fraud ver 2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 32
 FRAUD KPMG K-Foundation 2012 Team 2: Cookie-Lovers
FRAUD KPMG K-Foundation 2012 Team 2: Cookie-Lovers
 Agenda § § § Explain the meaning of fraud Identify and describe the prerequisities of fraud Describe examples of fraud in a business organization Define money laundering Explain the possible implications of fraud to the company Describe the duties and responsibilities of management for prevention and discovery of fraud
Agenda § § § Explain the meaning of fraud Identify and describe the prerequisities of fraud Describe examples of fraud in a business organization Define money laundering Explain the possible implications of fraud to the company Describe the duties and responsibilities of management for prevention and discovery of fraud
 What is fraud? Fraud is an intentional act by one or more individuals among management, those charged with governance, employees or third parties, involving the use of deception to obtain an unjust or illegal disadvantage
What is fraud? Fraud is an intentional act by one or more individuals among management, those charged with governance, employees or third parties, involving the use of deception to obtain an unjust or illegal disadvantage
 Should be distinguished Fraud Error Irregularity Misstatement • Intentional act • Unintentional mistake • Objective – unjust or illegal advantage • Inevitable part of human nature • Something contrary to a particular rule or standard • Something stated wrongly • Can arise due to fraud, irregularity or error
Should be distinguished Fraud Error Irregularity Misstatement • Intentional act • Unintentional mistake • Objective – unjust or illegal advantage • Inevitable part of human nature • Something contrary to a particular rule or standard • Something stated wrongly • Can arise due to fraud, irregularity or error
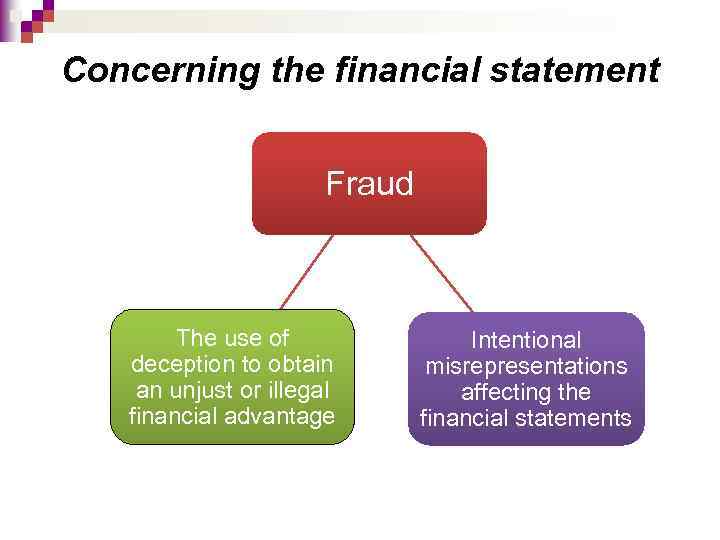 Concerning the financial statement Fraud The use of deception to obtain an unjust or illegal financial advantage Intentional misrepresentations affecting the financial statements
Concerning the financial statement Fraud The use of deception to obtain an unjust or illegal financial advantage Intentional misrepresentations affecting the financial statements
 Examples of fraud n Deliberate falsification of documents/records n Deliberate ignoring of errors requiring correction n Deliberate suppression of relevant information
Examples of fraud n Deliberate falsification of documents/records n Deliberate ignoring of errors requiring correction n Deliberate suppression of relevant information
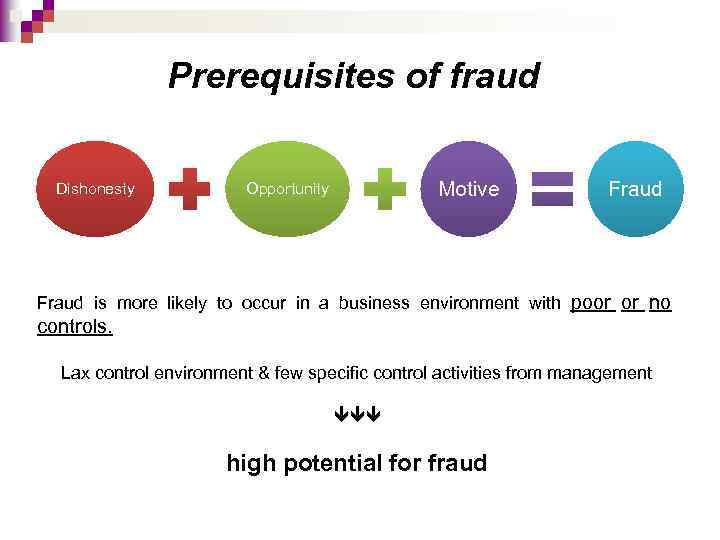 Prerequisites of fraud Dishonesty Motive Opportunity Fraud is more likely to occur in a business environment with poor or no controls. Lax control environment & few specific control activities from management high potential for fraud
Prerequisites of fraud Dishonesty Motive Opportunity Fraud is more likely to occur in a business environment with poor or no controls. Lax control environment & few specific control activities from management high potential for fraud
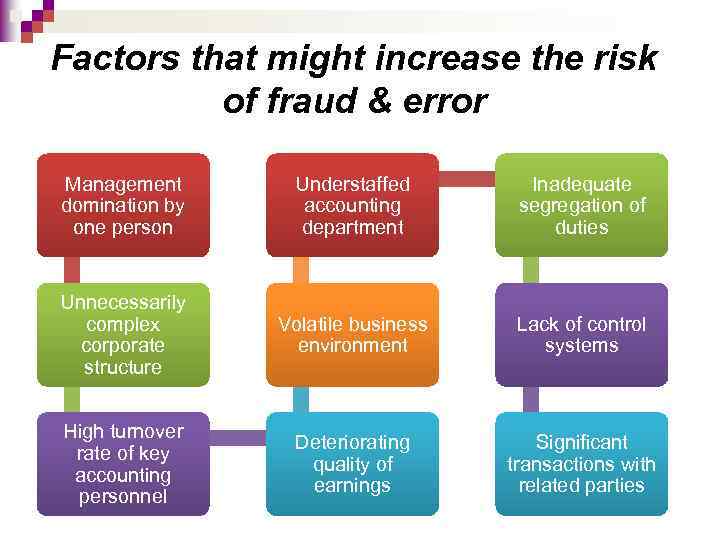 Factors that might increase the risk of fraud & error Management domination by one person Understaffed accounting department Inadequate segregation of duties Unnecessarily complex corporate structure Volatile business environment Lack of control systems High turnover rate of key accounting personnel Deteriorating quality of earnings Significant transactions with related parties
Factors that might increase the risk of fraud & error Management domination by one person Understaffed accounting department Inadequate segregation of duties Unnecessarily complex corporate structure Volatile business environment Lack of control systems High turnover rate of key accounting personnel Deteriorating quality of earnings Significant transactions with related parties
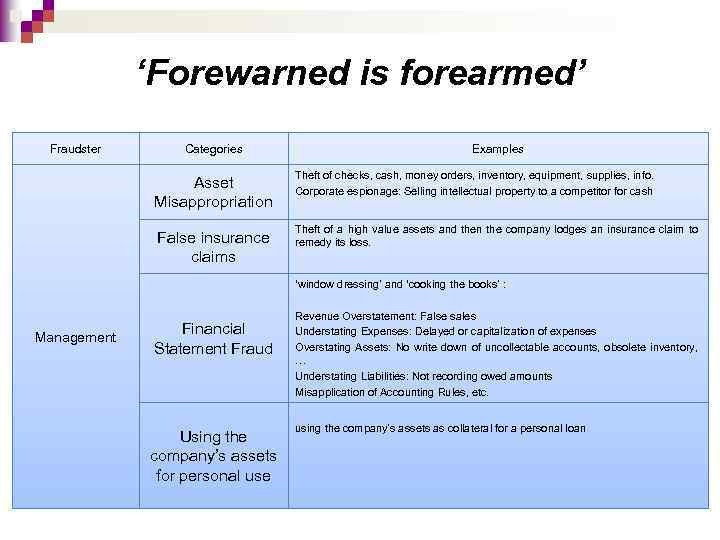 ‘Forewarned is forearmed’ Fraudster Categories Examples Asset Misappropriation Theft of checks, cash, money orders, inventory, equipment, supplies, info. Corporate espionage: Selling intellectual property to a competitor for cash False insurance claims Theft of a high value assets and then the company lodges an insurance claim to remedy its loss. ‘window dressing’ and ‘cooking the books’ : Management Financial Statement Fraud Using the company’s assets for personal use Revenue Overstatement: False sales Understating Expenses: Delayed or capitalization of expenses Overstating Assets: No write down of uncollectable accounts, obsolete inventory, … Understating Liabilities: Not recording owed amounts Misapplication of Accounting Rules, etc. using the company’s assets as collateral for a personal loan
‘Forewarned is forearmed’ Fraudster Categories Examples Asset Misappropriation Theft of checks, cash, money orders, inventory, equipment, supplies, info. Corporate espionage: Selling intellectual property to a competitor for cash False insurance claims Theft of a high value assets and then the company lodges an insurance claim to remedy its loss. ‘window dressing’ and ‘cooking the books’ : Management Financial Statement Fraud Using the company’s assets for personal use Revenue Overstatement: False sales Understating Expenses: Delayed or capitalization of expenses Overstating Assets: No write down of uncollectable accounts, obsolete inventory, … Understating Liabilities: Not recording owed amounts Misapplication of Accounting Rules, etc. using the company’s assets as collateral for a personal loan
 Financial Statement Fraud n Before bankruptcy: 20, 000 staff ¨ revenues of $101 billion in 2000 ¨ one of the world's leading electricity, natural gas, communications, and pulp and paper companies ¨ n Discovered facts: Debts and losses were put into entities formed "offshore“ ¨ Enron's recorded assets and profits were inflated or even wholly fraudulent and nonexistent ¨
Financial Statement Fraud n Before bankruptcy: 20, 000 staff ¨ revenues of $101 billion in 2000 ¨ one of the world's leading electricity, natural gas, communications, and pulp and paper companies ¨ n Discovered facts: Debts and losses were put into entities formed "offshore“ ¨ Enron's recorded assets and profits were inflated or even wholly fraudulent and nonexistent ¨
 Fraud is carried out by: Management Employees 3 rd parties • Financial statement fraud (window dressing and cooking the books) • Misappropriation of assets • False insurance claims • Using the company’s assets for personal use • Sales ledger fraud: steeling cash sales and cheques received • Purchase ledger fraud • Skimming schemes • Payroll fraud • • False billing fraud Bank account fraud advance fee fraud Ponzi schemes
Fraud is carried out by: Management Employees 3 rd parties • Financial statement fraud (window dressing and cooking the books) • Misappropriation of assets • False insurance claims • Using the company’s assets for personal use • Sales ledger fraud: steeling cash sales and cheques received • Purchase ledger fraud • Skimming schemes • Payroll fraud • • False billing fraud Bank account fraud advance fee fraud Ponzi schemes
 Ponzi schemes n A Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment offer that involves paying abnormally high returns to early investors out of the new money paid in by subsequent investors, rather than a genuine underlying business. n n MMM established in 1989. The company started attracting money from private investors, promising annual returns of up to 1000% Madoff's market-maker division traded up to 5% of the total volume made on the New York Stock Exchange n n Madoff Investment Securities Madoff's returns were most likely due to front running his firm's brokerage clients
Ponzi schemes n A Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment offer that involves paying abnormally high returns to early investors out of the new money paid in by subsequent investors, rather than a genuine underlying business. n n MMM established in 1989. The company started attracting money from private investors, promising annual returns of up to 1000% Madoff's market-maker division traded up to 5% of the total volume made on the New York Stock Exchange n n Madoff Investment Securities Madoff's returns were most likely due to front running his firm's brokerage clients
 Fraudulent financial reporting - «cooking the books» - «earnings management» - «creative accounting»
Fraudulent financial reporting - «cooking the books» - «earnings management» - «creative accounting»
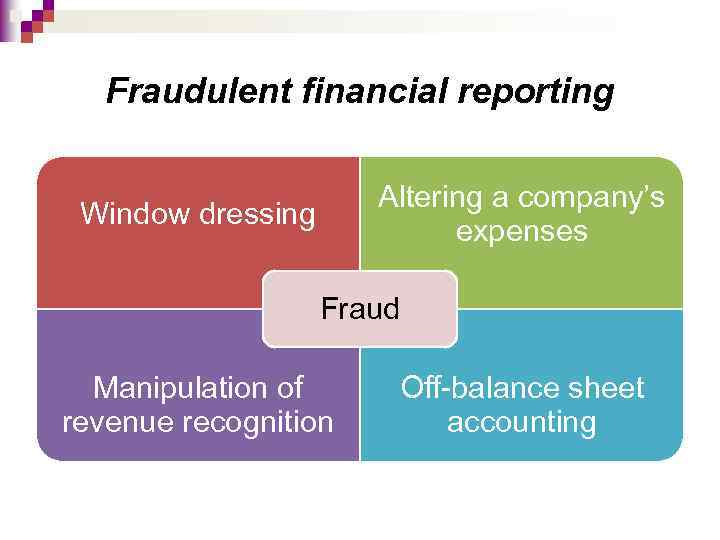 Fraudulent financial reporting Altering a company’s expenses Window dressing Fraud Manipulation of revenue recognition Off-balance sheet accounting
Fraudulent financial reporting Altering a company’s expenses Window dressing Fraud Manipulation of revenue recognition Off-balance sheet accounting
 Fraudulent financial reporting Window dressing Aim: Improve the appearance of the compamy's financial statement. Delaying or accelerating company’s Aim: Improve reported profits or the next year's reported profit figure. expenses Manipulation of revenue recognition Off-balance sheet accounting Aim: Recognise revenue in the first year of the contract Aim: Exclude certain assets and liabilities from the published balance sheet
Fraudulent financial reporting Window dressing Aim: Improve the appearance of the compamy's financial statement. Delaying or accelerating company’s Aim: Improve reported profits or the next year's reported profit figure. expenses Manipulation of revenue recognition Off-balance sheet accounting Aim: Recognise revenue in the first year of the contract Aim: Exclude certain assets and liabilities from the published balance sheet
 Money laundering n Transformation of “dirty money” into “clean” money
Money laundering n Transformation of “dirty money” into “clean” money
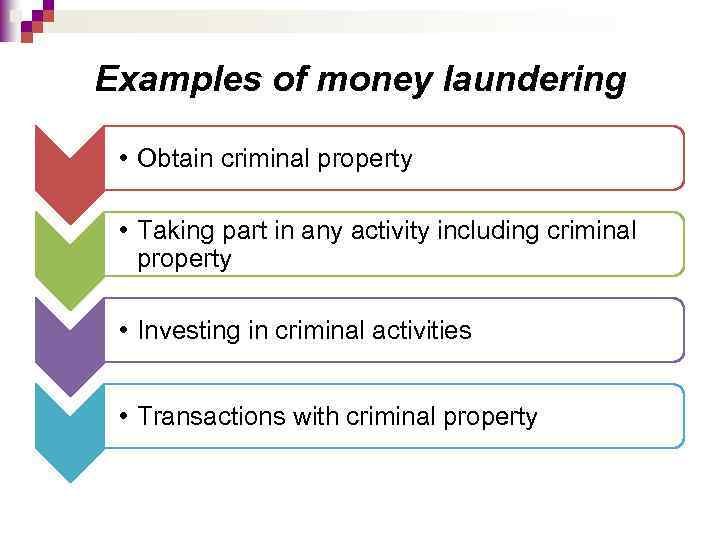 Examples of money laundering • Obtain criminal property • Taking part in any activity including criminal property • Investing in criminal activities • Transactions with criminal property
Examples of money laundering • Obtain criminal property • Taking part in any activity including criminal property • Investing in criminal activities • Transactions with criminal property
 Controls and procedures required by law n n Drawing attention to suspicious transactions The course of spending large sums of money Finding existing clients Making a special post in the company to supervise suspicious activity
Controls and procedures required by law n n Drawing attention to suspicious transactions The course of spending large sums of money Finding existing clients Making a special post in the company to supervise suspicious activity
 Smurfing VS
Smurfing VS
 Quiz on history of fraud By Cookie Lovers
Quiz on history of fraud By Cookie Lovers
 1) What the Chicago gangster Al Capone was convicted for?
1) What the Chicago gangster Al Capone was convicted for?
 2) How much money obtained Bernard Madoff through his criminal activities? a) $105 billion b) $65 billion c) $67 billion
2) How much money obtained Bernard Madoff through his criminal activities? a) $105 billion b) $65 billion c) $67 billion
 3) In what industry World. Com company, notorious for its $107 billion accounting tricks, was operating?
3) In what industry World. Com company, notorious for its $107 billion accounting tricks, was operating?
 To whom suspicions of money should be reported? Relevant companies are required to put in place controls and procedures to identify money laundering transactions.
To whom suspicions of money should be reported? Relevant companies are required to put in place controls and procedures to identify money laundering transactions.
 To whom suspicions of money should be reported? It is important that a business has a defined reporting process for any suspected money laundering. This will normally involve: Employees reporting suspicious activity to the Nominated Officer The Nominated Officer investigating further If there are grounds for reasonable suspicion, the Nominated Officer reporting to the relevant authorities
To whom suspicions of money should be reported? It is important that a business has a defined reporting process for any suspected money laundering. This will normally involve: Employees reporting suspicious activity to the Nominated Officer The Nominated Officer investigating further If there are grounds for reasonable suspicion, the Nominated Officer reporting to the relevant authorities
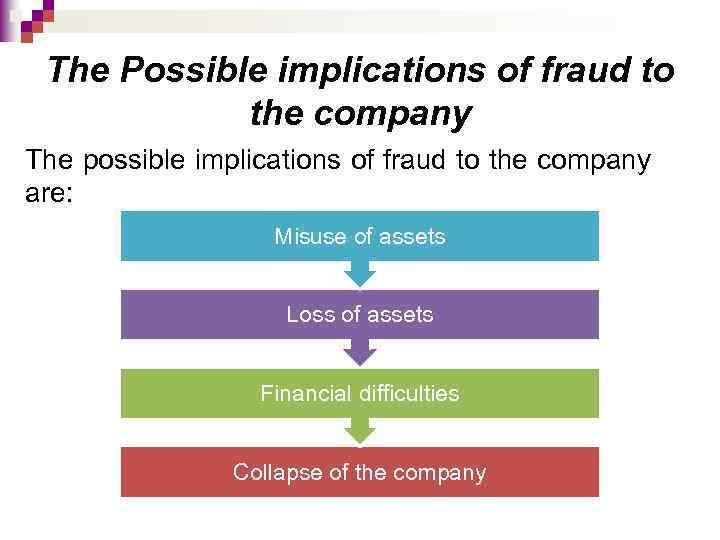 The Possible implications of fraud to the company The possible implications of fraud to the company are: Misuse of assets Loss of assets Financial difficulties Collapse of the company
The Possible implications of fraud to the company The possible implications of fraud to the company are: Misuse of assets Loss of assets Financial difficulties Collapse of the company
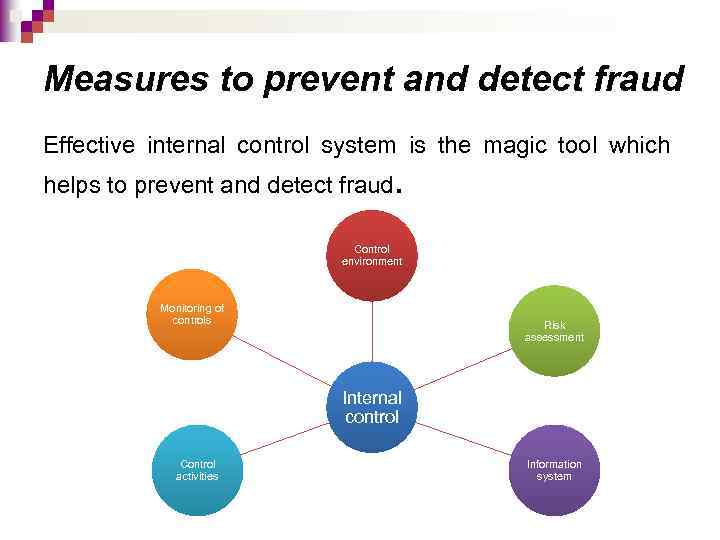 Measures to prevent and detect fraud Effective internal control system is the magic tool which helps to prevent and detect fraud. Control environment Monitoring of controls Risk assessment Internal control Control activities Information system
Measures to prevent and detect fraud Effective internal control system is the magic tool which helps to prevent and detect fraud. Control environment Monitoring of controls Risk assessment Internal control Control activities Information system
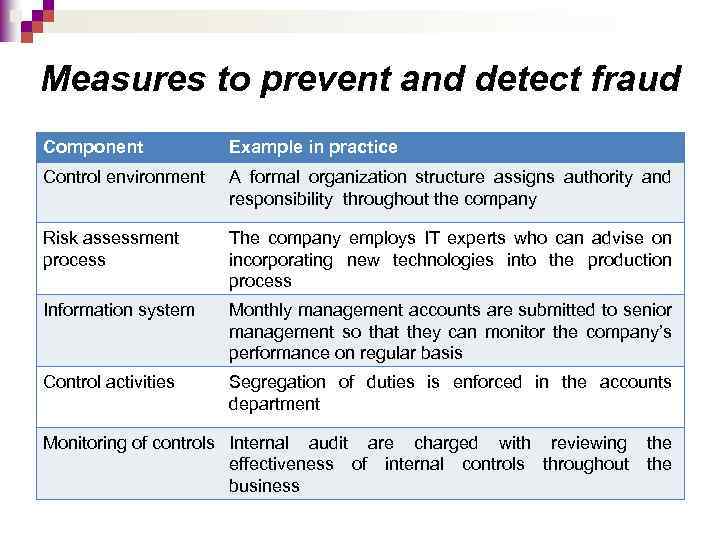 Measures to prevent and detect fraud Component Example in practice Control environment A formal organization structure assigns authority and responsibility throughout the company Risk assessment process The company employs IT experts who can advise on incorporating new technologies into the production process Information system Monthly management accounts are submitted to senior management so that they can monitor the company’s performance on regular basis Control activities Segregation of duties is enforced in the aсcounts department Monitoring of controls Internal audit are charged with reviewing the effectiveness of internal controls throughout the business
Measures to prevent and detect fraud Component Example in practice Control environment A formal organization structure assigns authority and responsibility throughout the company Risk assessment process The company employs IT experts who can advise on incorporating new technologies into the production process Information system Monthly management accounts are submitted to senior management so that they can monitor the company’s performance on regular basis Control activities Segregation of duties is enforced in the aсcounts department Monitoring of controls Internal audit are charged with reviewing the effectiveness of internal controls throughout the business
 ДЕНИС
ДЕНИС
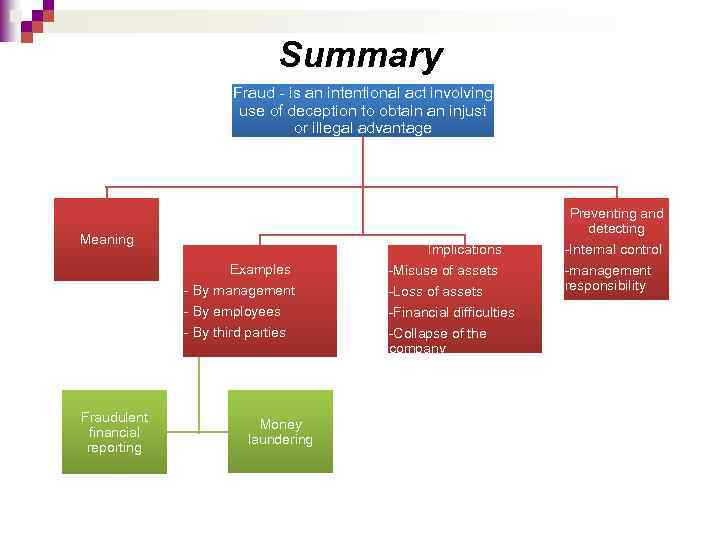 Summary Fraud - is an intentional act involving use of deception to obtain an injust or illegal advantage Meaning Implications Examples - By management - By employees - By third parties Fraudulent financial reporting Money laundering -Misuse of assets -Loss of assets -Financial difficulties -Collapse of the company Preventing and detecting -Internal control -management responsibility
Summary Fraud - is an intentional act involving use of deception to obtain an injust or illegal advantage Meaning Implications Examples - By management - By employees - By third parties Fraudulent financial reporting Money laundering -Misuse of assets -Loss of assets -Financial difficulties -Collapse of the company Preventing and detecting -Internal control -management responsibility
 We are ready to find what is hidden!
We are ready to find what is hidden!
 Thanks for your attention!
Thanks for your attention!


