority.
 Keep in mind: The conversion of so many nobles made the Huguenots a potentially dangerous political threat to power of the monarchy. WHY? 1. House of Bourbon = Huguenots a) Stood next to the Valois in the royal line of succession. b) ruled the southern French kingdom of Navarre. Where’s Navarre?
Keep in mind: The conversion of so many nobles made the Huguenots a potentially dangerous political threat to power of the monarchy. WHY? 1. House of Bourbon = Huguenots a) Stood next to the Valois in the royal line of succession. b) ruled the southern French kingdom of Navarre. Where’s Navarre?
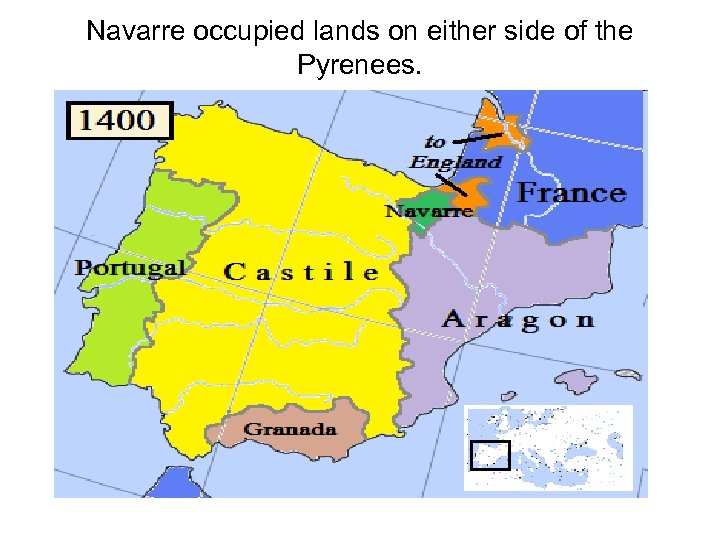 Navarre occupied lands on either side of the Pyrenees.
Navarre occupied lands on either side of the Pyrenees.
 III. The Valois Monarchy 1. Staunchly Catholic 2. King Henry II killed in tournament accident (He was the son of Francis I who was? ? ? ) a) weak sons succeed him – 2 are dominated by their mother… 3. Catherine de Medici a) a politique – How?
III. The Valois Monarchy 1. Staunchly Catholic 2. King Henry II killed in tournament accident (He was the son of Francis I who was? ? ? ) a) weak sons succeed him – 2 are dominated by their mother… 3. Catherine de Medici a) a politique – How?
 IV. The Guise Family 1. Staunch Catholics who strictly opposed the _________. 2. Had loyalty of 3. Had money to recruit and pay for 4. Family had support from the _______ & _____.
IV. The Guise Family 1. Staunch Catholics who strictly opposed the _________. 2. Had loyalty of 3. Had money to recruit and pay for 4. Family had support from the _______ & _____.
 V. Religion not the only factor in French Civil Wars 1. Towns and provinces 2. Nobility
V. Religion not the only factor in French Civil Wars 1. Towns and provinces 2. Nobility
 VI. Wars erupt in 1562…because 1. The powerful duke of Guise massacred _____________at_____. • Why did he do this…and what about Catherine de Medici? 2. Catherine’s in a tough spot a) The _______posed a religious threat. b) Guises posed a _____ threat.
VI. Wars erupt in 1562…because 1. The powerful duke of Guise massacred _____________at_____. • Why did he do this…and what about Catherine de Medici? 2. Catherine’s in a tough spot a) The _______posed a religious threat. b) Guises posed a _____ threat.
 3. Catherine the politique a) tried, unsuccessfully, to reconcile ______&_____factions. b) Sought allies among the ______. Why? i. Her #1 objective=preserve the______ c) Issued January Edict (1562) i. Granted 4. Duke of Guise angry, ergo massacre of 100 s 5. When Protestants didn’t immediately come to her support, she was forced to cooperate with _______.
3. Catherine the politique a) tried, unsuccessfully, to reconcile ______&_____factions. b) Sought allies among the ______. Why? i. Her #1 objective=preserve the______ c) Issued January Edict (1562) i. Granted 4. Duke of Guise angry, ergo massacre of 100 s 5. When Protestants didn’t immediately come to her support, she was forced to cooperate with _______.
 VII. Meanwhile…the Bourbon & Montmorency. Chatillon Familes 1. Each develops strong ____ sympathies 2. So…Bourbon Louis I (prince of Conde) and MC admiral, Coligny, became leaders of the French Protestant resistance. 3. Duke of Guise killed & Prince Louis I later killed. 4. Huguenot leadership passed to Coligny.
VII. Meanwhile…the Bourbon & Montmorency. Chatillon Familes 1. Each develops strong ____ sympathies 2. So…Bourbon Louis I (prince of Conde) and MC admiral, Coligny, became leaders of the French Protestant resistance. 3. Duke of Guise killed & Prince Louis I later killed. 4. Huguenot leadership passed to Coligny.
 VIII. Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye 1. Acknowledged power of 2. Granted Huguenots religious freedoms within 3. Granted Huguenots right to
VIII. Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye 1. Acknowledged power of 2. Granted Huguenots religious freedoms within 3. Granted Huguenots right to
 IX. Coligny becomes Charles IX’s closest advisor. 1. Catherine concerned so 2. Her main concern? a) Coligny encouraging king to send troops into ________ to support _______Protestants. b) This would put France on a collision course with _____. c) She knew France would lose…why?
IX. Coligny becomes Charles IX’s closest advisor. 1. Catherine concerned so 2. Her main concern? a) Coligny encouraging king to send troops into ________ to support _______Protestants. b) This would put France on a collision course with _____. c) She knew France would lose…why?
 X. St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre - 1572 1. Marriage b/t sister of Charles IX (Valois) and Henry of Navarre (Bourbon ruler) 2. Henry = political leader of the Huguenots, and many Huguenots traveled to _______ for the wedding. 3. Guise family persuades 4. Charles IX & advisors decided to
X. St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre - 1572 1. Marriage b/t sister of Charles IX (Valois) and Henry of Navarre (Bourbon ruler) 2. Henry = political leader of the Huguenots, and many Huguenots traveled to _______ for the wedding. 3. Guise family persuades 4. Charles IX & advisors decided to
 5. Massacre lasted 3 days 6. 20, 000 Huguenots killed, but __________ survived by promising to convert to_______. 7. KEY: French Monarch and Cath Church blew it!! This massacre turned ________ into_______
5. Massacre lasted 3 days 6. 20, 000 Huguenots killed, but __________ survived by promising to convert to_______. 7. KEY: French Monarch and Cath Church blew it!! This massacre turned ________ into_______
 XI. War of the 3 Henries and Edict of Nantes 1. It’s the Guise vs Valois a) Henry, duke of Guise (Catholic) b) Henry III (succeeded bro Charles IX) c) Henry of Navarre (by now, had converted back to Calvinism)
XI. War of the 3 Henries and Edict of Nantes 1. It’s the Guise vs Valois a) Henry, duke of Guise (Catholic) b) Henry III (succeeded bro Charles IX) c) Henry of Navarre (by now, had converted back to Calvinism)
 2. Ultra-Cath’s vow to put Henry of Guise on throne in place of Henry III 3. H of Guise (backed by Philip II of Spain) seized Paris and forced H III to make him chief minister. 4. H III assassinates H of Guise and joined with H of Navarre to retake Paris 5. H III assassinated by angry monk. 6. H of Navarre takes throne as Henry IV and converts back to Catholicism. a) war is over with his coronation
2. Ultra-Cath’s vow to put Henry of Guise on throne in place of Henry III 3. H of Guise (backed by Philip II of Spain) seized Paris and forced H III to make him chief minister. 4. H III assassinates H of Guise and joined with H of Navarre to retake Paris 5. H III assassinated by angry monk. 6. H of Navarre takes throne as Henry IV and converts back to Catholicism. a) war is over with his coronation
 XII. Edict of Nantes 1. Recognized minority religious rights within 2. Granted Huguenots 3. Limited to 4. A sad note:
XII. Edict of Nantes 1. Recognized minority religious rights within 2. Granted Huguenots 3. Limited to 4. A sad note:


