454a4233fd58d4303934cb2a39d83159.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51

Foreign Tax Credit Tx 8300

Learning Objectives You should be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identify characteristics of a _____ tax, Determine a DC’s ______ paid credit, Calculate the foreign tax credit _____, Explain the function of FTC _______, Compute a U. S. person’s ____ from outbound investments, and Explain tax _______.

Dealing with Double Tax • ______ systems exempt FSI. • ______ systems allow FTC. • ______ systems exempt some income and otherwise allow the FTC. • ____ often modify how these systems address double tax problems.

Basic Choices in U. S. • Deduct: – Foreign ______ tax, § 164(a)(3) – Any foreign ___ of trade or business, § 162(a) – Any foreign ___ of investment activity, § 212(1) • Credit foreign income tax, § 901(a) – Annual _____ – _____ return to change election

Creditable Foreign Levies • Must be a ___ and • Either: – Its ______ character is that of income tax in ____ sense or – It ______ for generallyimposed income tax

What Is a Tax? • _____ transfer – Excludes payments > ____ foreign tax liability – Must exhaust all practical ____ • Pursuant to government’s ______ authority – Excludes _____, penalties, interest, custom duties, and compulsory _____ – Excludes levies for specific _____ not otherwise available

Example: Dual Capacity Domco earns $4. 2 million before-tax profit mining diamonds in Hostia imposes a “diamond tax” at ___% of the profit. Since Domco pays the diamond tax, it does not pay the general income tax of 25%. What is Domco’s creditable tax? CHECK Profit (pre-royalty) Diamond tax Income tax Royalty deduction Profit Income tax rate Creditable tax

Predominant Character • Likely to reach net ____ – ______ test, – Gross _______ test, and – ___ income test • Not a ____-up levy

Realization Test • Focuses on ______ of tax’s assessment • Satisfied if assessment follows: – ______ event – Pre-______ event in some cases

Gross Receipts Test • Foreign tax base must begin with: – Actual ________ or – Estimated gross receipts if result does not ______ actual gross receipts • Gross receipts may be estimated when transactions occur between _______ persons • _____estimating gross receipts is okay

Net Income Test • Foreign tax must allow _____ of costs and expenses to determine tax base • ____estimating costs and expenses okay

Soak-Up Tax • Applies only to extent ___ is permitted • Since U. S. law does not allow, foreign government does not ______ soak-up tax

Substitute for Income Tax • Requirements: – Must apply __ __ income tax – Cannot be a _______ tax • Examples: – ______ taxes on nonresidents – Special ____ taxes
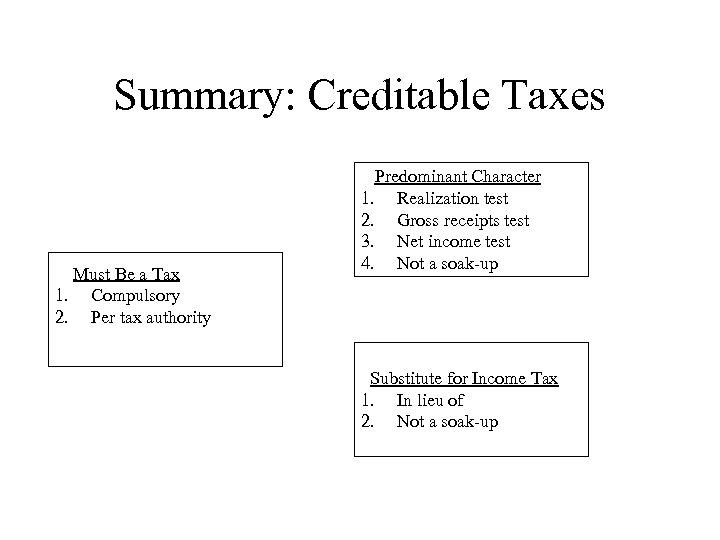
Summary: Creditable Taxes Must Be a Tax 1. Compulsory 2. Per tax authority Predominant Character 1. Realization test 2. Gross receipts test 3. Net income test 4. Not a soak-up Substitute for Income Tax 1. In lieu of 2. Not a soak-up

Creditable Taxes Include • Foreign income tax paid ____, § 901 – Partnership’s tax _____ through to U. S. partners – Foreign branch’s tax _____ to U. S. corporation • Foreign tax in lieu of income tax, §___ – Withholding tax on foreign investment income – Special industry tax • ______ paid tax, § 902

Cite Code Section Identifying Each Levy as Creditable Tax U. S. “green card holder” pays Belgian income tax on foreign profits U. S. citizen has Dutch tax withheld on her Dutch dividends U. S. individual is partner in U. K. partnership that pays U. K. income tax U. S. corporation has Cyprian sales office that pays Cyprian income tax U. S. corporation pays Polish income tax on profit dependent agent generates U. S. corporation’s German subsidiary pays German income tax U. S. family’s closely-held Mexican corporation pays Mexican income tax
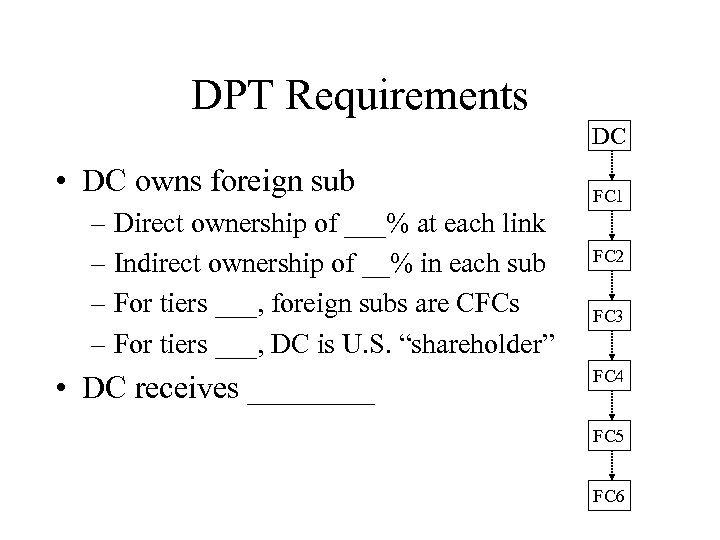
DPT Requirements DC • DC owns foreign sub – Direct ownership of ___% at each link – Indirect ownership of __% in each sub – For tiers ___, foreign subs are CFCs – For tiers ___, DC is U. S. “shareholder” • DC receives ____ FC 1 FC 2 FC 3 FC 4 FC 5 FC 6
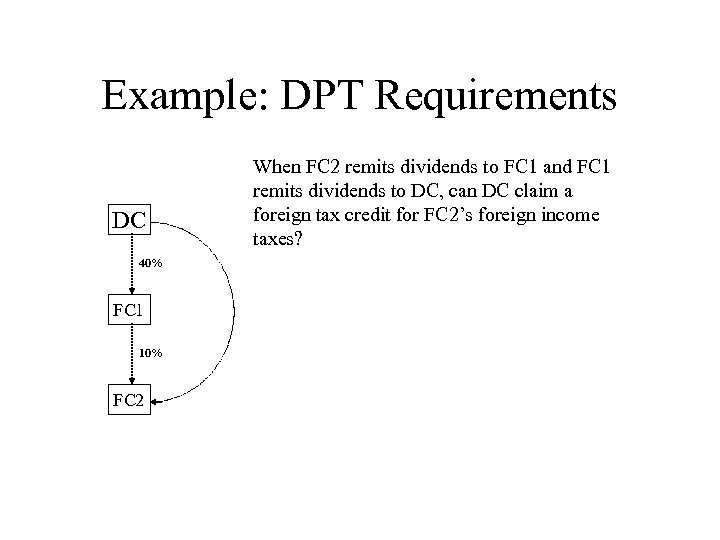
Example: DPT Requirements DC 40% FC 1 10% FC 2 When FC 2 remits dividends to FC 1 and FC 1 remits dividends to DC, can DC claim a foreign tax credit for FC 2’s foreign income taxes?
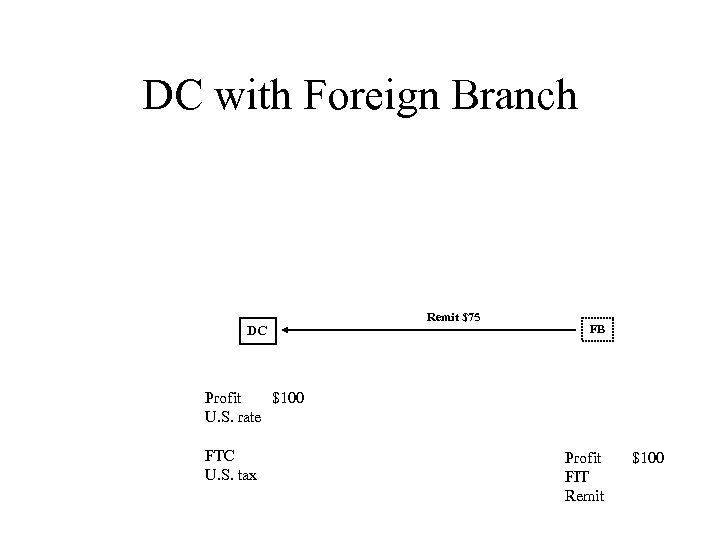
DC with Foreign Branch DC Remit $75 FB Profit $100 U. S. rate FTC U. S. tax Profit FIT Remit $100
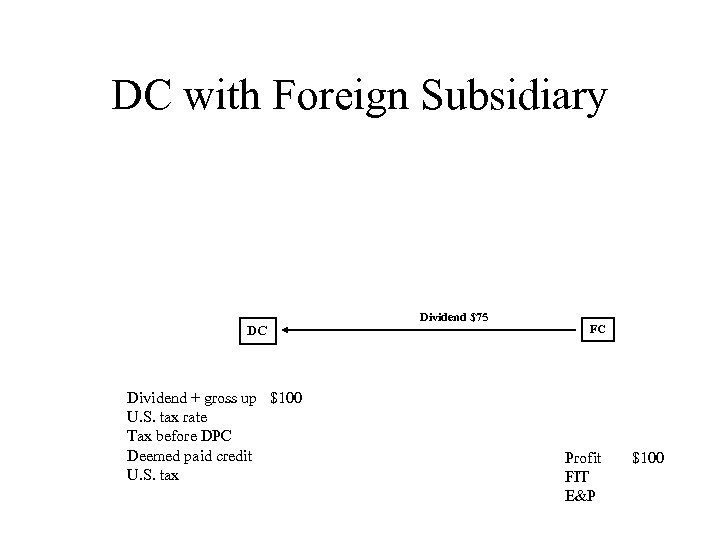
DC with Foreign Subsidiary DC Dividend + gross up $100 U. S. tax rate Tax before DPC Deemed paid credit U. S. tax Dividend $75 FC Profit FIT E&P $100

Calculating Deemed Paid Tax
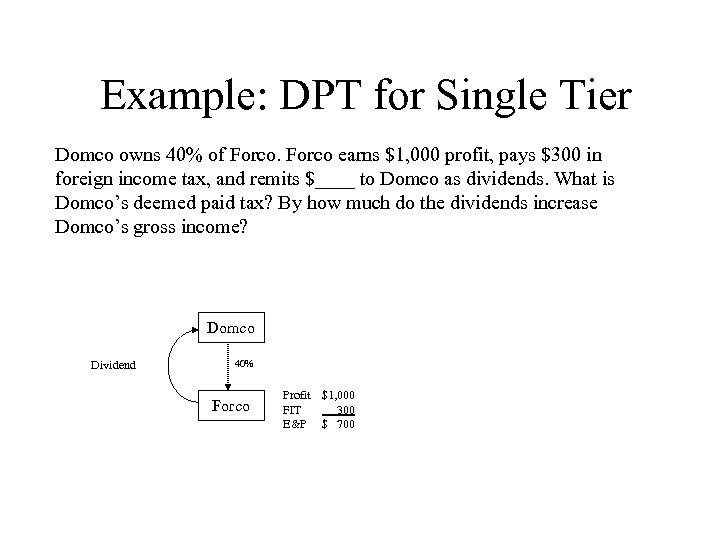
Example: DPT for Single Tier Domco owns 40% of Forco earns $1, 000 profit, pays $300 in foreign income tax, and remits $____ to Domco as dividends. What is Domco’s deemed paid tax? By how much do the dividends increase Domco’s gross income? Domco Dividend 40% Forco Profit $1, 000 FIT 300 E&P $ 700
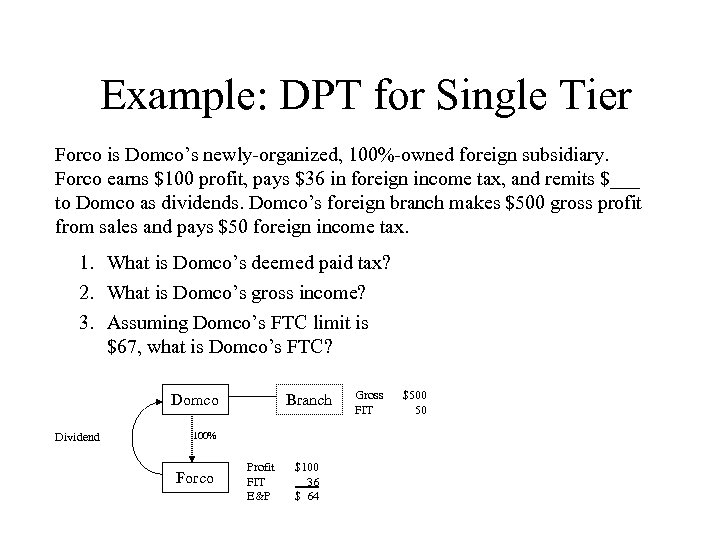
Example: DPT for Single Tier Forco is Domco’s newly-organized, 100%-owned foreign subsidiary. Forco earns $100 profit, pays $36 in foreign income tax, and remits $___ to Domco as dividends. Domco’s foreign branch makes $500 gross profit from sales and pays $50 foreign income tax. 1. What is Domco’s deemed paid tax? 2. What is Domco’s gross income? 3. Assuming Domco’s FTC limit is $67, what is Domco’s FTC? Domco Dividend Branch 100% Forco Profit FIT E&P $100 36 $ 64 Gross FIT $500 50
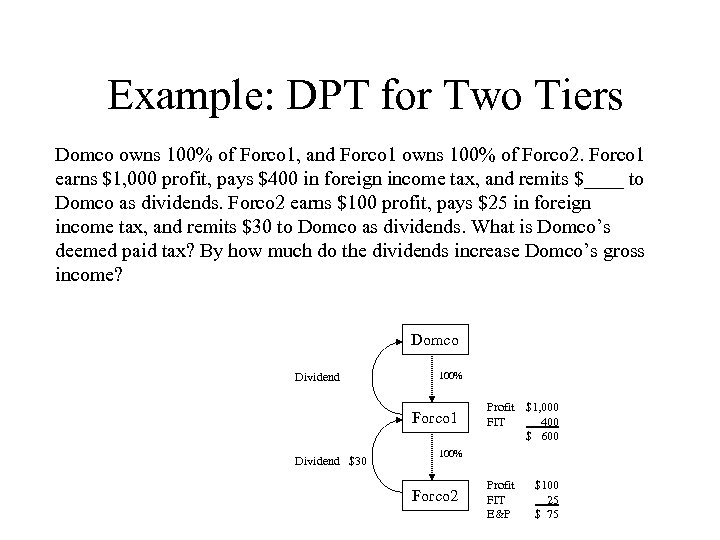
Example: DPT for Two Tiers Domco owns 100% of Forco 1, and Forco 1 owns 100% of Forco 2. Forco 1 earns $1, 000 profit, pays $400 in foreign income tax, and remits $____ to Domco as dividends. Forco 2 earns $100 profit, pays $25 in foreign income tax, and remits $30 to Domco as dividends. What is Domco’s deemed paid tax? By how much do the dividends increase Domco’s gross income? Domco Dividend 100% Forco 1 Dividend $30 Profit $1, 000 FIT 400 $ 600 100% Forco 2 Profit FIT E&P $100 25 $ 75
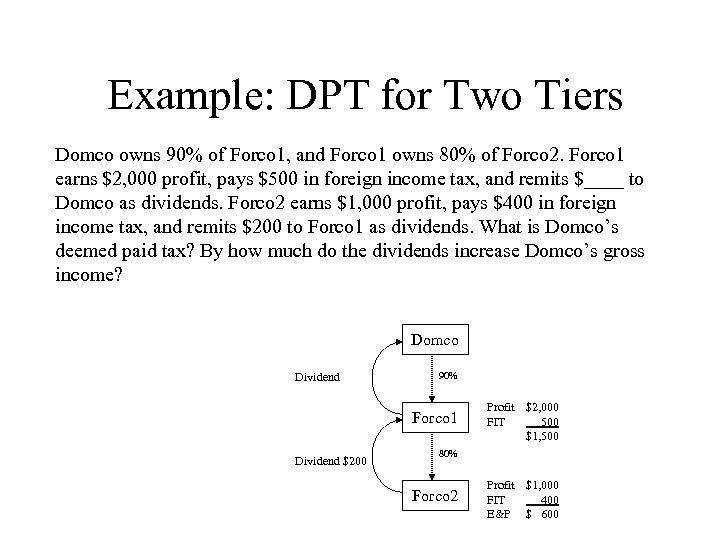
Example: DPT for Two Tiers Domco owns 90% of Forco 1, and Forco 1 owns 80% of Forco 2. Forco 1 earns $2, 000 profit, pays $500 in foreign income tax, and remits $____ to Domco as dividends. Forco 2 earns $1, 000 profit, pays $400 in foreign income tax, and remits $200 to Forco 1 as dividends. What is Domco’s deemed paid tax? By how much do the dividends increase Domco’s gross income? Domco Dividend 90% Forco 1 Dividend $200 Profit $2, 000 FIT 500 $1, 500 80% Forco 2 Profit $1, 000 FIT 400 E&P $ 600

Foreign Tax Credit Basics Foreign tax credit is lesser of: Creditable tax or FTC limitation Creditable tax is sum of: Foreign income tax (§____) Tax in lieu of FIT (§____) Deemed paid tax (§____)

Tax Rate Basics

Example: Foreign Tax Credit Domco’s U. S. ETR is 34%. Domco earns $____ foreign profit and $300 U. S. profit. Its creditable taxes are $60. Compute the following for Domco: 1. Foreign ETR 2. § 904 limitation 3. Foreign tax credit 4. U. S. tax liability 5. Excess credit or excess limit 6. Worldwide ETR 7. MTR on foreign profit

Example: Foreign Tax Credit Domco’s U. S. ETR is 34%. Domco earns $200 foreign profit and $300 U. S. profit. Its creditable taxes are $___. Compute the following for Domco: 1. Foreign ETR 2. § 904 limitation 3. Foreign tax credit 4. U. S. tax liability 5. Excess credit or excess limit 6. Worldwide ETR 7. MTR on foreign profit
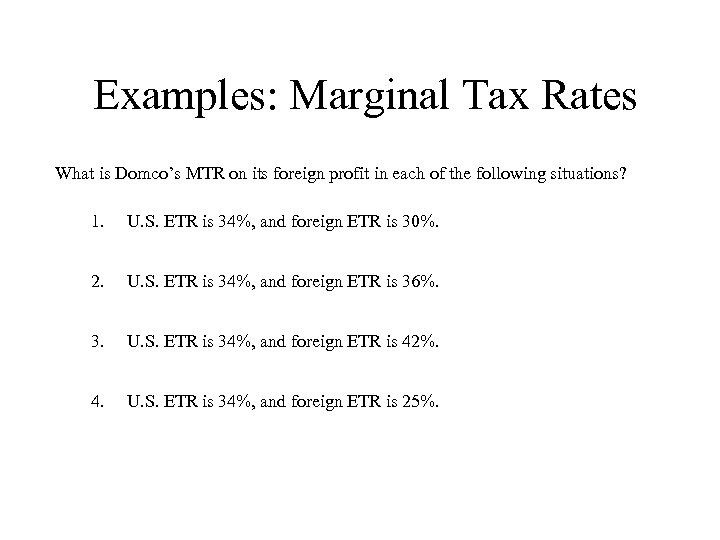
Examples: Marginal Tax Rates What is Domco’s MTR on its foreign profit in each of the following situations? 1. U. S. ETR is 34%, and foreign ETR is 30%. 2. U. S. ETR is 34%, and foreign ETR is 36%. 3. U. S. ETR is 34%, and foreign ETR is 42%. 4. U. S. ETR is 34%, and foreign ETR is 25%.

Examples: U. S. Residual Tax Assume the U. S. effective tax rate is 35%. In the following situations, what is Domco’s U. S. residual tax rate on its foreign profits? 1. Foreign ETR is 30%. 2. Foreign ETR is 36%. 3. Foreign ETR is 42%. 4. Foreign ETR is 25%.

Business in Low-Tax Countries • Capital ______ neutral • Residual U. S. tax due when ________ • MTR equals ____ if profits remitted currently • Creates incentive for ____taxed _______ income

Business in High-Tax Countries • • Capital ______ neutral No ________ tax due MTR equals _______ Creates incentive for ___taxed _______ income

Excess Credit Planning • Decrease foreign ETR – Remit foreign profits in _____ form – ______ offshore in high-tax countries – Use _______ to shift income from high-to low-tax countries • Increase low-taxed FSTI – Export, passing title ______ – Lease ______ assets and buy ____ assets – License technology for use abroad in country with ___ royalty ______ tax
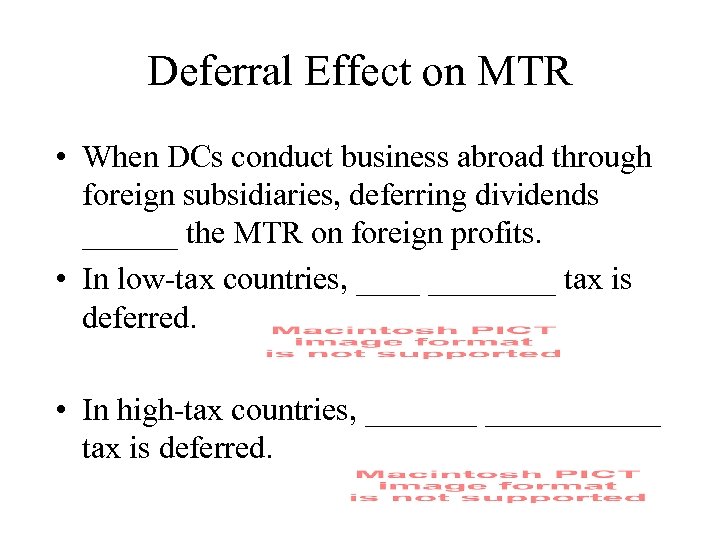
Deferral Effect on MTR • When DCs conduct business abroad through foreign subsidiaries, deferring dividends ______ the MTR on foreign profits. • In low-tax countries, ________ tax is deferred. • In high-tax countries, ___________ tax is deferred.

Example: MTR in Low-Tax Country Domco’s wholly-owned foreign subsidiary, Forco, operates in a country with a ___% ETR. Assume the U. S. ETR is 34%, and Forco distributes all its E&P as dividends in the current year. What is Domco’s MTR on Forco’s foreign profits? Assume the same facts except that Forco does not plan to distribute current profits for 4 years and the applicable discount rate is 12%. What is Domco’s MTR on Forco’s foreign profits?

Example: MTR in High-Tax Country Domco’s wholly-owned foreign subsidiary, Forco, operates in a country with a ___% ETR and a ___% dividend withholding tax. Assume the U. S. ETR is 34%, and Forco distributes all its E&P as dividends in the current year. What is Domco’s MTR on Forco’s foreign profits? Assume the same facts except that Forco does not plan to distribute current profits for 4 years and the applicable discount rate is 12%. What is Domco’s MTR on Forco’s foreign profits?
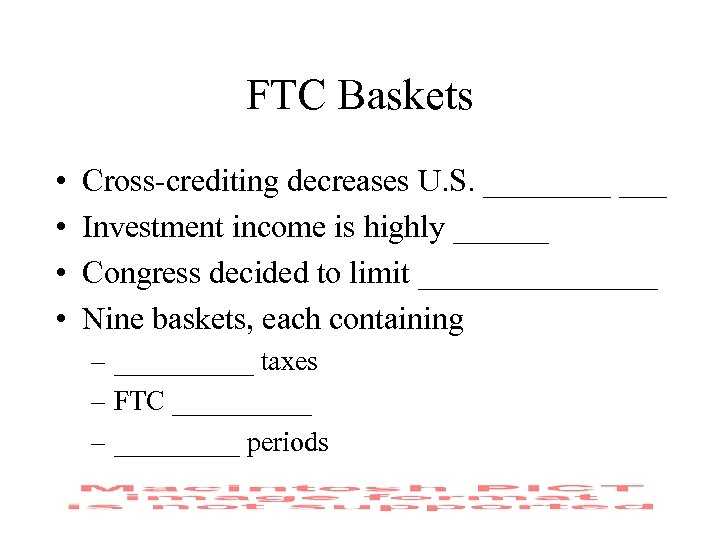
FTC Baskets • • Cross-crediting decreases U. S. ____ ___ Investment income is highly ______ Congress decided to limit ________ Nine baskets, each containing – _____ taxes – FTC _____ – _____ periods
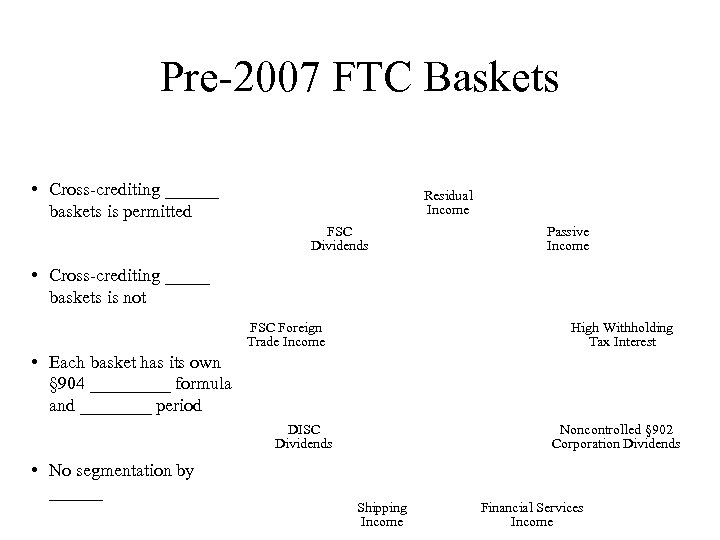
Pre-2007 FTC Baskets • Cross-crediting ______ baskets is permitted Residual Income FSC Dividends Passive Income • Cross-crediting _____ baskets is not FSC Foreign Trade Income High Withholding Tax Interest • Each basket has its own § 904 _____ formula and ____ period DISC Dividends • No segmentation by ______ Noncontrolled § 902 Corporation Dividends Shipping Income Financial Services Income

Passive Income Basket • Portfolio dividends, some interest, non-business _____ and royalties, annuities, some net _____ • High-taxed income is “_____” • ___-tax basket

Residual Basket • ______, marketing, and service income • _______ profit (other than FSC or DISC) • Business rent and _______ income • “______ ___” passive income
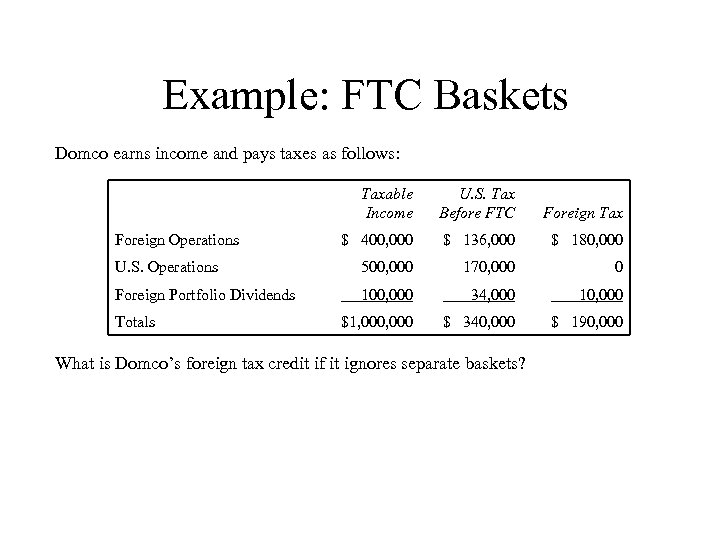
Example: FTC Baskets Domco earns income and pays taxes as follows: Taxable Income U. S. Tax Before FTC Foreign Tax $ 400, 000 $ 136, 000 $ 180, 000 U. S. Operations 500, 000 170, 000 0 Foreign Portfolio Dividends 100, 000 34, 000 10, 000 $1, 000 $ 340, 000 $ 190, 000 Foreign Operations Totals What is Domco’s foreign tax credit if it ignores separate baskets?
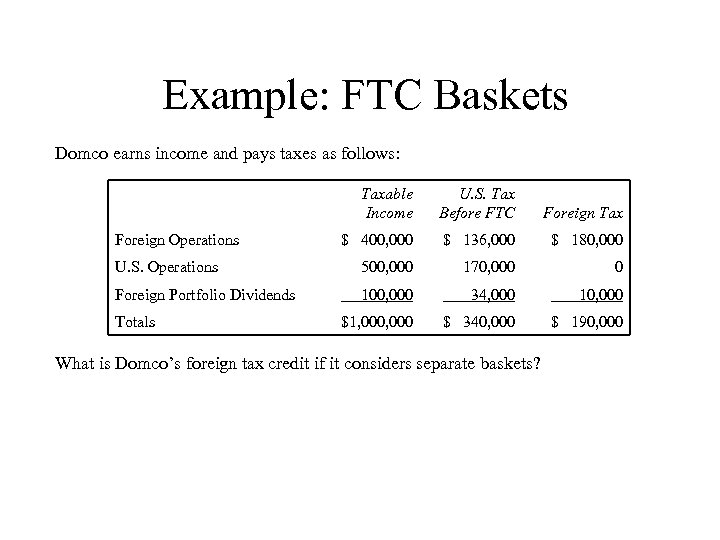
Example: FTC Baskets Domco earns income and pays taxes as follows: Taxable Income U. S. Tax Before FTC Foreign Tax $ 400, 000 $ 136, 000 $ 180, 000 U. S. Operations 500, 000 170, 000 0 Foreign Portfolio Dividends 100, 000 34, 000 10, 000 $1, 000 $ 340, 000 $ 190, 000 Foreign Operations Totals What is Domco’s foreign tax credit if it considers separate baskets?

CFC Look-Through • CFCs are foreign corporations that U. S. shareholders _______. • Look through rules allocate foreign _______ income U. S. companies receive from ____ among baskets.

Example: Look-Through Domco receives $______ dividends from its wholly-owned foreign subsidiary, Forco pays ___% of its dividends from E&P attributable to its business operations and the rest from E&P attributable to its passive investment activities. How does Domco treat these dividends for FTC purposes?

Recapture of Foreign Loss • U. S. companies pay U. S. tax on _____ income. • Thus, overall losses from foreign activities are deductible against ____ source income. • However, this reduces ____ tax on ____ source income. • So, § 904(f) contains a _____ rule.

Recapture of Foreign Loss • If overall foreign loss occurs, – ______ against U. S. income but – Recapture in later year • Involves treating ___ as ____ • Affects ___ limitation • Recapture lesser of: – _______ foreign ____ account or – ___% of current year’s ____
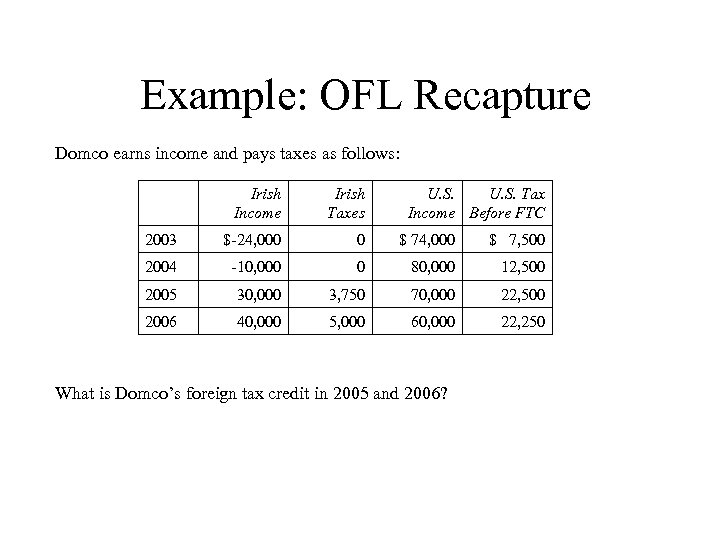
Example: OFL Recapture Domco earns income and pays taxes as follows: Irish Income Irish Taxes U. S. Tax Income Before FTC 2003 $-24, 000 0 $ 74, 000 $ 7, 500 2004 -10, 000 0 80, 000 12, 500 2005 30, 000 3, 750 70, 000 22, 500 2006 40, 000 5, 000 60, 000 22, 250 What is Domco’s foreign tax credit in 2005 and 2006?

Tax Sparing • Host countries may allow “tax ____” • Holiday creates incentive to invest when ____ country has: – ______ system or – Tax _______ • Sparing allows residents to ______ foreign taxes the host country ______

Tax Sparing • “Tax sparing credits” are the same as foreign tax credits except investors ___ __ foreign income tax • __ U. S. treaties allow tax sparing A company invests abroad and earns $100. Assuming home and host country tax rates of 50% and ___%, respectively, determine the total tax liability with: • No tax holiday • Tax holiday without tax sparing • Tax holiday with tax sparing

Tax Sparing Example No Tax Holiday Host Country Tax liability Home Country Initial tax Tax credit Tax liability Tax Holiday without Sparing Tax Holiday with Sparing
454a4233fd58d4303934cb2a39d83159.ppt