 Forging new generations of engineers
Forging new generations of engineers
 What is Fluid Power? • Fluid power is energy transmitted and controlled by means of a pressurized fluid, either liquid or gas. The term fluid power applies to both hydraulics and pneumatics. • Hydraulics uses pressurized liquid, for example, oil or water; • Pneumatics uses compressed air or other neutral gases. • Fluid power can be effectively combined with other technologies through the use of sensors, transducers and microprocessors. From: http: //www. nfpa. com/Our. Industry/Our. Ind_About. FP_What. Is. Fluid. Power. asp
What is Fluid Power? • Fluid power is energy transmitted and controlled by means of a pressurized fluid, either liquid or gas. The term fluid power applies to both hydraulics and pneumatics. • Hydraulics uses pressurized liquid, for example, oil or water; • Pneumatics uses compressed air or other neutral gases. • Fluid power can be effectively combined with other technologies through the use of sensors, transducers and microprocessors. From: http: //www. nfpa. com/Our. Industry/Our. Ind_About. FP_What. Is. Fluid. Power. asp
 How does Fluid Power Work? Pascal's Law expresses the central concept of fluid power: "Pressure exerted by a confined fluid acts undiminished equally in all directions. "
How does Fluid Power Work? Pascal's Law expresses the central concept of fluid power: "Pressure exerted by a confined fluid acts undiminished equally in all directions. "
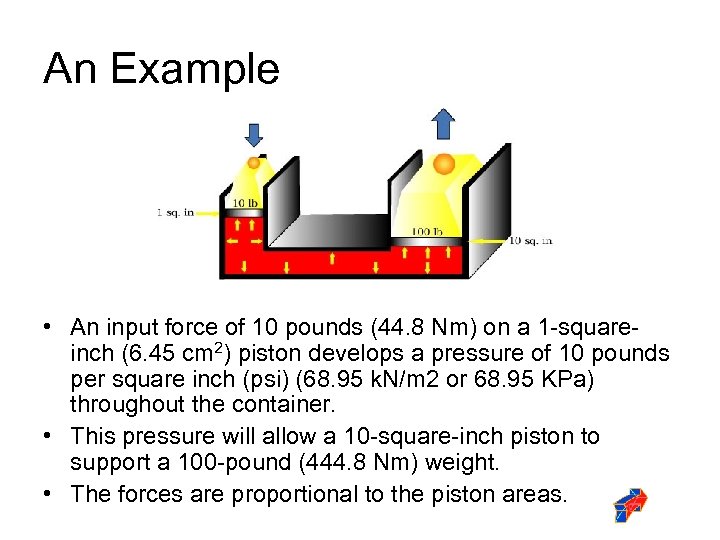 An Example • An input force of 10 pounds (44. 8 Nm) on a 1 -squareinch (6. 45 cm 2) piston develops a pressure of 10 pounds per square inch (psi) (68. 95 k. N/m 2 or 68. 95 KPa) throughout the container. • This pressure will allow a 10 -square-inch piston to support a 100 -pound (444. 8 Nm) weight. • The forces are proportional to the piston areas.
An Example • An input force of 10 pounds (44. 8 Nm) on a 1 -squareinch (6. 45 cm 2) piston develops a pressure of 10 pounds per square inch (psi) (68. 95 k. N/m 2 or 68. 95 KPa) throughout the container. • This pressure will allow a 10 -square-inch piston to support a 100 -pound (444. 8 Nm) weight. • The forces are proportional to the piston areas.
 The Advantages • • Multiplication and variation of force Easy, accurate control Multi-function control High horsepower, low weight Low speed torque Constant force or torque Safety in hazardous environments Established standards and engineering
The Advantages • • Multiplication and variation of force Easy, accurate control Multi-function control High horsepower, low weight Low speed torque Constant force or torque Safety in hazardous environments Established standards and engineering
 Fluid Power Applications • Mobile – Backhoes – Graders – Tractors – – Truck brakes Suspensions Spreaders Highway maintenance vehicles
Fluid Power Applications • Mobile – Backhoes – Graders – Tractors – – Truck brakes Suspensions Spreaders Highway maintenance vehicles
 Fluid Power Applications • Industrial – Metalworking equipment – Controllers – Automated manipulators – Material handling – Assembly equipment
Fluid Power Applications • Industrial – Metalworking equipment – Controllers – Automated manipulators – Material handling – Assembly equipment
 Fluid Power Applications • Aerospace – – – Landing gear Brakes Flight controls Motor controls Cargo loading equipment
Fluid Power Applications • Aerospace – – – Landing gear Brakes Flight controls Motor controls Cargo loading equipment
 Fluid Power Components
Fluid Power Components
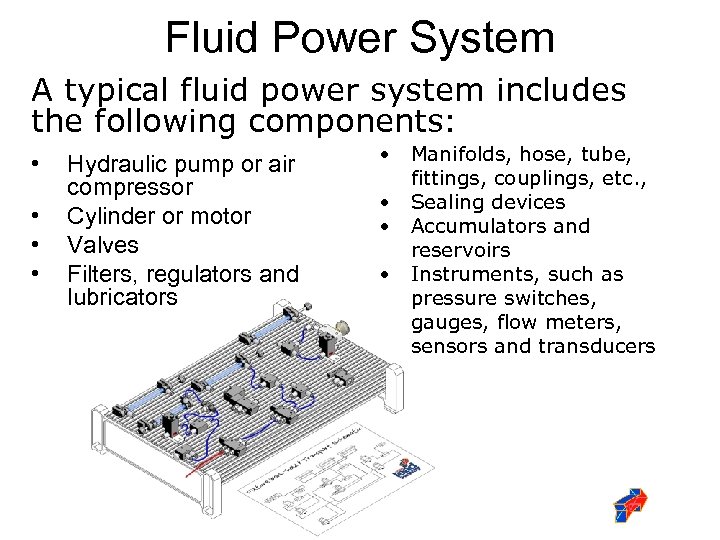 Fluid Power System A typical fluid power system includes the following components: • • Hydraulic pump or air compressor Cylinder or motor Valves Filters, regulators and lubricators • Manifolds, hose, tube, fittings, couplings, etc. , • Sealing devices • Accumulators and reservoirs • Instruments, such as pressure switches, gauges, flow meters, sensors and transducers
Fluid Power System A typical fluid power system includes the following components: • • Hydraulic pump or air compressor Cylinder or motor Valves Filters, regulators and lubricators • Manifolds, hose, tube, fittings, couplings, etc. , • Sealing devices • Accumulators and reservoirs • Instruments, such as pressure switches, gauges, flow meters, sensors and transducers