14c21d25b68833a6210e311bcd4f9725.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Forging a new standard in metastatic CRC Eric Van Cutsem University Hospital Gasthuisberg Leuven, Belgium
Forging a new standard in metastatic CRC Eric Van Cutsem University Hospital Gasthuisberg Leuven, Belgium
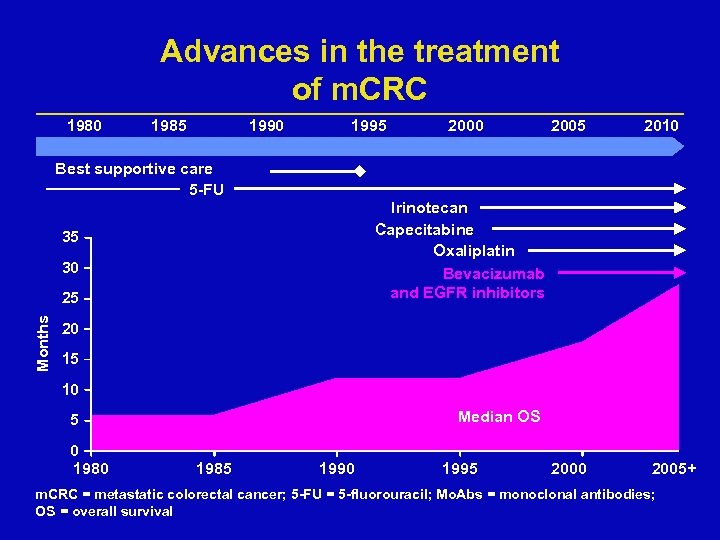 Advances in the treatment of m. CRC 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Best supportive care 5 -FU Irinotecan Capecitabine Oxaliplatin Bevacizumab and EGFR inhibitors 35 30 Months 25 20 15 10 Median OS 5 0 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005+ m. CRC = metastatic colorectal cancer; 5 -FU = 5 -fluorouracil; Mo. Abs = monoclonal antibodies; OS = overall survival
Advances in the treatment of m. CRC 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Best supportive care 5 -FU Irinotecan Capecitabine Oxaliplatin Bevacizumab and EGFR inhibitors 35 30 Months 25 20 15 10 Median OS 5 0 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005+ m. CRC = metastatic colorectal cancer; 5 -FU = 5 -fluorouracil; Mo. Abs = monoclonal antibodies; OS = overall survival
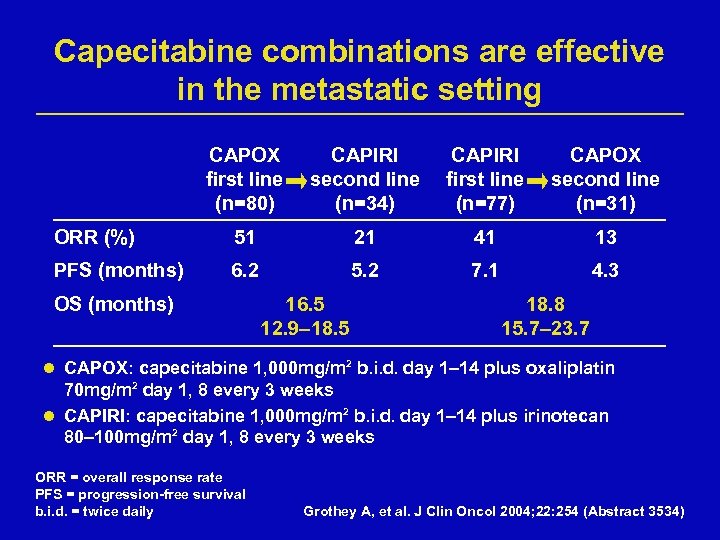 Capecitabine combinations are effective in the metastatic setting CAPOX first line (n=80) CAPIRI second line (n=34) CAPIRI first line (n=77) CAPOX second line (n=31) ORR (%) 51 21 41 13 PFS (months) 6. 2 5. 2 7. 1 4. 3 OS (months) 16. 5 12. 9– 18. 5 18. 8 15. 7– 23. 7 l CAPOX: capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 b. i. d. day 1– 14 plus oxaliplatin 70 mg/m 2 day 1, 8 every 3 weeks l CAPIRI: capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 b. i. d. day 1– 14 plus irinotecan 80– 100 mg/m 2 day 1, 8 every 3 weeks ORR = overall response rate PFS = progression-free survival b. i. d. = twice daily Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 254 (Abstract 3534)
Capecitabine combinations are effective in the metastatic setting CAPOX first line (n=80) CAPIRI second line (n=34) CAPIRI first line (n=77) CAPOX second line (n=31) ORR (%) 51 21 41 13 PFS (months) 6. 2 5. 2 7. 1 4. 3 OS (months) 16. 5 12. 9– 18. 5 18. 8 15. 7– 23. 7 l CAPOX: capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 b. i. d. day 1– 14 plus oxaliplatin 70 mg/m 2 day 1, 8 every 3 weeks l CAPIRI: capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 b. i. d. day 1– 14 plus irinotecan 80– 100 mg/m 2 day 1, 8 every 3 weeks ORR = overall response rate PFS = progression-free survival b. i. d. = twice daily Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 254 (Abstract 3534)
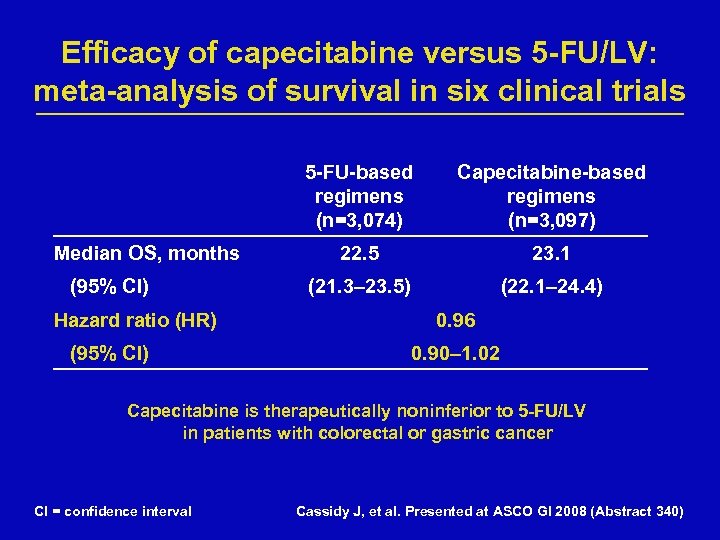 Efficacy of capecitabine versus 5 -FU/LV: meta-analysis of survival in six clinical trials 5 -FU-based regimens (n=3, 074) Median OS, months (95% CI) Hazard ratio (HR) (95% CI) Capecitabine-based regimens (n=3, 097) 22. 5 23. 1 (21. 3– 23. 5) (22. 1– 24. 4) 0. 96 0. 90– 1. 02 Capecitabine is therapeutically noninferior to 5 -FU/LV in patients with colorectal or gastric cancer CI = confidence interval Cassidy J, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 340)
Efficacy of capecitabine versus 5 -FU/LV: meta-analysis of survival in six clinical trials 5 -FU-based regimens (n=3, 074) Median OS, months (95% CI) Hazard ratio (HR) (95% CI) Capecitabine-based regimens (n=3, 097) 22. 5 23. 1 (21. 3– 23. 5) (22. 1– 24. 4) 0. 96 0. 90– 1. 02 Capecitabine is therapeutically noninferior to 5 -FU/LV in patients with colorectal or gastric cancer CI = confidence interval Cassidy J, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 340)
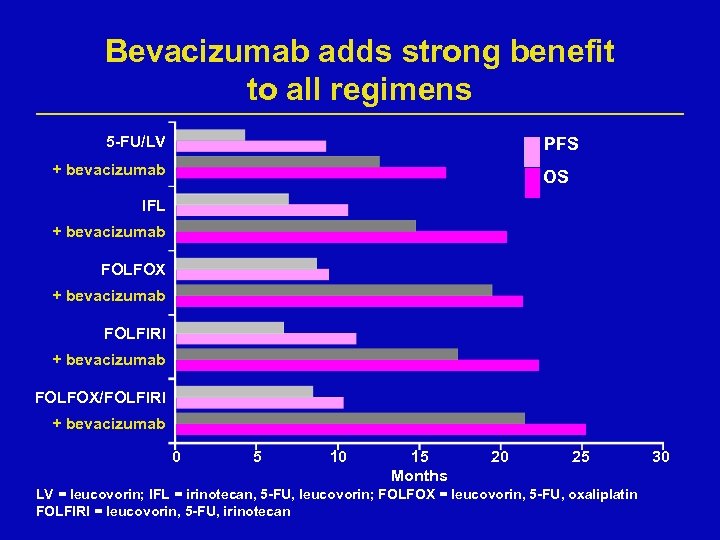 Bevacizumab adds strong benefit to all regimens 5 -FU/LV PFS + bevacizumab OS IFL + bevacizumab FOLFOX + bevacizumab FOLFIRI + bevacizumab FOLFOX/FOLFIRI + bevacizumab 0 5 10 15 Months 20 25 LV = leucovorin; IFL = irinotecan, 5 -FU, leucovorin; FOLFOX = leucovorin, 5 -FU, oxaliplatin FOLFIRI = leucovorin, 5 -FU, irinotecan 30
Bevacizumab adds strong benefit to all regimens 5 -FU/LV PFS + bevacizumab OS IFL + bevacizumab FOLFOX + bevacizumab FOLFIRI + bevacizumab FOLFOX/FOLFIRI + bevacizumab 0 5 10 15 Months 20 25 LV = leucovorin; IFL = irinotecan, 5 -FU, leucovorin; FOLFOX = leucovorin, 5 -FU, oxaliplatin FOLFIRI = leucovorin, 5 -FU, irinotecan 30
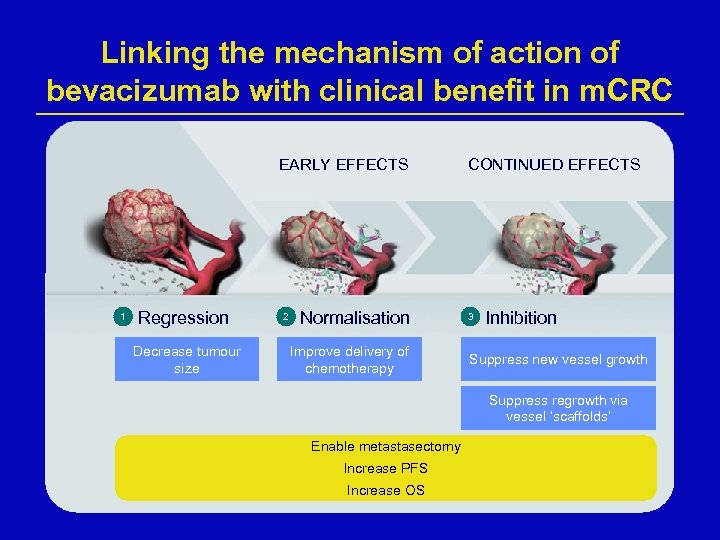 Linking the mechanism of action of bevacizumab with clinical benefit in m. CRC EARLY EFFECTS 1 Regression Decrease tumour size 2 Normalisation Improve delivery of chemotherapy CONTINUED EFFECTS 3 Inhibition Suppress new vessel growth Suppress regrowth via vessel ‘scaffolds’ Enable metastasectomy Increase PFS Increase OS
Linking the mechanism of action of bevacizumab with clinical benefit in m. CRC EARLY EFFECTS 1 Regression Decrease tumour size 2 Normalisation Improve delivery of chemotherapy CONTINUED EFFECTS 3 Inhibition Suppress new vessel growth Suppress regrowth via vessel ‘scaffolds’ Enable metastasectomy Increase PFS Increase OS
 Irinotecan-containing regimens with bevacizumab and/or capecitabine
Irinotecan-containing regimens with bevacizumab and/or capecitabine
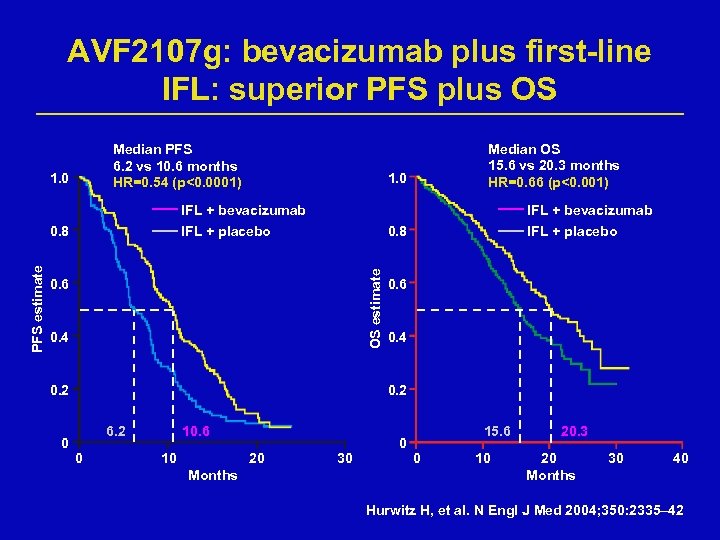 AVF 2107 g: bevacizumab plus first-line IFL: superior PFS plus OS Median PFS 6. 2 vs 10. 6 months HR=0. 54 (p<0. 0001) 1. 0 Median OS 15. 6 vs 20. 3 months HR=0. 66 (p<0. 001) 1. 0 IFL + bevacizumab 0. 8 IFL + placebo OS estimate PFS estimate 0. 8 IFL + bevacizumab 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 IFL + placebo 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 6. 2 0 10. 6 10 20 Months 30 0 15. 6 0 10 20. 3 20 Months 30 40 Hurwitz H, et al. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2335– 42
AVF 2107 g: bevacizumab plus first-line IFL: superior PFS plus OS Median PFS 6. 2 vs 10. 6 months HR=0. 54 (p<0. 0001) 1. 0 Median OS 15. 6 vs 20. 3 months HR=0. 66 (p<0. 001) 1. 0 IFL + bevacizumab 0. 8 IFL + placebo OS estimate PFS estimate 0. 8 IFL + bevacizumab 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 IFL + placebo 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 6. 2 0 10. 6 10 20 Months 30 0 15. 6 0 10 20. 3 20 Months 30 40 Hurwitz H, et al. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2335– 42
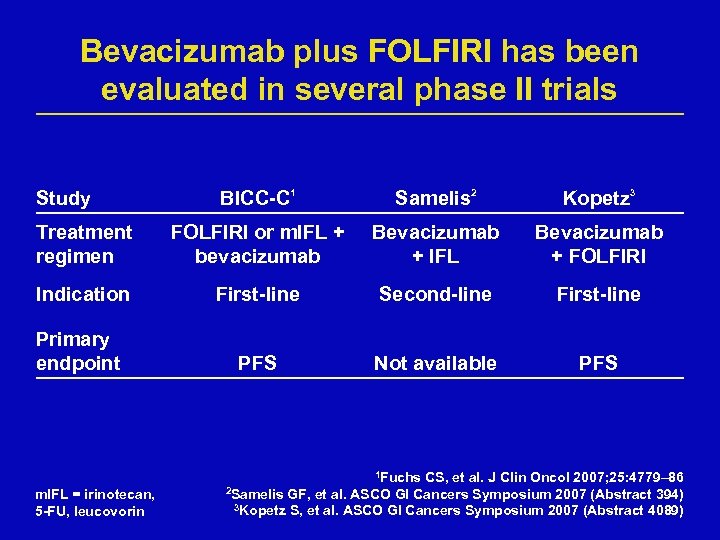 Bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI has been evaluated in several phase II trials Study BICC-C 1 Samelis 2 Kopetz 3 Treatment regimen FOLFIRI or m. IFL + bevacizumab Bevacizumab + IFL Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI Indication First-line Second-line First-line Primary endpoint PFS Not available PFS 1 Fuchs m. IFL = irinotecan, 5 -FU, leucovorin CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86 GF, et al. ASCO GI Cancers Symposium 2007 (Abstract 394) 3 Kopetz S, et al. ASCO GI Cancers Symposium 2007 (Abstract 4089) 2 Samelis
Bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI has been evaluated in several phase II trials Study BICC-C 1 Samelis 2 Kopetz 3 Treatment regimen FOLFIRI or m. IFL + bevacizumab Bevacizumab + IFL Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI Indication First-line Second-line First-line Primary endpoint PFS Not available PFS 1 Fuchs m. IFL = irinotecan, 5 -FU, leucovorin CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86 GF, et al. ASCO GI Cancers Symposium 2007 (Abstract 394) 3 Kopetz S, et al. ASCO GI Cancers Symposium 2007 (Abstract 4089) 2 Samelis
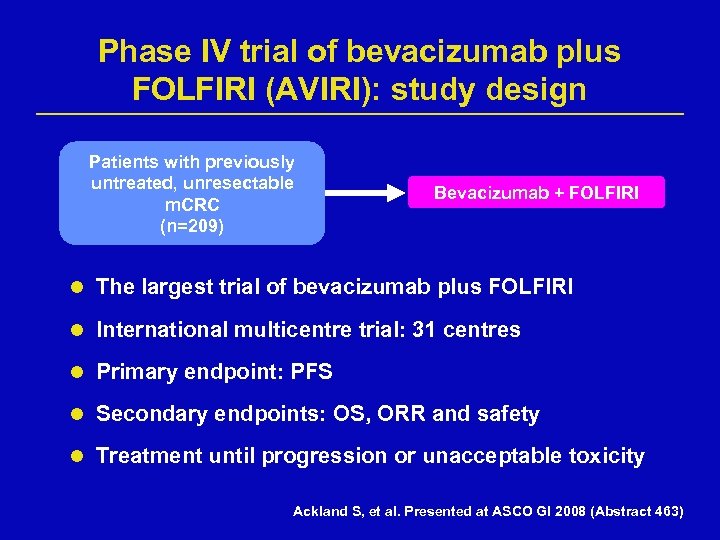 Phase IV trial of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI (AVIRI): study design Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=209) Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI l The largest trial of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI l International multicentre trial: 31 centres l Primary endpoint: PFS l Secondary endpoints: OS, ORR and safety l Treatment until progression or unacceptable toxicity Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
Phase IV trial of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI (AVIRI): study design Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=209) Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI l The largest trial of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI l International multicentre trial: 31 centres l Primary endpoint: PFS l Secondary endpoints: OS, ORR and safety l Treatment until progression or unacceptable toxicity Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
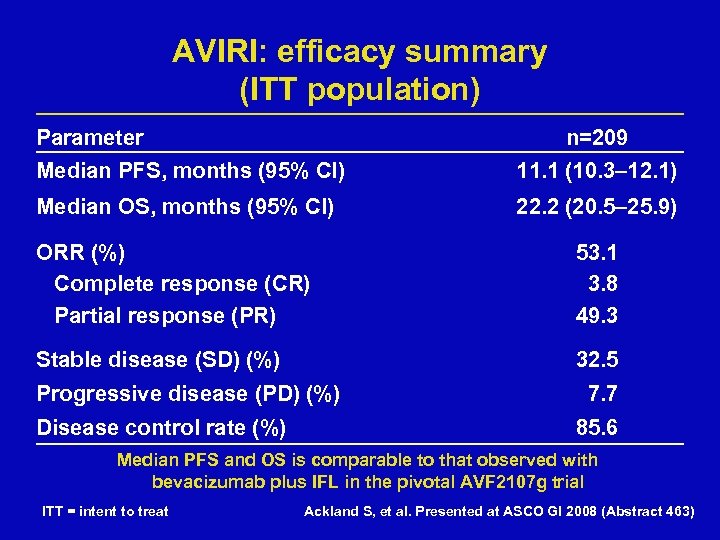 AVIRI: efficacy summary (ITT population) Parameter n=209 Median PFS, months (95% CI) 11. 1 (10. 3– 12. 1) Median OS, months (95% CI) 22. 2 (20. 5– 25. 9) ORR (%) Complete response (CR) Partial response (PR) 53. 1 3. 8 49. 3 Stable disease (SD) (%) 32. 5 Progressive disease (PD) (%) Disease control rate (%) 7. 7 85. 6 Median PFS and OS is comparable to that observed with bevacizumab plus IFL in the pivotal AVF 2107 g trial ITT = intent to treat Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
AVIRI: efficacy summary (ITT population) Parameter n=209 Median PFS, months (95% CI) 11. 1 (10. 3– 12. 1) Median OS, months (95% CI) 22. 2 (20. 5– 25. 9) ORR (%) Complete response (CR) Partial response (PR) 53. 1 3. 8 49. 3 Stable disease (SD) (%) 32. 5 Progressive disease (PD) (%) Disease control rate (%) 7. 7 85. 6 Median PFS and OS is comparable to that observed with bevacizumab plus IFL in the pivotal AVF 2107 g trial ITT = intent to treat Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
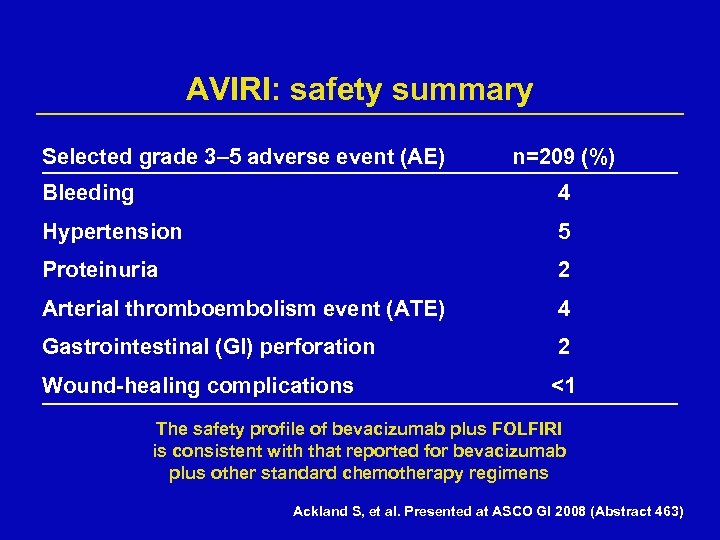 AVIRI: safety summary Selected grade 3– 5 adverse event (AE) n=209 (%) Bleeding 4 Hypertension 5 Proteinuria 2 Arterial thromboembolism event (ATE) 4 Gastrointestinal (GI) perforation 2 Wound-healing complications <1 The safety profile of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI is consistent with that reported for bevacizumab plus other standard chemotherapy regimens Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
AVIRI: safety summary Selected grade 3– 5 adverse event (AE) n=209 (%) Bleeding 4 Hypertension 5 Proteinuria 2 Arterial thromboembolism event (ATE) 4 Gastrointestinal (GI) perforation 2 Wound-healing complications <1 The safety profile of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI is consistent with that reported for bevacizumab plus other standard chemotherapy regimens Ackland S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 463)
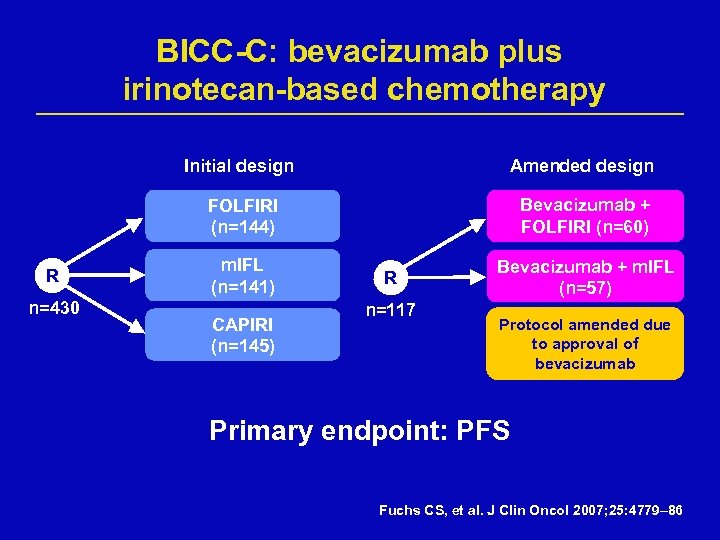 BICC-C: bevacizumab plus irinotecan-based chemotherapy Initial design FOLFIRI (n=144) R n=430 Amended design Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI (n=60) m. IFL (n=141) CAPIRI (n=145) R n=117 Bevacizumab + m. IFL (n=57) Protocol amended due to approval of bevacizumab Primary endpoint: PFS Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86
BICC-C: bevacizumab plus irinotecan-based chemotherapy Initial design FOLFIRI (n=144) R n=430 Amended design Bevacizumab + FOLFIRI (n=60) m. IFL (n=141) CAPIRI (n=145) R n=117 Bevacizumab + m. IFL (n=57) Protocol amended due to approval of bevacizumab Primary endpoint: PFS Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86
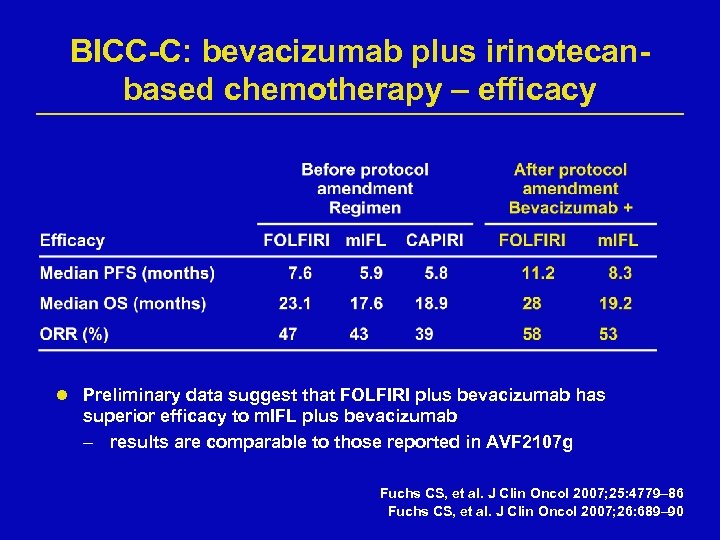 BICC-C: bevacizumab plus irinotecanbased chemotherapy – efficacy l Preliminary data suggest that FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab has superior efficacy to m. IFL plus bevacizumab – results are comparable to those reported in AVF 2107 g Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86 Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 26: 689– 90
BICC-C: bevacizumab plus irinotecanbased chemotherapy – efficacy l Preliminary data suggest that FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab has superior efficacy to m. IFL plus bevacizumab – results are comparable to those reported in AVF 2107 g Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86 Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 26: 689– 90
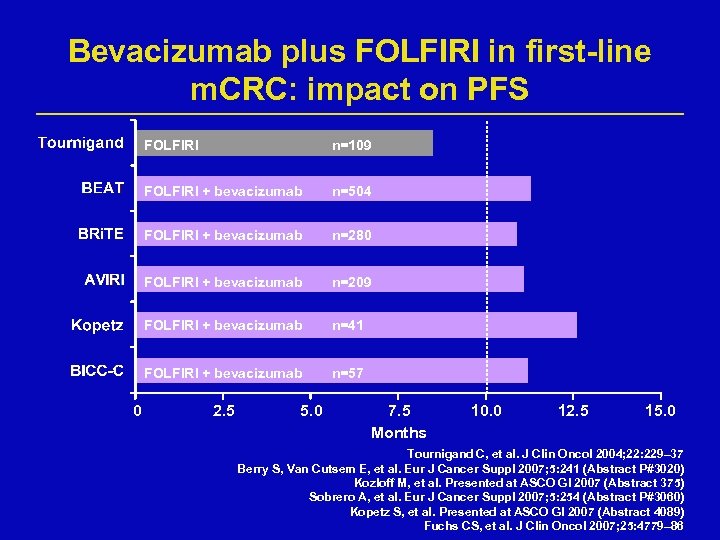 Bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI in first-line m. CRC: impact on PFS FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=504 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=280 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=209 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=41 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab 0 n=109 n=57 2. 5 5. 0 7. 5 Months 10. 0 12. 5 15. 0 Tournigand C, et al. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 229– 37 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) Kozloff M, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 375) Sobrero A, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 254 (Abstract P#3060) Kopetz S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 4089) Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86
Bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI in first-line m. CRC: impact on PFS FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=504 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=280 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=209 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab n=41 FOLFIRI + bevacizumab 0 n=109 n=57 2. 5 5. 0 7. 5 Months 10. 0 12. 5 15. 0 Tournigand C, et al. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 229– 37 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) Kozloff M, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 375) Sobrero A, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 254 (Abstract P#3060) Kopetz S, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 4089) Fuchs CS, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4779– 86
 Oxaliplatin-containing regimens with bevacizumab and/or capecitabine
Oxaliplatin-containing regimens with bevacizumab and/or capecitabine
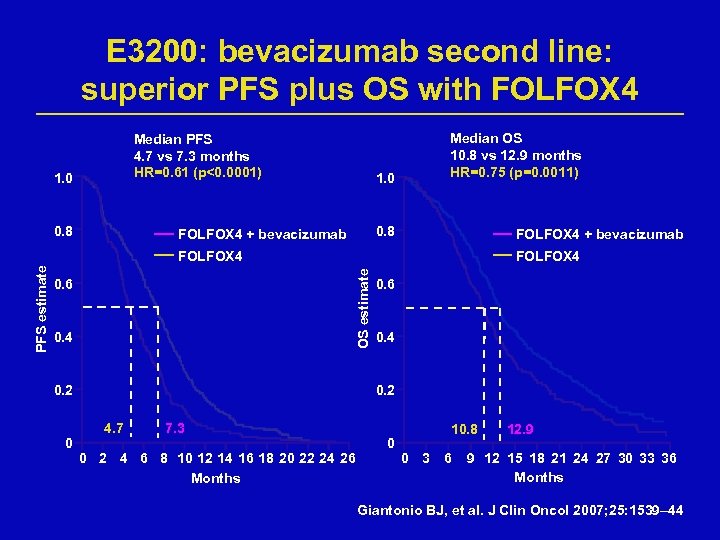 E 3200: bevacizumab second line: superior PFS plus OS with FOLFOX 4 Median PFS 4. 7 vs 7. 3 months HR=0. 61 (p<0. 0001) 1. 0 0. 8 Median OS 10. 8 vs 12. 9 months HR=0. 75 (p=0. 0011) 1. 0 0. 8 FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab FOLFOX 4 OS estimate PFS estimate FOLFOX 4 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 4. 7 7. 3 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 Months 0 10. 8 0 3 6 12. 9 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 Months Giantonio BJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1539– 44
E 3200: bevacizumab second line: superior PFS plus OS with FOLFOX 4 Median PFS 4. 7 vs 7. 3 months HR=0. 61 (p<0. 0001) 1. 0 0. 8 Median OS 10. 8 vs 12. 9 months HR=0. 75 (p=0. 0011) 1. 0 0. 8 FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab FOLFOX 4 OS estimate PFS estimate FOLFOX 4 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 4. 7 7. 3 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 Months 0 10. 8 0 3 6 12. 9 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 Months Giantonio BJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1539– 44
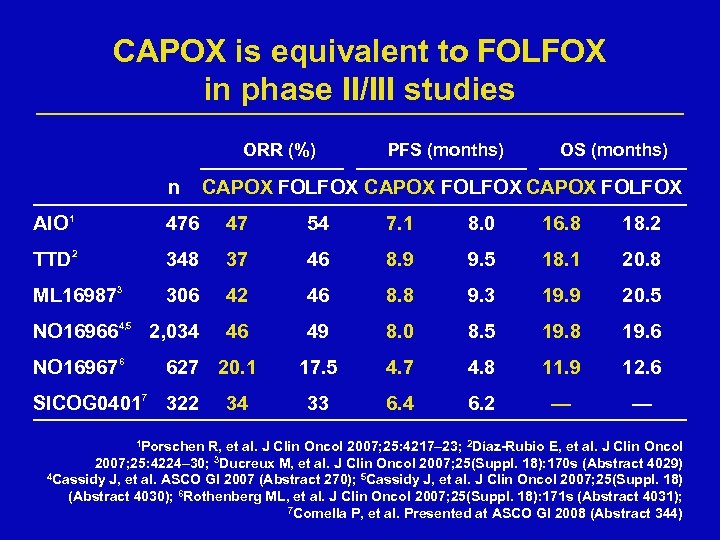 CAPOX is equivalent to FOLFOX in phase II/III studies ORR (%) n PFS (months) OS (months) CAPOX FOLFOX AIO 1 476 47 54 7. 1 8. 0 16. 8 18. 2 TTD 2 348 37 46 8. 9 9. 5 18. 1 20. 8 ML 169873 306 42 46 8. 8 9. 3 19. 9 20. 5 NO 169664, 5 2, 034 46 49 8. 0 8. 5 19. 8 19. 6 17. 5 4. 7 4. 8 11. 9 12. 6 33 6. 4 6. 2 — — NO 169676 627 20. 1 SICOG 04017 322 1 Porschen 34 R, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4217– 23; 2 Díaz-Rubio E, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4224– 30; 3 Ducreux M, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4029) 4 Cassidy J, et al. ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 270); 5 Cassidy J, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18) (Abstract 4030); 6 Rothenberg ML, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 171 s (Abstract 4031); 7 Comella P, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 344)
CAPOX is equivalent to FOLFOX in phase II/III studies ORR (%) n PFS (months) OS (months) CAPOX FOLFOX AIO 1 476 47 54 7. 1 8. 0 16. 8 18. 2 TTD 2 348 37 46 8. 9 9. 5 18. 1 20. 8 ML 169873 306 42 46 8. 8 9. 3 19. 9 20. 5 NO 169664, 5 2, 034 46 49 8. 0 8. 5 19. 8 19. 6 17. 5 4. 7 4. 8 11. 9 12. 6 33 6. 4 6. 2 — — NO 169676 627 20. 1 SICOG 04017 322 1 Porschen 34 R, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4217– 23; 2 Díaz-Rubio E, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4224– 30; 3 Ducreux M, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4029) 4 Cassidy J, et al. ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 270); 5 Cassidy J, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18) (Abstract 4030); 6 Rothenberg ML, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 171 s (Abstract 4031); 7 Comella P, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 344)
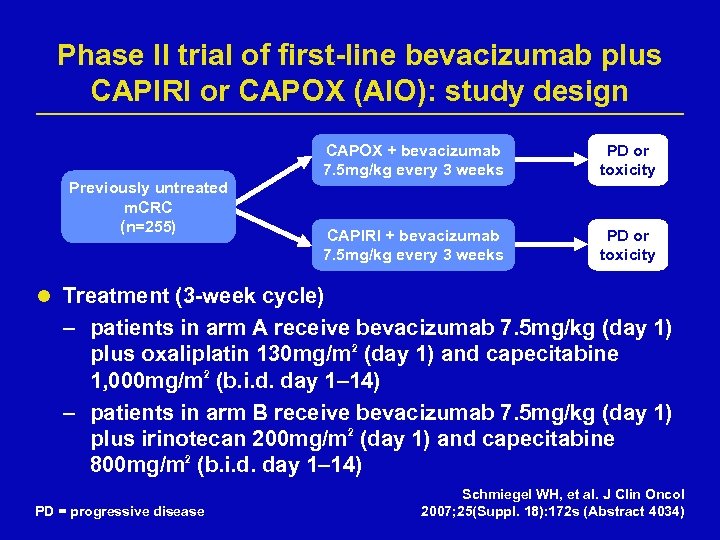 Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): study design CAPOX + bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg every 3 weeks Previously untreated m. CRC (n=255) PD or toxicity CAPIRI + bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg every 3 weeks PD or toxicity l Treatment (3 -week cycle) – patients in arm A receive bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg (day 1) plus oxaliplatin 130 mg/m 2 (day 1) and capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 (b. i. d. day 1– 14) – patients in arm B receive bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg (day 1) plus irinotecan 200 mg/m 2 (day 1) and capecitabine 800 mg/m 2 (b. i. d. day 1– 14) PD = progressive disease Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): study design CAPOX + bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg every 3 weeks Previously untreated m. CRC (n=255) PD or toxicity CAPIRI + bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg every 3 weeks PD or toxicity l Treatment (3 -week cycle) – patients in arm A receive bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg (day 1) plus oxaliplatin 130 mg/m 2 (day 1) and capecitabine 1, 000 mg/m 2 (b. i. d. day 1– 14) – patients in arm B receive bevacizumab 7. 5 mg/kg (day 1) plus irinotecan 200 mg/m 2 (day 1) and capecitabine 800 mg/m 2 (b. i. d. day 1– 14) PD = progressive disease Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
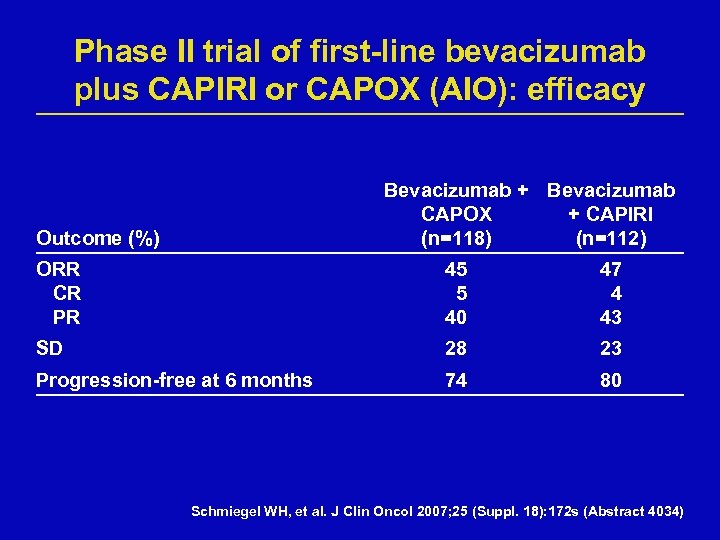 Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): efficacy Bevacizumab + Bevacizumab CAPOX + CAPIRI (n=118) (n=112) Outcome (%) ORR CR PR 45 5 40 47 4 43 SD 28 23 Progression-free at 6 months 74 80 Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): efficacy Bevacizumab + Bevacizumab CAPOX + CAPIRI (n=118) (n=112) Outcome (%) ORR CR PR 45 5 40 47 4 43 SD 28 23 Progression-free at 6 months 74 80 Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
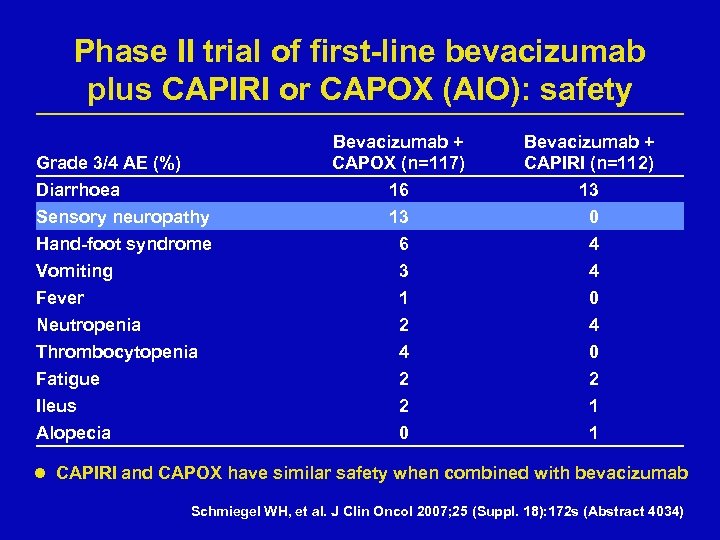 Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): safety Bevacizumab + CAPOX (n=117) 16 13 6 Bevacizumab + CAPIRI (n=112) 13 0 4 Vomiting 3 4 Fever Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia 1 2 4 0 Fatigue 2 2 Ileus Alopecia 2 0 1 1 Grade 3/4 AE (%) Diarrhoea Sensory neuropathy Hand-foot syndrome l CAPIRI and CAPOX have similar safety when combined with bevacizumab Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
Phase II trial of first-line bevacizumab plus CAPIRI or CAPOX (AIO): safety Bevacizumab + CAPOX (n=117) 16 13 6 Bevacizumab + CAPIRI (n=112) 13 0 4 Vomiting 3 4 Fever Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia 1 2 4 0 Fatigue 2 2 Ileus Alopecia 2 0 1 1 Grade 3/4 AE (%) Diarrhoea Sensory neuropathy Hand-foot syndrome l CAPIRI and CAPOX have similar safety when combined with bevacizumab Schmiegel WH, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4034)
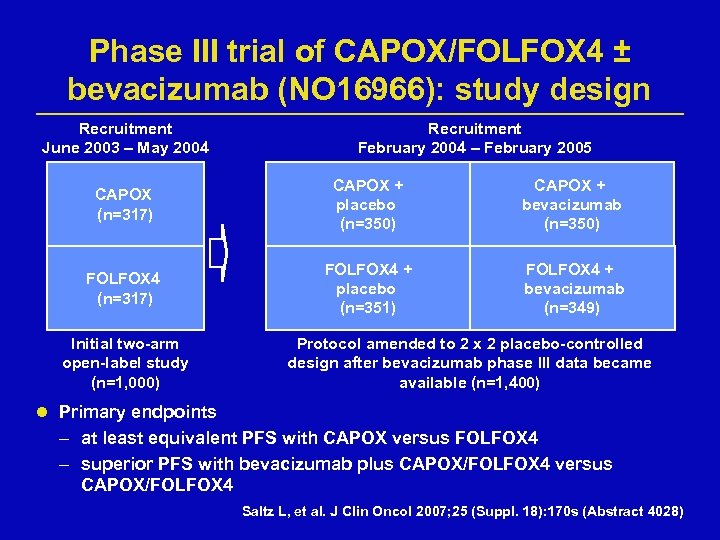 Phase III trial of CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 ± bevacizumab (NO 16966): study design Recruitment June 2003 – May 2004 Recruitment February 2004 – February 2005 CAPOX (n=317) CAPOX + placebo (n=350) CAPOX + bevacizumab (n=350) FOLFOX 4 (n=317) FOLFOX 4 + placebo (n=351) FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab (n=349) Initial two-arm open-label study (n=1, 000) Protocol amended to 2 x 2 placebo-controlled design after bevacizumab phase III data became available (n=1, 400) l Primary endpoints – at least equivalent PFS with CAPOX versus FOLFOX 4 – superior PFS with bevacizumab plus CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 versus CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
Phase III trial of CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 ± bevacizumab (NO 16966): study design Recruitment June 2003 – May 2004 Recruitment February 2004 – February 2005 CAPOX (n=317) CAPOX + placebo (n=350) CAPOX + bevacizumab (n=350) FOLFOX 4 (n=317) FOLFOX 4 + placebo (n=351) FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab (n=349) Initial two-arm open-label study (n=1, 000) Protocol amended to 2 x 2 placebo-controlled design after bevacizumab phase III data became available (n=1, 400) l Primary endpoints – at least equivalent PFS with CAPOX versus FOLFOX 4 – superior PFS with bevacizumab plus CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 versus CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
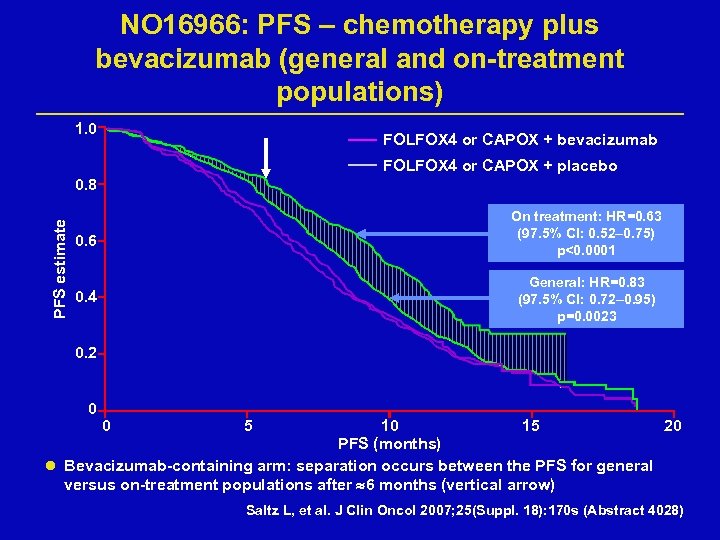 NO 16966: PFS – chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (general and on-treatment populations) 1. 0 FOLFOX 4 or CAPOX + bevacizumab FOLFOX 4 or CAPOX + placebo PFS estimate 0. 8 On treatment: HR=0. 63 (97. 5% CI: 0. 52– 0. 75) p<0. 0001 0. 6 General: HR=0. 83 (97. 5% CI: 0. 72– 0. 95) p=0. 0023 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 PFS (months) l Bevacizumab-containing arm: separation occurs between the PFS for general versus on-treatment populations after 6 months (vertical arrow) Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
NO 16966: PFS – chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (general and on-treatment populations) 1. 0 FOLFOX 4 or CAPOX + bevacizumab FOLFOX 4 or CAPOX + placebo PFS estimate 0. 8 On treatment: HR=0. 63 (97. 5% CI: 0. 52– 0. 75) p<0. 0001 0. 6 General: HR=0. 83 (97. 5% CI: 0. 72– 0. 95) p=0. 0023 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 PFS (months) l Bevacizumab-containing arm: separation occurs between the PFS for general versus on-treatment populations after 6 months (vertical arrow) Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
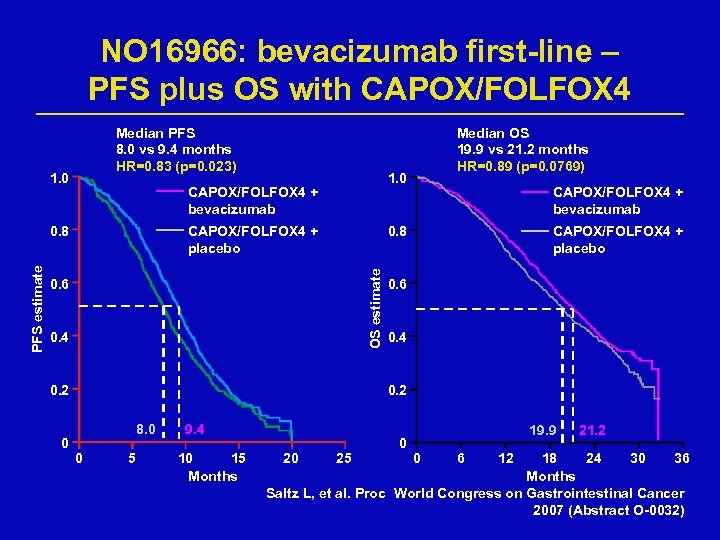 NO 16966: bevacizumab first-line – PFS plus OS with CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 Median PFS 8. 0 vs 9. 4 months HR=0. 83 (p=0. 023) 1. 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo 0. 8 OS estimate PFS estimate 1. 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab 0. 8 Median OS 19. 9 vs 21. 2 months HR=0. 89 (p=0. 0769) 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 8. 0 0 5 9. 4 10 15 Months 20 25 0 19. 9 0 6 12 21. 2 18 24 30 36 Months Saltz L, et al. Proc World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2007 (Abstract O-0032)
NO 16966: bevacizumab first-line – PFS plus OS with CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 Median PFS 8. 0 vs 9. 4 months HR=0. 83 (p=0. 023) 1. 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo 0. 8 OS estimate PFS estimate 1. 0 CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab 0. 8 Median OS 19. 9 vs 21. 2 months HR=0. 89 (p=0. 0769) 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 8. 0 0 5 9. 4 10 15 Months 20 25 0 19. 9 0 6 12 21. 2 18 24 30 36 Months Saltz L, et al. Proc World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2007 (Abstract O-0032)
 NO 16966: efficacy results for superiority – major points l Bevacizumab provides significant/superior PFS when added to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy regimens l Treatment until progression is crucial to demonstrate full potential of bevacizumab l Analyses of withdrawal data and PFS on treatment show excellent efficacy for bevacizumab l IRC analysis clearly demonstrates superior PFS for bevacizumab in all treatment groups IRC = independent review committee
NO 16966: efficacy results for superiority – major points l Bevacizumab provides significant/superior PFS when added to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy regimens l Treatment until progression is crucial to demonstrate full potential of bevacizumab l Analyses of withdrawal data and PFS on treatment show excellent efficacy for bevacizumab l IRC analysis clearly demonstrates superior PFS for bevacizumab in all treatment groups IRC = independent review committee
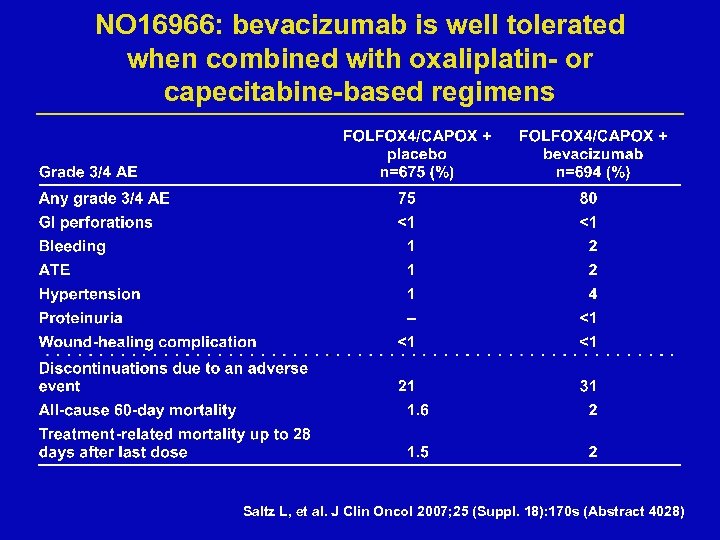 NO 16966: bevacizumab is well tolerated when combined with oxaliplatin- or capecitabine-based regimens Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
NO 16966: bevacizumab is well tolerated when combined with oxaliplatin- or capecitabine-based regimens Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028)
 Bevacizumab in the clinical setting Data from BEAT and BRi. TE
Bevacizumab in the clinical setting Data from BEAT and BRi. TE
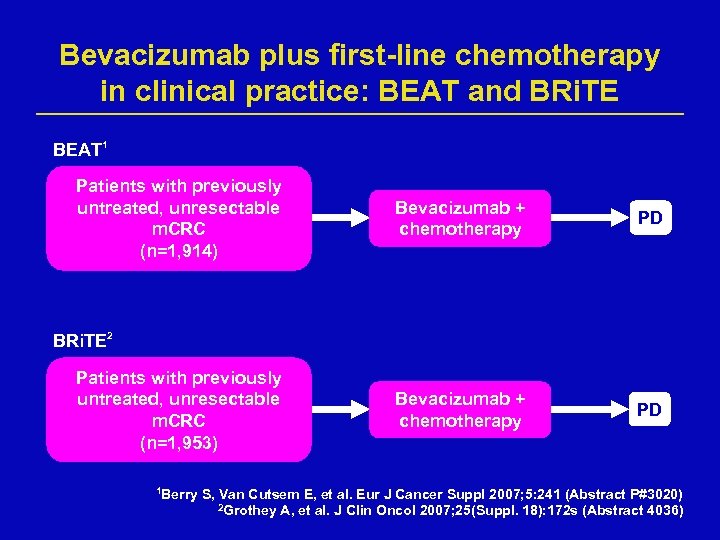 Bevacizumab plus first-line chemotherapy in clinical practice: BEAT and BRi. TE BEAT 1 Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=1, 914) Bevacizumab + chemotherapy PD BRi. TE 2 Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=1, 953) 1 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) 2 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036)
Bevacizumab plus first-line chemotherapy in clinical practice: BEAT and BRi. TE BEAT 1 Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=1, 914) Bevacizumab + chemotherapy PD BRi. TE 2 Patients with previously untreated, unresectable m. CRC (n=1, 953) 1 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) 2 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036)
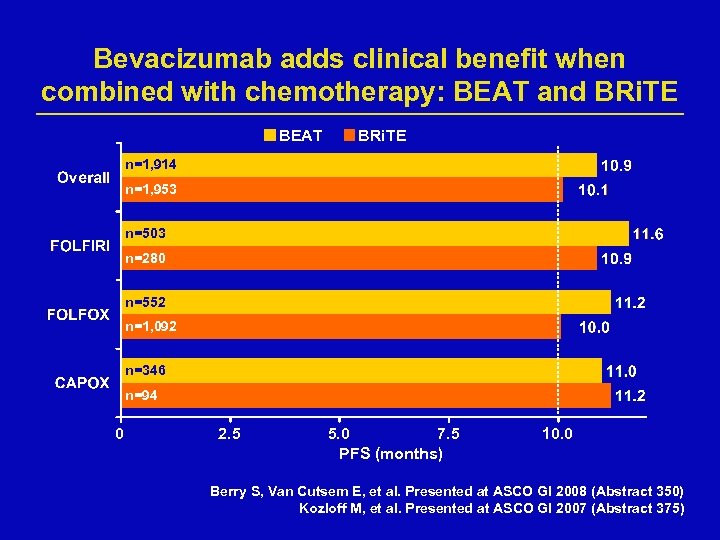 Bevacizumab adds clinical benefit when combined with chemotherapy: BEAT and BRi. TE BEAT BRi. TE n=1, 914 n=1, 953 n=503 n=280 n=552 n=1, 092 n=346 n=94 0 2. 5 5. 0 7. 5 PFS (months) 10. 0 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 350) Kozloff M, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 375)
Bevacizumab adds clinical benefit when combined with chemotherapy: BEAT and BRi. TE BEAT BRi. TE n=1, 914 n=1, 953 n=503 n=280 n=552 n=1, 092 n=346 n=94 0 2. 5 5. 0 7. 5 PFS (months) 10. 0 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2008 (Abstract 350) Kozloff M, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 375)
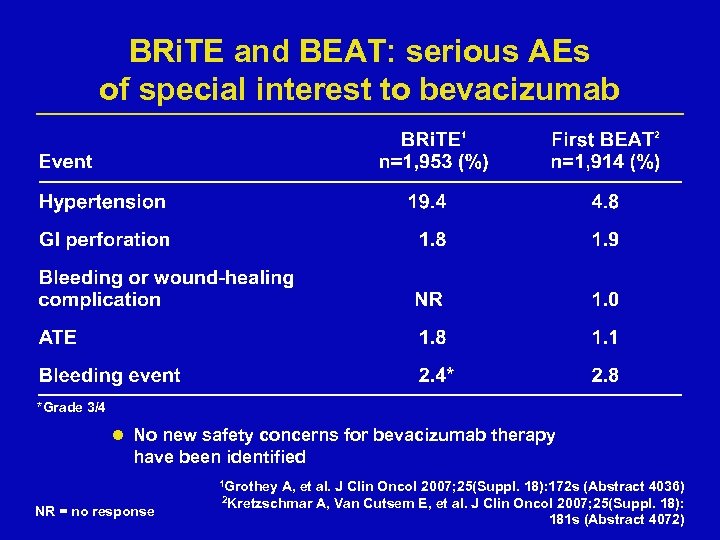 BRi. TE and BEAT: serious AEs of special interest to bevacizumab *Grade 3/4 l No new safety concerns for bevacizumab therapy have been identified 1 Grothey NR = no response A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036) A, Van Cutsem E, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 181 s (Abstract 4072) 2 Kretzschmar
BRi. TE and BEAT: serious AEs of special interest to bevacizumab *Grade 3/4 l No new safety concerns for bevacizumab therapy have been identified 1 Grothey NR = no response A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036) A, Van Cutsem E, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 181 s (Abstract 4072) 2 Kretzschmar
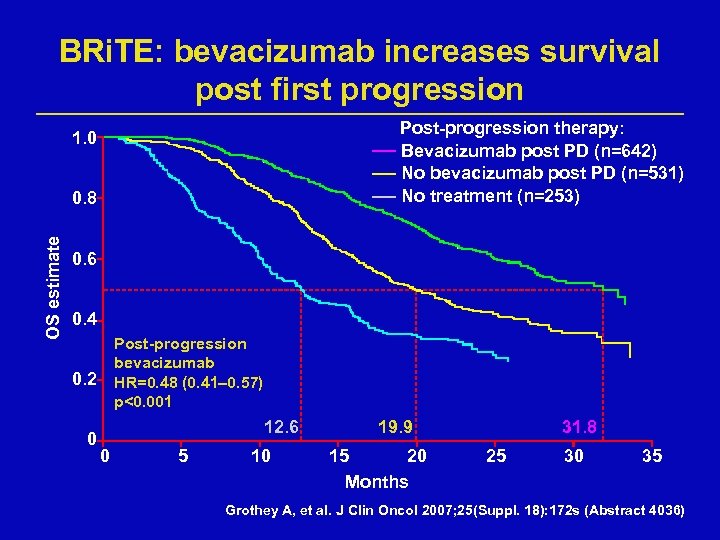 BRi. TE: bevacizumab increases survival post first progression Post-progression therapy: Bevacizumab post PD (n=642) No bevacizumab post PD (n=531) No treatment (n=253) 1. 0 OS estimate 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 Post-progression bevacizumab HR=0. 48 (0. 41– 0. 57) p<0. 001 0. 2 0 12. 6 0 5 10 19. 9 15 20 Months 31. 8 25 30 35 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036)
BRi. TE: bevacizumab increases survival post first progression Post-progression therapy: Bevacizumab post PD (n=642) No bevacizumab post PD (n=531) No treatment (n=253) 1. 0 OS estimate 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 Post-progression bevacizumab HR=0. 48 (0. 41– 0. 57) p<0. 001 0. 2 0 12. 6 0 5 10 19. 9 15 20 Months 31. 8 25 30 35 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036)
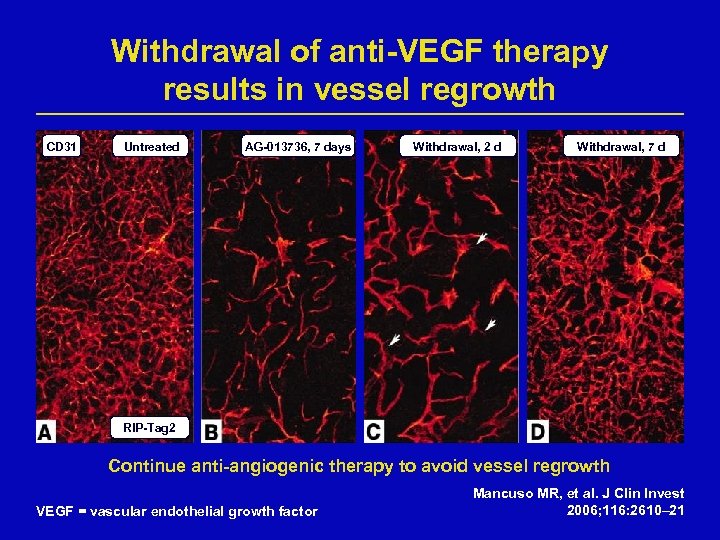 Withdrawal of anti-VEGF therapy results in vessel regrowth CD 31 Untreated AG-013736, 7 days Withdrawal, 2 d Withdrawal, 7 d RIP-Tag 2 Continue anti-angiogenic therapy to avoid vessel regrowth VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor Mancuso MR, et al. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2610– 21
Withdrawal of anti-VEGF therapy results in vessel regrowth CD 31 Untreated AG-013736, 7 days Withdrawal, 2 d Withdrawal, 7 d RIP-Tag 2 Continue anti-angiogenic therapy to avoid vessel regrowth VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor Mancuso MR, et al. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2610– 21
 Bevacizumab in the neoadjuvant setting
Bevacizumab in the neoadjuvant setting
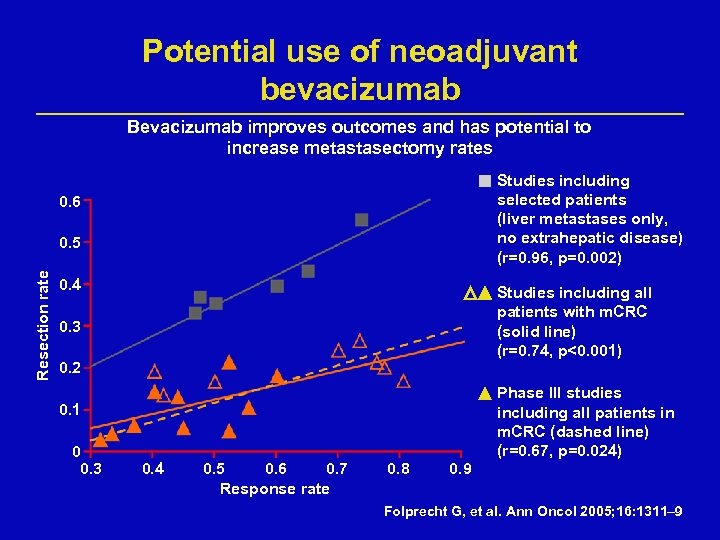 Potential use of neoadjuvant bevacizumab Bevacizumab improves outcomes and has potential to increase metastasectomy rates Studies including selected patients (liver metastases only, no extrahepatic disease) (r=0. 96, p=0. 002) 0. 6 Resection rate 0. 5 0. 4 Studies including all patients with m. CRC (solid line) (r=0. 74, p<0. 001) 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 0. 3 0. 4 0. 5 0. 6 0. 7 Response rate 0. 8 0. 9 Phase III studies including all patients in m. CRC (dashed line) (r=0. 67, p=0. 024) Folprecht G, et al. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 1311– 9
Potential use of neoadjuvant bevacizumab Bevacizumab improves outcomes and has potential to increase metastasectomy rates Studies including selected patients (liver metastases only, no extrahepatic disease) (r=0. 96, p=0. 002) 0. 6 Resection rate 0. 5 0. 4 Studies including all patients with m. CRC (solid line) (r=0. 74, p<0. 001) 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 0. 3 0. 4 0. 5 0. 6 0. 7 Response rate 0. 8 0. 9 Phase III studies including all patients in m. CRC (dashed line) (r=0. 67, p=0. 024) Folprecht G, et al. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 1311– 9
 Potential use of neoadjuvant bevacizumab (cont’d) l Impaired wound healing and liver regeneration have been associated with anti-VEGF therapies l Using bevacizumab in patients who may become eligible for surgery raises the question of scheduling/best practice
Potential use of neoadjuvant bevacizumab (cont’d) l Impaired wound healing and liver regeneration have been associated with anti-VEGF therapies l Using bevacizumab in patients who may become eligible for surgery raises the question of scheduling/best practice
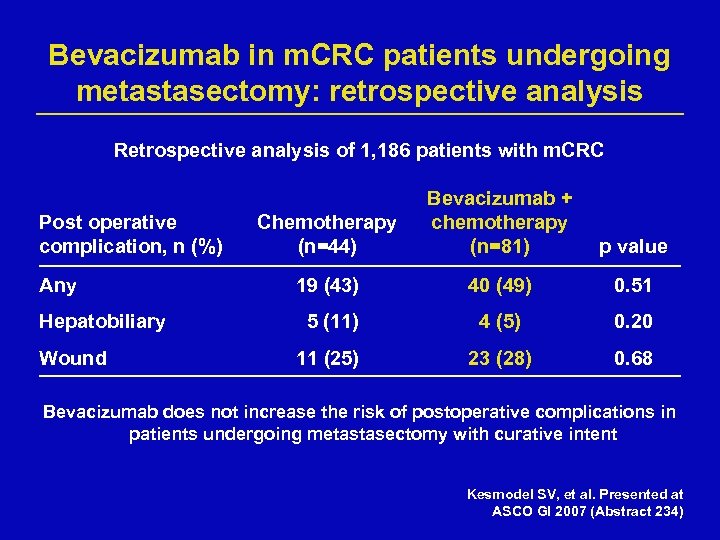 Bevacizumab in m. CRC patients undergoing metastasectomy: retrospective analysis Retrospective analysis of 1, 186 patients with m. CRC Post operative complication, n (%) Any Hepatobiliary Wound Chemotherapy (n=44) Bevacizumab + chemotherapy (n=81) p value 19 (43) 40 (49) 0. 51 5 (11) 4 (5) 0. 20 11 (25) 23 (28) 0. 68 Bevacizumab does not increase the risk of postoperative complications in patients undergoing metastasectomy with curative intent Kesmodel SV, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 234)
Bevacizumab in m. CRC patients undergoing metastasectomy: retrospective analysis Retrospective analysis of 1, 186 patients with m. CRC Post operative complication, n (%) Any Hepatobiliary Wound Chemotherapy (n=44) Bevacizumab + chemotherapy (n=81) p value 19 (43) 40 (49) 0. 51 5 (11) 4 (5) 0. 20 11 (25) 23 (28) 0. 68 Bevacizumab does not increase the risk of postoperative complications in patients undergoing metastasectomy with curative intent Kesmodel SV, et al. Presented at ASCO GI 2007 (Abstract 234)
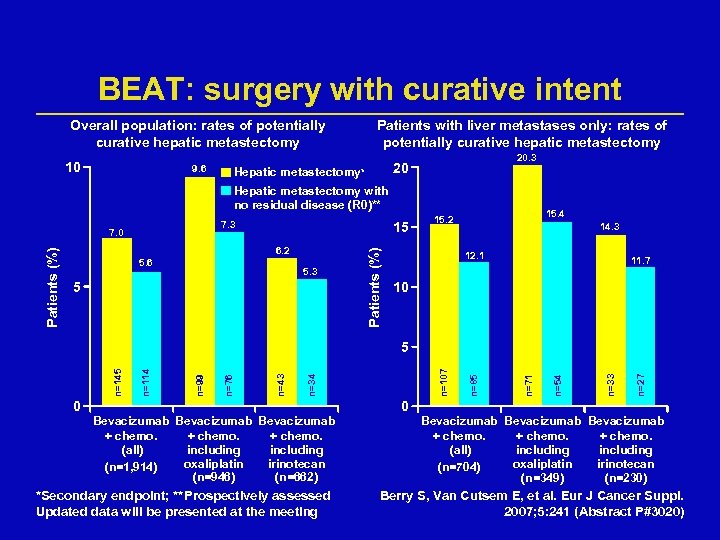 BEAT: surgery with curative intent Overall population: rates of potentially curative hepatic metastectomy 10 9. 6 Patients with liver metastases only: rates of potentially curative hepatic metastectomy 20. 3 20 Hepatic metastectomy* Hepatic metastectomy with no residual disease (R 0)** 7. 3 15 6. 2 5. 6 5. 3 5 Patients (%) 7. 0 15. 4 15. 2 14. 3 12. 1 11. 7 10 0 Bevacizumab + chemo. (all) including oxaliplatin irinotecan (n=1, 914) (n=946) (n=662) *Secondary endpoint; **Prospectively assessed Updated data will be presented at the meeting 0 n=27 n=33 n=54 n=71 n=85 n=107 n=34 n=43 n=76 n=99 n=114 n=145 5 Bevacizumab + chemo. (all) including oxaliplatin irinotecan (n=704) (n=349) (n=230) Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl. 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020)
BEAT: surgery with curative intent Overall population: rates of potentially curative hepatic metastectomy 10 9. 6 Patients with liver metastases only: rates of potentially curative hepatic metastectomy 20. 3 20 Hepatic metastectomy* Hepatic metastectomy with no residual disease (R 0)** 7. 3 15 6. 2 5. 6 5. 3 5 Patients (%) 7. 0 15. 4 15. 2 14. 3 12. 1 11. 7 10 0 Bevacizumab + chemo. (all) including oxaliplatin irinotecan (n=1, 914) (n=946) (n=662) *Secondary endpoint; **Prospectively assessed Updated data will be presented at the meeting 0 n=27 n=33 n=54 n=71 n=85 n=107 n=34 n=43 n=76 n=99 n=114 n=145 5 Bevacizumab + chemo. (all) including oxaliplatin irinotecan (n=704) (n=349) (n=230) Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl. 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020)
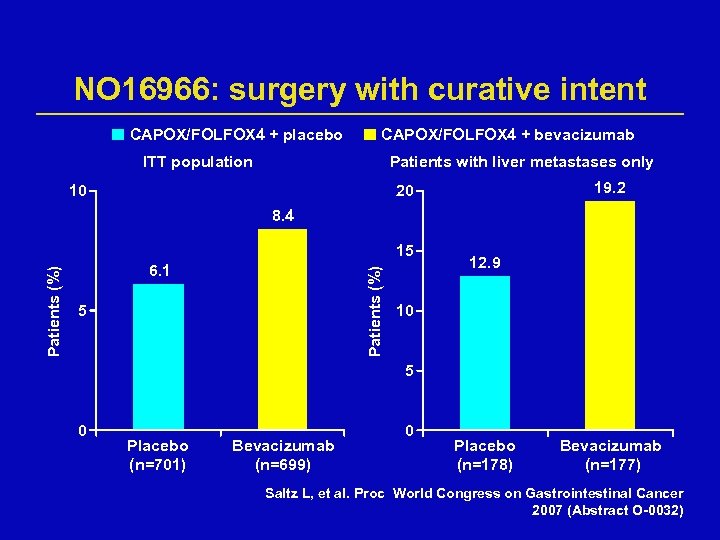 NO 16966: surgery with curative intent CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab ITT population Patients with liver metastases only 10 19. 2 20 8. 4 6. 1 Patients (%) 15 5 12. 9 10 5 0 Placebo (n=701) Bevacizumab (n=699) 0 Placebo (n=178) Bevacizumab (n=177) Saltz L, et al. Proc World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2007 (Abstract O-0032)
NO 16966: surgery with curative intent CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + placebo CAPOX/FOLFOX 4 + bevacizumab ITT population Patients with liver metastases only 10 19. 2 20 8. 4 6. 1 Patients (%) 15 5 12. 9 10 5 0 Placebo (n=701) Bevacizumab (n=699) 0 Placebo (n=178) Bevacizumab (n=177) Saltz L, et al. Proc World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2007 (Abstract O-0032)
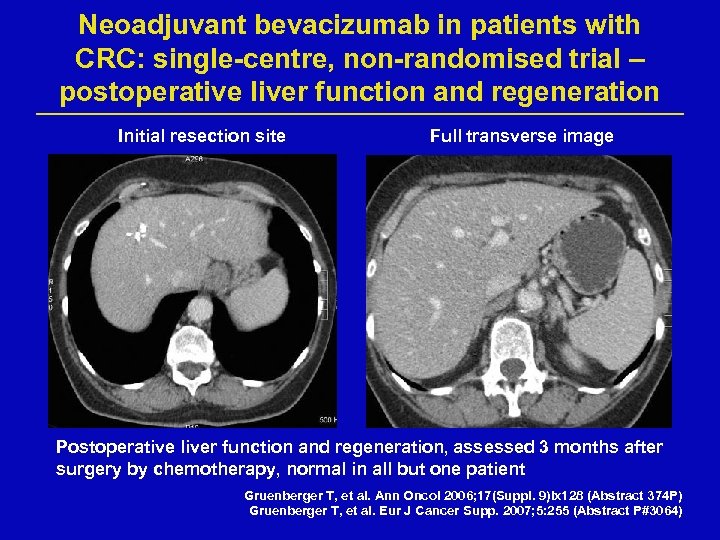 Neoadjuvant bevacizumab in patients with CRC: single-centre, non-randomised trial – postoperative liver function and regeneration Initial resection site Full transverse image Postoperative liver function and regeneration, assessed 3 months after surgery by chemotherapy, normal in all but one patient Gruenberger T, et al. Ann Oncol 2006; 17(Suppl. 9)ix 128 (Abstract 374 P) Gruenberger T, et al. Eur J Cancer Supp. 2007; 5: 255 (Abstract P#3064)
Neoadjuvant bevacizumab in patients with CRC: single-centre, non-randomised trial – postoperative liver function and regeneration Initial resection site Full transverse image Postoperative liver function and regeneration, assessed 3 months after surgery by chemotherapy, normal in all but one patient Gruenberger T, et al. Ann Oncol 2006; 17(Suppl. 9)ix 128 (Abstract 374 P) Gruenberger T, et al. Eur J Cancer Supp. 2007; 5: 255 (Abstract P#3064)
 Surgery with curative intent in patients receiving bevacizumab is feasible l With appropriate management, bevacizumab can be used in combination with chemotherapy with minimal risk of bleeding/wound-healing complications in patients with m. CRC undergoing resection of metastases l Data suggest that bevacizumab can be administered until 5 weeks prior to liver resection without any wound healing/ bleeding complications l Liver generation following resection does not appear to be affected in patients receiving bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy
Surgery with curative intent in patients receiving bevacizumab is feasible l With appropriate management, bevacizumab can be used in combination with chemotherapy with minimal risk of bleeding/wound-healing complications in patients with m. CRC undergoing resection of metastases l Data suggest that bevacizumab can be administered until 5 weeks prior to liver resection without any wound healing/ bleeding complications l Liver generation following resection does not appear to be affected in patients receiving bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy
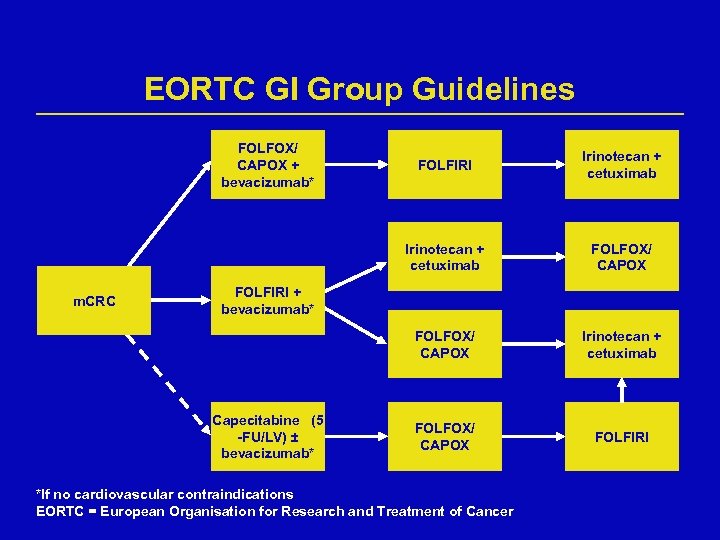 EORTC GI Group Guidelines FOLFOX/ CAPOX + bevacizumab* Irinotecan + cetuximab FOLFOX/ CAPOX m. CRC FOLFIRI Irinotecan + cetuximab FOLFOX/ CAPOX FOLFIRI + bevacizumab* Capecitabine (5 -FU/LV) ± bevacizumab* *If no cardiovascular contraindications EORTC = European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
EORTC GI Group Guidelines FOLFOX/ CAPOX + bevacizumab* Irinotecan + cetuximab FOLFOX/ CAPOX m. CRC FOLFIRI Irinotecan + cetuximab FOLFOX/ CAPOX FOLFIRI + bevacizumab* Capecitabine (5 -FU/LV) ± bevacizumab* *If no cardiovascular contraindications EORTC = European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
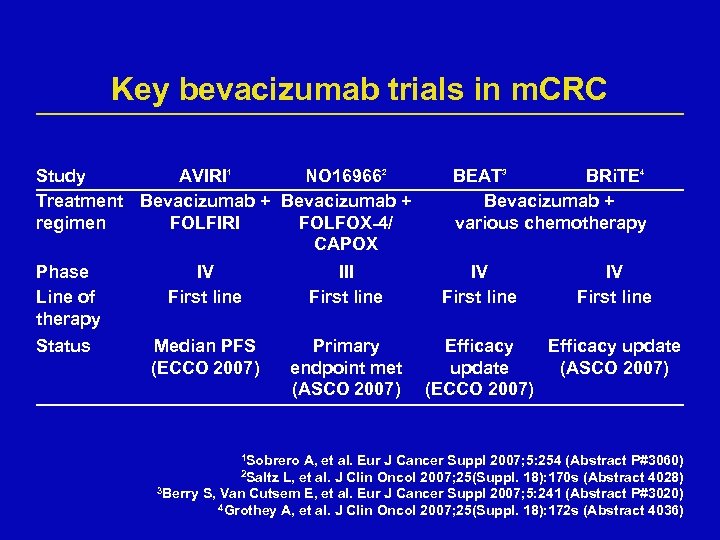 Key bevacizumab trials in m. CRC Study AVIRI 1 NO 169662 Treatment Bevacizumab + regimen FOLFIRI FOLFOX-4/ CAPOX Phase Line of therapy IV First line III First line Status Median PFS (ECCO 2007) Primary endpoint met (ASCO 2007) 1 Sobrero BEAT 3 BRi. TE 4 Bevacizumab + various chemotherapy IV First line Efficacy update (ASCO 2007) (ECCO 2007) A, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 254 (Abstract P#3060) L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028) 3 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) 4 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036) 2 Saltz
Key bevacizumab trials in m. CRC Study AVIRI 1 NO 169662 Treatment Bevacizumab + regimen FOLFIRI FOLFOX-4/ CAPOX Phase Line of therapy IV First line III First line Status Median PFS (ECCO 2007) Primary endpoint met (ASCO 2007) 1 Sobrero BEAT 3 BRi. TE 4 Bevacizumab + various chemotherapy IV First line Efficacy update (ASCO 2007) (ECCO 2007) A, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 254 (Abstract P#3060) L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028) 3 Berry S, Van Cutsem E, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 2007; 5: 241 (Abstract P#3020) 4 Grothey A, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 172 s (Abstract 4036) 2 Saltz
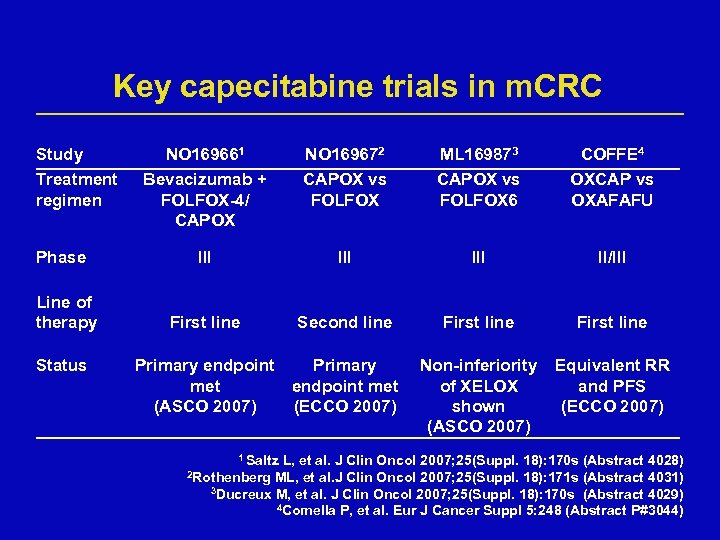 Key capecitabine trials in m. CRC Study Treatment regimen Phase Line of therapy Status NO 169661 Bevacizumab + FOLFOX-4/ CAPOX NO 169672 CAPOX vs FOLFOX ML 169873 CAPOX vs FOLFOX 6 COFFE 4 OXCAP vs OXAFAFU III III II/III First line Second line First line Non-inferiority of XELOX shown (ASCO 2007) Equivalent RR and PFS (ECCO 2007) Primary endpoint Primary met endpoint met (ASCO 2007) (ECCO 2007) 1 Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028) ML, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 171 s (Abstract 4031) 3 Ducreux M, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4029) 4 Comella P, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 5: 248 (Abstract P#3044) 2 Rothenberg
Key capecitabine trials in m. CRC Study Treatment regimen Phase Line of therapy Status NO 169661 Bevacizumab + FOLFOX-4/ CAPOX NO 169672 CAPOX vs FOLFOX ML 169873 CAPOX vs FOLFOX 6 COFFE 4 OXCAP vs OXAFAFU III III II/III First line Second line First line Non-inferiority of XELOX shown (ASCO 2007) Equivalent RR and PFS (ECCO 2007) Primary endpoint Primary met endpoint met (ASCO 2007) (ECCO 2007) 1 Saltz L, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4028) ML, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 171 s (Abstract 4031) 3 Ducreux M, et al. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(Suppl. 18): 170 s (Abstract 4029) 4 Comella P, et al. Eur J Cancer Suppl 5: 248 (Abstract P#3044) 2 Rothenberg
 Conclusions l Bevacizumab combined with standard therapies is an effective first-line treatment strategy for m. CRC l Bevacizumab is generally well tolerated l Efficacy and safety outcomes in clinical evaluation studies are similar to those reported in clinical trials l Capecitabine is effectively replacing 5 -FU in m. CRC l Data suggest that metastasectomy is feasible in patients with m. CRC treated with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy
Conclusions l Bevacizumab combined with standard therapies is an effective first-line treatment strategy for m. CRC l Bevacizumab is generally well tolerated l Efficacy and safety outcomes in clinical evaluation studies are similar to those reported in clinical trials l Capecitabine is effectively replacing 5 -FU in m. CRC l Data suggest that metastasectomy is feasible in patients with m. CRC treated with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy


