58e875388896b56240ced99708433821.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
Free Slides from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. co m/ Chocolate Lovers Keep Nervous Watch on Volatile Cocoa Prices Post prepared October 10, 2010 Terms of Use: These slides are made available under Creative Commons License Attribution—Share Alike 3. 0. You are free to use these slides as a resource for your economics classes together with whatever textbook you are using. If you like the slides, you may also want to take a look at my textbook, Introduction to Economics, from BVT Publishers.
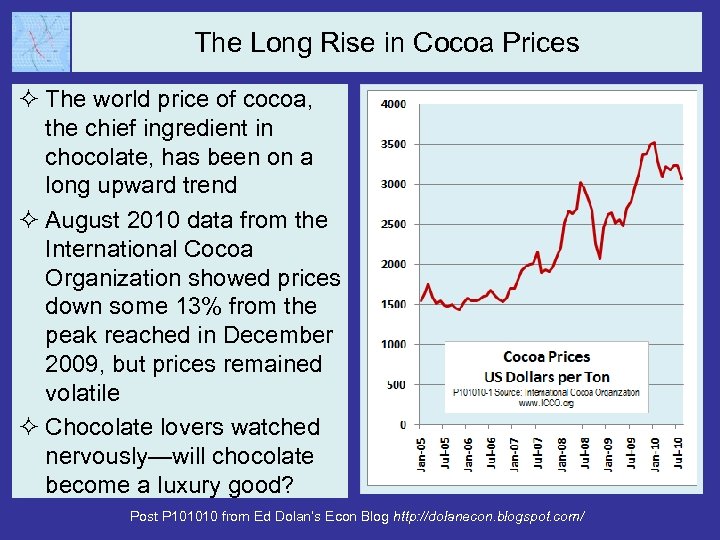
The Long Rise in Cocoa Prices ² The world price of cocoa, the chief ingredient in chocolate, has been on a long upward trend ² August 2010 data from the International Cocoa Organization showed prices down some 13% from the peak reached in December 2009, but prices remained volatile ² Chocolate lovers watched nervously—will chocolate become a luxury good? Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/

Strong Income Elasticity ² One factor driving chocolate prices higher has been strong income elasticity of demand ² In the US, a 10% increase in income has been estimated to raise per capita chocolate consumption by 9. 2% ² In Europe income elasticity is about half that, but chocolate is still a normal good—higher income leads to greater consumption The elasticity data in this post are based on a study by Henri Jason, “Trends in Cocoa and Chocolate Consumption with Particular Reference to Developments in the Major Markets, ” Malaysian International Cocoa Conference, Kuala Lumpur, 20 -21 October 1994 (ICCO, ED(MEM) 686). Data from the paper, but not the original paper itself, can be found on line at http: //www. cs. trinity. edu/~agros/factors_of_demand. htm What could be more luxurious? Photo by Simon James Kent, http: //commons. wikimedia. org/wiki/File: 300 x 300_choc_rose_cake. jpg Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
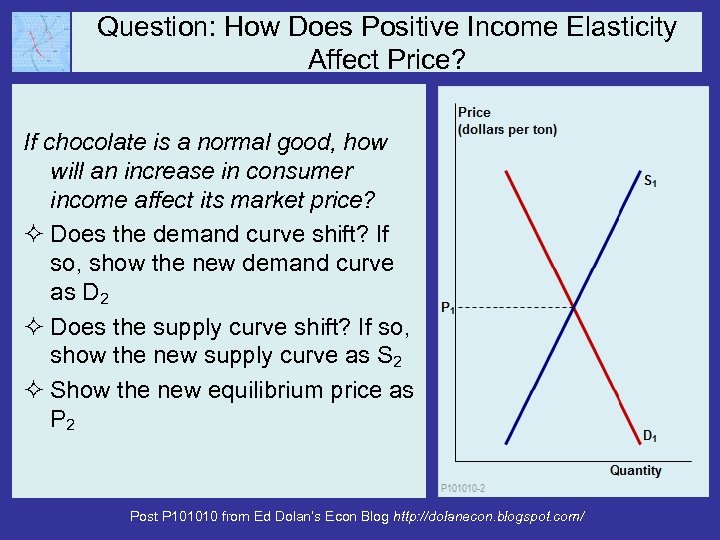
Question: How Does Positive Income Elasticity Affect Price? If chocolate is a normal good, how will an increase in consumer income affect its market price? ² Does the demand curve shift? If so, show the new demand curve as D 2 ² Does the supply curve shift? If so, show the new supply curve as S 2 ² Show the new equilibrium price as P 2 Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
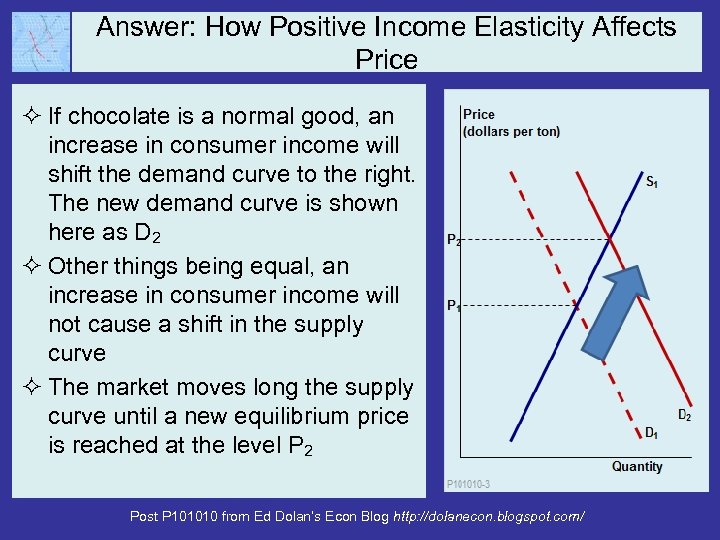
Answer: How Positive Income Elasticity Affects Price ² If chocolate is a normal good, an increase in consumer income will shift the demand curve to the right. The new demand curve is shown here as D 2 ² Other things being equal, an increase in consumer income will not cause a shift in the supply curve ² The market moves long the supply curve until a new equilibrium price is reached at the level P 2 Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/

Short-Run Supply Effects: Growing Conditions ² Cocoa supply, like that of any farm product, is subject to changes in growing conditions ² For example, in 2010, a virus causing stunted shoot disease threatened the crop in the Ivory Coast, the world’s biggest producer ² The virus causes the leaves to turn red and fall off, and ruins the pods ² At the same time, in neighboring Ghana, the second largest producer, favorable weather indicated good prospects for the harvest Healthy Cocoa Pods Photo source: http: //commons. wikimedia. org/wiki/File: Cocoa_Pods. JPG Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
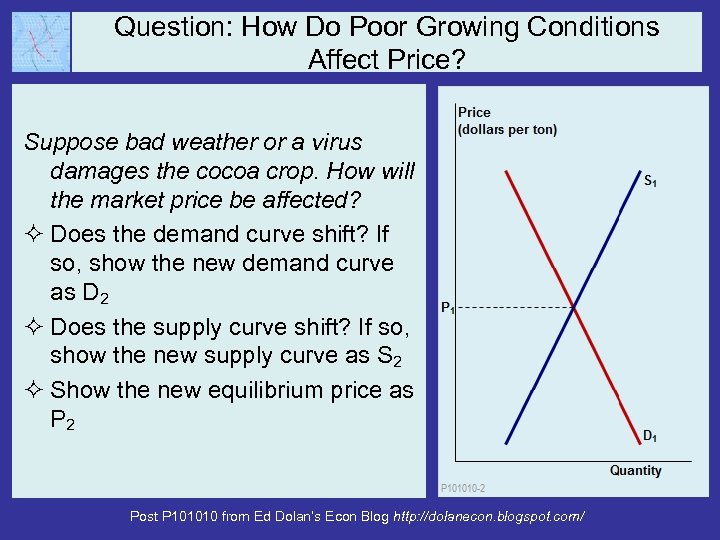
Question: How Do Poor Growing Conditions Affect Price? Suppose bad weather or a virus damages the cocoa crop. How will the market price be affected? ² Does the demand curve shift? If so, show the new demand curve as D 2 ² Does the supply curve shift? If so, show the new supply curve as S 2 ² Show the new equilibrium price as P 2 Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
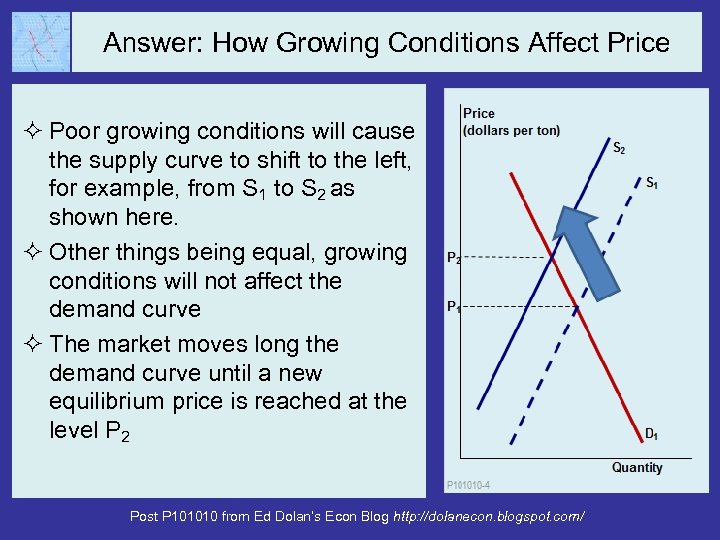
Answer: How Growing Conditions Affect Price ² Poor growing conditions will cause the supply curve to shift to the left, for example, from S 1 to S 2 as shown here. ² Other things being equal, growing conditions will not affect the demand curve ² The market moves long the demand curve until a new equilibrium price is reached at the level P 2 Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
Inelastic Demand Short-Run Price Volatility ² Another factor contributing to the volatility of chocolate prices is very inelastic demand ² Short-run price elasticity of demand in the US is estimated at -0. 2, and even less than that in big consumer countries like France and Germany ² When demand is inelastic, even a small shift in the supply curve causes a large change in the market price Is there any limit to what you would pay for these beauties? Photo by Frank Wouters http: //commons. wikimedia. org/wiki/File: Belgian_chocolates. jpg Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
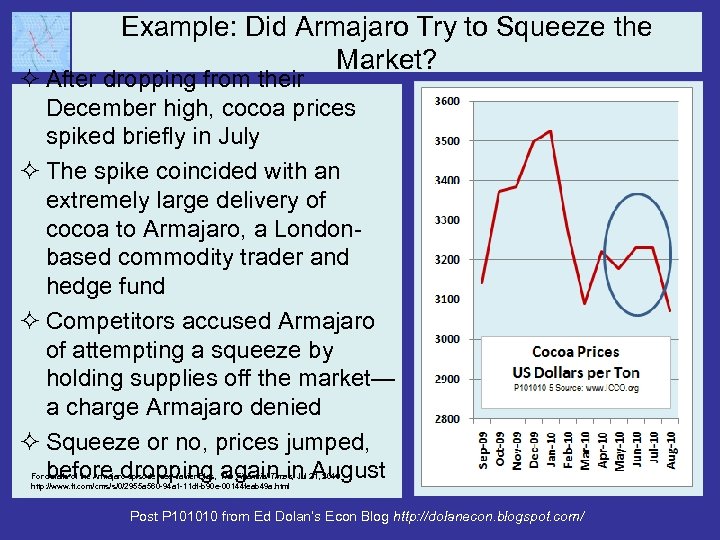
Example: Did Armajaro Try to Squeeze the Market? ² After dropping from their December high, cocoa prices spiked briefly in July ² The spike coincided with an extremely large delivery of cocoa to Armajaro, a Londonbased commodity trader and hedge fund ² Competitors accused Armajaro of attempting a squeeze by holding supplies off the market— a charge Armajaro denied ² Squeeze or no, prices jumped, before dropping again in August For details of the Armajaro episode, see Javier Blas, The Financial Times, Jul 21, 2010 http: //www. ft. com/cms/s/0/2955 a 560 -94 a 1 -11 df-b 90 e-00144 feab 49 a. html Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
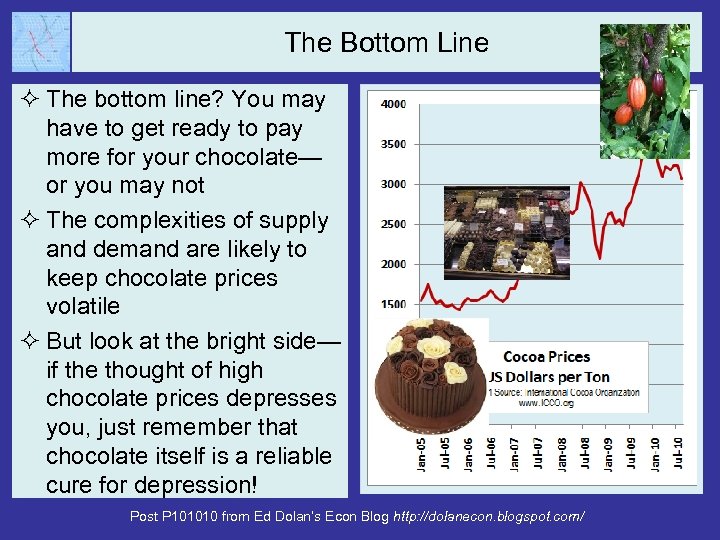
The Bottom Line ² The bottom line? You may have to get ready to pay more for your chocolate— or you may not ² The complexities of supply and demand are likely to keep chocolate prices volatile ² But look at the bright side— if the thought of high chocolate prices depresses you, just remember that chocolate itself is a reliable cure for depression! Post P 101010 from Ed Dolan’s Econ Blog http: //dolanecon. blogspot. com/
58e875388896b56240ced99708433821.ppt