S-Biomechanics 1(Stephen).pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Foundation Year Program A multi-disciplinary approach: An introduction to Biomechanics and Sports Physiology Seminar 1 –Biomechanics 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program A multi-disciplinary approach: An introduction to Biomechanics and Sports Physiology Seminar 1 –Biomechanics 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Feedback • Do artificial legs provide an unfair advantage? • If yes, how? • If no, why? 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Feedback • Do artificial legs provide an unfair advantage? • If yes, how? • If no, why? 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program One Opinion: Prosthetic technology may give Paralympic advantage The prosthetic technology available to paralympians in more affluent countries may be providing an unfair advantage for competitors. http: //www. abc. net. au/lateline/content/2012/s 3436359. htm 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program One Opinion: Prosthetic technology may give Paralympic advantage The prosthetic technology available to paralympians in more affluent countries may be providing an unfair advantage for competitors. http: //www. abc. net. au/lateline/content/2012/s 3436359. htm 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program 'Blade Runner's' artificial legs controversial at Olympics https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. SGBw. UEc. M 6 c 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program 'Blade Runner's' artificial legs controversial at Olympics https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. SGBw. UEc. M 6 c 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Usain Bolt's Bio Mechanics https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Wdm 7 xw. T-v. EQ 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Usain Bolt's Bio Mechanics https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Wdm 7 xw. T-v. EQ 2015 -16
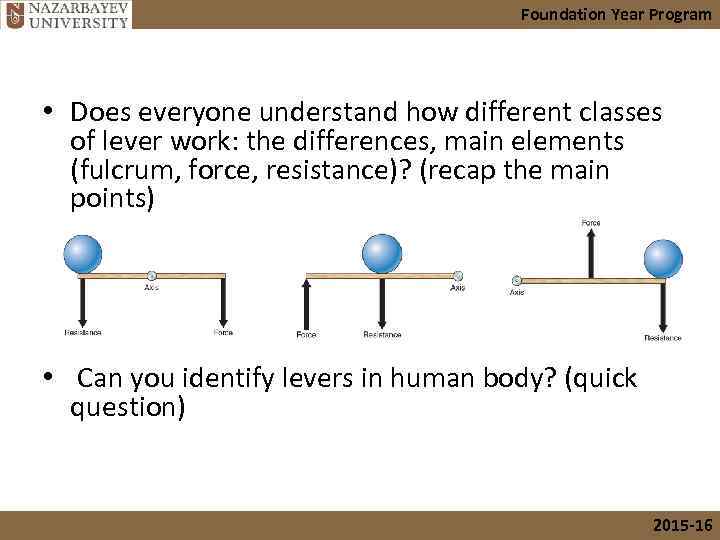 Foundation Year Program • Does everyone understand how different classes of lever work: the differences, main elements (fulcrum, force, resistance)? (recap the main points) • Can you identify levers in human body? (quick question) 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program • Does everyone understand how different classes of lever work: the differences, main elements (fulcrum, force, resistance)? (recap the main points) • Can you identify levers in human body? (quick question) 2015 -16
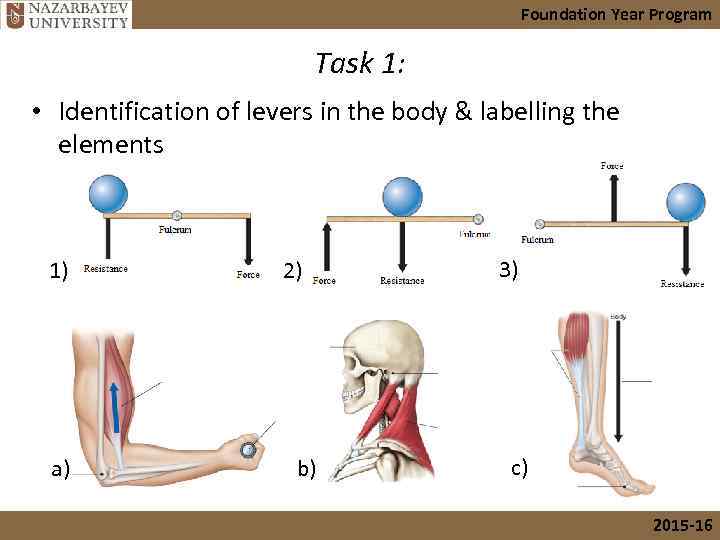 Foundation Year Program Task 1: • Identification of levers in the body & labelling the elements 1) a) 2) b) 3) c) 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 1: • Identification of levers in the body & labelling the elements 1) a) 2) b) 3) c) 2015 -16
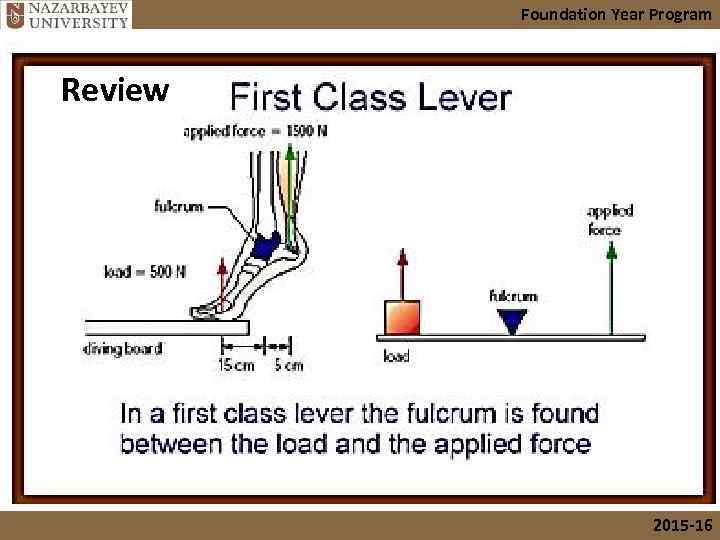 Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
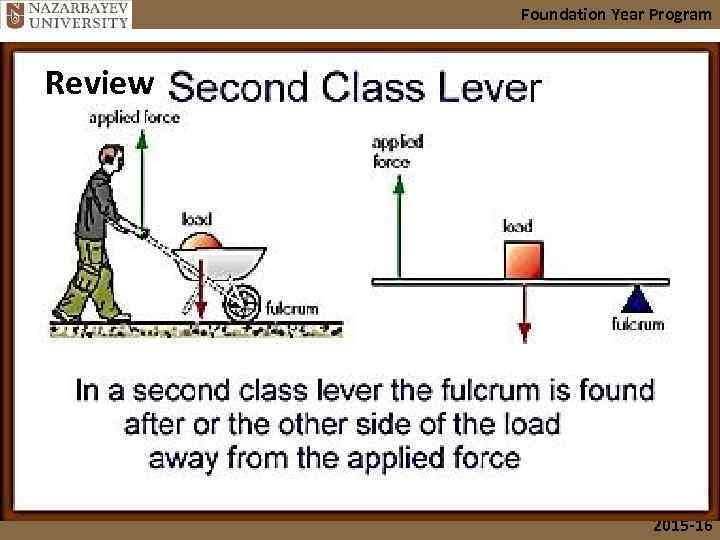 Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
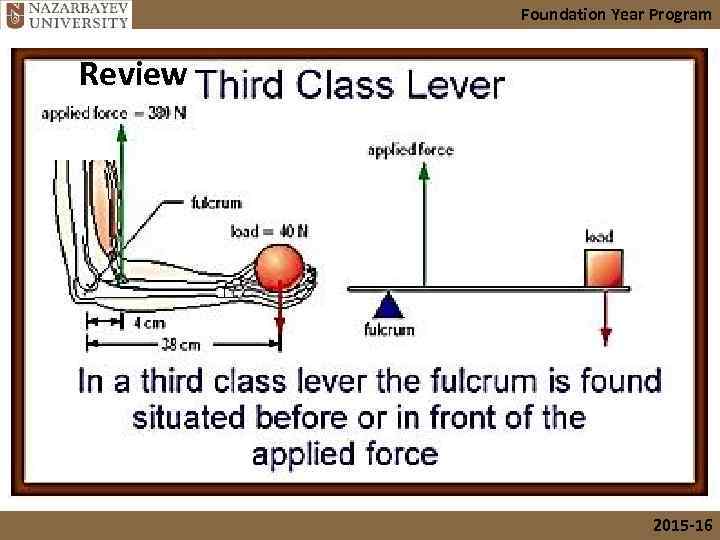 Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Review 2015 -16
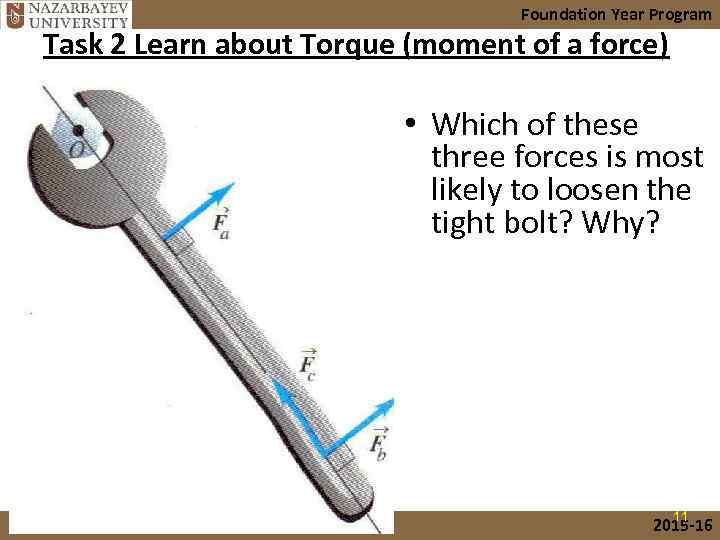 Foundation Year Program Task 2 Learn about Torque (moment of a force) • Which of these three forces is most likely to loosen the tight bolt? Why? 11 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 2 Learn about Torque (moment of a force) • Which of these three forces is most likely to loosen the tight bolt? Why? 11 2015 -16
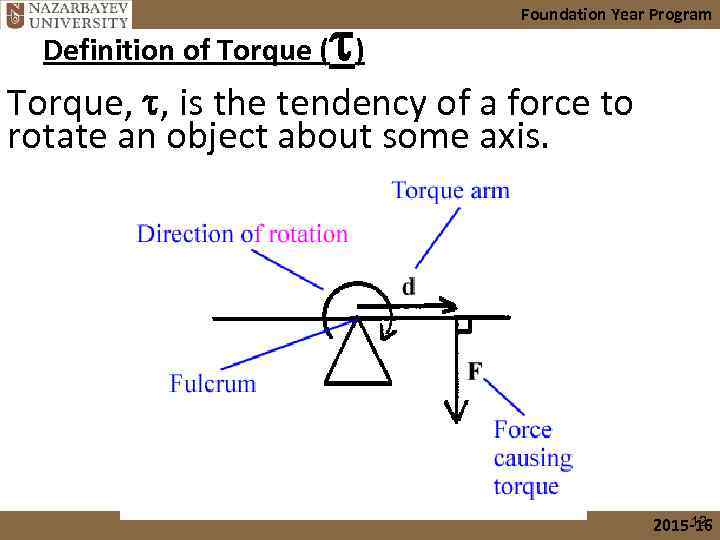 t Foundation Year Program Definition of Torque ( ) Torque, t, is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis. 12 2015 -16
t Foundation Year Program Definition of Torque ( ) Torque, t, is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis. 12 2015 -16
 t Foundation Year Program Formula for Torque ( ) • t is the torque magnitude (Greek letter tau) • F is the magnitude of the force F • d is the length of the arm from pivot to the force • θ is the anticlockwise angle between d and F For this class, the force will be perpendicular to the force arm d, so ϴ = 90⁰, and Sin 90⁰ = 1 13 2015 -16
t Foundation Year Program Formula for Torque ( ) • t is the torque magnitude (Greek letter tau) • F is the magnitude of the force F • d is the length of the arm from pivot to the force • θ is the anticlockwise angle between d and F For this class, the force will be perpendicular to the force arm d, so ϴ = 90⁰, and Sin 90⁰ = 1 13 2015 -16
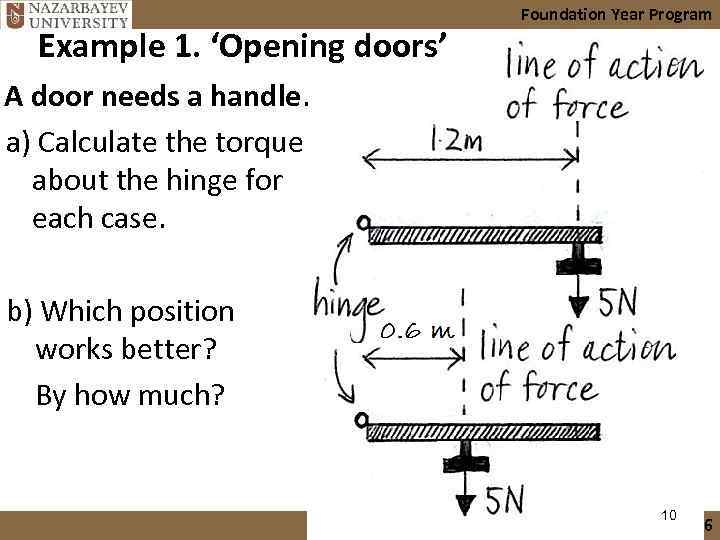 Example 1. ‘Opening doors’ Foundation Year Program A door needs a handle. a) Calculate the torque about the hinge for each case. b) Which position works better? By how much? 10 2015 -16
Example 1. ‘Opening doors’ Foundation Year Program A door needs a handle. a) Calculate the torque about the hinge for each case. b) Which position works better? By how much? 10 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Static Equilibrium • When two or more forces are applied to an object that is not moving, it is considered to be Static (not moving). • If this is true, the torques pulling one direction are equal to the torques pulling the other direction, and the net torque is zero 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Static Equilibrium • When two or more forces are applied to an object that is not moving, it is considered to be Static (not moving). • If this is true, the torques pulling one direction are equal to the torques pulling the other direction, and the net torque is zero 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Task 3: • Compare potential forces being applied to muscles of comparable size – biceps in biceps curls and gastrocnemius in calf raises. – Try doing a biceps curl with a 10 kg bar. Which class lever are you doing? What are the advantages and disadvantages of both types of lever mechanism? 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 3: • Compare potential forces being applied to muscles of comparable size – biceps in biceps curls and gastrocnemius in calf raises. – Try doing a biceps curl with a 10 kg bar. Which class lever are you doing? What are the advantages and disadvantages of both types of lever mechanism? 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Task 2: • Now use a second class lever system. Raise yourself up onto your toes and back down again. Using math… A 75 -kg man stands on his toes by exerting an upward force through the Achilles tendon. (a) What is the force in the Achilles tendon if he stands on one foot? (b) Calculate the force at the ankle joint. Answers: (a) FA=2. 21× 103 N upward and (b) FB=2. 94× 103 N downward. 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 2: • Now use a second class lever system. Raise yourself up onto your toes and back down again. Using math… A 75 -kg man stands on his toes by exerting an upward force through the Achilles tendon. (a) What is the force in the Achilles tendon if he stands on one foot? (b) Calculate the force at the ankle joint. Answers: (a) FA=2. 21× 103 N upward and (b) FB=2. 94× 103 N downward. 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Task 3: • How knowledge of levers can help/improve running techniques? (Discuss in a group of 4 -5 students, then one will present in a simple schematic diagram) 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 3: • How knowledge of levers can help/improve running techniques? (Discuss in a group of 4 -5 students, then one will present in a simple schematic diagram) 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Task 4: • Numerical problem solving questions on levers • What causes muscle injuries? 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 4: • Numerical problem solving questions on levers • What causes muscle injuries? 2015 -16
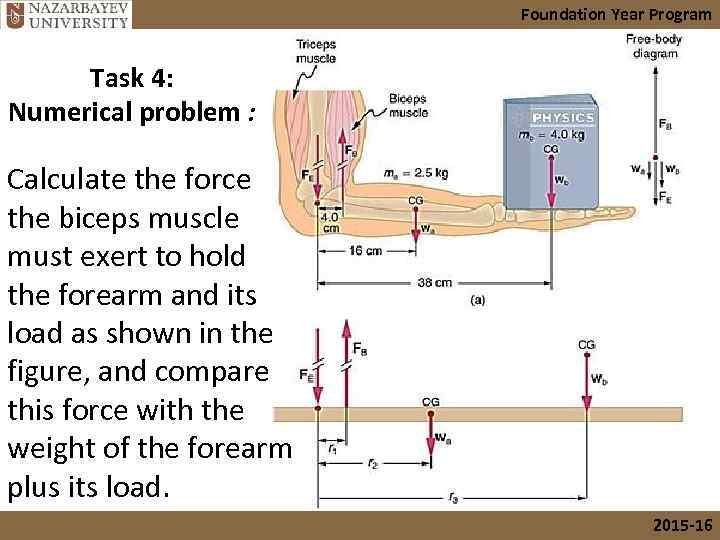 Foundation Year Program Task 4: Numerical problem : Calculate the force the biceps muscle must exert to hold the forearm and its load as shown in the figure, and compare this force with the weight of the forearm plus its load. 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 4: Numerical problem : Calculate the force the biceps muscle must exert to hold the forearm and its load as shown in the figure, and compare this force with the weight of the forearm plus its load. 2015 -16
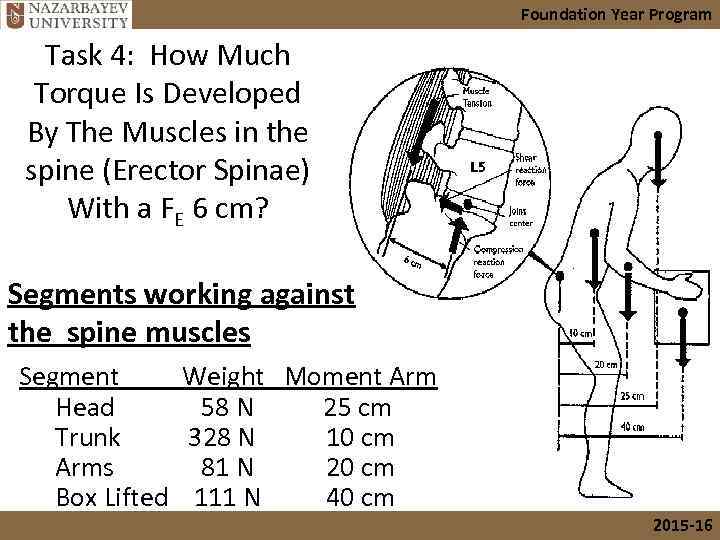 Foundation Year Program Task 4: How Much Torque Is Developed By The Muscles in the spine (Erector Spinae) With a FE 6 cm? Segments working against the spine muscles Segment Weight Moment Arm Head 58 N 25 cm Trunk 328 N 10 cm Arms 81 N 20 cm Box Lifted 111 N 40 cm 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Task 4: How Much Torque Is Developed By The Muscles in the spine (Erector Spinae) With a FE 6 cm? Segments working against the spine muscles Segment Weight Moment Arm Head 58 N 25 cm Trunk 328 N 10 cm Arms 81 N 20 cm Box Lifted 111 N 40 cm 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Solution: Torque at Spine point fulcrum=0 FE (EA) = Head (force)(distance) + Trunk (force)(distance) + Arms (force)(distance) + Box (force)(distance) FE (EA)=(58 N)(25 cm) + (328 N)(10 cm) + (81 N)(20 cm) + (111 N)(40 cm) =? FE (EA) = 10, 790 Ncm Force FE if EA = 6 cm? FE = 1798. 33 N. 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Solution: Torque at Spine point fulcrum=0 FE (EA) = Head (force)(distance) + Trunk (force)(distance) + Arms (force)(distance) + Box (force)(distance) FE (EA)=(58 N)(25 cm) + (328 N)(10 cm) + (81 N)(20 cm) + (111 N)(40 cm) =? FE (EA) = 10, 790 Ncm Force FE if EA = 6 cm? FE = 1798. 33 N. 2015 -16
 Foundation Year Program Another Practice Problem … for a 61. 4 kg Person How much force must be developed by the erector spinae with a moment arm of 6 cm. From the L 5 -S 1 joint center to maintain the body in a lifting position with segment moment arms as Specified? Segment Weight Head 50 N Trunk 280 N Arms 65 N Box Lifted 100 N Torque =? 10, 285 Ncm FE = 1714 N Moment Arm 22 cm. 12 cm. 25 cm. 42 cm. 2015 -16
Foundation Year Program Another Practice Problem … for a 61. 4 kg Person How much force must be developed by the erector spinae with a moment arm of 6 cm. From the L 5 -S 1 joint center to maintain the body in a lifting position with segment moment arms as Specified? Segment Weight Head 50 N Trunk 280 N Arms 65 N Box Lifted 100 N Torque =? 10, 285 Ncm FE = 1714 N Moment Arm 22 cm. 12 cm. 25 cm. 42 cm. 2015 -16


