ch-11-fraudppt2564.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Fraud Auditing Chapter 11
Fraud Auditing Chapter 11
 Types of Fraudulent financial reporting Misappropriation of assets
Types of Fraudulent financial reporting Misappropriation of assets
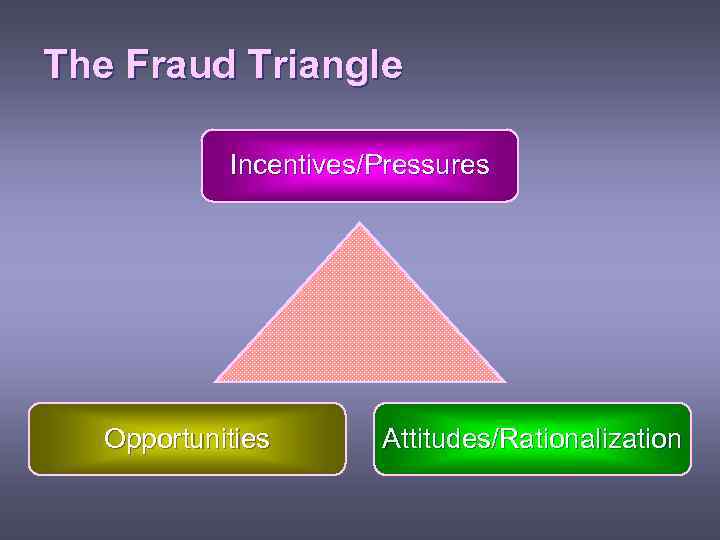 The Fraud Triangle Incentives/Pressures Opportunities Attitudes/Rationalization
The Fraud Triangle Incentives/Pressures Opportunities Attitudes/Rationalization
 Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting Financial stability or profitability is threatened by economic, industry, or entity operating conditions. Excessive pressure exists for management to meet debt requirements. Personal net worth is materially threatened.
Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting Financial stability or profitability is threatened by economic, industry, or entity operating conditions. Excessive pressure exists for management to meet debt requirements. Personal net worth is materially threatened.
 Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting There are significant accounting estimates that are difficult to verify. There is ineffective oversight over financial reporting. High turnover or ineffective accounting internal Audit staff.
Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting There are significant accounting estimates that are difficult to verify. There is ineffective oversight over financial reporting. High turnover or ineffective accounting internal Audit staff.
 Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting Little communication and support of the entity’s core values is evident. A history of violations of laws is known. Management has a practice of making overly aggressive or unrealistic forecasts.
Examples of Risks Factors for Fraudulent Reporting Little communication and support of the entity’s core values is evident. A history of violations of laws is known. Management has a practice of making overly aggressive or unrealistic forecasts.
 Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets Personal financial obligations create pressure to misappropriate assets. Adverse relationships between management and employees motivate employees to misappropriate assets.
Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets Personal financial obligations create pressure to misappropriate assets. Adverse relationships between management and employees motivate employees to misappropriate assets.
 Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets There is a presence of large amounts of cash on hand or inventory items. There is an inadequate internal control over assets.
Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets There is a presence of large amounts of cash on hand or inventory items. There is an inadequate internal control over assets.
 Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets Disregard for the need to monitor or reduce risk of misappropriating assets exists. There is a disregard for internal controls.
Examples of Risks Factors for Misappropriation of Assets Disregard for the need to monitor or reduce risk of misappropriating assets exists. There is a disregard for internal controls.
 Assessing the Risk of Fraud SAS 99 provides guidance to auditors in assessing the risk of fraud.
Assessing the Risk of Fraud SAS 99 provides guidance to auditors in assessing the risk of fraud.
 Professional Skepticism SAS 1 states that, in exercising professional skepticism, an auditor “neither assumes that management is dishonest nor assumes unquestioned honesty. ”
Professional Skepticism SAS 1 states that, in exercising professional skepticism, an auditor “neither assumes that management is dishonest nor assumes unquestioned honesty. ”
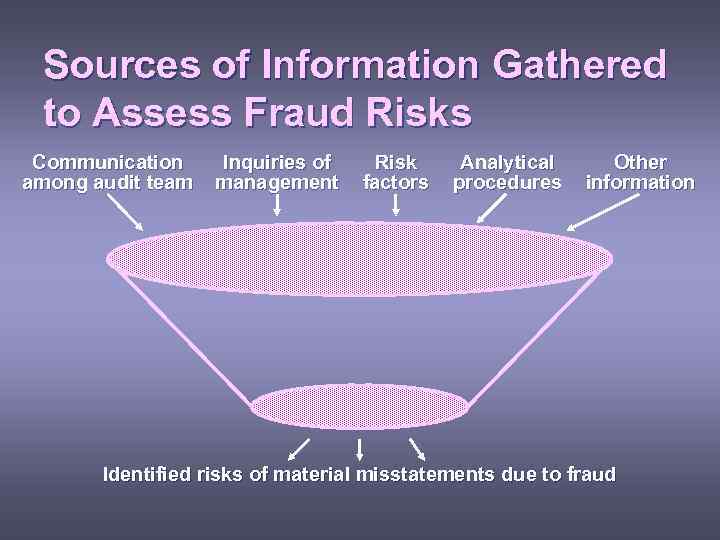 Sources of Information Gathered to Assess Fraud Risks Communication among audit team Inquiries of management Risk factors Analytical procedures Other information Identified risks of material misstatements due to fraud
Sources of Information Gathered to Assess Fraud Risks Communication among audit team Inquiries of management Risk factors Analytical procedures Other information Identified risks of material misstatements due to fraud
 Identify corporate governance and other control environment factors that reduce fraud risks.
Identify corporate governance and other control environment factors that reduce fraud risks.
 Corporate Governance Oversight to Reduce Fraud Risks 1. Create and maintain a culture of honesty and high ethics. 2. Evaluate fraud risks and implement programs and controls to mitigate identified fraud risks. 3. Develop an appropriate fraud oversight process.
Corporate Governance Oversight to Reduce Fraud Risks 1. Create and maintain a culture of honesty and high ethics. 2. Evaluate fraud risks and implement programs and controls to mitigate identified fraud risks. 3. Develop an appropriate fraud oversight process.
 Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Organizational code of conduct General employee conduct Conflicts of interest Outside activities, employment, and directorships
Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Organizational code of conduct General employee conduct Conflicts of interest Outside activities, employment, and directorships
 Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Relationships with clients and suppliers Gifts, entertainment, and favors Kickbacks and secret commissions Organization funds and other assets
Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Relationships with clients and suppliers Gifts, entertainment, and favors Kickbacks and secret commissions Organization funds and other assets
 Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Organization records and communications Dealing with outside people and organizations Prompt communications Privacy and confidentiality
Example Elements for a Code of Conduct Organization records and communications Dealing with outside people and organizations Prompt communications Privacy and confidentiality
 Organizational Factors Contributing to Risk of Fraud Collusion between employees and third parties Inadequate internal controls Management override of internal controls 2003 1998 48 31 33 39 58 59 31 36 36 1994
Organizational Factors Contributing to Risk of Fraud Collusion between employees and third parties Inadequate internal controls Management override of internal controls 2003 1998 48 31 33 39 58 59 31 36 36 1994
 Organizational Factors Contributing to Risk of Fraud Collusion between employees and management Lack of control over management be directors Ineffective or nonexistent ethics or compliance program 2003 1998 15 19 23 12 11 6 10 8 7 1994
Organizational Factors Contributing to Risk of Fraud Collusion between employees and management Lack of control over management be directors Ineffective or nonexistent ethics or compliance program 2003 1998 15 19 23 12 11 6 10 8 7 1994
 Learning Objective 5 Develop responses to identified fraud risks.
Learning Objective 5 Develop responses to identified fraud risks.
 Responding to the Risk of Fraud Change the overall conduct of the audit to respond to identified fraud risks. Design and perform audit procedures to address identified risks. Design and perform procedures to address the risk of management override of controls.
Responding to the Risk of Fraud Change the overall conduct of the audit to respond to identified fraud risks. Design and perform audit procedures to address identified risks. Design and perform procedures to address the risk of management override of controls.
 Specific Fraud Risk Areas Revenue and accounts receivable fraud risks Inventory fraud risks Purchases and accounts payable fraud risks
Specific Fraud Risk Areas Revenue and accounts receivable fraud risks Inventory fraud risks Purchases and accounts payable fraud risks
 Methods of Uncovering Fraud 77% 51% 52% 65% 43% 47% Internal controls Internal audit 63% 58% 51% Notification by employee 2003 1998 1994
Methods of Uncovering Fraud 77% 51% 52% 65% 43% 47% Internal controls Internal audit 63% 58% 51% Notification by employee 2003 1998 1994
 Methods of Uncovering Fraud 54% 37% 28% 41% 35% 26% Accident Anonymous tip 34% 41% 34% Notification by customer 2003 1998 1994
Methods of Uncovering Fraud 54% 37% 28% 41% 35% 26% Accident Anonymous tip 34% 41% 34% Notification by customer 2003 1998 1994
 Methods of Uncovering Fraud Notification by regulatory or law enforcement agency 19% 16% 8% 16% 11% 15% Notification by vendor 12% 4% 5% External audit 2003 1998 1994
Methods of Uncovering Fraud Notification by regulatory or law enforcement agency 19% 16% 8% 16% 11% 15% Notification by vendor 12% 4% 5% External audit 2003 1998 1994
 Responding to Misstatements that May be the Result of Fraud When fraud is suspected, the auditor gathers additional information to determine whether fraud actually exists.
Responding to Misstatements that May be the Result of Fraud When fraud is suspected, the auditor gathers additional information to determine whether fraud actually exists.
 End of Chapter 11
End of Chapter 11


