d4464bf1837deaa5cab041c0911b2c1f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79



Forget the big bang, tune in to the big hum THE big bang sounded more like a deep hum than a bang, according to an analysis of the radiation left over from the cataclysm. Physicist John Cramer of the University of Washington in Seattle has created audio files of the event which can be played on a PC. "The sound is rather like a large jet plane flying 100 feet above your house in the middle of the night, " he says. Giant sound waves propagated through the blazing hot matter that filled the universe shortly after the big bang. These squeezed and stretched matter, heating the compressed regions and cooling the rarefied ones. Even though the universe has been expanding and cooling ever since, the sound waves have left their imprint as temperature variations on the afterglow of the big bang fireball, the so-called cosmic microwave background. Cramer was prompted to recreate the din- last heard 13. 7 billion years ago- by an 11 -year-old boy who wanted to know what the big bang sounded like for a school project. To produce the sound, Cramer took data from NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe. Launched in 2001, the probe has been measuring tiny differences in the temperature between different parts of the sky. From these variations, he could calculate the frequencies of the sound waves propagating through the universe during its first 760, 000 years, when it was just 18 million light years across. At that time the sound waves were too low in frequency to be audible. To hear them, Cramer had to scale the frequencies 100, 000 billion times. Nevertheless, the loudness and pitch of the sound waves reflect what happened in the early universe. During the 100 -second recording (http: //www. npl. washington. edu/AV/Big. Bang. Sound_2. wav), the frequencies fall because the sound waves get stretched as the universe expands. "It becomes more of a bass instrument, " says Cramer. ### Author: Marcus Chown

The universe started as a single point. That point was extremely dense. It became unstable and exploded outward. Today the universe continues to expand.




Put these in order of size: galaxy solar system universe galaxy universe solar system


ESRTs p 15

ESRTs p 15

What type of star is our Sun classified as? ESRTs p 15 Circle where it is on the chart

Shade the chart where all of the stars are hotter than our sun. Draw a line on the chart which separates those stars brighter than our sun and those less bright. ESRTs p 15

ESRTs p 15

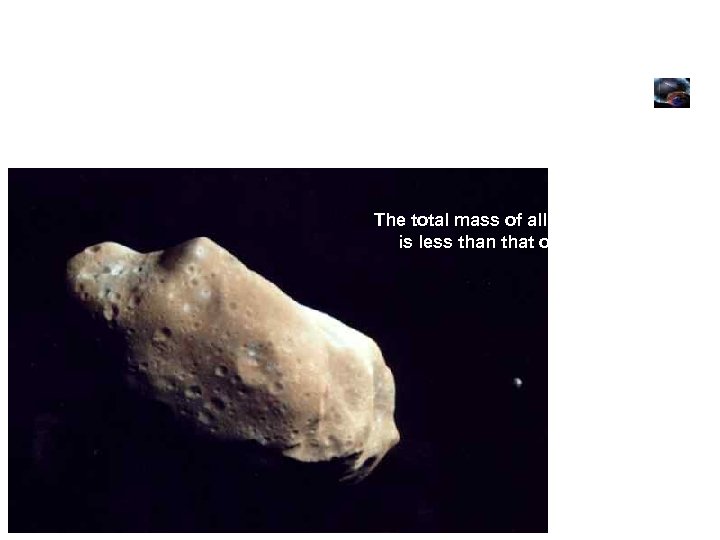
Asteroids rocky objects with round or irregular shapes lie in a belt between Mars and Jupiter The total mass of all the asteroids is less than that of the Moon.

only visible when they are close to the sun

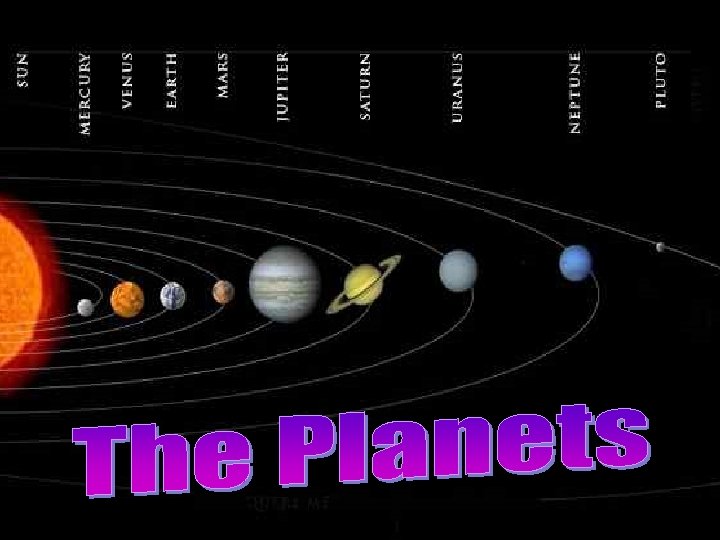
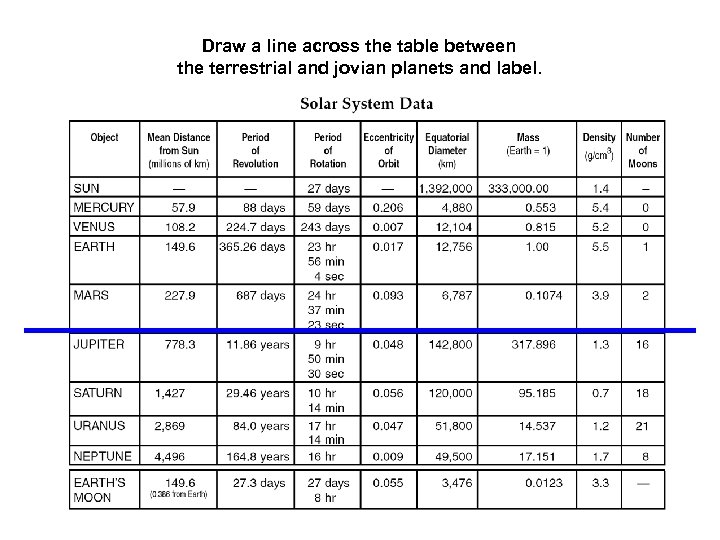
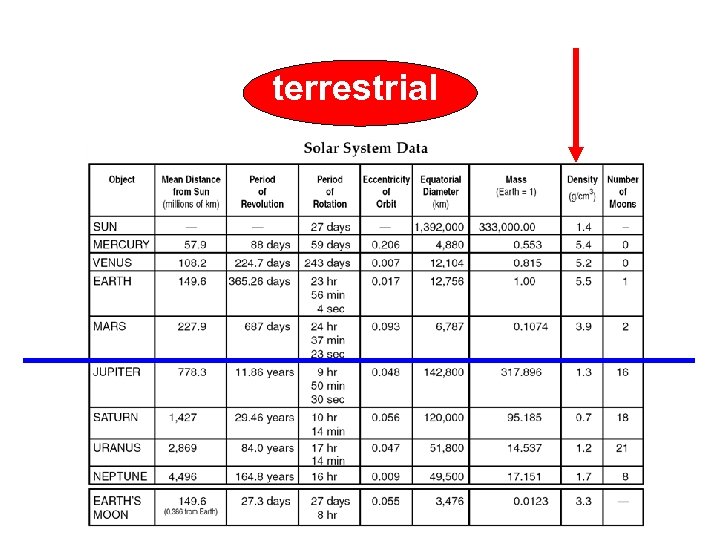
Draw a line across the table between the terrestrial and jovian planets and label.
Which are more dense? Jovian or terrestrial
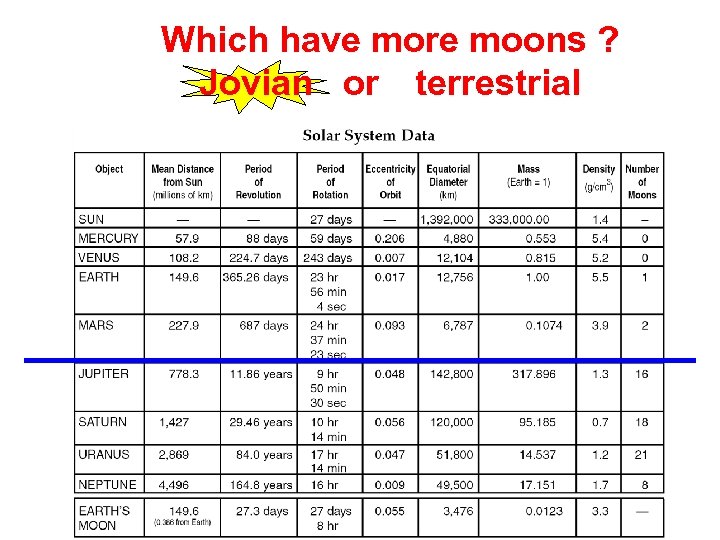
Which have more moons ? Jovian or terrestrial
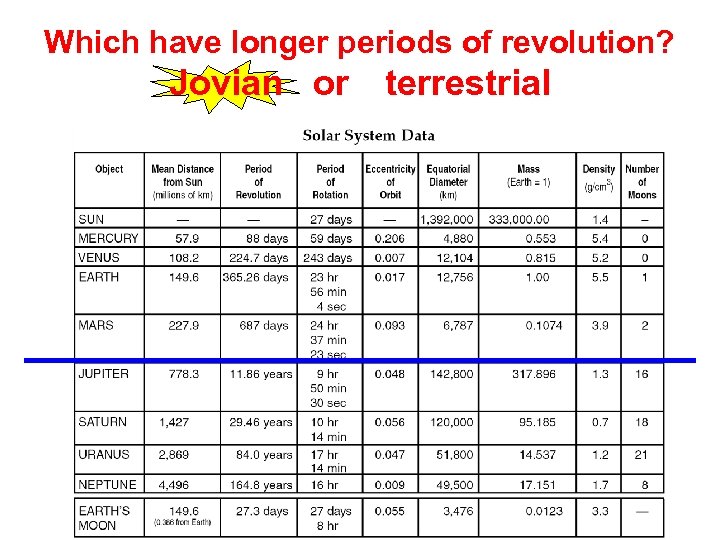
Which have longer periods of revolution? Jovian or terrestrial
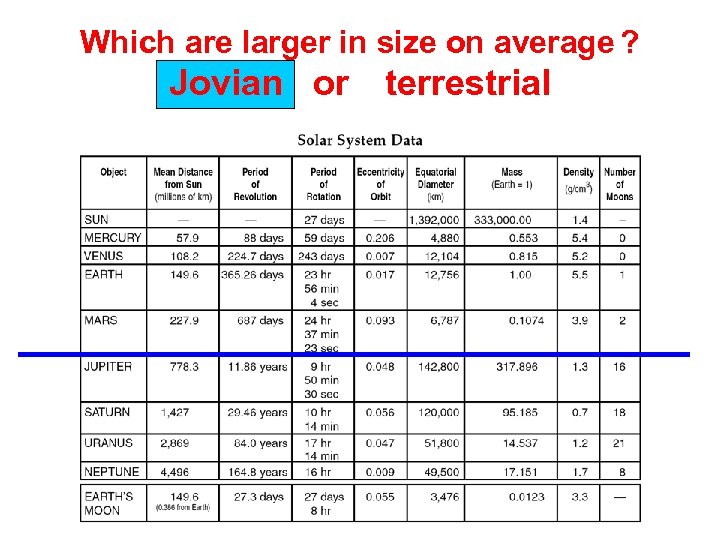
Which are larger in size on average ? Jovian or terrestrial
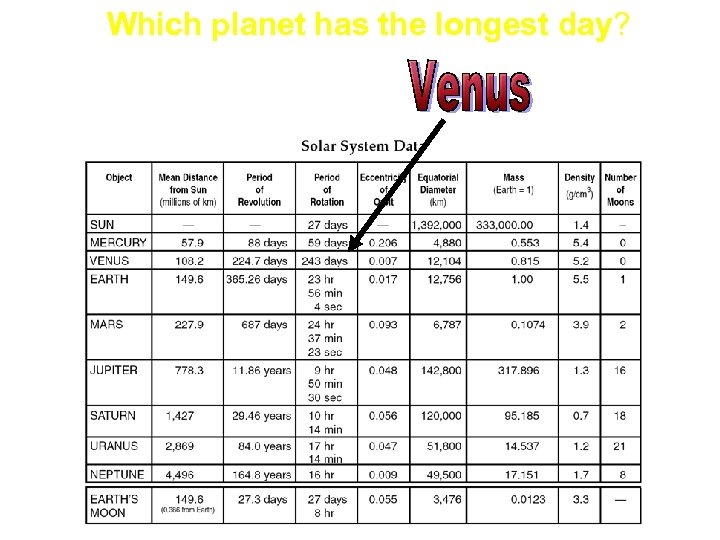
Which planet has the longest day?
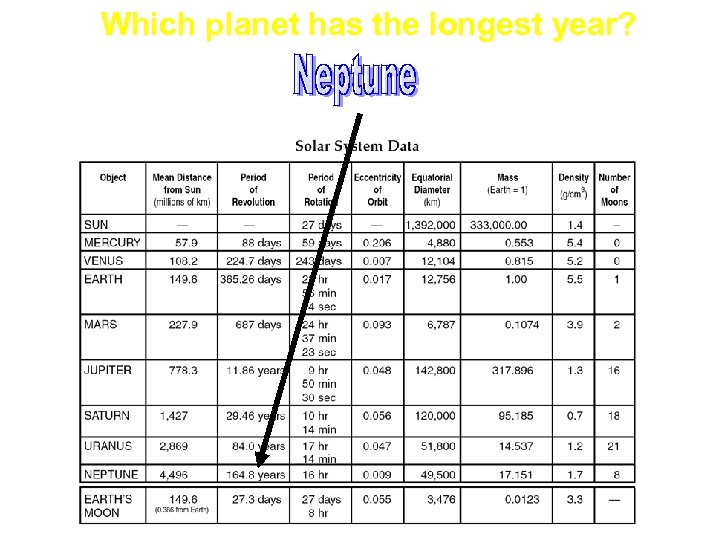
Which planet has the longest year?

eccentricity website
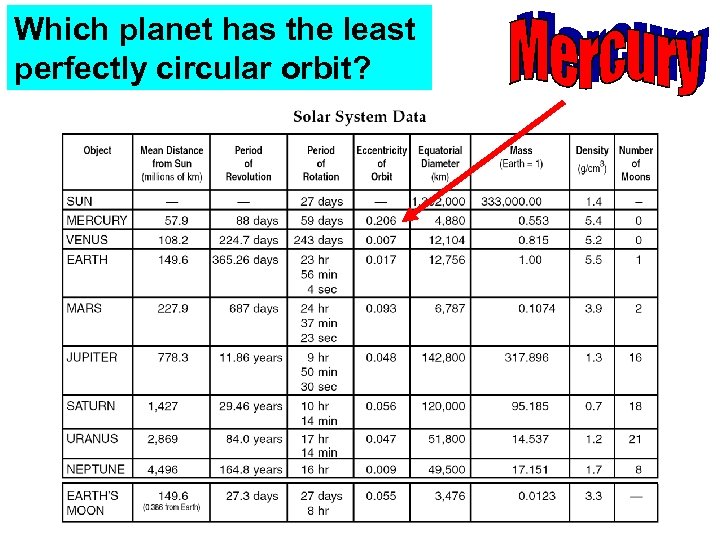
Which planet has the least perfectly circular orbit?
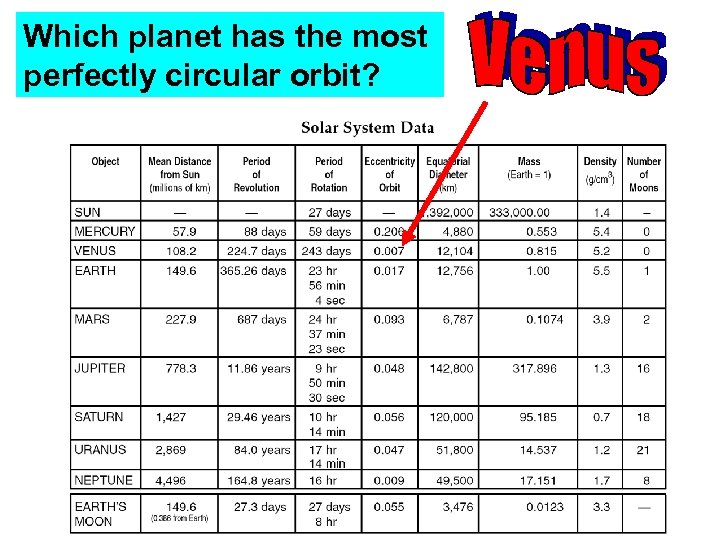
Which planet has the most perfectly circular orbit?
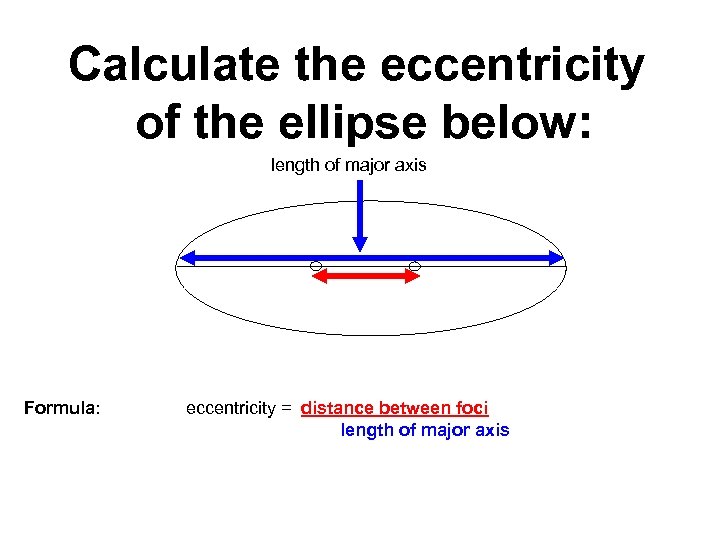
Calculate the eccentricity of the ellipse below: length of major axis Formula: eccentricity = distance between foci length of major axis
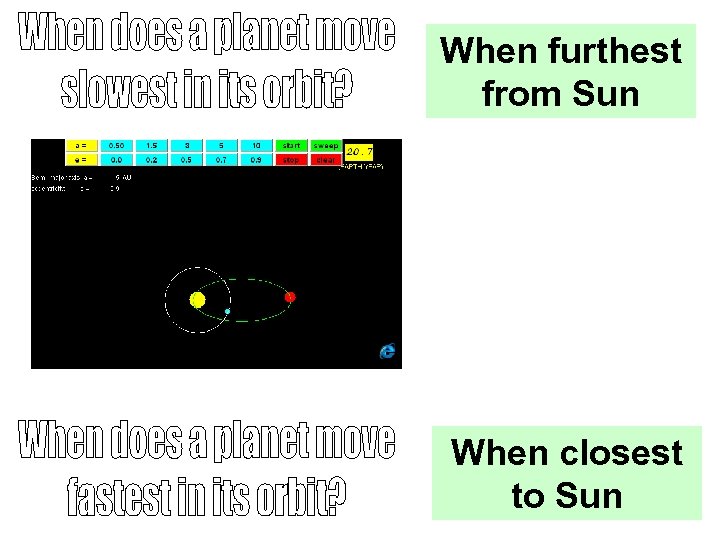
When furthest from Sun When closest to Sun
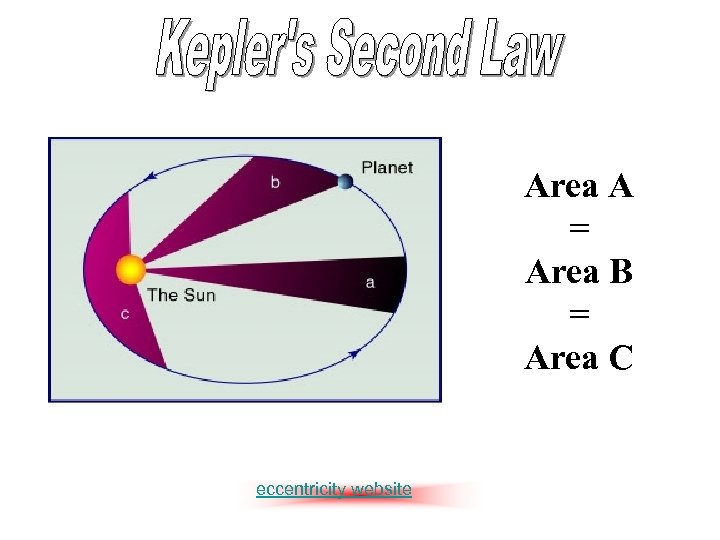
Area A = Area B = Area C eccentricity website
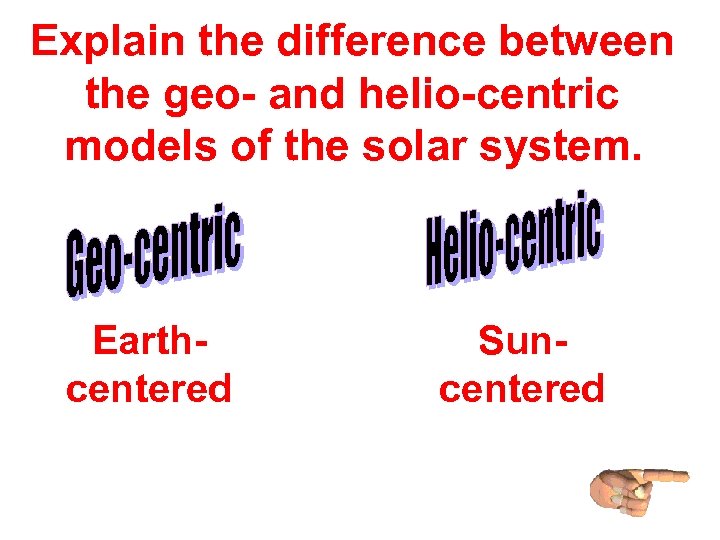
Explain the difference between the geo- and helio-centric models of the solar system. Earthcentered Suncentered


How long is one rotation of Earth? How long is one revolution of Earth?
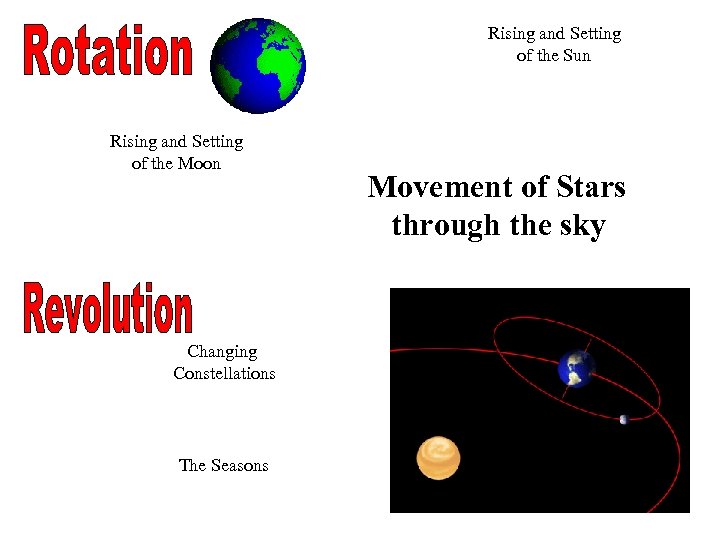
Rising and Setting of the Sun Rising and Setting of the Moon Changing Constellations The Seasons Movement of Stars through the sky

One rotation = 360° Time for one rotation = 24 hours 360° ÷ 24 = 15°/hr
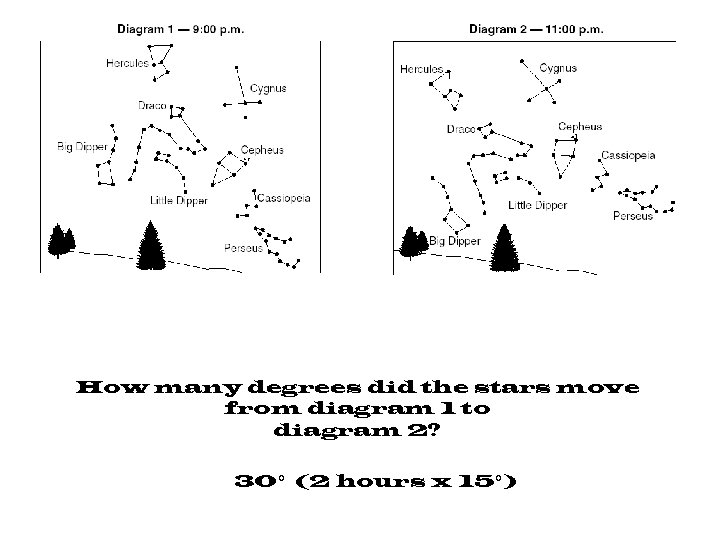
How many degrees did the stars move from diagram 1 to diagram 2? 30° (2 hours x 15°)
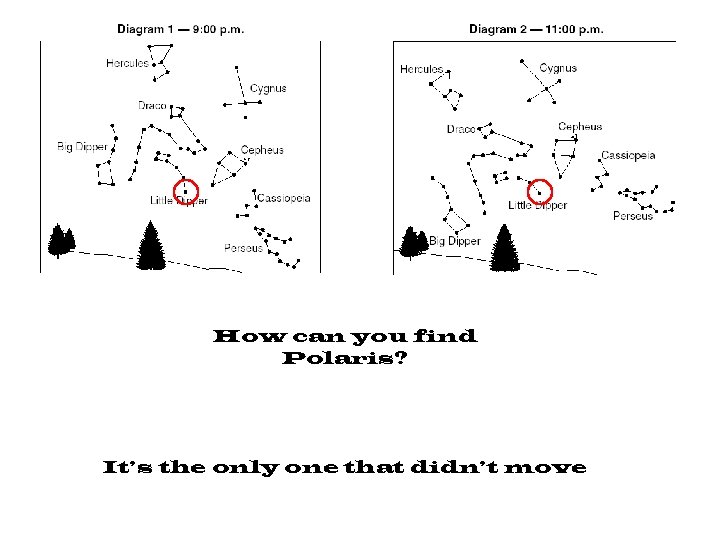
How can you find Polaris? It’s the only one that didn’t move
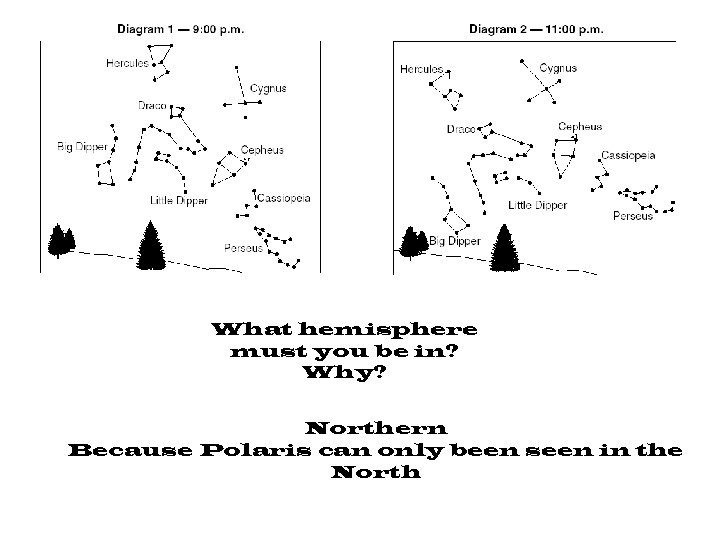
What hemisphere must you be in? Why? Northern Because Polaris can only been seen in the North
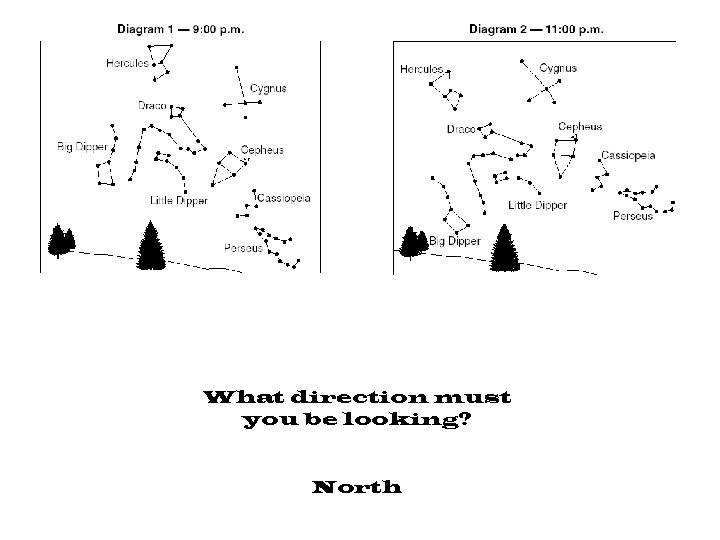
What direction must you be looking? North
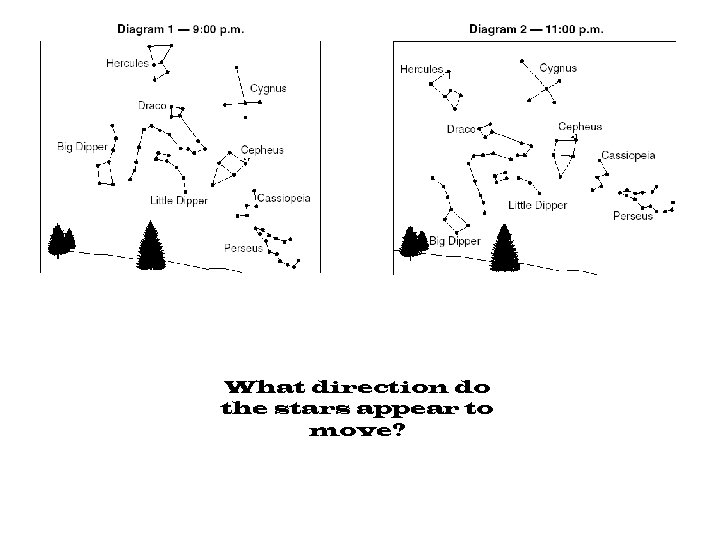
What direction do the stars appear to move?
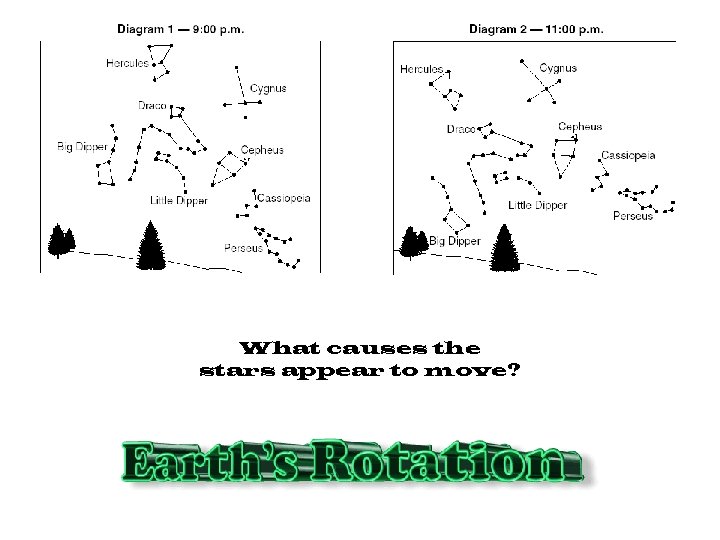
What causes the stars appear to move?






ESRTs p 15


because as the Earth rotates, the moon revolves

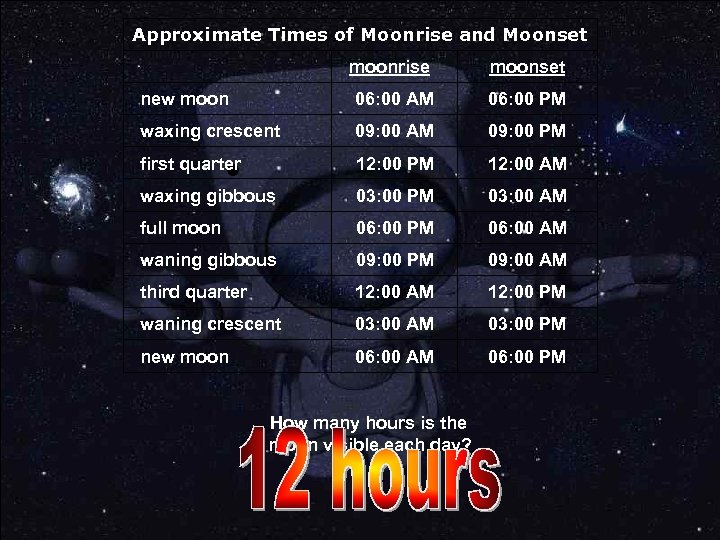
Approximate Times of Moonrise and Moonset moonrise moonset new moon 06: 00 AM 06: 00 PM waxing crescent 09: 00 AM 09: 00 PM first quarter 12: 00 PM 12: 00 AM waxing gibbous 03: 00 PM 03: 00 AM full moon 06: 00 PM 06: 00 AM waning gibbous 09: 00 PM 09: 00 AM third quarter 12: 00 AM 12: 00 PM waning crescent 03: 00 AM 03: 00 PM new moon 06: 00 AM 06: 00 PM How many hours is the moon visible each day?




Restaurant on the Moon. Great food but no atmosphere!







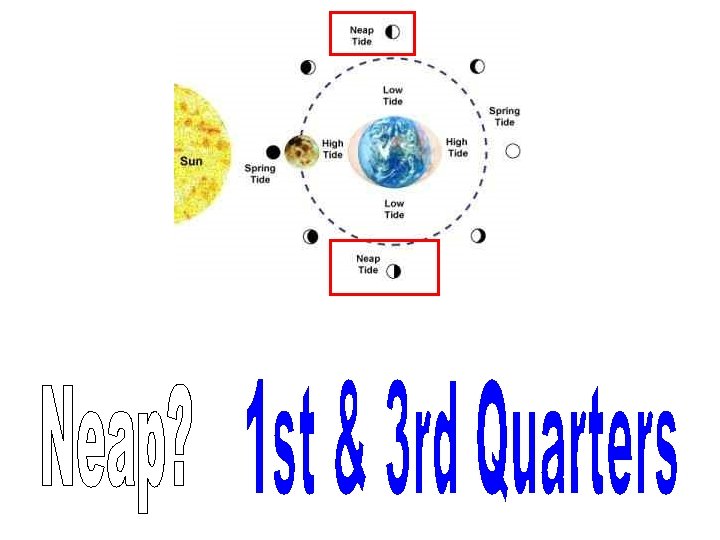
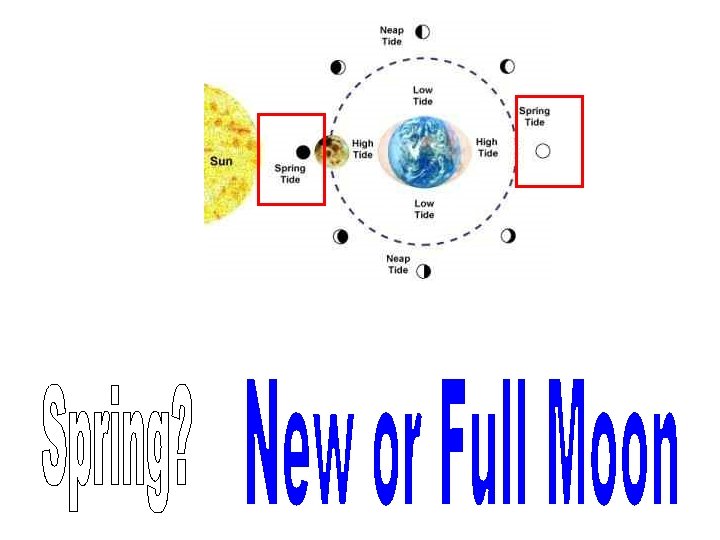



What’s the difference between solar and lunar eclipses? Earth goes into moon’s shadow moon goes into Earth’s shadow
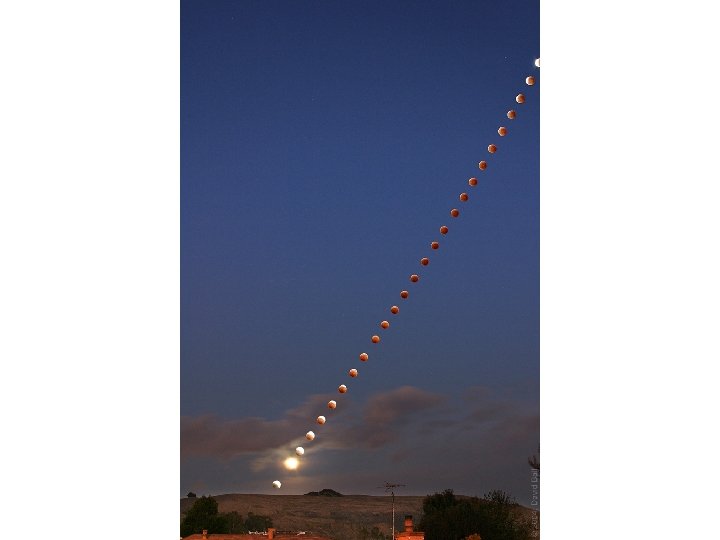

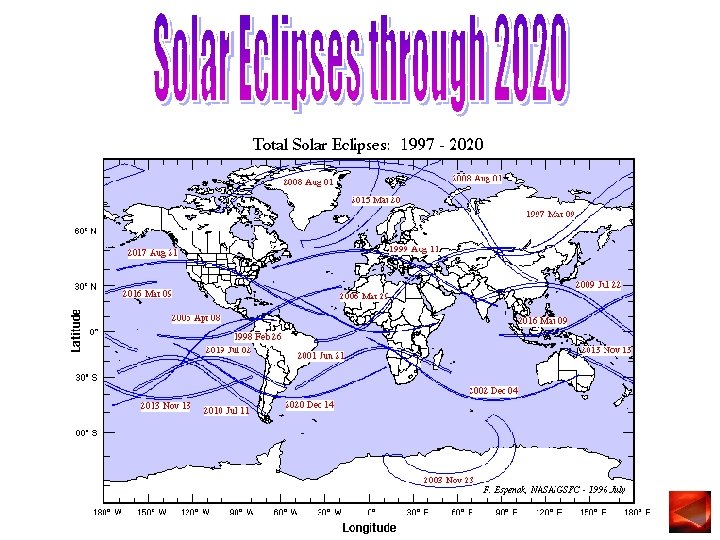



Why don’t we have solar and lunar eclipses every month? The moon’s orbit is tilted 5° from the Earth’s orbit.
d4464bf1837deaa5cab041c0911b2c1f.ppt