0287617a0cdf2ba1c7d363e2b889cb6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
Four-Step Problem Solving Process First Grade 1

Four-Step Process for Problem Solving • Teaches the importance of language within math problems • Provides foundation for algebraic understanding • Provides for differentiated instruction • Developed in Singapore • Visual representation of details and actions which assists children with problem solving • Helps children logically think using visual models to determine their computations • Fosters quantitative reasoning (number sense) when teachers question • Empowers students to think systematically and master more difficult problems • Makes 2 step problems easy to work 2
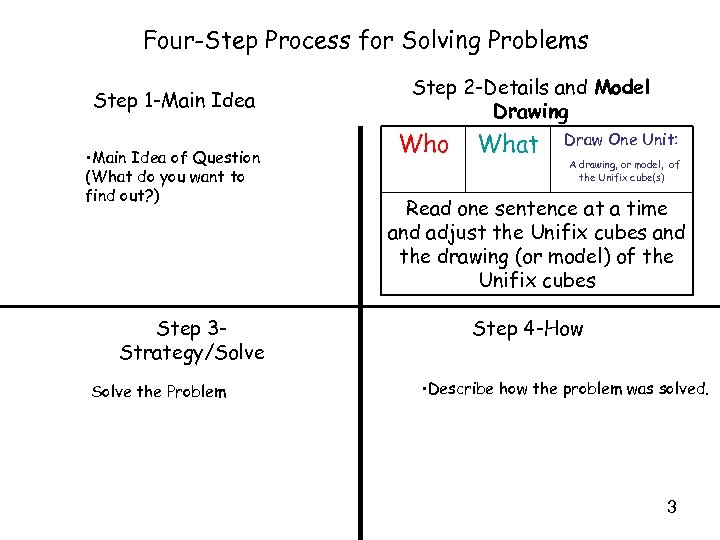
Four-Step Process for Solving Problems Step 1 -Main Idea • Main Idea of Question (What do you want to find out? ) Step 3 Strategy/Solve the Problem Step 2 -Details and Model Drawing Who What Draw One Unit: A drawing, or model, of the Unifix cube(s) Read one sentence at a time and adjust the Unifix cubes and the drawing (or model) of the Unifix cubes Step 4 -How • Describe how the problem was solved. 3

Four Step Process 1. Main Idea • • Read the problem. What do you want to find out? Write the main idea from the question. 2. Details or • • • Write who the problem is about Write what the problem is about Use one Unifix cube to represent each “what” or variable. • Then, draw the Unifix cube to represent one unit. – Reread the problem one sentence at a time. • • Adjust the Unifix cubes and the drawing (model) of the Unifix cubes to match the story problem and label. Put a question mark on the drawing, or model, to show what you are trying to find out. 4

Four-Step Process Continued 3. Strategy/Solve the Problem • Write the number sentence and solve the problem. 4. How • Describe how the problem was solved. 5
Addition Action: Put Together 6

Ann has 2 toys. Jeff has 3 toys. How many toys do they have together? Step 1 Main Idea Step 2: Details and Model Drawing 2 Toys together? Ann- toys or A. T. 3 Jeff- toys or J. T. Step 3: Strategy/Solve 2 ] Step 4: How Add 2 and 3 +3 5 sum 7 ?

Andy and Henry went to the zoo. Andy saw 4. Henry saw 5. How many animals did the 2 boys see? Main Idea animals 2 boys see? Details A. T. (Abbreviate for Andy-Turkeys) 5 H. P. (Abbreviate for Henry-Penguins) Strategy/Solve 4 4 ] How Put together 4 and 5 +5 9 sum 8 ?
Subtraction Action: Take Away 9

Amy has 4 toys. She gave away 1 toy. How many toys are left? Step 2 Step 1 ] Toys left Step 3 4 4 A. T. X (abbreviate for Anntoys) 1 ? Step 4 Subtract 1 from 4. - 1 3 10
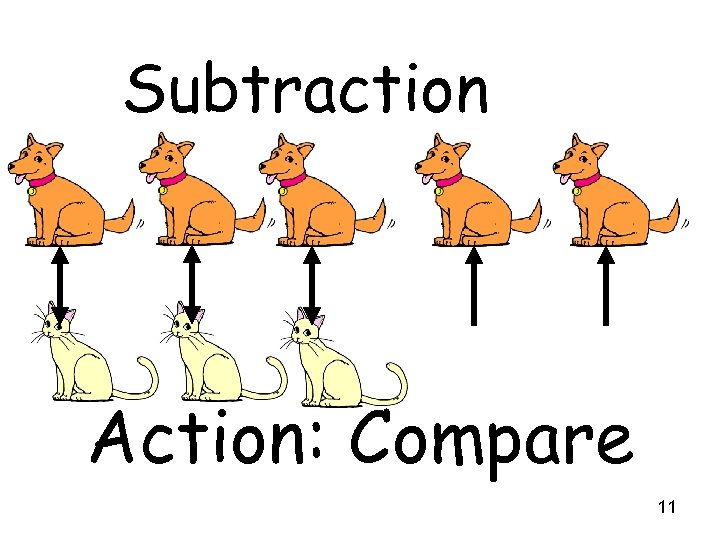
Subtraction Action: Compare 11
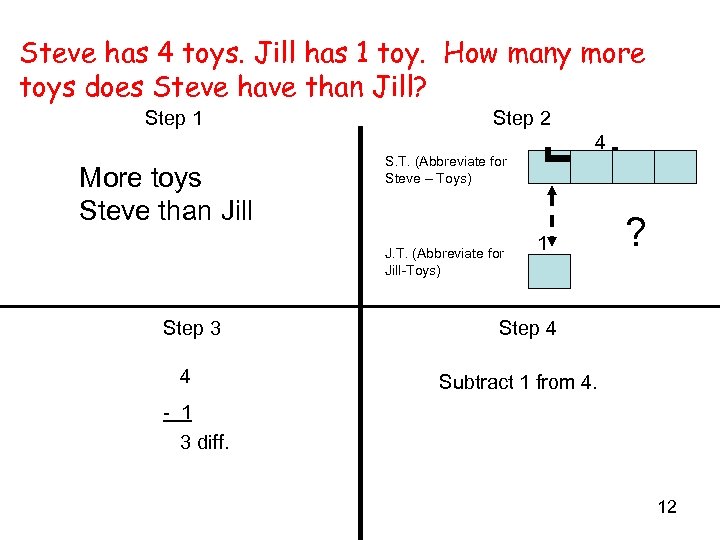
Steve has 4 toys. Jill has 1 toy. How many more toys does Steve have than Jill? Step 1 S. T. (Abbreviate for Steve – Toys) J. T. (Abbreviate for Jill-Toys) Step 3 4 4 ] More toys Steve than Jill Step 2 1 ? Step 4 Subtract 1 from 4. - 1 3 diff. 12
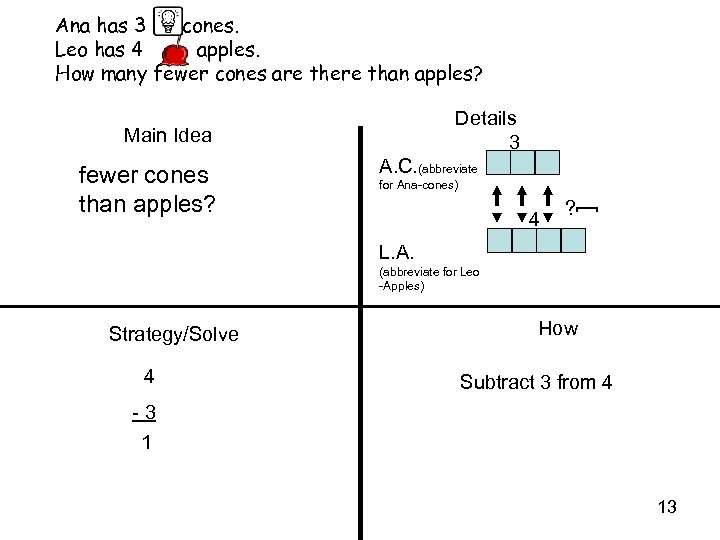
Ana has 3 cones. Leo has 4 apples. How many fewer cones are there than apples? Details 3 Main Idea A. C. (abbreviate for Ana-cones) 4 ? ] fewer cones than apples? L. A. (abbreviate for Leo -Apples) Strategy/Solve 4 How Subtract 3 from 4 -3 1 13

Subtraction Action: Missing Part 14
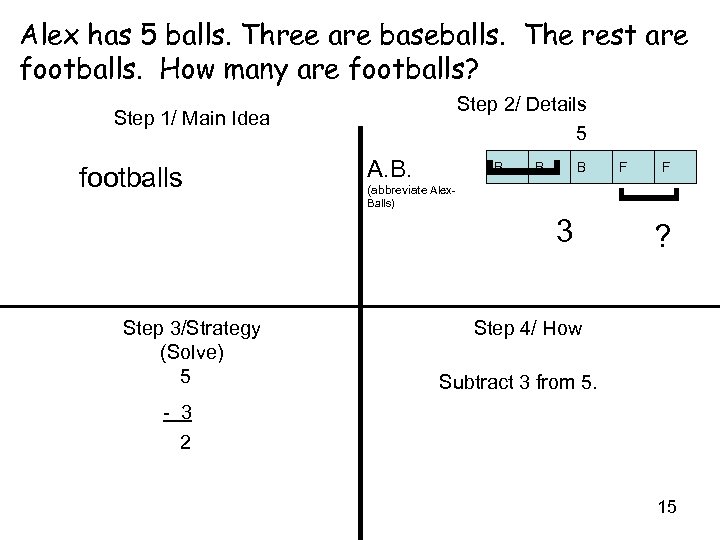
Alex has 5 balls. Three are baseballs. The rest are footballs. How many are footballs? Step 2/ Details 5 Step 1/ Main Idea A. B. ] B B B (abbreviate Alex. Balls) 3 Step 3/Strategy (Solve) 5 F F ] footballs ? Step 4/ How Subtract 3 from 5. - 3 2 15

Tips • Be sure all the drawings of the Unifix cubes (units) for each variable are touching each other so comparisons are clearer. • In the drawing, list the variables in the order they appear in the problem. • Include labels and brackets to help clarify drawings. • Too often, students rush through a problem and answer the wrong question. Placing the question mark beside what you are trying to find helps to prevent that. 16

Extra Information in Word Problems • Sometimes there will be extra information in a word problem. Try to keep students focused on what the question is asking them to find. • If a child understands that the details are usually what is needed to answer the main idea of the question, he will be less likely to include information that is not needed. • However, if the child includes the extra information in the drawing, placing the ? in the model will help them understand what information is needed to answer the question. 17
0287617a0cdf2ba1c7d363e2b889cb6c.ppt