328cb58dc980d93b94a72cf53740c81b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Fourth Grade Government Resource Unit ED 629 Spring Quarter 2007 Ben Borger, Matt Diewald, Jennifer Garvey Matt Nisenoff, Jessica Seaman
Fourth Grade Government Resource Unit ED 629 Spring Quarter 2007 Ben Borger, Matt Diewald, Jennifer Garvey Matt Nisenoff, Jessica Seaman
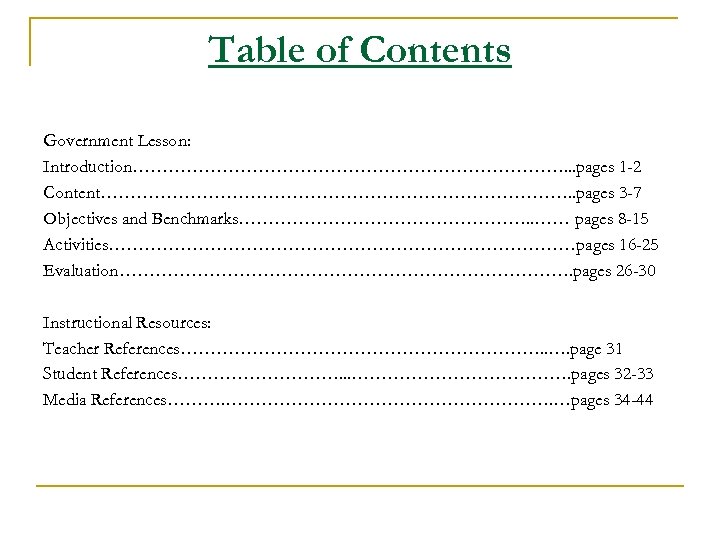 Table of Contents Government Lesson: Introduction………………………………. . . pages 1 -2 Content…………………………………. . pages 3 -7 Objectives and Benchmarks……………………. . …… pages 8 -15 Activities…………………………………pages 16 -25 Evaluation…………………………………. pages 26 -30 Instructional Resources: Teacher References…………………………. . …. page 31 Student References……………. . . ………………. pages 32 -33 Media References………. ………………………. …pages 34 -44
Table of Contents Government Lesson: Introduction………………………………. . . pages 1 -2 Content…………………………………. . pages 3 -7 Objectives and Benchmarks……………………. . …… pages 8 -15 Activities…………………………………pages 16 -25 Evaluation…………………………………. pages 26 -30 Instructional Resources: Teacher References…………………………. . …. page 31 Student References……………. . . ………………. pages 32 -33 Media References………. ………………………. …pages 34 -44
 Introduction -I- Government Structure n Since the founding of our nation our government has been built on the premise that we the people are to interact with it. We have to know government to interact with it. Ohio’s Social Studies Academic Content Standards outline knowing Local Government in 3 rd grade, State Government in 4 th grade, and Federal Government in 5 th grade. We are addressing the form and content of the three levels of government, the branches of government, how government is created, what are democracy is about, and how we as citizens interact with this system. "Democracy is not what we have. It is what we do. " -Frances Moore Lappé and Paul Du Bois
Introduction -I- Government Structure n Since the founding of our nation our government has been built on the premise that we the people are to interact with it. We have to know government to interact with it. Ohio’s Social Studies Academic Content Standards outline knowing Local Government in 3 rd grade, State Government in 4 th grade, and Federal Government in 5 th grade. We are addressing the form and content of the three levels of government, the branches of government, how government is created, what are democracy is about, and how we as citizens interact with this system. "Democracy is not what we have. It is what we do. " -Frances Moore Lappé and Paul Du Bois
 Introduction -I- Government Structure n This two week resource unit is designed to teach the structure of the government at a fourth grade level. Using several different instructional methods, students will be presented with information about the three branches of government and the three levels of government. The students will then be asked to demonstrate their understanding through a simulation, a game of Jeopardy and an exam. “Democracy is not a spectator sport. ” -Attributed to Robert Greenwald
Introduction -I- Government Structure n This two week resource unit is designed to teach the structure of the government at a fourth grade level. Using several different instructional methods, students will be presented with information about the three branches of government and the three levels of government. The students will then be asked to demonstrate their understanding through a simulation, a game of Jeopardy and an exam. “Democracy is not a spectator sport. ” -Attributed to Robert Greenwald
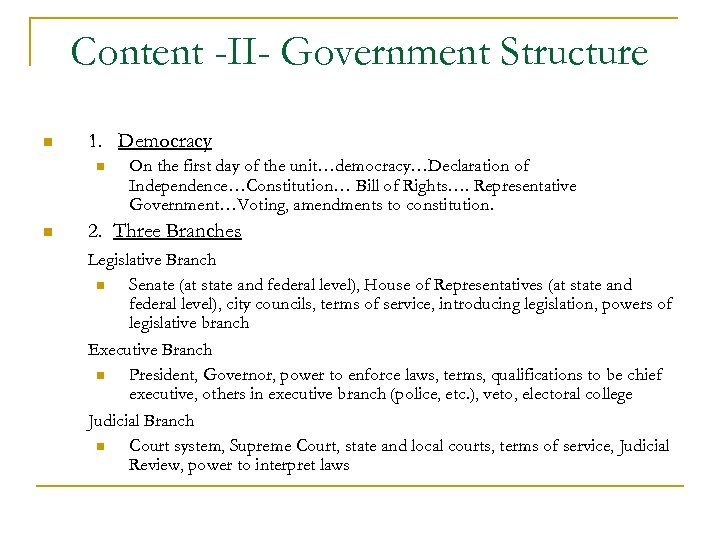 Content -II- Government Structure n 1. Democracy n n On the first day of the unit…democracy…Declaration of Independence…Constitution… Bill of Rights…. Representative Government…Voting, amendments to constitution. 2. Three Branches Legislative Branch n Senate (at state and federal level), House of Representatives (at state and federal level), city councils, terms of service, introducing legislation, powers of legislative branch Executive Branch n President, Governor, power to enforce laws, terms, qualifications to be chief executive, others in executive branch (police, etc. ), veto, electoral college Judicial Branch n Court system, Supreme Court, state and local courts, terms of service, Judicial Review, power to interpret laws
Content -II- Government Structure n 1. Democracy n n On the first day of the unit…democracy…Declaration of Independence…Constitution… Bill of Rights…. Representative Government…Voting, amendments to constitution. 2. Three Branches Legislative Branch n Senate (at state and federal level), House of Representatives (at state and federal level), city councils, terms of service, introducing legislation, powers of legislative branch Executive Branch n President, Governor, power to enforce laws, terms, qualifications to be chief executive, others in executive branch (police, etc. ), veto, electoral college Judicial Branch n Court system, Supreme Court, state and local courts, terms of service, Judicial Review, power to interpret laws
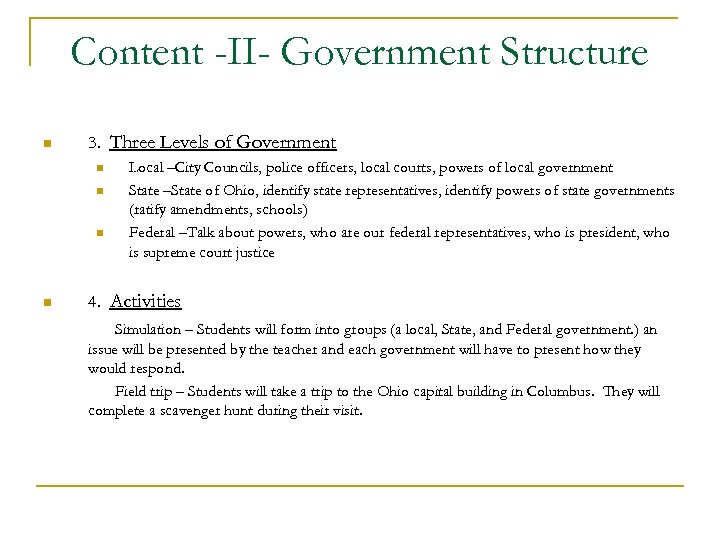 Content -II- Government Structure n 3. Three Levels of Government n n Local –City Councils, police officers, local courts, powers of local government State –State of Ohio, identify state representatives, identify powers of state governments (ratify amendments, schools) Federal –Talk about powers, who are our federal representatives, who is president, who is supreme court justice 4. Activities Simulation – Students will form into groups (a local, State, and Federal government. ) an issue will be presented by the teacher and each government will have to present how they would respond. Field trip – Students will take a trip to the Ohio capital building in Columbus. They will complete a scavenger hunt during their visit.
Content -II- Government Structure n 3. Three Levels of Government n n Local –City Councils, police officers, local courts, powers of local government State –State of Ohio, identify state representatives, identify powers of state governments (ratify amendments, schools) Federal –Talk about powers, who are our federal representatives, who is president, who is supreme court justice 4. Activities Simulation – Students will form into groups (a local, State, and Federal government. ) an issue will be presented by the teacher and each government will have to present how they would respond. Field trip – Students will take a trip to the Ohio capital building in Columbus. They will complete a scavenger hunt during their visit.
 Content -II- Government Structure n Evaluation n Verbal reviews during lecture. n Worksheets will be evaluated. n Points of groups from Jeopardy will be tallied. n Participation noted on worksheets, ballots on voting, teamwork on Jeopardy. n Simulation of issue
Content -II- Government Structure n Evaluation n Verbal reviews during lecture. n Worksheets will be evaluated. n Points of groups from Jeopardy will be tallied. n Participation noted on worksheets, ballots on voting, teamwork on Jeopardy. n Simulation of issue
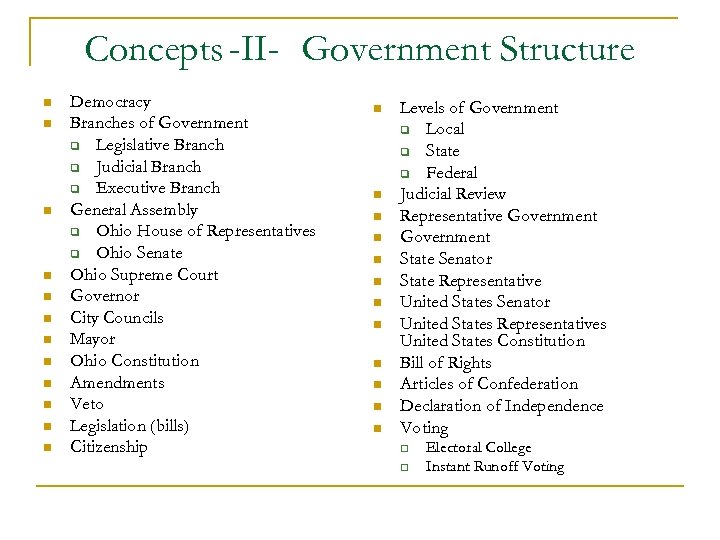 Concepts -II- Government Structure n n n Democracy Branches of Government q Legislative Branch q Judicial Branch q Executive Branch General Assembly q Ohio House of Representatives q Ohio Senate Ohio Supreme Court Governor City Councils Mayor Ohio Constitution Amendments Veto Legislation (bills) Citizenship n n n Levels of Government q Local q State q Federal Judicial Review Representative Government State Senator State Representative United States Senator United States Representatives United States Constitution Bill of Rights Articles of Confederation Declaration of Independence Voting q q Electoral College Instant Runoff Voting
Concepts -II- Government Structure n n n Democracy Branches of Government q Legislative Branch q Judicial Branch q Executive Branch General Assembly q Ohio House of Representatives q Ohio Senate Ohio Supreme Court Governor City Councils Mayor Ohio Constitution Amendments Veto Legislation (bills) Citizenship n n n Levels of Government q Local q State q Federal Judicial Review Representative Government State Senator State Representative United States Senator United States Representatives United States Constitution Bill of Rights Articles of Confederation Declaration of Independence Voting q q Electoral College Instant Runoff Voting
 Objectives -III- Government Structure n The students will be able to: q Explain the job of the Judicial Branch. q Explain the job of the Executive Branch. q Understanding the formation of government structure. n Using Jeopardy and the social studies book to build understanding of government.
Objectives -III- Government Structure n The students will be able to: q Explain the job of the Judicial Branch. q Explain the job of the Executive Branch. q Understanding the formation of government structure. n Using Jeopardy and the social studies book to build understanding of government.
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Government: n Students use knowledge of the purposes, structures and processes of political systems at the local, state, national and international levels to understand that people create systems of government as structures of power and authority to provide order, maintain stability and promote the general welfare.
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Government: n Students use knowledge of the purposes, structures and processes of political systems at the local, state, national and international levels to understand that people create systems of government as structures of power and authority to provide order, maintain stability and promote the general welfare.
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark A: Identify the responsibilities of the branches of the U. S. government and explain why they are necessary. Grade Four n Role of Government 1. Explain major responsibilities of each of the three branches of government in Ohio: n a. The legislative branch, headed by the General Assembly, makes state laws. n b. The executive branch, headed by the governor, carries out and enforces laws made by the General Assembly. n c. The judicial branch, headed by the Ohio Supreme Court, interprets and applies the law. n 2. Explain why elections are used to select leaders and decide issues. n (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 219)
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark A: Identify the responsibilities of the branches of the U. S. government and explain why they are necessary. Grade Four n Role of Government 1. Explain major responsibilities of each of the three branches of government in Ohio: n a. The legislative branch, headed by the General Assembly, makes state laws. n b. The executive branch, headed by the governor, carries out and enforces laws made by the General Assembly. n c. The judicial branch, headed by the Ohio Supreme Court, interprets and applies the law. n 2. Explain why elections are used to select leaders and decide issues. n (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 219)
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark B: Give examples of documents that specify the structure of state and national governments in the United States and explain how these documents foster self-government in a democracy. Grade Four Rules and Laws n 3. Explain the purpose of a democratic constitution: q a. To provide a framework for a government; q b. To limit the power of government; q c. To define the authority of elected officials. n 4. Explain that the Ohio Constitution tells how the state government should be organized and guarantees the rights of individuals. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 220)
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark B: Give examples of documents that specify the structure of state and national governments in the United States and explain how these documents foster self-government in a democracy. Grade Four Rules and Laws n 3. Explain the purpose of a democratic constitution: q a. To provide a framework for a government; q b. To limit the power of government; q c. To define the authority of elected officials. n 4. Explain that the Ohio Constitution tells how the state government should be organized and guarantees the rights of individuals. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 220)
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities n Students use knowledge of the rights and responsibilities of citizenship in order to examine and evaluate civic ideals and to participate in community life and the American democratic system.
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities n Students use knowledge of the rights and responsibilities of citizenship in order to examine and evaluate civic ideals and to participate in community life and the American democratic system.
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark A: Explain how citizens take part in civic life in order to promote the common good. Grade Four n Participation 1. Describe the ways in which citizens can promote the common good and influence their government including: q a. Voting; q b. Communicating with officials; q c. Participating in civic and service organizations; q d. Performing voluntary service (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 220)
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark A: Explain how citizens take part in civic life in order to promote the common good. Grade Four n Participation 1. Describe the ways in which citizens can promote the common good and influence their government including: q a. Voting; q b. Communicating with officials; q c. Participating in civic and service organizations; q d. Performing voluntary service (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 220)
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark B: Identify rights and responsibilities of citizenship in the United States that are important for preserving democratic government. Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities n Participation 1. q Describe the ways in which citizens can promote the common good and influence their government including: n n n a. Voting; b. Communicating with officials; c. Participating in civic and service organizations; d. Performing voluntary service. Rights and Responsibilities q q q 2. Explain why personal responsibilities (e. g. , taking advantage of the opportunity to be educated) and civic responsibilities (e. g. , obeying the law and respecting the rights of others) are important. 3. Explain the importance of leadership and public service. 4. Explain why characteristics such as respect for the rights of others, fairness, reliability, honesty, wisdom and courage are desirable qualities in the people citizens select as their leaders. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 129)
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Benchmark B: Identify rights and responsibilities of citizenship in the United States that are important for preserving democratic government. Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities n Participation 1. q Describe the ways in which citizens can promote the common good and influence their government including: n n n a. Voting; b. Communicating with officials; c. Participating in civic and service organizations; d. Performing voluntary service. Rights and Responsibilities q q q 2. Explain why personal responsibilities (e. g. , taking advantage of the opportunity to be educated) and civic responsibilities (e. g. , obeying the law and respecting the rights of others) are important. 3. Explain the importance of leadership and public service. 4. Explain why characteristics such as respect for the rights of others, fairness, reliability, honesty, wisdom and courage are desirable qualities in the people citizens select as their leaders. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 129)
 Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Social Studies Skills and Methods Thinking and Organizing n 5. Identify main ideas and supporting details from factual information. n 6. Distinguish between fact and opinion. Communicating Information n 9. Communicate relevant information in a written report including the acknowledgement of sources. Problem Solving n 10. Use a problem-solving/decision-making process which includes: q q q a. Identifying a problem; b. Gathering information; c. Listing and considering options; d. Considering advantages and disadvantages of options; e. Choosing and implementing a solution; f. Developing criteria for judging its effectiveness. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 130)
Benchmarks -III- Government Structure Social Studies Skills and Methods Thinking and Organizing n 5. Identify main ideas and supporting details from factual information. n 6. Distinguish between fact and opinion. Communicating Information n 9. Communicate relevant information in a written report including the acknowledgement of sources. Problem Solving n 10. Use a problem-solving/decision-making process which includes: q q q a. Identifying a problem; b. Gathering information; c. Listing and considering options; d. Considering advantages and disadvantages of options; e. Choosing and implementing a solution; f. Developing criteria for judging its effectiveness. (Social Studies, Academic Content Standard, p. 130)
 Activities -IV- Government Structure Day One: Democracy n The teacher, using reproducible copies from The Constitution (listed in references), will lead the students through a discussion that covers constitutional democracy, origins of the constitution, and the purpose of government. Day Two: Three Branches n The teacher will give a presentation in class on the three branches of government followed by the video, THE THREE BRANCHES OF THE AMERICAN GOVERNMENT (20 min. ).
Activities -IV- Government Structure Day One: Democracy n The teacher, using reproducible copies from The Constitution (listed in references), will lead the students through a discussion that covers constitutional democracy, origins of the constitution, and the purpose of government. Day Two: Three Branches n The teacher will give a presentation in class on the three branches of government followed by the video, THE THREE BRANCHES OF THE AMERICAN GOVERNMENT (20 min. ).
 Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Three: Levels of Government n Show DVD UNDERSTANDING GOVERNMENT: Just the Facts Clips n Popcorn (teacher reads and has class fill in the blanks as we go) read information in textbook (314 -317 municipal; 318 -323 state in Textbook cited in reference) on Levels of Government. n Use work sheets to reinforce lesson answering a few questions and have the balance of questions done for homework. n Review budgets of a local government and state government to point out areas of focus for different levels of government. (see local and state government websites). Note credit and debits, total amounts, and largest areas of spending. n Discuss elections and their role to pass issues and candidates (local issue of levies for special district funding, State issue of Governor’s election, Federal issue of Presidential election). Use current election information from newspaper, print and media ad, and pamphlets from candidates. (Kids voting USA material can be used to support lesson. )
Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Three: Levels of Government n Show DVD UNDERSTANDING GOVERNMENT: Just the Facts Clips n Popcorn (teacher reads and has class fill in the blanks as we go) read information in textbook (314 -317 municipal; 318 -323 state in Textbook cited in reference) on Levels of Government. n Use work sheets to reinforce lesson answering a few questions and have the balance of questions done for homework. n Review budgets of a local government and state government to point out areas of focus for different levels of government. (see local and state government websites). Note credit and debits, total amounts, and largest areas of spending. n Discuss elections and their role to pass issues and candidates (local issue of levies for special district funding, State issue of Governor’s election, Federal issue of Presidential election). Use current election information from newspaper, print and media ad, and pamphlets from candidates. (Kids voting USA material can be used to support lesson. )
 Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Four: Review Branches and Levels n Open with clip from School House Rock: “I’m Just a Bill” n Popcorn (teacher reads and has class fill in the blanks as we go)) Read information in book on Federal Government. n Review with worksheet as in-class work. n Play Jeopardy (topics being Local, State, Federal, Branches, Facts) reinforcing facts on government structure, the levels, and branches thereof.
Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Four: Review Branches and Levels n Open with clip from School House Rock: “I’m Just a Bill” n Popcorn (teacher reads and has class fill in the blanks as we go)) Read information in book on Federal Government. n Review with worksheet as in-class work. n Play Jeopardy (topics being Local, State, Federal, Branches, Facts) reinforcing facts on government structure, the levels, and branches thereof.
 Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Five: Have local elected official come in to talk to students (mayor, legislator and/or judge). q q Have students prepare questions ahead of time. Have mayor/elected official assign brochure assignment. The brochure project is for the students to create a brochure with each branch of government explained for other children to read. Partners will work together to create the brochure. The final project will be reviewed by at least two other teams. Use HOW AMERICA WORKS: Kids Discover Magazine as a basis to work on brochures.
Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Five: Have local elected official come in to talk to students (mayor, legislator and/or judge). q q Have students prepare questions ahead of time. Have mayor/elected official assign brochure assignment. The brochure project is for the students to create a brochure with each branch of government explained for other children to read. Partners will work together to create the brochure. The final project will be reviewed by at least two other teams. Use HOW AMERICA WORKS: Kids Discover Magazine as a basis to work on brochures.
 Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Six: Visit State level legislature at Capital Building in Columbus, Ohio. See Ohio General Assembly at work q q Prepare a scavenger hunt for students to complete while on the trip. Lead students in review of materials provided by House members and Senate members. See House and Senate in session, if possible. Visit Governor’s working office, if possible.
Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Six: Visit State level legislature at Capital Building in Columbus, Ohio. See Ohio General Assembly at work q q Prepare a scavenger hunt for students to complete while on the trip. Lead students in review of materials provided by House members and Senate members. See House and Senate in session, if possible. Visit Governor’s working office, if possible.
 Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Seven: Good/Bad Democracy n Discuss pros and cons of representational government. Perhaps look at other ways of organizing government. n Compare and contrast other governments to the U. S. (Britain – Monarchy, Russia – Socialism) n DVD Participating in Citizenship, An American past when people were more engaged in clubs, associations, and other forms of civic participation is contrasted with contemporary alienation and passivity. Voting and other forms of civic engagement are recommended Good Democracy/Bad Democracy
Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Seven: Good/Bad Democracy n Discuss pros and cons of representational government. Perhaps look at other ways of organizing government. n Compare and contrast other governments to the U. S. (Britain – Monarchy, Russia – Socialism) n DVD Participating in Citizenship, An American past when people were more engaged in clubs, associations, and other forms of civic participation is contrasted with contemporary alienation and passivity. Voting and other forms of civic engagement are recommended Good Democracy/Bad Democracy
 Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Eight: Government Simulation: n Students will be divided into three groups. Each of the groups will be assigned a branch of government. Within their group they will divide into federal, state, and city. An issue will be introduced and each group will have decide if their branch is responsible for the problem. If the issue pertains to them, then they must decide what level of government is responsible for solving the problem. Once that is accomplished, the responsible group must decide how the problem should be handled.
Activities -IV- Government Structure Day Eight: Government Simulation: n Students will be divided into three groups. Each of the groups will be assigned a branch of government. Within their group they will divide into federal, state, and city. An issue will be introduced and each group will have decide if their branch is responsible for the problem. If the issue pertains to them, then they must decide what level of government is responsible for solving the problem. Once that is accomplished, the responsible group must decide how the problem should be handled.
 Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Nine: Reader’s Theater q Try out Reader’s Theater plays concerning government in small groups from: PLAYS AMERICAN HISTORY READER'S THEATER: Develop Reading Fluency and Comprehension Skills (see references).
Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Nine: Reader’s Theater q Try out Reader’s Theater plays concerning government in small groups from: PLAYS AMERICAN HISTORY READER'S THEATER: Develop Reading Fluency and Comprehension Skills (see references).
 Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Ten: Evaluation
Activities -IV- Government Structure n Day Ten: Evaluation
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure Unit Test – Government Structure Multiple Choice (5 points each) 1. What is the role of the Judicial Branch? q To create the laws q To carry out the laws q To interpret the laws q To declare war 2. What is the role of the Executive Branch? q Name those who head departments q Veto power q Carries out the laws q All of the above q None of the above 3. What is the role of the Legislative Branch? q To make the laws q To interpret the law q To carry out the laws q To ensure elections are run fairly
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure Unit Test – Government Structure Multiple Choice (5 points each) 1. What is the role of the Judicial Branch? q To create the laws q To carry out the laws q To interpret the laws q To declare war 2. What is the role of the Executive Branch? q Name those who head departments q Veto power q Carries out the laws q All of the above q None of the above 3. What is the role of the Legislative Branch? q To make the laws q To interpret the law q To carry out the laws q To ensure elections are run fairly
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 4. Name the Legislative branch from each level of government. A. President, Governor, Mayor B. Congress, General Assembly, Council C. Steve, George, Bill, Sam D. United States Supreme Court Justice, State Supreme Court Justice, Municipal Judge. 5. Which level of government runs the public libraries? A. Municipal Government B. Federal Government C. State Government D. Foreign Government E. None of the above 6. Which level of Government would you be the executive of if you ran for Governor? A. Municipal Government B. Federal Government C. State Government D. Foreign Government E. None of the above 7. Which level of government is your school? A. Municipal District B. Federal District C. State District D. Special District
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 4. Name the Legislative branch from each level of government. A. President, Governor, Mayor B. Congress, General Assembly, Council C. Steve, George, Bill, Sam D. United States Supreme Court Justice, State Supreme Court Justice, Municipal Judge. 5. Which level of government runs the public libraries? A. Municipal Government B. Federal Government C. State Government D. Foreign Government E. None of the above 6. Which level of Government would you be the executive of if you ran for Governor? A. Municipal Government B. Federal Government C. State Government D. Foreign Government E. None of the above 7. Which level of government is your school? A. Municipal District B. Federal District C. State District D. Special District
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 8. Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) q q q q q Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch Tree Branch No branch, the three balance each other Constitution Declaration of Independence Rosetta Stone Habeas Corpus 9. How do the following officials gain their office: n United States President, United States Congressman, Ohio General Assembly members, Ohio Judicial, Local Mayor, Local Council members? q q q a. They show up and just do the job b. They are appointed c. They are friends of the those who had the position before them d. They take the position from their parent e. They are elected
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 8. Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) q q q q q Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch Tree Branch No branch, the three balance each other Constitution Declaration of Independence Rosetta Stone Habeas Corpus 9. How do the following officials gain their office: n United States President, United States Congressman, Ohio General Assembly members, Ohio Judicial, Local Mayor, Local Council members? q q q a. They show up and just do the job b. They are appointed c. They are friends of the those who had the position before them d. They take the position from their parent e. They are elected
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n True/False (5 points each) 1. True or False: All appealed cases end up in the Supreme Court. 2. True or False: Every citizen has the right to equal protection guaranteed by the Constitution. 3. True or False: A citizen must be 18 and registered to vote in any election. 4. True or False: Both the Senate and the House of Representatives must unanimously agree before a bill can be signed into a law. 5. True or False: Each Supreme Court Justice has the power to veto any laws in the Constitution. 6. True or False: Policemen are a part of the Executive branch and enforce the laws passed by the Federal government. 7. True or False: A court system exists at local, state, and federal levels of the government.
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n True/False (5 points each) 1. True or False: All appealed cases end up in the Supreme Court. 2. True or False: Every citizen has the right to equal protection guaranteed by the Constitution. 3. True or False: A citizen must be 18 and registered to vote in any election. 4. True or False: Both the Senate and the House of Representatives must unanimously agree before a bill can be signed into a law. 5. True or False: Each Supreme Court Justice has the power to veto any laws in the Constitution. 6. True or False: Policemen are a part of the Executive branch and enforce the laws passed by the Federal government. 7. True or False: A court system exists at local, state, and federal levels of the government.
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 8. True or False: Supreme Court Justices are appointed by Congress. 9. True or False: Supreme Court Justices are appointed for life. 10. True or False: The President of the United States is the Commander in Chief of our military. 11. True or False: Every level of government is in charge of some part of the road system. 12. True or False: The federal government is in charge of fixing city streets. 13. True or False: The state government is in charge of giving out driver licenses.
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 8. True or False: Supreme Court Justices are appointed by Congress. 9. True or False: Supreme Court Justices are appointed for life. 10. True or False: The President of the United States is the Commander in Chief of our military. 11. True or False: Every level of government is in charge of some part of the road system. 12. True or False: The federal government is in charge of fixing city streets. 13. True or False: The state government is in charge of giving out driver licenses.
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 14. True or False: Both the President of the United States and the governors of each state are permitted to serve two 6 year terms. 15. True or False: Citizens from neighboring cities or towns are permitted to vote for a mayor. 16. True or False: The first ten amendments make up of the Bill of Rights in the U. S. Constitution. 17. True or False: The state level of government does not have to listen to the federal level of government.
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure 14. True or False: Both the President of the United States and the governors of each state are permitted to serve two 6 year terms. 15. True or False: Citizens from neighboring cities or towns are permitted to vote for a mayor. 16. True or False: The first ten amendments make up of the Bill of Rights in the U. S. Constitution. 17. True or False: The state level of government does not have to listen to the federal level of government.
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n Short Essay (10 points each) 1. What branch of government were you part of during the simulation and what problems did your branch cover. How did your branch solve the problems? 2. In your own words, describe the concept of checks and balances between the different branches of the federal government. 3. Please name three different levels of government and in your own words describe any of jobs that they perform. This can be anything that you have learned from class or from what you already know. 4. The Constitution gives us rights. Which right, given to us by the Constitution, is most interesting to you? 5. What are three forms of citizenship activities that you have learned about? n Extra Credit: (2 points) Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) q Legislative Branch q Executive Branch q Judicial Branch q Tree Branch q No branch, the three balance each other q Constitution q Declaration of Independence q Rosetta Stone q Habeas Corpus
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n Short Essay (10 points each) 1. What branch of government were you part of during the simulation and what problems did your branch cover. How did your branch solve the problems? 2. In your own words, describe the concept of checks and balances between the different branches of the federal government. 3. Please name three different levels of government and in your own words describe any of jobs that they perform. This can be anything that you have learned from class or from what you already know. 4. The Constitution gives us rights. Which right, given to us by the Constitution, is most interesting to you? 5. What are three forms of citizenship activities that you have learned about? n Extra Credit: (2 points) Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) q Legislative Branch q Executive Branch q Judicial Branch q Tree Branch q No branch, the three balance each other q Constitution q Declaration of Independence q Rosetta Stone q Habeas Corpus
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n Adaptations for Evaluations q Student may take test in oral format. q Students may have more time. q Student may have test read to them. n Test Question Adaptations (for essay) q 1. Please name one level of government. Next, name one job that they do. This can be anything that you have learned from class or from what you already know. q 2. In your own words, describe the concept of checks and balances between the different branches of the federal government. q Choose fewer of true/false questions for student to answer. q The Supreme Court _____ laws. Congress ______ laws. The president ______ laws. This is part of checks and balances. passes interprets enforces
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure n Adaptations for Evaluations q Student may take test in oral format. q Students may have more time. q Student may have test read to them. n Test Question Adaptations (for essay) q 1. Please name one level of government. Next, name one job that they do. This can be anything that you have learned from class or from what you already know. q 2. In your own words, describe the concept of checks and balances between the different branches of the federal government. q Choose fewer of true/false questions for student to answer. q The Supreme Court _____ laws. Congress ______ laws. The president ______ laws. This is part of checks and balances. passes interprets enforces
 Evaluation -IV- Government Structure Multiple Choice Adaptation Questions n n What is the role of the Judicial Branch? To declare war To interpret the laws What is the role of the Executive Branch? Veto power Carries out laws All of the above n Name the Legislative Branch from each level of government. President, Governor, Mayor Congress, General Assembly, Council Which level of government would you be in charge of if you ran for governor? State government Federal government n Which level of government is your school? Federal District Municipal District n Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) Tree Branch No branch, the three balance each other Legislative Branch Rosetta Stone Constitution n How do the following officials gain their office: United States President, Local Mayor, Ohio General Assembly? They just show up They are appointed They are elected What is the role of the Legislative Branch? To interpret the laws To make the laws n n
Evaluation -IV- Government Structure Multiple Choice Adaptation Questions n n What is the role of the Judicial Branch? To declare war To interpret the laws What is the role of the Executive Branch? Veto power Carries out laws All of the above n Name the Legislative Branch from each level of government. President, Governor, Mayor Congress, General Assembly, Council Which level of government would you be in charge of if you ran for governor? State government Federal government n Which level of government is your school? Federal District Municipal District n Who has the most power in government and what document gives that power? (must choose two answers) Tree Branch No branch, the three balance each other Legislative Branch Rosetta Stone Constitution n How do the following officials gain their office: United States President, Local Mayor, Ohio General Assembly? They just show up They are appointed They are elected What is the role of the Legislative Branch? To interpret the laws To make the laws n n
 Teacher References -VI- Government Structure n http: //www. nea. org/lessons/2005/tt 050905. html Students work in groups to create charts showing the structure and functions of the three branches of government as outlined in the first three articles to the Constitution. n Ohio History Teachers - Lesson Plans - Government From Morgan's Raid and Ohio's statehood to canal transportation and civil rights, the Ohio Historical Society has developed lesson plans and classroom activities to meet your needs in the teaching of Ohio history. All of the materials have been designed to enhance the Ohio Department of Education's new Academic Content standards and reflect the vast resources within the Society. The following Lesson Plans are condensed files that include links, content standards and other resources. n EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO TEACH ABOUT U. S. GOVERNMENT (Book, Poser, Videos) This exceptional resource contains a wealth of material for teaching about the complexities of our federal government. Students will come away with a thorough understanding of how the three branches of government are organized, what their specific duties are, and how they cooperatively run our country. Grades 6– 12. Knowledge Unlimited. This kit contains: 3 videos (approximately 18 minutes each): The Presidency, The Congress, The Supreme Court Set of 3 posters (17"h x 11"w): Branches of Government Poster (22"h x 34"w): How a Bill Becomes a Law 42 -page reproducible resource book: Our Federal Government n TEACHING THE CONSTITUTION OVERHEAD TRANSPARENCY KIT This easy-to-use kit contains nine charts on overhead transparencies, nine student charts, 10 pages of narrative text, and 10 pages of student worksheets. The charts display the powers of America’s federal and state governments and the branches of the federal government. Similar charts allow students to compare and contrast America’s government framework with that of ancient governments, Britain’s government in the 1700 s, and the U. S. during the Articles Of Confederation period. A short, engaging narrative brings the charts to life with interesting examples and anecdotes. The worksheets emphasize critical thinking skills. Reproducible. Grades 7– 12. 8½" x 11". Education Innovations. © 2001.
Teacher References -VI- Government Structure n http: //www. nea. org/lessons/2005/tt 050905. html Students work in groups to create charts showing the structure and functions of the three branches of government as outlined in the first three articles to the Constitution. n Ohio History Teachers - Lesson Plans - Government From Morgan's Raid and Ohio's statehood to canal transportation and civil rights, the Ohio Historical Society has developed lesson plans and classroom activities to meet your needs in the teaching of Ohio history. All of the materials have been designed to enhance the Ohio Department of Education's new Academic Content standards and reflect the vast resources within the Society. The following Lesson Plans are condensed files that include links, content standards and other resources. n EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO TEACH ABOUT U. S. GOVERNMENT (Book, Poser, Videos) This exceptional resource contains a wealth of material for teaching about the complexities of our federal government. Students will come away with a thorough understanding of how the three branches of government are organized, what their specific duties are, and how they cooperatively run our country. Grades 6– 12. Knowledge Unlimited. This kit contains: 3 videos (approximately 18 minutes each): The Presidency, The Congress, The Supreme Court Set of 3 posters (17"h x 11"w): Branches of Government Poster (22"h x 34"w): How a Bill Becomes a Law 42 -page reproducible resource book: Our Federal Government n TEACHING THE CONSTITUTION OVERHEAD TRANSPARENCY KIT This easy-to-use kit contains nine charts on overhead transparencies, nine student charts, 10 pages of narrative text, and 10 pages of student worksheets. The charts display the powers of America’s federal and state governments and the branches of the federal government. Similar charts allow students to compare and contrast America’s government framework with that of ancient governments, Britain’s government in the 1700 s, and the U. S. during the Articles Of Confederation period. A short, engaging narrative brings the charts to life with interesting examples and anecdotes. The worksheets emphasize critical thinking skills. Reproducible. Grades 7– 12. 8½" x 11". Education Innovations. © 2001.
 Student References -VI- Government Structure n n n http: //bensguide. gpo. gov/index. html Ben’s Guide to U. S. Government: This site covers civics, broken down into age appropriate categories K-12. There is even a section for parents and teachers. Check out the links to US government web sites for kids. http: //pbskids. org/democracy/ The Democracy Project by PBS: Find out how the government affects you. Afterwards, try your hand at being President for the day. This site is clear, simple and fun. http: //congressforkids. net/Constitution_threebranches. htm Using appealing, full-color illustrations, and engaging activities, this site will extend your learning in the basics about the American federal government. http: //library. thinkquest. org/5873/ The Government for Kids webpage will teach elementary students about the United States government. Students can learn about why we have laws, the branches of government, the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, and more. We also have some fun activities to help students learn. http: //www. kidsvoting. USA. org Various materials on elections including class kits with interactive demonstrations.
Student References -VI- Government Structure n n n http: //bensguide. gpo. gov/index. html Ben’s Guide to U. S. Government: This site covers civics, broken down into age appropriate categories K-12. There is even a section for parents and teachers. Check out the links to US government web sites for kids. http: //pbskids. org/democracy/ The Democracy Project by PBS: Find out how the government affects you. Afterwards, try your hand at being President for the day. This site is clear, simple and fun. http: //congressforkids. net/Constitution_threebranches. htm Using appealing, full-color illustrations, and engaging activities, this site will extend your learning in the basics about the American federal government. http: //library. thinkquest. org/5873/ The Government for Kids webpage will teach elementary students about the United States government. Students can learn about why we have laws, the branches of government, the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, and more. We also have some fun activities to help students learn. http: //www. kidsvoting. USA. org Various materials on elections including class kits with interactive demonstrations.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n Executive Branch of the Government , Legislative Branch of the Government , Judicial Branch of the Government. (activity booklets) In order to help young people understand the three branches of government, the thought-provoking activities in this set show the powers of each branch, how they interact with one another in a system requiring separation of powers and how each branch is designed to prevent the other two from assuming too much power. Each book includes background information and reproducible handouts. Grades 4– 8. Answer keys. Illustrated. 8½" x 11". Teaching & Learning. 32 pages each (except as noted). © 2000. n HOW AMERICA WORKS: Kids Discover Magazine (magazine) Eight two-page spreads brim with colorful graphics and text that convey basic facts on the history and functions of government in the U. S. Guided by a friendly George Washington, students learn about branches of government, the flag’s story, how bills become law, presidential elections, and more. Activities and book links appear at the end. A separate guide sheet is provided. Grades 4 – 8. Answer key. Illustrated. 8" x 10½". Kids Discover. 20 pages. © 2003
Media References -VI- Government Structure n Executive Branch of the Government , Legislative Branch of the Government , Judicial Branch of the Government. (activity booklets) In order to help young people understand the three branches of government, the thought-provoking activities in this set show the powers of each branch, how they interact with one another in a system requiring separation of powers and how each branch is designed to prevent the other two from assuming too much power. Each book includes background information and reproducible handouts. Grades 4– 8. Answer keys. Illustrated. 8½" x 11". Teaching & Learning. 32 pages each (except as noted). © 2000. n HOW AMERICA WORKS: Kids Discover Magazine (magazine) Eight two-page spreads brim with colorful graphics and text that convey basic facts on the history and functions of government in the U. S. Guided by a friendly George Washington, students learn about branches of government, the flag’s story, how bills become law, presidential elections, and more. Activities and book links appear at the end. A separate guide sheet is provided. Grades 4 – 8. Answer key. Illustrated. 8" x 10½". Kids Discover. 20 pages. © 2003
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n HOW OUR GOVERNMENT WORKS (posters) Color enumerate the powers and duties of President Bush, Vice President Cheney, the president's cabinet, the Supreme Court, and members of the Senate and the House of Representatives. Printed on glossy poster paper. 24"h x 36"w. World Almanac Library. © 2005. n FAMOUS U. S. DOCUMENTS BULLETIN BOARD SET (posters) Four full-color posters printed on a beige background depict facsimiles of the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, and the Emancipation Proclamation; illustrate a dramatic moment in the history of each document; and provide a brief explanatory text. Grades 4– 8. 17"h x 24"w. Mark Twain. n BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT (posters) Three color posters delineate the differences among the branches of the federal government. At the left of each poster, a column of text spells out the structure and powers of one particular branch, while the main portion of the poster uses pictures and text to point out a high point in the history of that branch: to wit, FDR’s administration (the executive branch), women’s suffrage and the 19 th Amendment (legislative), and the battle to end racial segregation (judicial). 22"h x 17"w. Cambridge Educational. © 2000.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n HOW OUR GOVERNMENT WORKS (posters) Color enumerate the powers and duties of President Bush, Vice President Cheney, the president's cabinet, the Supreme Court, and members of the Senate and the House of Representatives. Printed on glossy poster paper. 24"h x 36"w. World Almanac Library. © 2005. n FAMOUS U. S. DOCUMENTS BULLETIN BOARD SET (posters) Four full-color posters printed on a beige background depict facsimiles of the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, and the Emancipation Proclamation; illustrate a dramatic moment in the history of each document; and provide a brief explanatory text. Grades 4– 8. 17"h x 24"w. Mark Twain. n BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT (posters) Three color posters delineate the differences among the branches of the federal government. At the left of each poster, a column of text spells out the structure and powers of one particular branch, while the main portion of the poster uses pictures and text to point out a high point in the history of that branch: to wit, FDR’s administration (the executive branch), women’s suffrage and the 19 th Amendment (legislative), and the battle to end racial segregation (judicial). 22"h x 17"w. Cambridge Educational. © 2000.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD School House Rock (I’m just a Bill, Three Ring Circus) n Textbook. Ohio Adventures in Time and Place. 1997. Macmillan/Mc. Graw-Hill. (readings from page 314 -331 - 314 to 317 for local, 316 to 323 for state, 323 to 331 for Federal) Practice Book and Project Book. Ohio Adventures in Time and Place. 1997. Macmillan/Mc. Graw. Hill. (page 64 relates to the textbook section on local gov, page 65 relates to the textbook section on state gov, page 67 relates to the textbook section on federal gov) n n Website, Ohio Department of Education, Ohio Academic Content Standard, Social Studies http: //www. ode. state. oh. us/GD/Templates/Pages/ODEDetail. aspx? page=3&Topic. Rela tion. ID=335&Content. ID=852&Content=18582 n DVD AMERICAN DEMOCRACY IN ACTION Are young people alienated from the democratic process? Does declining citizen participation endanger democracy? Arguing the need for revitalizing the spirit of political engagement, the three programs demonstrate how active engagement has righted the wrongs of the past and show young role models today who recognize that enlightened self-interest demands community action.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD School House Rock (I’m just a Bill, Three Ring Circus) n Textbook. Ohio Adventures in Time and Place. 1997. Macmillan/Mc. Graw-Hill. (readings from page 314 -331 - 314 to 317 for local, 316 to 323 for state, 323 to 331 for Federal) Practice Book and Project Book. Ohio Adventures in Time and Place. 1997. Macmillan/Mc. Graw. Hill. (page 64 relates to the textbook section on local gov, page 65 relates to the textbook section on state gov, page 67 relates to the textbook section on federal gov) n n Website, Ohio Department of Education, Ohio Academic Content Standard, Social Studies http: //www. ode. state. oh. us/GD/Templates/Pages/ODEDetail. aspx? page=3&Topic. Rela tion. ID=335&Content. ID=852&Content=18582 n DVD AMERICAN DEMOCRACY IN ACTION Are young people alienated from the democratic process? Does declining citizen participation endanger democracy? Arguing the need for revitalizing the spirit of political engagement, the three programs demonstrate how active engagement has righted the wrongs of the past and show young role models today who recognize that enlightened self-interest demands community action.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD Participating in Citizenship An American past when people were more engaged in clubs, associations, and other forms of civic participation is contrasted with contemporary alienation and passivity. Voting and other forms of civic engagement are recommended. n DVD Active Citizenship: Making a Difference Will the surge of volunteerism after September 11, 2001, be followed by a decline in civic-mindedness? Explores citizen engagement and disengagement since WWII, lauding contemporary service projects by secondary and college students. ] n Books and handouts AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Key learnings: government organization (all levels), development of American democracy, the election process, how court decisions have shaped government. n e. Book and Handouts AMERICAN GOVERNMENT AND CIVICS Topics include democracy, civil liberties and disagreements, the intentions of government, degrees of democracy, the value of the vote, and civil rights and responsibilities. Board game included.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD Participating in Citizenship An American past when people were more engaged in clubs, associations, and other forms of civic participation is contrasted with contemporary alienation and passivity. Voting and other forms of civic engagement are recommended. n DVD Active Citizenship: Making a Difference Will the surge of volunteerism after September 11, 2001, be followed by a decline in civic-mindedness? Explores citizen engagement and disengagement since WWII, lauding contemporary service projects by secondary and college students. ] n Books and handouts AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Key learnings: government organization (all levels), development of American democracy, the election process, how court decisions have shaped government. n e. Book and Handouts AMERICAN GOVERNMENT AND CIVICS Topics include democracy, civil liberties and disagreements, the intentions of government, degrees of democracy, the value of the vote, and civil rights and responsibilities. Board game included.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n VHS/DVD THE CONGRESS: The History and Promise of Representative Government Directed by Ken Burns. The personalities, controversies, and compromises of Congress's first 200 years are covered with wit and dramatic force, and the enduring strength and resilience of Congress as "the people's voice" and "the engine of democracy" are affirmed. Labeled segments correspond to historical eras: "The Builders, " "The Debaters, " "The Bosses, " "The Progressives, " "The Hill, " and "The Managers. " Archival photographs, newsreels, and live footage are interpreted in interviews with journalists (David Broder, Cokie Roberts) and historians (James Mac. Gregor Burns, Alistair Cooke). Julie Harris, Garrison Keillor, Arthur Miller, and Kurt Vonnegut read the diary entries, letters, and famous floor speeches of Congressional leaders. Narrated by historian David Mc. Cullough. Grades 7 and up. Closed captioned. Black-and-white and color. 90 minutes. © 1988. n Reproducible THE CONSTITUTION Lessons include constitutional democracy, the origins of the Constitution, the purpose of government, the Constitutional Convention, principals underlying the Constitution, separation of powers, checks and balances, enumerated powers, federalism, the presidency, Congress, Supreme Court, and more. 209 lessons, 832 test questions.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n VHS/DVD THE CONGRESS: The History and Promise of Representative Government Directed by Ken Burns. The personalities, controversies, and compromises of Congress's first 200 years are covered with wit and dramatic force, and the enduring strength and resilience of Congress as "the people's voice" and "the engine of democracy" are affirmed. Labeled segments correspond to historical eras: "The Builders, " "The Debaters, " "The Bosses, " "The Progressives, " "The Hill, " and "The Managers. " Archival photographs, newsreels, and live footage are interpreted in interviews with journalists (David Broder, Cokie Roberts) and historians (James Mac. Gregor Burns, Alistair Cooke). Julie Harris, Garrison Keillor, Arthur Miller, and Kurt Vonnegut read the diary entries, letters, and famous floor speeches of Congressional leaders. Narrated by historian David Mc. Cullough. Grades 7 and up. Closed captioned. Black-and-white and color. 90 minutes. © 1988. n Reproducible THE CONSTITUTION Lessons include constitutional democracy, the origins of the Constitution, the purpose of government, the Constitutional Convention, principals underlying the Constitution, separation of powers, checks and balances, enumerated powers, federalism, the presidency, Congress, Supreme Court, and more. 209 lessons, 832 test questions.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n POSTERS AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Informative and colorful, this handsome set can be used for direct teaching or bulletin board display. Each 17" x 22" poster has bold titles, easy-to -read lettering, and a simple, eye-pleasing design. Themes include checks and balances, how a bill becomes law, political parties, elections, citizen participation, the president's cabinet, differences between branches of Congress, and functions of government at local, state, and federal levels. n POSTERS BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Three color posters delineate the differences among the branches of the federal government. At the left of each poster, a column of text spells out the structure and powers of one particular branch, while the main portion of the poster uses pictures and text to point out a high point in the history of that branch: to wit, FDR’s administration (the executive branch), women’s suffrage and the 19 th Amendment (legislative), and the battle to end racial segregation (judicial). 22"h x 17"w. Cambridge Educational. © 2000. n BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT: Power. Point® Presentations Ideal for introducing a unit or units on any or all of the three branches of government, these ready-made Power. Point® presentations provide a quick and easy way to give students solid overviews in a single class period. A CD-ROM contains three 30– 40 slide Power. Point® presentations (one on each branch), teacher overviews, lecture notes in outline form, and multiple -choice quizzes to test student comprehension. Grades 7– 12. Social Studies School Service. Second Edition. © 2005.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n POSTERS AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Informative and colorful, this handsome set can be used for direct teaching or bulletin board display. Each 17" x 22" poster has bold titles, easy-to -read lettering, and a simple, eye-pleasing design. Themes include checks and balances, how a bill becomes law, political parties, elections, citizen participation, the president's cabinet, differences between branches of Congress, and functions of government at local, state, and federal levels. n POSTERS BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Three color posters delineate the differences among the branches of the federal government. At the left of each poster, a column of text spells out the structure and powers of one particular branch, while the main portion of the poster uses pictures and text to point out a high point in the history of that branch: to wit, FDR’s administration (the executive branch), women’s suffrage and the 19 th Amendment (legislative), and the battle to end racial segregation (judicial). 22"h x 17"w. Cambridge Educational. © 2000. n BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT: Power. Point® Presentations Ideal for introducing a unit or units on any or all of the three branches of government, these ready-made Power. Point® presentations provide a quick and easy way to give students solid overviews in a single class period. A CD-ROM contains three 30– 40 slide Power. Point® presentations (one on each branch), teacher overviews, lecture notes in outline form, and multiple -choice quizzes to test student comprehension. Grades 7– 12. Social Studies School Service. Second Edition. © 2005.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n THE BILL OF RIGHTS: Power. Point® Presentations Offering an accessible tool for introducing students to the first ten amendments to the U. S. Constitution, this standards-based unit delivers information using concise, informative text and a variety of visuals. The presentation explores the Bill of Rights' historical foundations and political origins as a whole, while each amendment receives a thorough analysis that explains specific motivations for its inclusion, applicable Supreme Court decisions, and four to six questions for spurring class discussion. A three-ring binder holds a CD-ROM containing the Power. Point® presentation and also includes lecture notes in outline form, a multiple-choice quiz, and extension activities. Grades 9– 12. Social Studies School Service. © 2006. n Reproducible Activity Book CREATIVE LESSONS ON AMERICAN HISTORY: PART FOUR q United States Constitution q Constitution Crossword Puzzle q Three Branches of Government q The Electoral College q The Presidents of the United States q The Beginning of Political Parties
Media References -VI- Government Structure n THE BILL OF RIGHTS: Power. Point® Presentations Offering an accessible tool for introducing students to the first ten amendments to the U. S. Constitution, this standards-based unit delivers information using concise, informative text and a variety of visuals. The presentation explores the Bill of Rights' historical foundations and political origins as a whole, while each amendment receives a thorough analysis that explains specific motivations for its inclusion, applicable Supreme Court decisions, and four to six questions for spurring class discussion. A three-ring binder holds a CD-ROM containing the Power. Point® presentation and also includes lecture notes in outline form, a multiple-choice quiz, and extension activities. Grades 9– 12. Social Studies School Service. © 2006. n Reproducible Activity Book CREATIVE LESSONS ON AMERICAN HISTORY: PART FOUR q United States Constitution q Constitution Crossword Puzzle q Three Branches of Government q The Electoral College q The Presidents of the United States q The Beginning of Political Parties
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD THE THREE BRANCHES OF THE AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Origins of the three branches, powers and functions of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, concept of checks and balances. 20 minutes. n BOOK THE U. S. CONSTITUTION AND YOU By Syl Sobel. With clear and simple language, this volume goes beyond just describing the history of the U. S. Constitution. It tells about the great document itself—explaining exactly how it affects and protects people today. Students discover how the Constitution provides for the federal government’s three branches— legislative, executive, and judicial. They see how it gives all citizens many rights, including the right to vote, to enjoy freedom of speech and press, to worship—or not to worship—according to one’s religious beliefs, to disagree openly with government policy, and to defend oneself in courts of law when accused of crimes or civil wrongs. Grades 3– 5. Index. Bibliography. Glossary. Illustrated. Barron’s. 48 pages. © 2001. n DVD/VHSUNDERSTANDING GOVERNMENT: Just the Facts These bread-and-butter programs supply essential information on the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government. Focusing on a single branch while showing its relation to the other two, each program (averaging 43 minutes) combines clear narration and expert commentary with a wealth of archival film, reenactments, photos, news video, and graphics. Designed like a living textbook with an abundance of detail and historic examples, the series is ideal for independent study, unit introduction, review of previously learned material, or test preparation. Goldhil. © 2004.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n DVD THE THREE BRANCHES OF THE AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Origins of the three branches, powers and functions of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, concept of checks and balances. 20 minutes. n BOOK THE U. S. CONSTITUTION AND YOU By Syl Sobel. With clear and simple language, this volume goes beyond just describing the history of the U. S. Constitution. It tells about the great document itself—explaining exactly how it affects and protects people today. Students discover how the Constitution provides for the federal government’s three branches— legislative, executive, and judicial. They see how it gives all citizens many rights, including the right to vote, to enjoy freedom of speech and press, to worship—or not to worship—according to one’s religious beliefs, to disagree openly with government policy, and to defend oneself in courts of law when accused of crimes or civil wrongs. Grades 3– 5. Index. Bibliography. Glossary. Illustrated. Barron’s. 48 pages. © 2001. n DVD/VHSUNDERSTANDING GOVERNMENT: Just the Facts These bread-and-butter programs supply essential information on the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government. Focusing on a single branch while showing its relation to the other two, each program (averaging 43 minutes) combines clear narration and expert commentary with a wealth of archival film, reenactments, photos, news video, and graphics. Designed like a living textbook with an abundance of detail and historic examples, the series is ideal for independent study, unit introduction, review of previously learned material, or test preparation. Goldhil. © 2004.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n Transparencies OUR DIVIDED GOVERNMENT: The Three Branches of Government in Cartoons This involving package utilizes political cartoons to teach four extended lessons on the workings of government: "The Legislative Branch, " "The Executive Branch, " "The Judicial Branch, " and "Checks and Balances. " Each lesson is based on six cartoons with matched discussion questions and activities presented in a 38 -page reproducible guide. In addition, blackand-white transparencies of all 24 cartoons are furnished for whole-class display. Mind. Sparks. Revised edition. © 2004. n PLAYS AMERICAN HISTORY READER'S THEATER: Develop Reading Fluency and Comprehension Skills Ten short scripts with age-appropriate characters and dialogue are backed with content lessons (background, vocabulary, performance guide, activities, thought questions) and worksheets. Sample subjects include Nantucket whaling, Sitting Bull, Gallaudet's school for the deaf, dreams of becoming a Pony Express rider, Houdini works some magic, Louis Armstrong (age 12) plays some jazz, Amelia Earhart (age 10) wins a paper airplane contest, and farm children get a Model T ride. Grades 3– 4 (or higher). Illustrated. 8½" x 10½". Creative Teaching Press. 96 pages. © 2004. n Audio CDS AMERICAN HISTORY THROUGH NARRATION AND SONG By Keith and Rusty Mc. Neil. These carefully chosen songs capture people's feelings about the history they lived through. Arranged chronologically with brief narrative bridges and very clearly rendered, the songs range from the familiar "Yankee Doodle Dandy" to the obscure "The Rich Lady Over the Sea" (sung at colonist "tea parties" in defiance of the British). Accompanied by instruments appropriate to the times—banjo, bagpipe, fiddle, harmonica, dulcimer. Notes on the songs are included. Grades 5 and up. Stereo. WEM.
Media References -VI- Government Structure n Transparencies OUR DIVIDED GOVERNMENT: The Three Branches of Government in Cartoons This involving package utilizes political cartoons to teach four extended lessons on the workings of government: "The Legislative Branch, " "The Executive Branch, " "The Judicial Branch, " and "Checks and Balances. " Each lesson is based on six cartoons with matched discussion questions and activities presented in a 38 -page reproducible guide. In addition, blackand-white transparencies of all 24 cartoons are furnished for whole-class display. Mind. Sparks. Revised edition. © 2004. n PLAYS AMERICAN HISTORY READER'S THEATER: Develop Reading Fluency and Comprehension Skills Ten short scripts with age-appropriate characters and dialogue are backed with content lessons (background, vocabulary, performance guide, activities, thought questions) and worksheets. Sample subjects include Nantucket whaling, Sitting Bull, Gallaudet's school for the deaf, dreams of becoming a Pony Express rider, Houdini works some magic, Louis Armstrong (age 12) plays some jazz, Amelia Earhart (age 10) wins a paper airplane contest, and farm children get a Model T ride. Grades 3– 4 (or higher). Illustrated. 8½" x 10½". Creative Teaching Press. 96 pages. © 2004. n Audio CDS AMERICAN HISTORY THROUGH NARRATION AND SONG By Keith and Rusty Mc. Neil. These carefully chosen songs capture people's feelings about the history they lived through. Arranged chronologically with brief narrative bridges and very clearly rendered, the songs range from the familiar "Yankee Doodle Dandy" to the obscure "The Rich Lady Over the Sea" (sung at colonist "tea parties" in defiance of the British). Accompanied by instruments appropriate to the times—banjo, bagpipe, fiddle, harmonica, dulcimer. Notes on the songs are included. Grades 5 and up. Stereo. WEM.
 Media References -VI- Government Structure n Powerpoint/Posters/Guide Book ANALYZING VISUAL PRIMARY SOURCES: Elementary Grades This lively and engaging Power. Point® presentation helps teachers walk students step by step through the process of analyzing and interpreting period illustrations, political cartoons, photographs, and other types of visual primary sources. Introductory slides place each source in historical context; subsequent slides combine animations that break down each source into its constituent parts with guided discussion questions. Topics covered include colonial life, Native Americans, the French and Indian War, the Boston Massacre, ratifying the Constitution, slavery, frontier life, and immigration. Notes pages provide historical background and suggested interpretations of each source. Also comes with a set of 11" x 17" posters of the primary sources examined in the presentation. Grades 4– 6. Social Studies School Service. © 2007. n EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO TEACH ABOUT U. S. GOVERNMENT (Book, Poser, Videos) This exceptional resource contains a wealth of material for teaching about the complexities of our federal government. Students will come away with a thorough understanding of how the three branches of government are organized, what their specific duties are, and how they cooperatively run our country. Grades 6– 12. Knowledge Unlimited. This kit contains: n n 3 videos (approximately 18 minutes each): The Presidency, The Congress, The Supreme. Court Set of 3 posters (17"h x 11"w): Branches of Government Poster (22"h x 34"w): How a Bill Becomes a Law 42 -page reproducible resource book: Our Federal Government
Media References -VI- Government Structure n Powerpoint/Posters/Guide Book ANALYZING VISUAL PRIMARY SOURCES: Elementary Grades This lively and engaging Power. Point® presentation helps teachers walk students step by step through the process of analyzing and interpreting period illustrations, political cartoons, photographs, and other types of visual primary sources. Introductory slides place each source in historical context; subsequent slides combine animations that break down each source into its constituent parts with guided discussion questions. Topics covered include colonial life, Native Americans, the French and Indian War, the Boston Massacre, ratifying the Constitution, slavery, frontier life, and immigration. Notes pages provide historical background and suggested interpretations of each source. Also comes with a set of 11" x 17" posters of the primary sources examined in the presentation. Grades 4– 6. Social Studies School Service. © 2007. n EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO TEACH ABOUT U. S. GOVERNMENT (Book, Poser, Videos) This exceptional resource contains a wealth of material for teaching about the complexities of our federal government. Students will come away with a thorough understanding of how the three branches of government are organized, what their specific duties are, and how they cooperatively run our country. Grades 6– 12. Knowledge Unlimited. This kit contains: n n 3 videos (approximately 18 minutes each): The Presidency, The Congress, The Supreme. Court Set of 3 posters (17"h x 11"w): Branches of Government Poster (22"h x 34"w): How a Bill Becomes a Law 42 -page reproducible resource book: Our Federal Government


