76ec867cc3c1ff415c8fa2dede249aad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Foundations of XBRL: Organisation and Concepts ® Walter Hamscher (walter@hamscher. com) Vice Chair, XBRL International Consultant to Pricewaterhouse. Coopers

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap
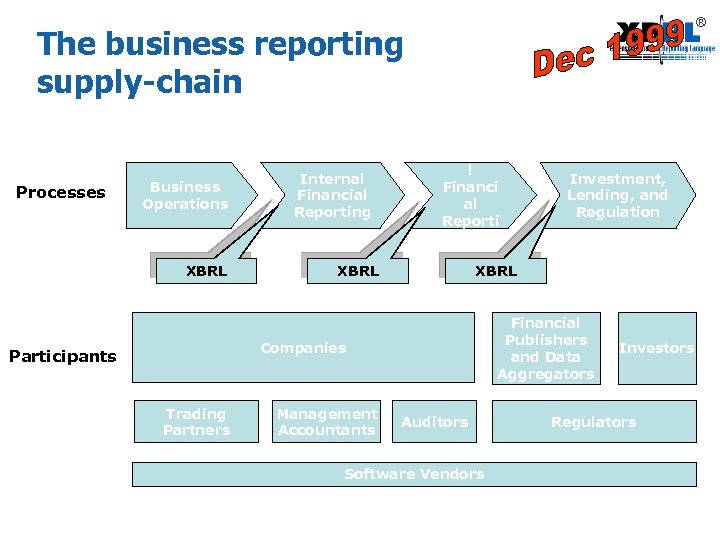
® The business reporting supply-chain Processes Business Operations XBRL Internal Financial Reporting Externa l Financi al Reporti ng XBRL Financial Publishers and Data Aggregators Companies Participants Trading Partners Management Accountants Investment, Lending, and Regulation Auditors Software Vendors Investors Regulators
®

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap
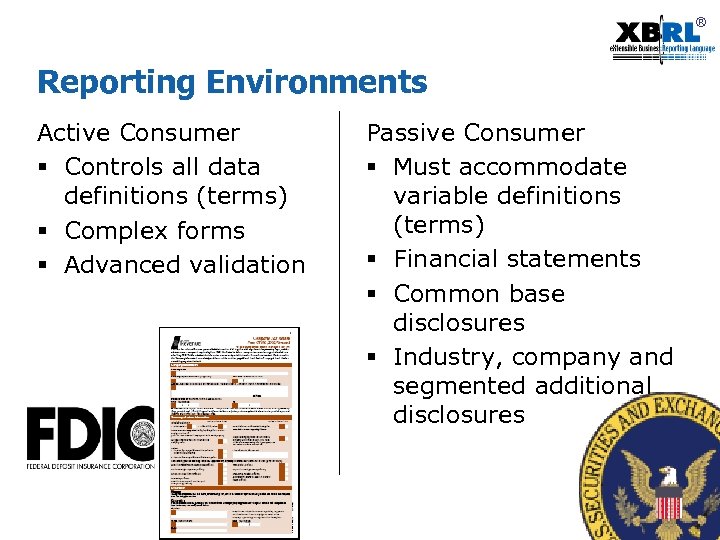
® Reporting Environments Active Consumer § Controls all data definitions (terms) § Complex forms § Advanced validation Passive Consumer § Must accommodate variable definitions (terms) § Financial statements § Common base disclosures § Industry, company and segmented additional disclosures
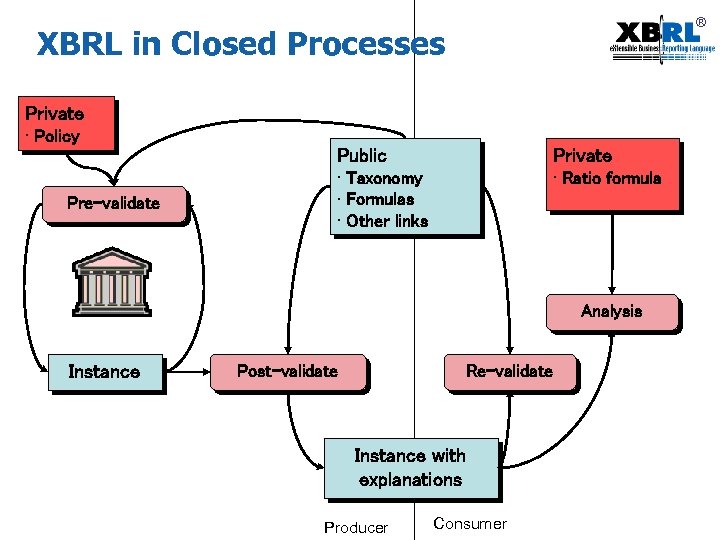
® XBRL in Closed Processes Private • Policy Public Pre-validate Private • Taxonomy • Formulas • Other links • Ratio formula Analysis Instance Post-validate Re-validate Instance with explanations Producer Consumer
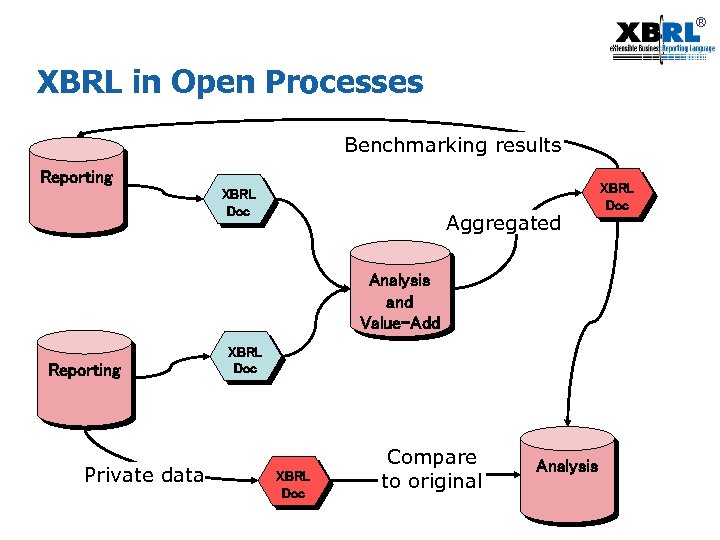
® XBRL in Open Processes Benchmarking results Reporting XBRL Doc Aggregated Analysis and Value-Add Reporting Private data XBRL Doc Compare to original Analysis XBRL Doc

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap

Extensibility Needs of XBRL as compared to other XML standards § Invoice Ø Ø § Depreciation Schedule Parties Ø Line Item *Meaning varies • Identifier • Asset name according to • Address • Asset category* accounting principles Line Item appropriate to purpose • Value brought forward** of information • Item • Value limitation* q Identifier • Period q Description • Acquisition Date • Quantities ** Name of otherwise • Method* • Amounts identical concept • Discounts varies by jurisdiction, • Amount not to mention native • Limitation* Taxes language • Value carried Delivery Terms forward** • Etc. , etc. ®
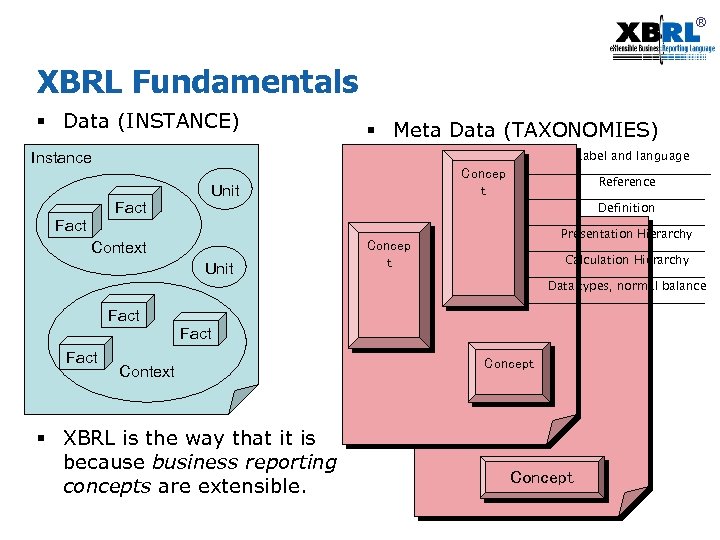
® XBRL Fundamentals § Data (INSTANCE) § Meta Data (TAXONOMIES) Label and language Instance Fact Concep t Unit Definition Fact Context Unit Reference Concep t Presentation Hierarchy Taxonomy Calculation Hierarchy Data types, normal balance Fact Context § XBRL is the way that it is because business reporting concepts are extensible. Concept

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap
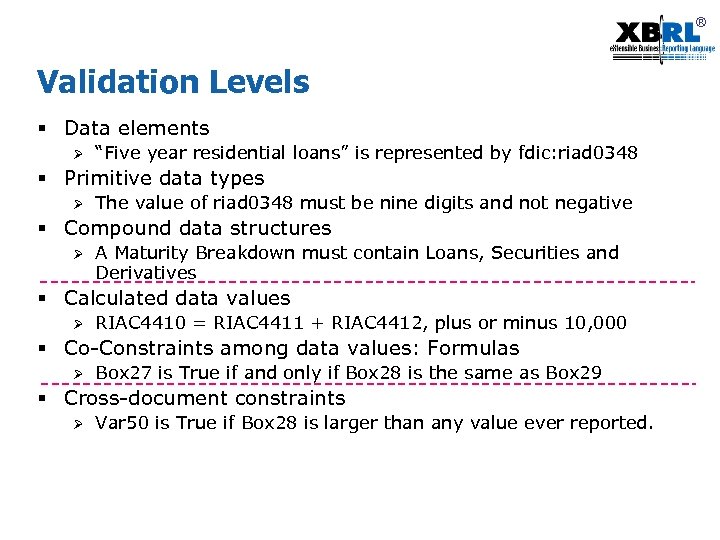
® Validation Levels § Data elements Ø “Five year residential loans” is represented by fdic: riad 0348 § Primitive data types Ø The value of riad 0348 must be nine digits and not negative § Compound data structures Ø A Maturity Breakdown must contain Loans, Securities and Derivatives § Calculated data values Ø RIAC 4410 = RIAC 4411 + RIAC 4412, plus or minus 10, 000 § Co-Constraints among data values: Formulas Ø Box 27 is True if and only if Box 28 is the same as Box 29 § Cross-document constraints Ø Var 50 is True if Box 28 is larger than any value ever reported.

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap
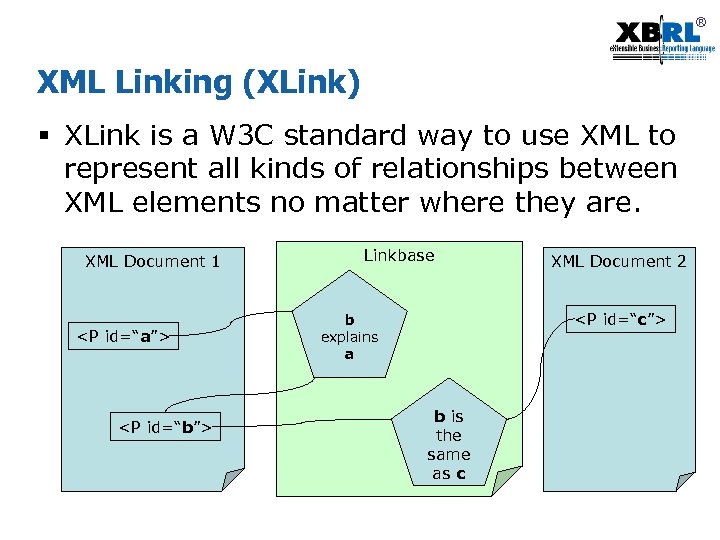
® XML Linking (XLink) § XLink is a W 3 C standard way to use XML to represent all kinds of relationships between XML elements no matter where they are. XML Document 1 <P id=“a”> <P id=“b”> Linkbase XML Document 2 <P id=“c”> b explains a b is the same as c
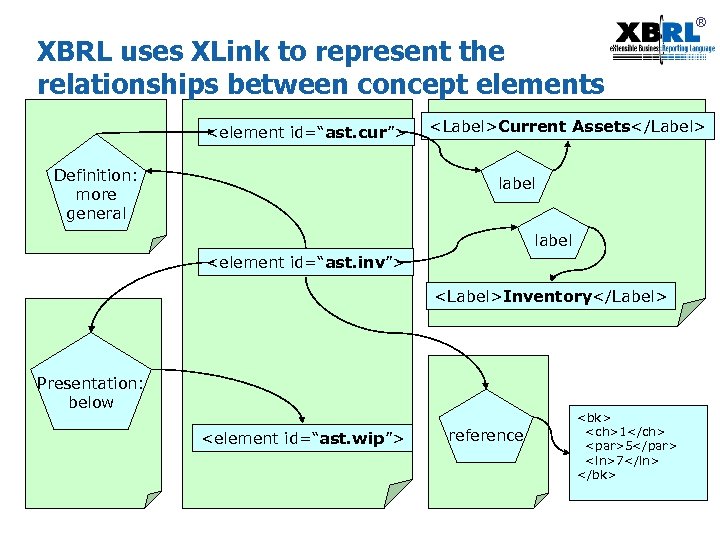
® XBRL uses XLink to represent the relationships between concept elements <element id=“ast. cur”> Definition: more general <Label>Current Assets</Label> label <element id=“ast. inv”> <Label>Inventory</Label> Presentation: below <element id=“ast. wip”> reference <bk> <ch>1</ch> <par>5</par> <ln>7</ln> </bk>
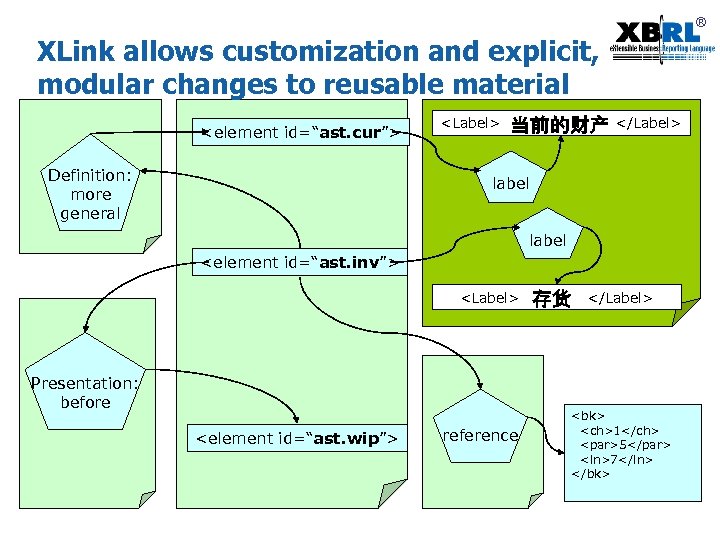
® XLink allows customization and explicit, modular changes to reusable material <element id=“ast. cur”> Definition: more general <Label> 当前的财产 </Label> label <element id=“ast. inv”> <Label> Presentation: before <element id=“ast. wip”> reference 存货 </Label> <bk> <ch>1</ch> <par>5</par> <ln>7</ln> </bk>

® Summary § § § The Business Reporting Supply-Chain Active and Passive Consumers Extensibility Requirements Role of XML Schema in XBRL Role of XML Linking Language in XBRL Current Roadmap
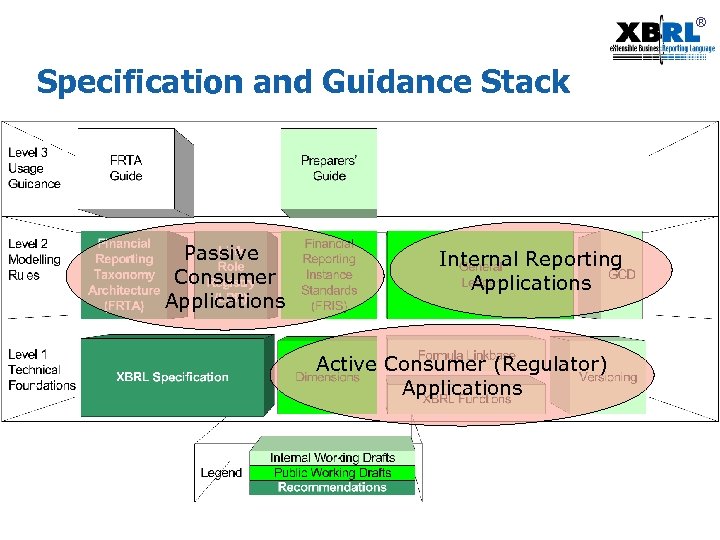
® Specification and Guidance Stack Passive Consumer Applications Internal Reporting Applications Active Consumer (Regulator) Applications

Foundations of XBRL: Organisation and Concepts ® Walter Hamscher (walter@hamscher. com) Vice Chair, XBRL International Consultant to Pricewaterhouse. Coopers

® Abstract § Why is XBRL the way it is? Returning to the fundamental goals and requirements of XBRL, and tracing its evolution from origin to the present, provides the answer. The current package of specifications and modules, encompassing the XBRL 2. 1 specification recommendation, functions, formulas, dimensions and versioning, together realises the vision we have all pursued. This talk will illustrate the interplay between XML Schema and XML Linking Language, as well as the relationship of "active consumer" versus "passive consumer" applications in the evolution of XBRL.
76ec867cc3c1ff415c8fa2dede249aad.ppt