02_Tires_FSG_Tires_FSG_Workshop_EuroMold.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Formula Student Germany All you need to know about suspension design Tires Creating a Future for Engineers
Formula Student Germany All you need to know about suspension design Tires Creating a Future for Engineers
 Tires – Content § Forces § Properties Creating a Future for Engineers
Tires – Content § Forces § Properties Creating a Future for Engineers
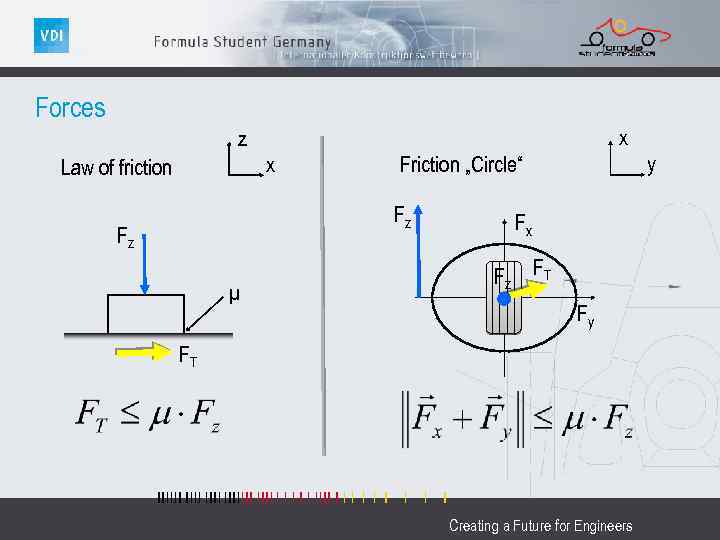 Forces x z x Law of friction Fz Fz µ y Friction „Circle“ Fx Fz FT Fy FT Creating a Future for Engineers
Forces x z x Law of friction Fz Fz µ y Friction „Circle“ Fx Fz FT Fy FT Creating a Future for Engineers
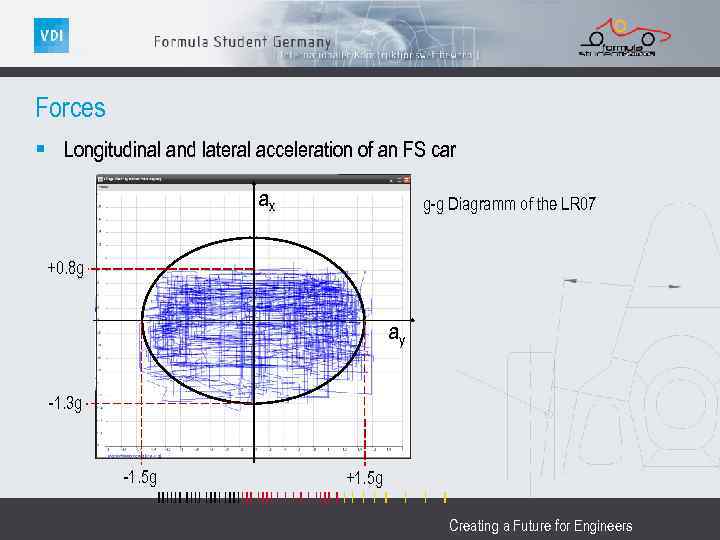 Forces § Longitudinal and lateral acceleration of an FS car ax g-g Diagramm of the LR 07 +0. 8 g ay -1. 3 g -1. 5 g +1. 5 g Creating a Future for Engineers
Forces § Longitudinal and lateral acceleration of an FS car ax g-g Diagramm of the LR 07 +0. 8 g ay -1. 3 g -1. 5 g +1. 5 g Creating a Future for Engineers
 Tires – Content § Forces § Properties Creating a Future for Engineers
Tires – Content § Forces § Properties Creating a Future for Engineers
 Properties Important for Formula Student § Tire Data § Construction § Dimensions § Weight § Reliability / Temperature Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties Important for Formula Student § Tire Data § Construction § Dimensions § Weight § Reliability / Temperature Creating a Future for Engineers
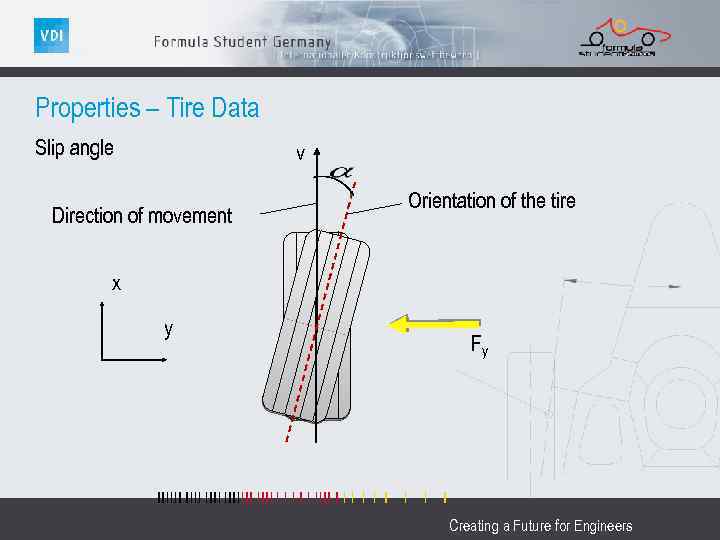 Properties – Tire Data Slip angle v Direction of movement Orientation of the tire x y Fy Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Slip angle v Direction of movement Orientation of the tire x y Fy Creating a Future for Engineers
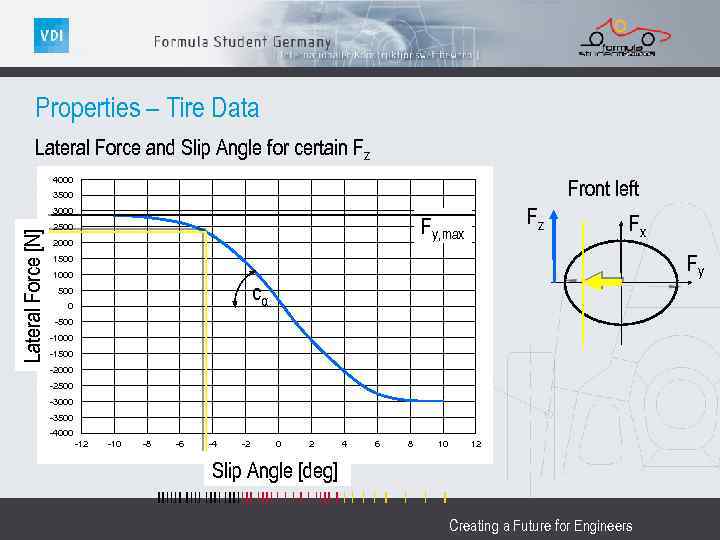 Properties – Tire Data Lateral Force and Slip Angle for certain Fz 4000 Front left 3500 Lateral Force [N] 3000 Fz Fy, max 2500 2000 Fx Fy 1500 1000 cα 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Lateral Force and Slip Angle for certain Fz 4000 Front left 3500 Lateral Force [N] 3000 Fz Fy, max 2500 2000 Fx Fy 1500 1000 cα 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
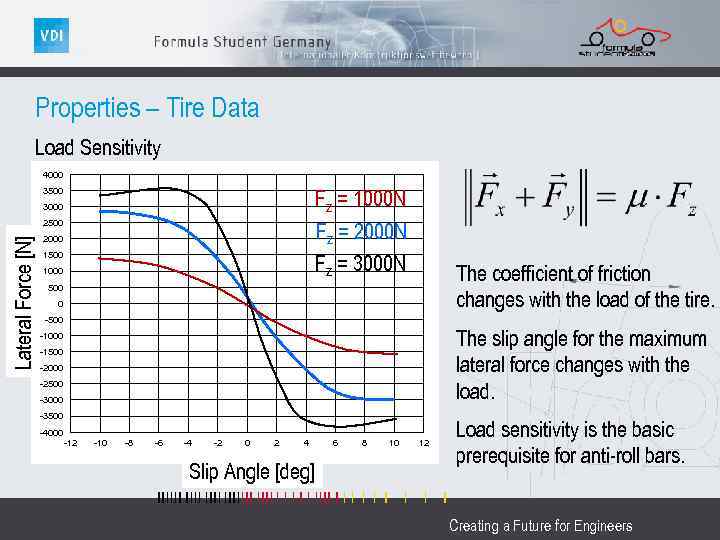 Properties – Tire Data Load Sensitivity 4000 3500 Fz = 1000 N Fz = 2000 N Fz = 3000 N 3000 Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 1500 1000 The coefficient of friction changes with the load of the tire. 500 0 -500 The slip angle for the maximum lateral force changes with the load. -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 Slip Angle [deg] 6 8 10 12 Load sensitivity is the basic prerequisite for anti-roll bars. Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Load Sensitivity 4000 3500 Fz = 1000 N Fz = 2000 N Fz = 3000 N 3000 Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 1500 1000 The coefficient of friction changes with the load of the tire. 500 0 -500 The slip angle for the maximum lateral force changes with the load. -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 Slip Angle [deg] 6 8 10 12 Load sensitivity is the basic prerequisite for anti-roll bars. Creating a Future for Engineers
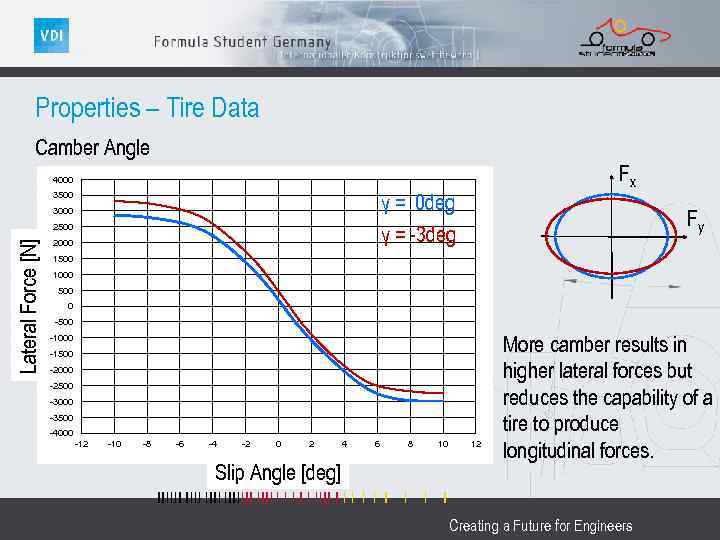 Properties – Tire Data Camber Angle Fx 4000 γ = 0 deg γ = -3 deg 3500 3000 Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 Fy 1500 1000 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 Slip Angle [deg] 4 6 8 10 12 More camber results in higher lateral forces but reduces the capability of a tire to produce longitudinal forces. Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Camber Angle Fx 4000 γ = 0 deg γ = -3 deg 3500 3000 Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 Fy 1500 1000 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 Slip Angle [deg] 4 6 8 10 12 More camber results in higher lateral forces but reduces the capability of a tire to produce longitudinal forces. Creating a Future for Engineers
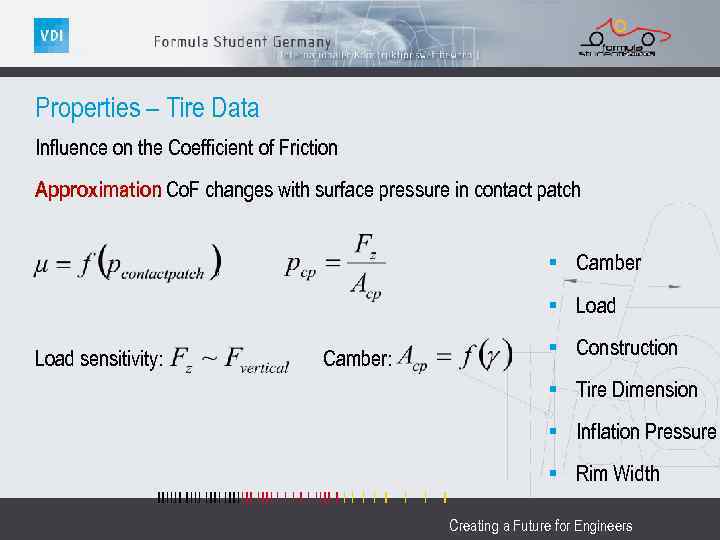 Properties – Tire Data Influence on the Coefficient of Friction Approximation Co. F changes with surface pressure in contact patch : § Camber § Load sensitivity: Camber: § Construction § Tire Dimension § Inflation Pressure § Rim Width Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Influence on the Coefficient of Friction Approximation Co. F changes with surface pressure in contact patch : § Camber § Load sensitivity: Camber: § Construction § Tire Dimension § Inflation Pressure § Rim Width Creating a Future for Engineers
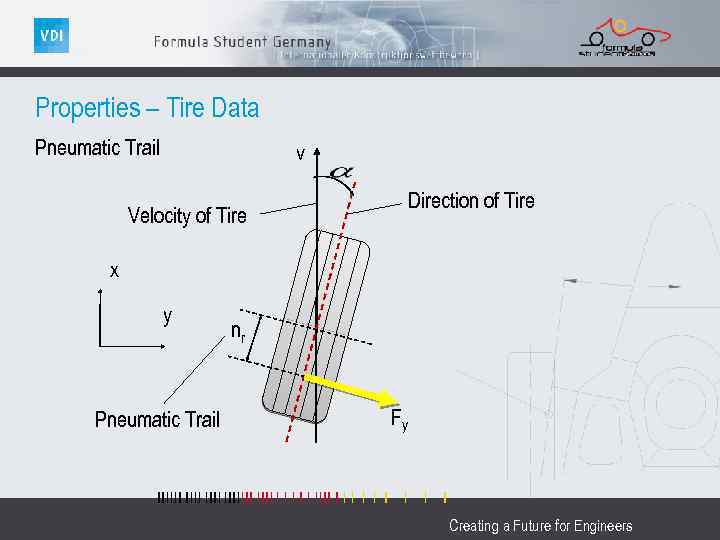 Properties – Tire Data Pneumatic Trail v Direction of Tire Velocity of Tire x y Pneumatic Trail nr Fy Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Pneumatic Trail v Direction of Tire Velocity of Tire x y Pneumatic Trail nr Fy Creating a Future for Engineers
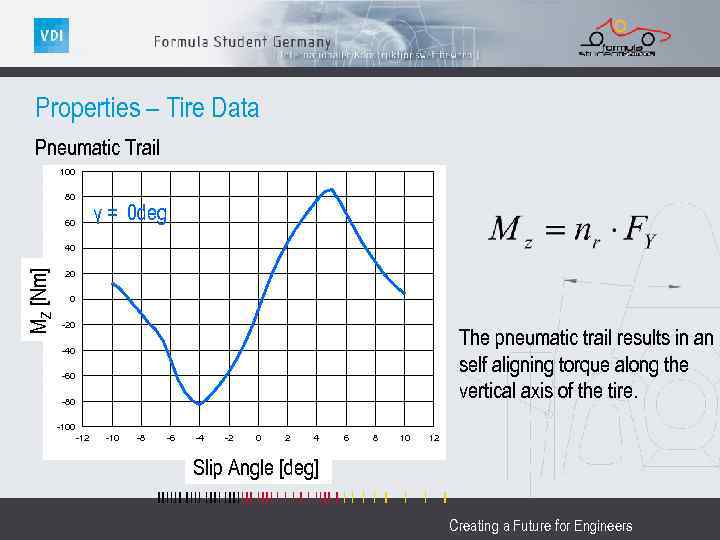 Properties – Tire Data Pneumatic Trail 100 80 γ = 0 deg 60 MZ [Nm] 40 20 0 -20 The pneumatic trail results in an self aligning torque along the vertical axis of the tire. -40 -60 -80 -100 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties – Tire Data Pneumatic Trail 100 80 γ = 0 deg 60 MZ [Nm] 40 20 0 -20 The pneumatic trail results in an self aligning torque along the vertical axis of the tire. -40 -60 -80 -100 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
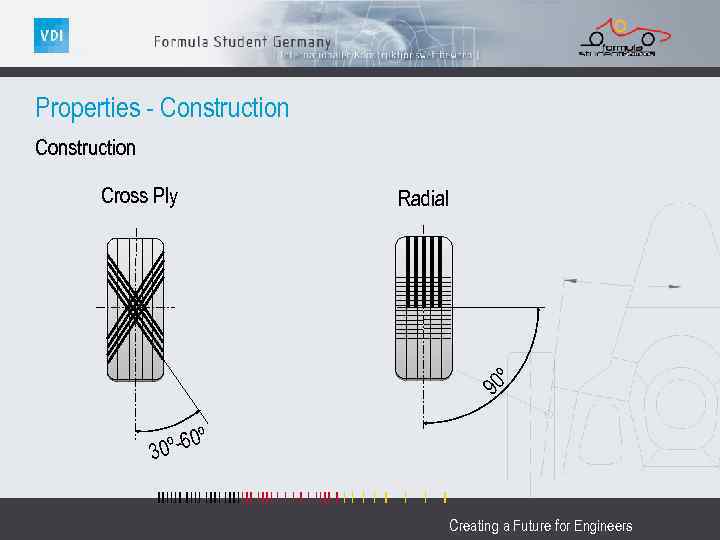 Properties - Construction Radial 90 º Cross Ply º-60º 30 Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties - Construction Radial 90 º Cross Ply º-60º 30 Creating a Future for Engineers
 Properties - Construction Cross Ply Properties Higher vertical and sidewall stiffness Lateral force and wear sensitive to camber Longitudinal force not really sensitive to camber Self aligning torque same as radial tire Lower weight than radial tire º-60º 30 Lower slip angle sensitivity No distinct maximum in lateral force over slip angle Slip ratio better to control under braking Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties - Construction Cross Ply Properties Higher vertical and sidewall stiffness Lateral force and wear sensitive to camber Longitudinal force not really sensitive to camber Self aligning torque same as radial tire Lower weight than radial tire º-60º 30 Lower slip angle sensitivity No distinct maximum in lateral force over slip angle Slip ratio better to control under braking Creating a Future for Engineers
 Properties - Construction Properties Radial Lower vertical and sidewall stiffness 90 º Used at higher cambers than cross ply tires Wear almost not sensitive to camber Lateral and longitudinal force very sensitive to camber Self aligning torque same as cross ply tire Higher weight than cross ply tire High slip angle sensitivity little slip angles Distinct maximum in lateral force over slip angle Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties - Construction Properties Radial Lower vertical and sidewall stiffness 90 º Used at higher cambers than cross ply tires Wear almost not sensitive to camber Lateral and longitudinal force very sensitive to camber Self aligning torque same as cross ply tire Higher weight than cross ply tire High slip angle sensitivity little slip angles Distinct maximum in lateral force over slip angle Creating a Future for Engineers
![Properties - Construction 4000 Radial 3500 3000 Cross Ply Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 Properties - Construction 4000 Radial 3500 3000 Cross Ply Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000](https://present5.com/presentation/151337966_437031732/image-17.jpg) Properties - Construction 4000 Radial 3500 3000 Cross Ply Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
Properties - Construction 4000 Radial 3500 3000 Cross Ply Lateral Force [N] 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 -500 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 -3000 -3500 -4000 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Slip Angle [deg] Creating a Future for Engineers
 Tire Properties - Testing Temperature: Absolute temperature influenced by: Local Temperatures influenced by: Slip, load, inflation pressure Camber, rim width, inflation pressure § Every section of the contact patch should operate at an reasonable temperature § Camber is not only a compromise between lateral and longitudinal performance High negative camber can lead to unequal temperatures in the contact patch Some section may be to cold or to hot § Toe and hard springs / dampers result in additional slip, temperature rises Creating a Future for Engineers
Tire Properties - Testing Temperature: Absolute temperature influenced by: Local Temperatures influenced by: Slip, load, inflation pressure Camber, rim width, inflation pressure § Every section of the contact patch should operate at an reasonable temperature § Camber is not only a compromise between lateral and longitudinal performance High negative camber can lead to unequal temperatures in the contact patch Some section may be to cold or to hot § Toe and hard springs / dampers result in additional slip, temperature rises Creating a Future for Engineers
 Tire Properties - Testing Test of Tire Properties: § Tire Test Consortium: www. google. de : FSAE TTC Huge amount of tire data, enables comparison between tires and basic design decisicon. 500$ entrance fee, new measurements are taken every 1 – 2 years § Test by the team on the track: To prefer for absolute numbers, problem: reproducability Creating a Future for Engineers
Tire Properties - Testing Test of Tire Properties: § Tire Test Consortium: www. google. de : FSAE TTC Huge amount of tire data, enables comparison between tires and basic design decisicon. 500$ entrance fee, new measurements are taken every 1 – 2 years § Test by the team on the track: To prefer for absolute numbers, problem: reproducability Creating a Future for Engineers
 Tire Properties - Testing Test of Tire Properties: § Have your setup ready before you do the comparison § Prepare weights to compensate for different diameters § Constant track conditions § Measure the reference tire again at the end of the day § Always the same track (similar to competition track) § Biggest influence: Driver. Ask the driver for feedback before judging the DAQ § Safety first: Full safety gear, track marshalls, fire extinguishers, test ground Creating a Future for Engineers
Tire Properties - Testing Test of Tire Properties: § Have your setup ready before you do the comparison § Prepare weights to compensate for different diameters § Constant track conditions § Measure the reference tire again at the end of the day § Always the same track (similar to competition track) § Biggest influence: Driver. Ask the driver for feedback before judging the DAQ § Safety first: Full safety gear, track marshalls, fire extinguishers, test ground Creating a Future for Engineers
 Literature § Race Car Vehicle Dynamics; William F. Milliken, Douglas L. Milliken Huge book on all parts of vehicle dynamics and tires Creating a Future for Engineers
Literature § Race Car Vehicle Dynamics; William F. Milliken, Douglas L. Milliken Huge book on all parts of vehicle dynamics and tires Creating a Future for Engineers
 See you at Hockenheim August 2010 Creating a Future for Engineers
See you at Hockenheim August 2010 Creating a Future for Engineers


