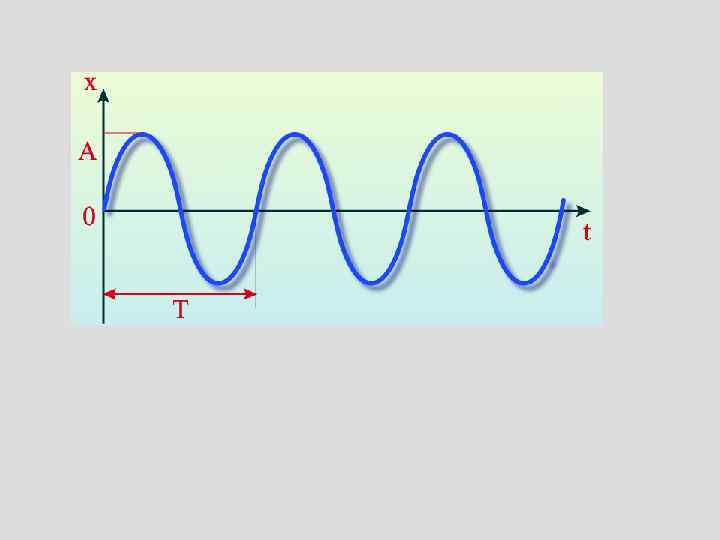
OSCILLATIONS_1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
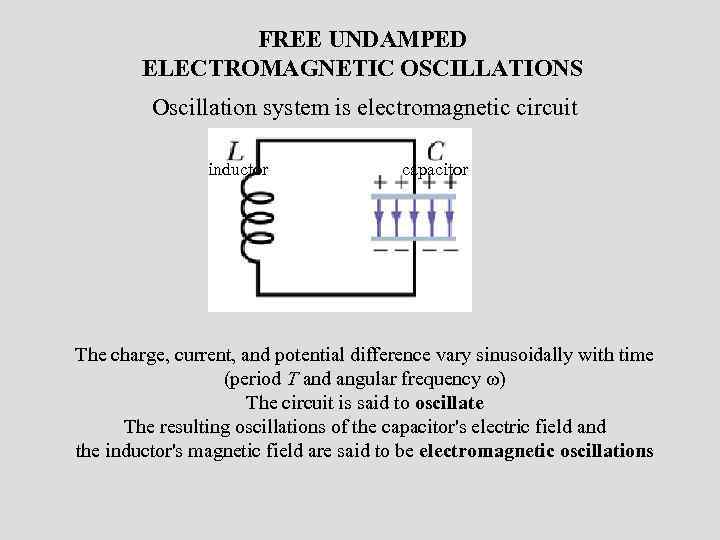 FREE UNDAMPED ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS Oscillation system is electromagnetic circuit inductor capacitor The charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally with time (period T and angular frequency ω) The circuit is said to oscillate The resulting oscillations of the capacitor's electric field and the inductor's magnetic field are said to be electromagnetic oscillations
FREE UNDAMPED ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS Oscillation system is electromagnetic circuit inductor capacitor The charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally with time (period T and angular frequency ω) The circuit is said to oscillate The resulting oscillations of the capacitor's electric field and the inductor's magnetic field are said to be electromagnetic oscillations
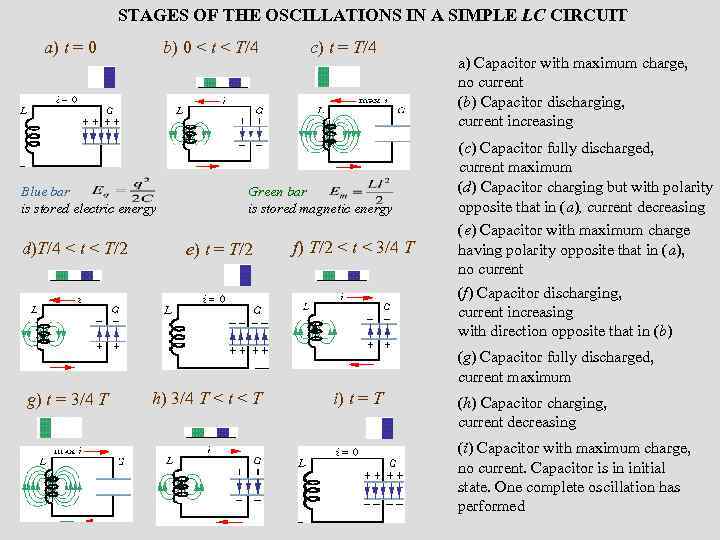 STAGES OF THE OSCILLATIONS IN A SIMPLE LC CIRCUIT a) t = 0 b) 0 < t < T/4 Blue bar is stored electric energy d)T/4 < t < T/2 c) t = T/4 Green bar is stored magnetic energy e) t = T/2 f) T/2 < t < 3/4 T a) Capacitor with maximum charge, no current (b) Capacitor discharging, current increasing (c) Capacitor fully discharged, current maximum (d) Capacitor charging but with polarity opposite that in (a), current decreasing (e) Capacitor with maximum charge having polarity opposite that in (a), no current (f) Capacitor discharging, current increasing with direction opposite that in (b) (g) Capacitor fully discharged, current maximum g) t = 3/4 T h) 3/4 T < t < T i) t = T (h) Capacitor charging, current decreasing (i) Capacitor with maximum charge, no current. Capacitor is in initial state. One complete oscillation has performed
STAGES OF THE OSCILLATIONS IN A SIMPLE LC CIRCUIT a) t = 0 b) 0 < t < T/4 Blue bar is stored electric energy d)T/4 < t < T/2 c) t = T/4 Green bar is stored magnetic energy e) t = T/2 f) T/2 < t < 3/4 T a) Capacitor with maximum charge, no current (b) Capacitor discharging, current increasing (c) Capacitor fully discharged, current maximum (d) Capacitor charging but with polarity opposite that in (a), current decreasing (e) Capacitor with maximum charge having polarity opposite that in (a), no current (f) Capacitor discharging, current increasing with direction opposite that in (b) (g) Capacitor fully discharged, current maximum g) t = 3/4 T h) 3/4 T < t < T i) t = T (h) Capacitor charging, current decreasing (i) Capacitor with maximum charge, no current. Capacitor is in initial state. One complete oscillation has performed
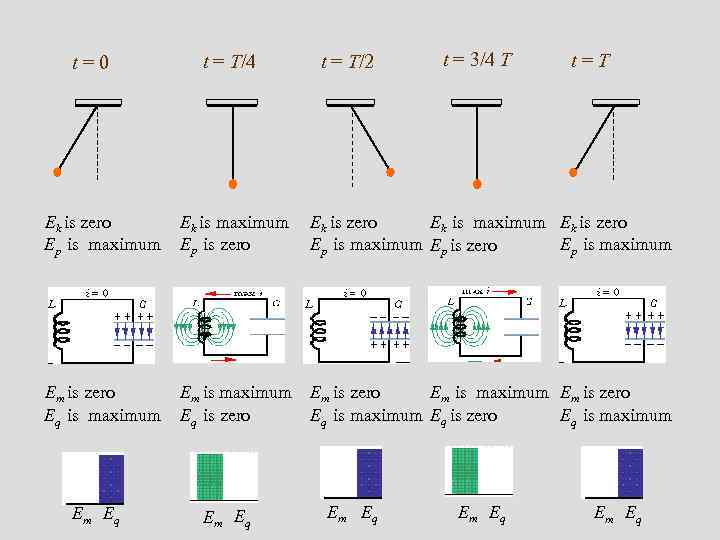 t = 0 t = T/4 t = T/2 t = 3/4 T t = T Ek is zero Ep is maximum Ek is maximum Ep is zero Ek is maximum Ek is zero Ep is maximum Ep is zero Ep is maximum Em is zero Eq is maximum Em is maximum Eq is zero Em is maximum Em is zero Eq is maximum Eq is zero Eq is maximum Em Eq Em Eq
t = 0 t = T/4 t = T/2 t = 3/4 T t = T Ek is zero Ep is maximum Ek is maximum Ep is zero Ek is maximum Ek is zero Ep is maximum Ep is zero Ep is maximum Em is zero Eq is maximum Em is maximum Eq is zero Em is maximum Em is zero Eq is maximum Eq is zero Eq is maximum Em Eq Em Eq
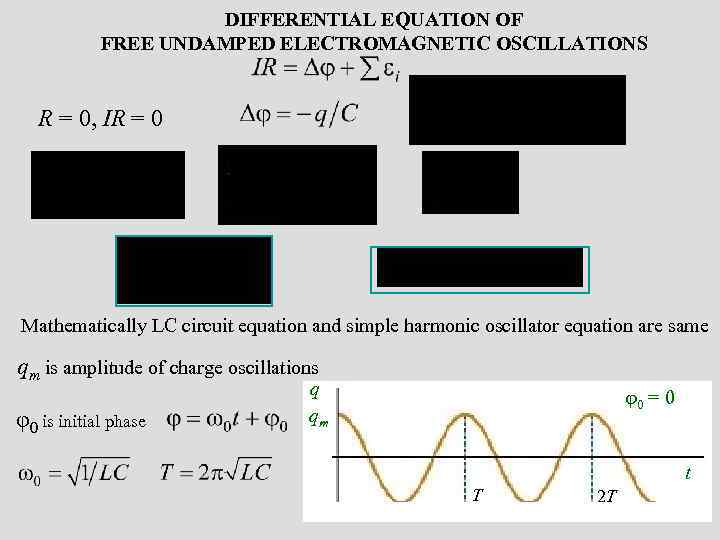 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF FREE UNDAMPED ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS R = 0, IR = 0 Mathematically LC circuit equation and simple harmonic oscillator equation are same qm is amplitude of charge oscillations φ0 is initial phase q qm 0 = 0 t T 2 T
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF FREE UNDAMPED ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS R = 0, IR = 0 Mathematically LC circuit equation and simple harmonic oscillator equation are same qm is amplitude of charge oscillations φ0 is initial phase q qm 0 = 0 t T 2 T
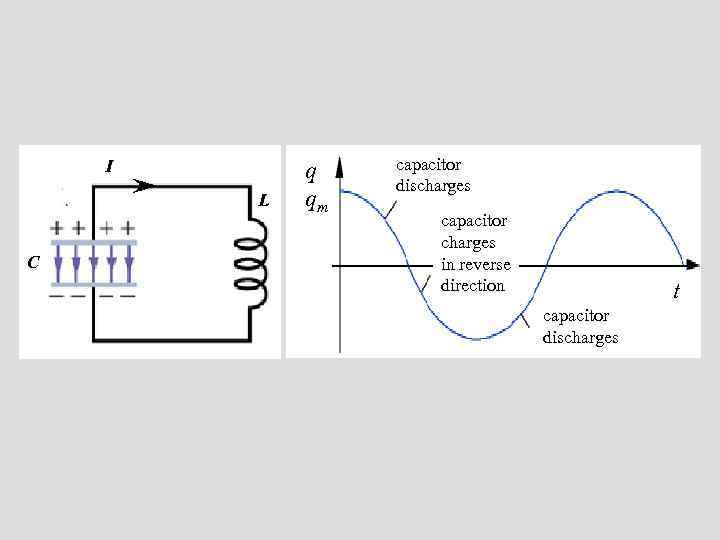 I L C q qm capacitor discharges capacitor charges in reverse direction t capacitor discharges
I L C q qm capacitor discharges capacitor charges in reverse direction t capacitor discharges
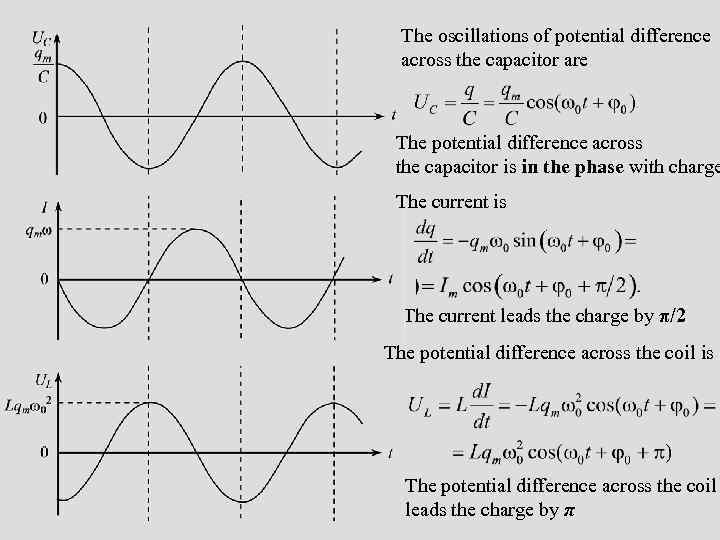 The oscillations of potential difference across the capacitor are The potential difference across the capacitor is in the phase with charge The current is The current leads the charge by π/2 The potential difference across the coil is The potential difference across the coil leads the charge by π
The oscillations of potential difference across the capacitor are The potential difference across the capacitor is in the phase with charge The current is The current leads the charge by π/2 The potential difference across the coil is The potential difference across the coil leads the charge by π
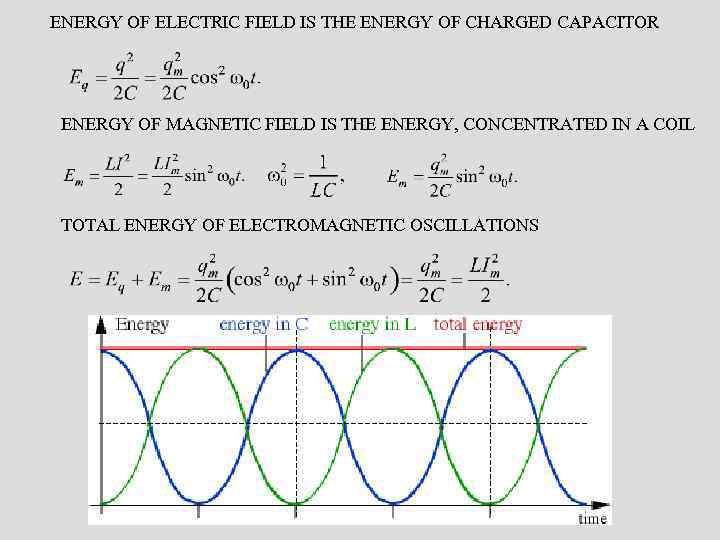 ENERGY OF ELECTRIC FIELD IS THE ENERGY OF CHARGED CAPACITOR ENERGY OF MAGNETIC FIELD IS THE ENERGY, CONCENTRATED IN A COIL TOTAL ENERGY OF ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS
ENERGY OF ELECTRIC FIELD IS THE ENERGY OF CHARGED CAPACITOR ENERGY OF MAGNETIC FIELD IS THE ENERGY, CONCENTRATED IN A COIL TOTAL ENERGY OF ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS
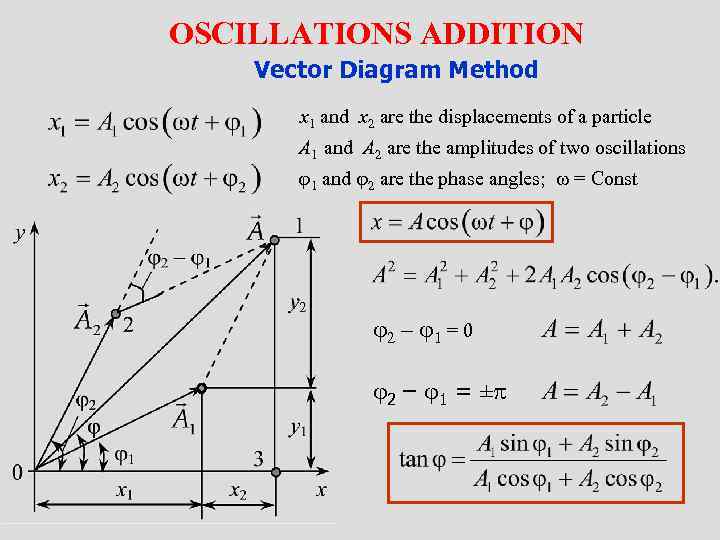 OSCILLATIONS ADDITION Vector Diagram Method x 1 and x 2 are the displacements of a particle A 1 and A 2 are the amplitudes of two oscillations 1 and 2 are the phase angles; = Const 2 – 1 = 0 2 – 1 = ±
OSCILLATIONS ADDITION Vector Diagram Method x 1 and x 2 are the displacements of a particle A 1 and A 2 are the amplitudes of two oscillations 1 and 2 are the phase angles; = Const 2 – 1 = 0 2 – 1 = ±
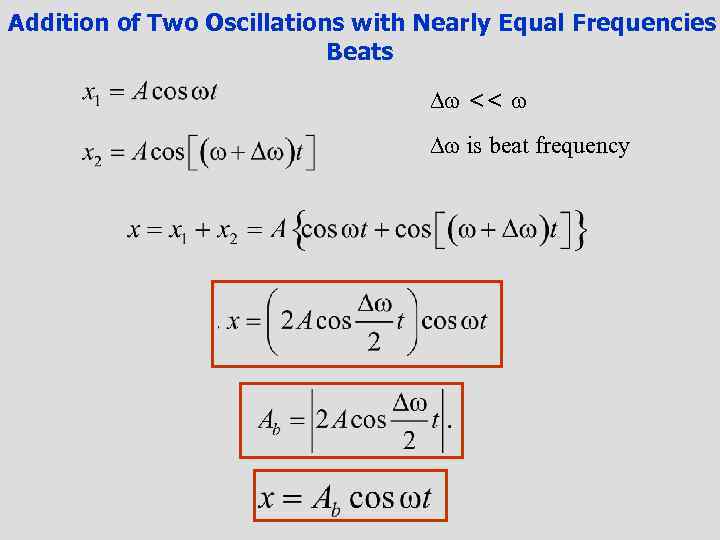 Addition of Two Oscillations with Nearly Equal Frequencies Beats << is beat frequency
Addition of Two Oscillations with Nearly Equal Frequencies Beats << is beat frequency
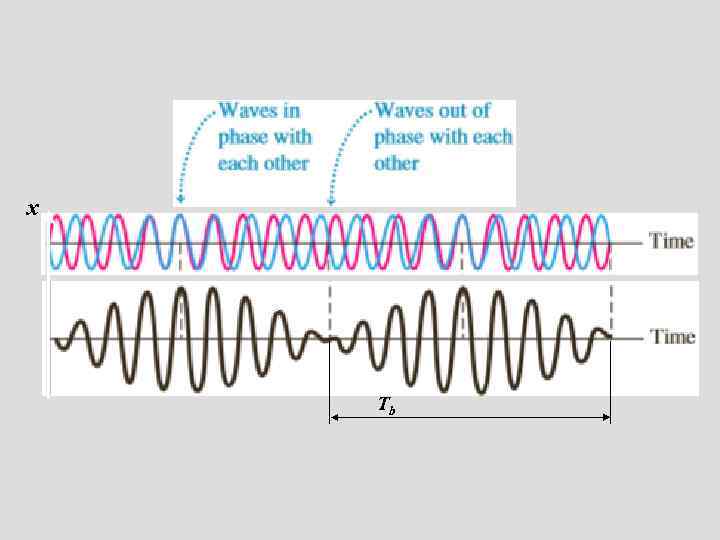 x Аb Tb
x Аb Tb
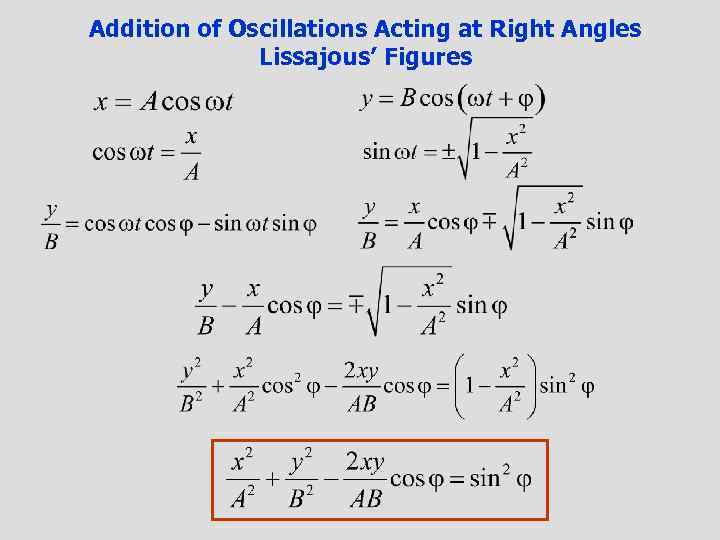 Addition of Oscillations Acting at Right Angles Lissajous’ Figures
Addition of Oscillations Acting at Right Angles Lissajous’ Figures
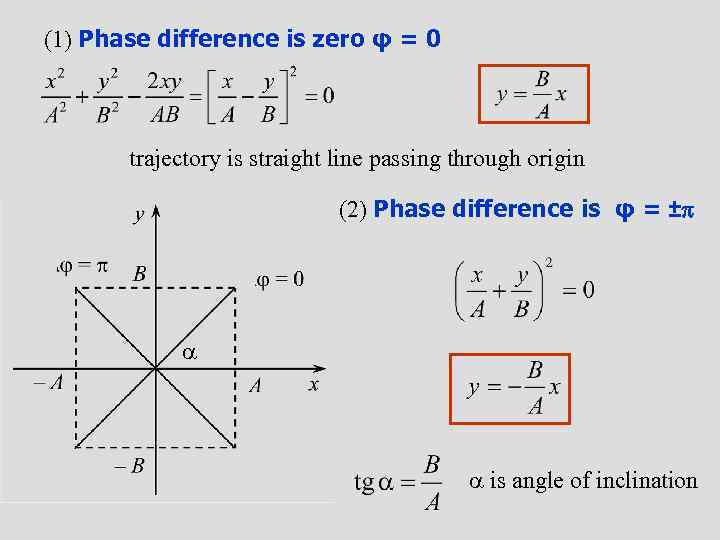 (1) Phase difference is zero φ = 0 trajectory is straight line passing through origin (2) Phase difference is φ = ± is angle of inclination
(1) Phase difference is zero φ = 0 trajectory is straight line passing through origin (2) Phase difference is φ = ± is angle of inclination
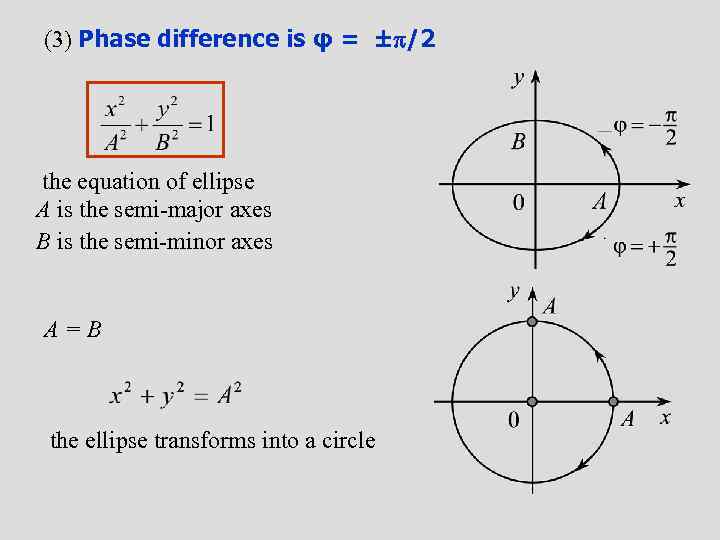 (3) Phase difference is φ = ± /2 the equation of ellipse A is the semi-major axes B is the semi-minor axes A=B the ellipse transforms into a circle
(3) Phase difference is φ = ± /2 the equation of ellipse A is the semi-major axes B is the semi-minor axes A=B the ellipse transforms into a circle
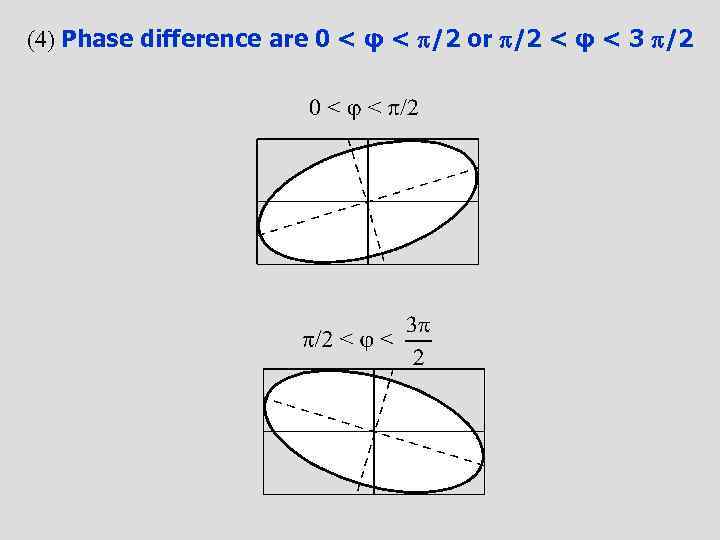 (4) Phase difference are 0 < φ < /2 or /2 < φ < 3 /2
(4) Phase difference are 0 < φ < /2 or /2 < φ < 3 /2
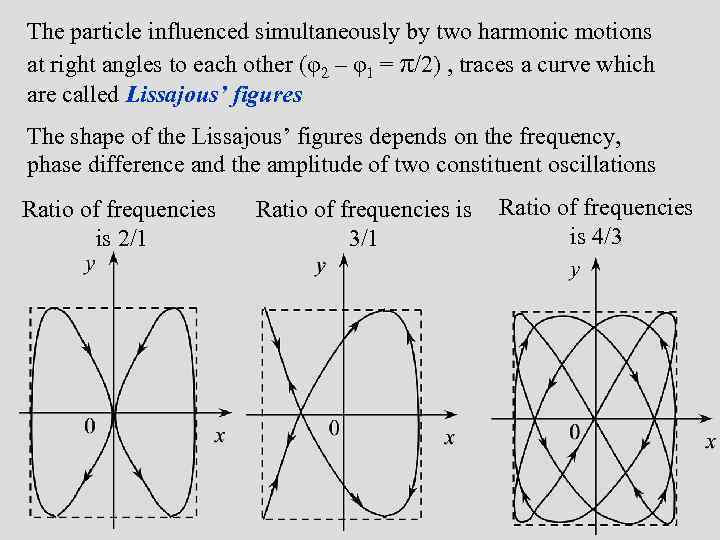 The particle influenced simultaneously by two harmonic motions at right angles to each other (φ2 – φ1 = π/2) , traces a curve which are called Lissajous’ figures The shape of the Lissajous’ figures depends on the frequency, phase difference and the amplitude of two constituent oscillations Ratio of frequencies is 2/1 Ratio of frequencies is 4/3 3/1
The particle influenced simultaneously by two harmonic motions at right angles to each other (φ2 – φ1 = π/2) , traces a curve which are called Lissajous’ figures The shape of the Lissajous’ figures depends on the frequency, phase difference and the amplitude of two constituent oscillations Ratio of frequencies is 2/1 Ratio of frequencies is 4/3 3/1
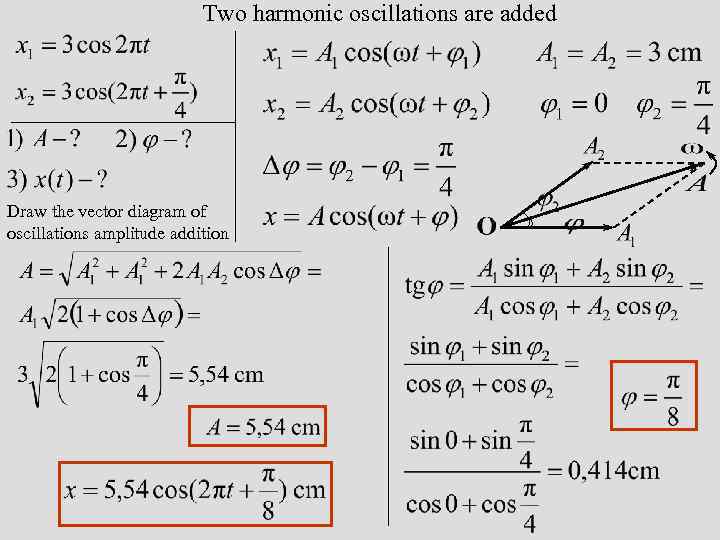 Two harmonic oscillations are added Draw the vector diagram of oscillations amplitude addition
Two harmonic oscillations are added Draw the vector diagram of oscillations amplitude addition