7829a8639e43c2993525552b8b9c9d54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Frame Relay, ATM and VPN 1
Frame Relay, ATM and VPN 1
 Packet-Switched Services u Offered by Carriers u X. 25 u Old, u Frame slow, and not sufficiently cheaper than frame relay Relay u Speeds in main range of user demand u Attractive prices u Dominates the market today u ATM u High speeds and costs 2
Packet-Switched Services u Offered by Carriers u X. 25 u Old, u Frame slow, and not sufficiently cheaper than frame relay Relay u Speeds in main range of user demand u Attractive prices u Dominates the market today u ATM u High speeds and costs 2
 X. 25 Packet-Switched Data Networks u Oldest u Low packet switched network service (1970 s) speed (maximum around 64 kbps) u Mature: u Uses easy to implement PVCs u Reliable u Mostly service, so latency in transmission replaced by Frame Relay 3
X. 25 Packet-Switched Data Networks u Oldest u Low packet switched network service (1970 s) speed (maximum around 64 kbps) u Mature: u Uses easy to implement PVCs u Reliable u Mostly service, so latency in transmission replaced by Frame Relay 3
 Frame Relay Packet-Switched Data Networks u Software u Uses upgrade to X. 25 switches PVCs u Unreliable, so much faster on same switches u Good speed range: 56 kbps - 40 Mbps: Meets most corporate needs (most under 2 Mbps) u Priced aggressively to kill leased lines (succeeding) u Best-selling packet switched network service See more here. 4
Frame Relay Packet-Switched Data Networks u Software u Uses upgrade to X. 25 switches PVCs u Unreliable, so much faster on same switches u Good speed range: 56 kbps - 40 Mbps: Meets most corporate needs (most under 2 Mbps) u Priced aggressively to kill leased lines (succeeding) u Best-selling packet switched network service See more here. 4
 ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) u Offers u 622 very high speeds Mbps, 2. 5 Gbps to 40 Gbps u Connection-oriented u Quality traffic (PVCs), unreliable of Service (QOS) guarantees critical u Minimize latency (delays) u Inherent reliability (low loss rate) u Technical details beyond this course Building more bandwidth than needed 5
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) u Offers u 622 very high speeds Mbps, 2. 5 Gbps to 40 Gbps u Connection-oriented u Quality traffic (PVCs), unreliable of Service (QOS) guarantees critical u Minimize latency (delays) u Inherent reliability (low loss rate) u Technical details beyond this course Building more bandwidth than needed 5
 ATM u Speeds are beyond most corporate needs today u High costs u Seen as the next generation u But Frame Relay keeps increasing in speed in low Mbps range where market demand is highest u Used u by providers e. g. AT&T, to support both ATM and Frame Relay for customers See AT&T ATM pricing 6
ATM u Speeds are beyond most corporate needs today u High costs u Seen as the next generation u But Frame Relay keeps increasing in speed in low Mbps range where market demand is highest u Used u by providers e. g. AT&T, to support both ATM and Frame Relay for customers See AT&T ATM pricing 6
 Pricing Packet Switched Services u Customer u Access u Port u Per Premises Equipment Line to Point of Presence Speed PVC Price u Distance and Traffic Volume 7
Pricing Packet Switched Services u Customer u Access u Port u Per Premises Equipment Line to Point of Presence Speed PVC Price u Distance and Traffic Volume 7
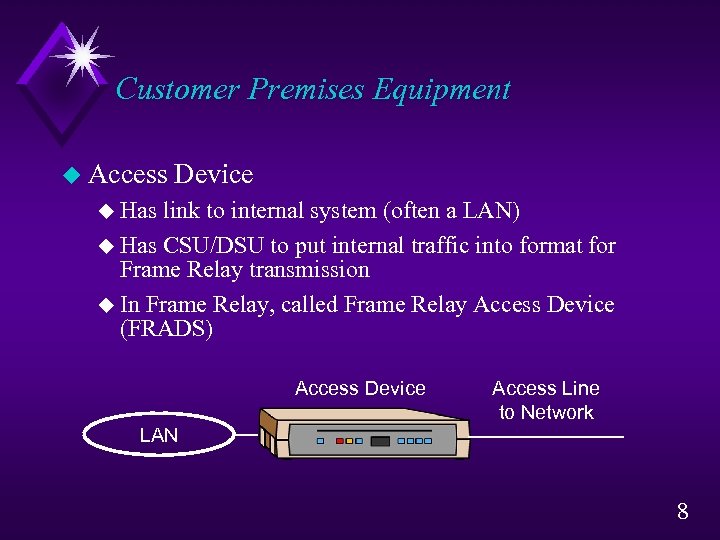 Customer Premises Equipment u Access Device u Has link to internal system (often a LAN) u Has CSU/DSU to put internal traffic into format for Frame Relay transmission u In Frame Relay, called Frame Relay Access Device (FRADS) Access Device Access Line to Network LAN 8
Customer Premises Equipment u Access Device u Has link to internal system (often a LAN) u Has CSU/DSU to put internal traffic into format for Frame Relay transmission u In Frame Relay, called Frame Relay Access Device (FRADS) Access Device Access Line to Network LAN 8
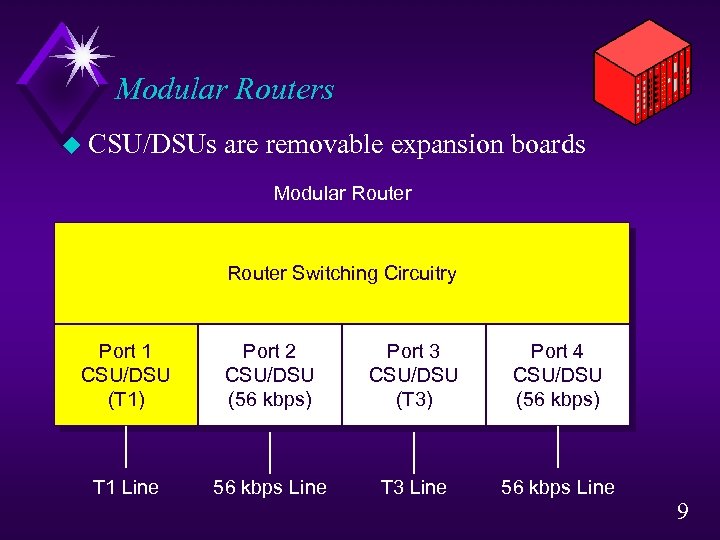 Modular Routers u CSU/DSUs are removable expansion boards Modular Router Switching Circuitry Port 1 CSU/DSU (T 1) Port 2 CSU/DSU (56 kbps) Port 3 CSU/DSU (T 3) Port 4 CSU/DSU (56 kbps) T 1 Line 56 kbps Line T 3 Line 56 kbps Line 9
Modular Routers u CSU/DSUs are removable expansion boards Modular Router Switching Circuitry Port 1 CSU/DSU (T 1) Port 2 CSU/DSU (56 kbps) Port 3 CSU/DSU (T 3) Port 4 CSU/DSU (56 kbps) T 1 Line 56 kbps Line T 3 Line 56 kbps Line 9
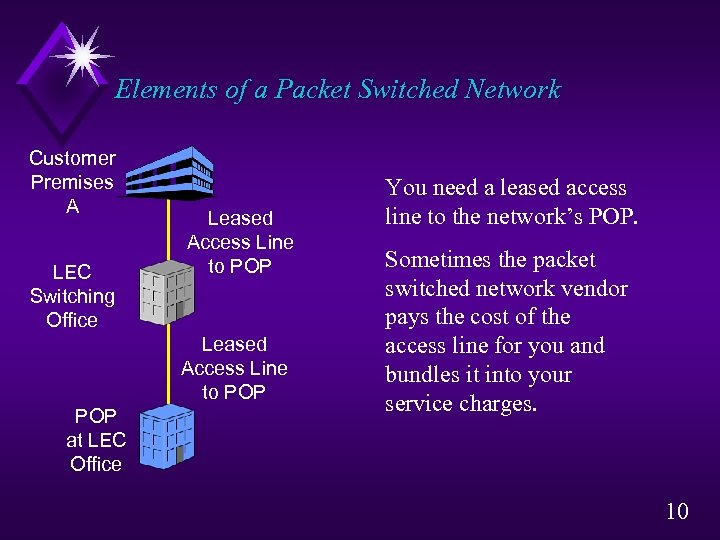 Elements of a Packet Switched Network Customer Premises A LEC Switching Office Leased Access Line to POP POP at LEC Office You need a leased access line to the network’s POP. Sometimes the packet switched network vendor pays the cost of the access line for you and bundles it into your service charges. 10
Elements of a Packet Switched Network Customer Premises A LEC Switching Office Leased Access Line to POP POP at LEC Office You need a leased access line to the network’s POP. Sometimes the packet switched network vendor pays the cost of the access line for you and bundles it into your service charges. 10
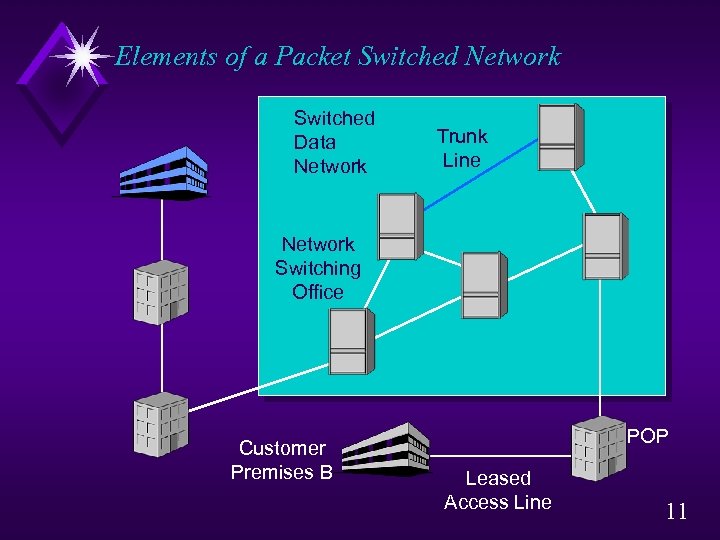 Elements of a Packet Switched Network Switched Data Network Trunk Line Network Switching Office Customer Premises B POP Leased Access Line 11
Elements of a Packet Switched Network Switched Data Network Trunk Line Network Switching Office Customer Premises B POP Leased Access Line 11
 Pricing of Frame Relay u Speed of the Access Line from Site to Network u Determines maximum transmission rate to the network u Often called the Port Speed (not in the book) u Often the most important price determinant u Must be fast enough for needs See Frame Relay over DSL -- a price issue 12
Pricing of Frame Relay u Speed of the Access Line from Site to Network u Determines maximum transmission rate to the network u Often called the Port Speed (not in the book) u Often the most important price determinant u Must be fast enough for needs See Frame Relay over DSL -- a price issue 12
 Pricing of Frame Relay u In Some Frame Relay networks, two speeds u Committed Information Rate (pretty much guaranteed) u Available Bit Rate (like flying standby) for bursts. Not guaranteed. u Price depends both on CIR and ABR u Access line speed must be fast enough for ABR 13
Pricing of Frame Relay u In Some Frame Relay networks, two speeds u Committed Information Rate (pretty much guaranteed) u Available Bit Rate (like flying standby) for bursts. Not guaranteed. u Price depends both on CIR and ABR u Access line speed must be fast enough for ABR 13
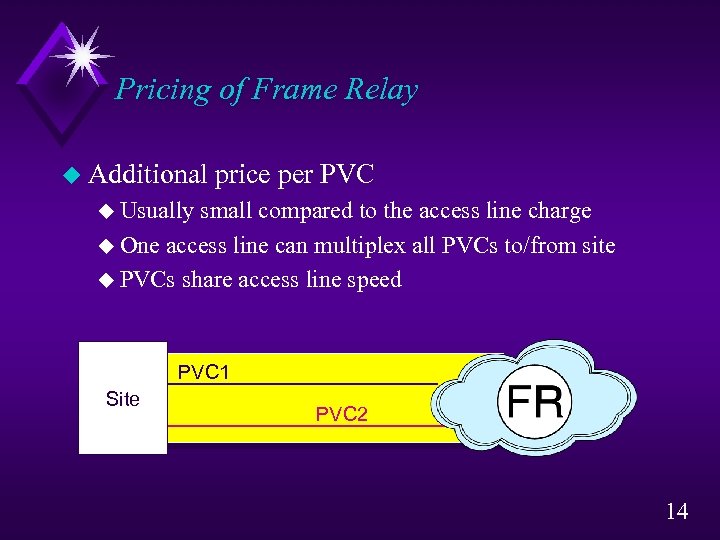 Pricing of Frame Relay u Additional price per PVC u Usually small compared to the access line charge u One access line can multiplex all PVCs to/from site u PVCs share access line speed PVC 1 Site PVC 2 14
Pricing of Frame Relay u Additional price per PVC u Usually small compared to the access line charge u One access line can multiplex all PVCs to/from site u PVCs share access line speed PVC 1 Site PVC 2 14
 Calculations u Situation u You have four sites u You want any one to be able to reach any other u Questions u How many PVCs do you need? u How many access lines do you need? 15
Calculations u Situation u You have four sites u You want any one to be able to reach any other u Questions u How many PVCs do you need? u How many access lines do you need? 15
 Calculations u PVCs u If you have N sites, there are N(N-1)/2 possible connections u In this case, you would have 4(3)/2 or 6 possible connections u Some vendors count this as 6 PVCs, others as 12 PVCs u Access Lines u You would need four access lines (one for each site) u Each will multiplex 3 PVCs u Must be fast enough for the needs of communication with the three other sites 16
Calculations u PVCs u If you have N sites, there are N(N-1)/2 possible connections u In this case, you would have 4(3)/2 or 6 possible connections u Some vendors count this as 6 PVCs, others as 12 PVCs u Access Lines u You would need four access lines (one for each site) u Each will multiplex 3 PVCs u Must be fast enough for the needs of communication with the three other sites 16
 Pricing of Frame Relay u May Depend on Distance u But often a flat monthly rate throughout the carrier’s service area u May Depend on Traffic u But often a flat monthly rate based only on the speed of the access line 17
Pricing of Frame Relay u May Depend on Distance u But often a flat monthly rate throughout the carrier’s service area u May Depend on Traffic u But often a flat monthly rate based only on the speed of the access line 17
 Leased Lines vs. Packet-Switched Data Networks u Leased Lines u Point-to-point, inexpensive for thick routes u Inflexible: must be established ahead of time u Packet Switched Networks u Also must be established ahead of time for PVCs u Competitor for leased line networks u Priced aggressively u Carrier does all the management u Killing the leased line business 18
Leased Lines vs. Packet-Switched Data Networks u Leased Lines u Point-to-point, inexpensive for thick routes u Inflexible: must be established ahead of time u Packet Switched Networks u Also must be established ahead of time for PVCs u Competitor for leased line networks u Priced aggressively u Carrier does all the management u Killing the leased line business 18
 Circuit-Switched vs. Packet-Switched Services u Circuit Switched Networks (ISDN, Switched 56) u Any-to-any connectivity by dialing number u Highest speed is ISDN: 64 kbps to 128 kbps u Packet Switched Networks (X. 25, Frame Relay, ATM) u PVCs make them primarily competitors to leased lines u Megabit to gigabit speeds u SVCs may provide any-to-any flexibility in the future u IP services, MPLS, ATM trends Note: more MPLS details 19
Circuit-Switched vs. Packet-Switched Services u Circuit Switched Networks (ISDN, Switched 56) u Any-to-any connectivity by dialing number u Highest speed is ISDN: 64 kbps to 128 kbps u Packet Switched Networks (X. 25, Frame Relay, ATM) u PVCs make them primarily competitors to leased lines u Megabit to gigabit speeds u SVCs may provide any-to-any flexibility in the future u IP services, MPLS, ATM trends Note: more MPLS details 19
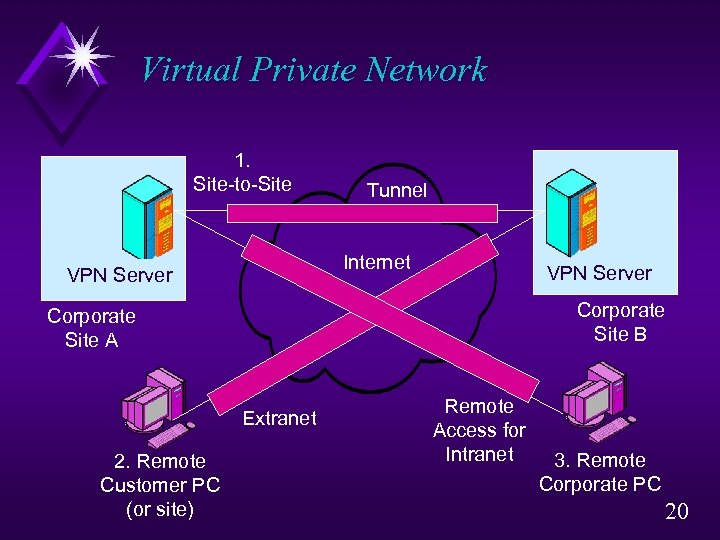 Virtual Private Network 1. Site-to-Site Tunnel Internet VPN Server Corporate Site B Corporate Site A Extranet 2. Remote Customer PC (or site) Remote Access for Intranet 3. Remote Corporate PC 20
Virtual Private Network 1. Site-to-Site Tunnel Internet VPN Server Corporate Site B Corporate Site A Extranet 2. Remote Customer PC (or site) Remote Access for Intranet 3. Remote Corporate PC 20
 VPN advantage u Virtual Private Network (VPN) u Transmission over the Internet with added security u Some analysts include transmission over a PSDN with added security u Why VPNs? u PSDNs are not interconnected u Only good for internal corporate communication u But Internet reaches almost all sites in all firms u Low transmission cost per bit transmitted 21
VPN advantage u Virtual Private Network (VPN) u Transmission over the Internet with added security u Some analysts include transmission over a PSDN with added security u Why VPNs? u PSDNs are not interconnected u Only good for internal corporate communication u But Internet reaches almost all sites in all firms u Low transmission cost per bit transmitted 21
 VPN issues u VPN Problems u Latency and Sound Quality u Internet can be congested u Creates latency, reduces sound quality u Use a single ISP as for Vo. IP (voice over IP) u Security u PPTP for remote access is popular u IPsec for site-to-site transmission is popular u New IP services (see MCI offerings) 22
VPN issues u VPN Problems u Latency and Sound Quality u Internet can be congested u Creates latency, reduces sound quality u Use a single ISP as for Vo. IP (voice over IP) u Security u PPTP for remote access is popular u IPsec for site-to-site transmission is popular u New IP services (see MCI offerings) 22
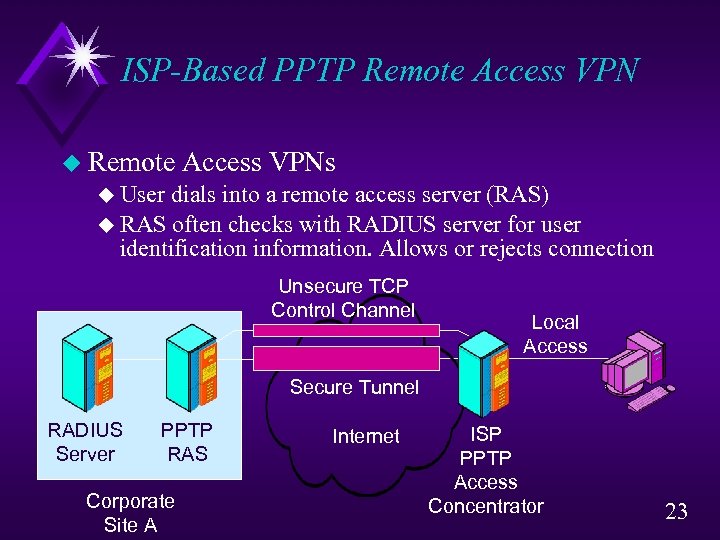 ISP-Based PPTP Remote Access VPN u Remote Access VPNs u User dials into a remote access server (RAS) u RAS often checks with RADIUS server for user identification information. Allows or rejects connection Unsecure TCP Control Channel Local Access Secure Tunnel RADIUS Server PPTP RAS Corporate Site A Internet ISP PPTP Access Concentrator 23
ISP-Based PPTP Remote Access VPN u Remote Access VPNs u User dials into a remote access server (RAS) u RAS often checks with RADIUS server for user identification information. Allows or rejects connection Unsecure TCP Control Channel Local Access Secure Tunnel RADIUS Server PPTP RAS Corporate Site A Internet ISP PPTP Access Concentrator 23
 VPN and PPTP u Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol u Available in Windows since Windows 95 u No need for added software on clients u Provided by many ISPs u PPTP access concentrator at ISP access point u Some security limitations u No security between user site and ISP u No message-by-message authentication of user u Uses unprotected TCP control channel 24
VPN and PPTP u Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol u Available in Windows since Windows 95 u No need for added software on clients u Provided by many ISPs u PPTP access concentrator at ISP access point u Some security limitations u No security between user site and ISP u No message-by-message authentication of user u Uses unprotected TCP control channel 24
 IPsec alternatives u IP Security (IPsec) u Tunnel mode: sets up a secure tunnel between IPsec servers at two sites u No security within sites u No need to install IPsec software on stations u Transfer mode: set up secure connection between two end hosts u Protected even on internal networks u Must install IPsec software on stations 25
IPsec alternatives u IP Security (IPsec) u Tunnel mode: sets up a secure tunnel between IPsec servers at two sites u No security within sites u No need to install IPsec software on stations u Transfer mode: set up secure connection between two end hosts u Protected even on internal networks u Must install IPsec software on stations 25
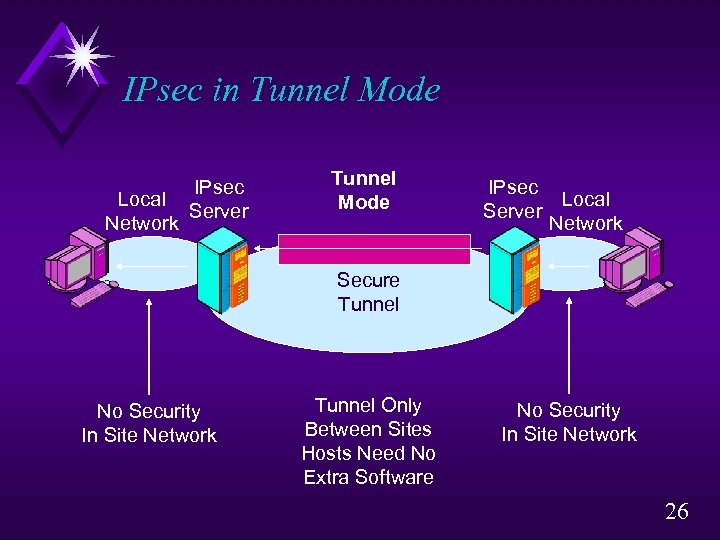 IPsec in Tunnel Mode Local Network IPsec Server Tunnel Mode IPsec Local Server Network Secure Tunnel No Security In Site Network Tunnel Only Between Sites Hosts Need No Extra Software No Security In Site Network 26
IPsec in Tunnel Mode Local Network IPsec Server Tunnel Mode IPsec Local Server Network Secure Tunnel No Security In Site Network Tunnel Only Between Sites Hosts Need No Extra Software No Security In Site Network 26
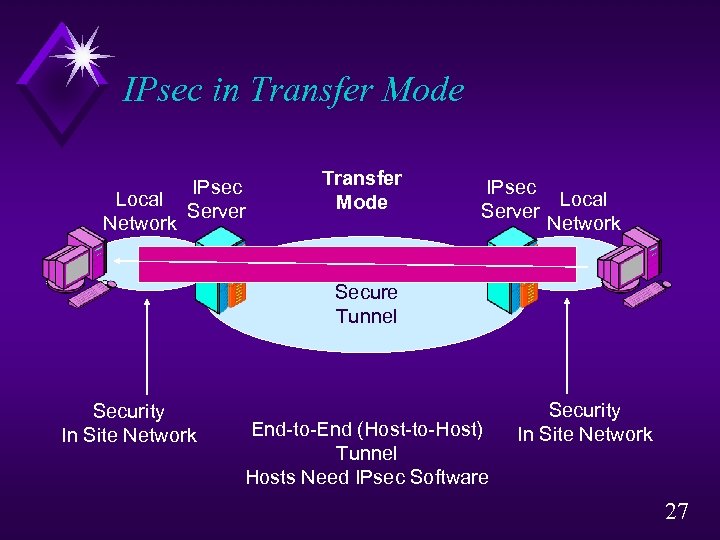 IPsec in Transfer Mode Local Network IPsec Server Transfer Mode IPsec Local Server Network Secure Tunnel Security In Site Network End-to-End (Host-to-Host) Tunnel Hosts Need IPsec Software Security In Site Network 27
IPsec in Transfer Mode Local Network IPsec Server Transfer Mode IPsec Local Server Network Secure Tunnel Security In Site Network End-to-End (Host-to-Host) Tunnel Hosts Need IPsec Software Security In Site Network 27
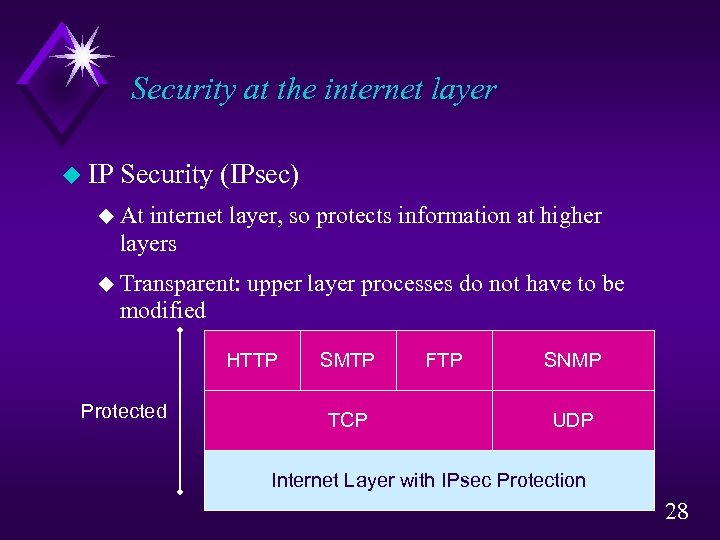 Security at the internet layer u IP Security (IPsec) u At internet layer, so protects information at higher layers u Transparent: upper layer processes do not have to be modified HTTP Protected SMTP TCP FTP SNMP UDP Internet Layer with IPsec Protection 28
Security at the internet layer u IP Security (IPsec) u At internet layer, so protects information at higher layers u Transparent: upper layer processes do not have to be modified HTTP Protected SMTP TCP FTP SNMP UDP Internet Layer with IPsec Protection 28
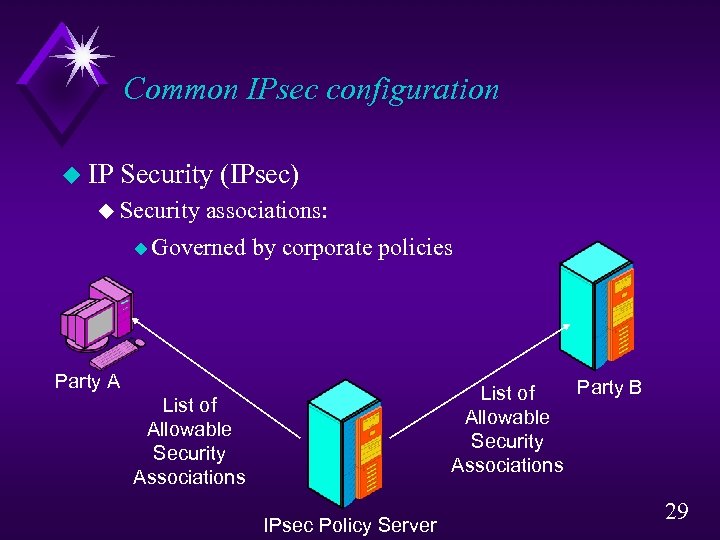 Common IPsec configuration u IP Security (IPsec) u Security associations: u Governed by corporate policies Party A Party B List of Allowable Security Associations IPsec Policy Server 29
Common IPsec configuration u IP Security (IPsec) u Security associations: u Governed by corporate policies Party A Party B List of Allowable Security Associations IPsec Policy Server 29


